AI's Role in Modern Accounting
Literature Review
Outline of the selected topic
The topic selected for the purpose of formulation of the prospective doctoral research has been ‘The impact of artificial intelligence on the accounting industry’. To this effect, it could be acknowledged that Artificial Intelligence (AI) has provided the foundation on which the entire multipronged endeavour of computational technology based transformation of accounting industry has been undertaken. The impact of AI on financial institutions could be palpable from the perspective that the associated functionalities have been progressively wbecoming dependent on technical novelties such as AI assisted work management procedures. Thus, the rationale of undertaking such a research literature review pertains to exploration of impact of AI in terms of upgrading the functionalities which are integral to accounting services across the entire industrial spectrum. Furthermore, the rationale of this research could be understood to be an attempt to build on the initial progress of impact of AI on accounting industries and to venture into greater depth on the possibilities of innovations through AI applications in commercial accounting management. According to Brynjolfsson, Rock and Syverson (2017), the development of accounting management has been accorded significant emphasis throughout the previous decade. The reason has been that AI has been utilised as a means to improve organisational performance by various accounting institutions within the commercial accounting industry. Bloem (2014) has pointed out that AI is becoming utilised progressively by various financial accounting management institutions in various measures. However, previous researches have rarely mentioned about the various dimensions of utilisation of AI in the accounting and finance management industries. Thus, the corresponding research project would be endeavouring to explore the empirical evidence which could be obtained through an exploratory survey regarding the influence of AI on multiple operational aspects associated with the accounting industry in general. Such operational aspects could be understood as the particular functionalities and decision formulation procedures which underscore such functionalities which have experienced extensive transformations through the impact of AI. One component of the general perception about the impact of AI on accounting professionals is that a negative influence on job prospect enhancement concerning the accounting industry could emerge. As per the opinion of Gordon (2018), such assumptions outline the necessity to conduct in-depth research into the available evidence and gather Quantitative as well as Qualitative data to address the research problem of the relative dearth of empirical understanding pertaining to the research question under consideration at the backdrop of the fast paced developments of utilisation of AI applications in global accounting industry. Furthermore, the research project could also contribute to evaluate a widened range of different business cases so as to highlight opportunities of contributing to accounting management and financing functionalities through outlining the pros and cons of AI applications in this discipline.
Academic exploration
Impact of AI on corporate accounting and finance
The implications of AI on accounting and finance have been suggested to be profound by (Guo, 2019). On an organisational level, according to Issa, Sun and Vasarhelyi (2016), it is the responsibility of the organisational faculty of corporate finance services to track the development of AI applications in context to utilisation of Big Data involving accounting functionalities (transactions, calculations and various other). Such implications also extend to the professional services which provide accountancy firms with necessary advisories regarding their clientele since the progressive automation and digitisation of accounting functionalities could herald in significant changes within the next decade. Kokina and Davenport (2017) have opined that AI based applications of corporate finance accounting management has progressively acquired significance since investment management and transaction management are two fundamental cornerstones of any industrial business process. To this effect, the accounting industry has direct implications, in countries such as the UK and USA, on generation of start-up and venture capital, on procedures such as mergers and acquisitions and management buyouts (MBOs) which have to be supported by private equity, on equity based capital markets regarding offering of Initial Public Offerings, on debt markets and alternative financing, infrastructure development based investments and, finally, on turnaround finances (Li and Zheng, 2018). According to Luo, Meng and Cai (2018), the objectives are ensuring of effective corporate financing and management of the same through responsible means of business innovation. Marshall and Lambert (2018) have emphasised upon this format of responsibility executed through innovation means as the primary harbinger of AI assisted technological applications which could be utilised to fast pace the work proceedings within accountancy disciplines. It is essential that AI processes should be implemented to access and sustain new markets for the accountancy industry, new technologies, new ventures and novel ideas. According to Mirzaey, Jamshidi and Hojatpour (2017), global generation of equity capital -during 2018-2019 had been $4 trillion through IPO issuance. These functionalities are meant to be assisted through application of AI in accounting processes. The research of Moudud-Ul-Huq (2014) has outlined that, involving calculations of tax estimate formulation processes, generation of invoices through self-automated AI assisted procedures could be utilised. Furthermore, the invoice types and their status of payment could be determined through AI applications. Apart from these, Nassaji (2015) have determined that precision formulation of particular systems for preservation of statistical records pertaining to accounting calculations and gleaning of information from previously performed as well as documented accounting projects could be further facilitated through utilisation of AI based memory segments management applications which could augur in greater accuracy and greater speed of memory retrieval mechanism.
Dig deeper into The Doctrine of Separate Legal Personality with our selection of articles.
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to Management Accounting in Strategy Formation.
According to Pannu (2015), the automation of payment remission systems and the auditing as well as management of accounting projects could be provided vital assistance through AI applications. Such developments had been commenced approximately 2 decades earlier and prior to that, the accounting functionalities were mostly performed through manual methods. Schwab (2017) has observed that the implications of AI applications utilisation within the accounting industry could be profoundly deduced from a comparative analysis of the functionalities which had been performed previously within the accounting industry when the AI applications had not been made available. Shi (2019) has emphasised on the factors of reliability, performance, credibility of outcomes, accuracy and consumption of time which have experienced the most extensive improvements through AI applications utilisation. However, Silverman (2016) has consistently outlined that even earlier solutions had been developed with the objective of obtaining the most coveted outcomes of such functionalities. Brynjolfsson, Rock and Syverson (2017) have delineated such objectives as the following:
1: Automation of tasks which are mostly repetitive, tedious and interminable in nature.
2: Optimisation of the processes through which financial calculations are undertaken so as to improve operational efficiency.
3: Greater accuracy management in statistical accounting and recording of data, processing of tasks and handling of additional flow of information.
4: Enforcement of compliance through changes in key procedural undertakings.

Skilton and Hovsepian (2017) have opined that subsequent impacts of AI on the accounting procedures in the concurrent era have facilitated the obtainment of extensively ensured measures of accuracy pertaining to accounting systems related data such as audit reports and balance sheet accounting outcomes. As manual inputs have been made redundant by the introduction of AI based self-generated automation, the time required to formulate such reports have diminished by many factors as well. Wagner (2017) has brought into focus the factor that the procedural alterations, which, have been introduced through AI applications within the disciplines of accounting management and data standardisation, could influence the recognition and categorisation of data which could be derived from multiplicity of sources. The accuracy in this process is associated with appropriation of such data to the required accounting heads. Nonetheless, AI assisted automated processes have also been able to handle multiplicity of tasks which required involvement of specialised, experienced and dedicated personnel through which such tasks could have been performed previously. These tasks have been identified by Wiek and Lang (2016) in the following manner:
1: Processing of account payables and variables.
2: Processing of data regarding previously remitted payments.
3: Cost management of respective accounting firms.
Fourth Industrial Revolution
Skilton and Hovsepian (2017) have drawn attention to the conceptualisation of AI as the prime factor regarding the changing digitised functionalities pertaining to the 4th Industrial Revolution. According to the research of Appelbaum et al (2017), the 1st Industrial Revolution had been based on the advent of steam powered locomotives and other machineries and, the 2nd Industrial Revolution had been spawned by mechanisation of manufacturing so as to develop mass production mechanisms. According to Brynjolfsson, Rock and Syverson (2017), the concept of this 4th Industrial Revolution had been established on the basis of digital technologies which had been developed during the 3rd Industrial Revolution. Extensive digitisation and Information Technology management had been the crux of such developments. Thus, Bloem et al (2014) have researched that innovations in the digital and physical disciplines of science have been brought to a convergence point from which the 4th Industrial Revolution has been developed. In this context, the research of Gordon (2018) has outlined that 4th Industrial Revolution has been oriented towards development of various novel technologies such as Augmented Reality (AU), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Genome Sequence Analysis and Editing, Bionic Robotics, 3-D printing technologies and multiple others. Furthermore, the dual mode of impact of AI on both accounting functionalities and the accounting professionals highlight the rapid transformations involved in the procedures through which formulation, exchanging and distribution of statistical and alphanumeric accounting information could be undertaken. From such observations, Kodama (2018) has determined that the 4th Industrial Revolution has accounted for the deliberate replication of human intelligence to execute workplace based responsibility at much greater pace and through improved accuracy. This includes the accounting industry as well. From the research perspectives of Schwab (2017), it could be determined that implications of AI within the accounting industry generally encompass much greater than that of usual management of information and statistics in the digitised manner. According to O'leary (1991), the most significant implication of AI is on the synergistic accounting management system development through automation of combinations of rote tasks, advancement of software suits through which accounting procedures could be executed with extensive measure of accuracy and alignment of operational mechanisms with alterations in the work procedures through which better adjustment of accounting functionalities could be achieved. Tredinnick (2017) has specified that combination of AI processes with existing accounting software mechanisms has been undertaken by such processes so as to ultimately improve the overall accounting operations.
Expert System based technical configuration with subsequent implications in the accounting disciplines
Regression
According to Sutton, Holt and Arnold (2016), this particular method has been outlined to undertake proper analysis of the domain knowledge which could be derived through application of the AI based Expert System (ES). The domain knowledge is crucial in terms of development of any operating model through which selection various numbers of variables could be performed (Moudud-Ul-Huq, 2014). Such variables are primarily continuous in terms of their sequences and the first observation of such a sequence and figuring out the various dimensions of the same had been performed through the ES application. The objective had been on the figuring out of the suitability measures in the proper manner, as per the opinions of (Luo, Meng and Cai, 2018). Johnson, Phillips, and Chase (2009) have identified the AI algorithms, which have been involved in this process, as the following:
1: Ordinary Least Squares Regression (OLSR).
2: Logistic and Linear Regression models.
3: Measures of Stepwise Regression.
4: Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines (MARS).
The research of Daft and Maclntosh (1978) have persistently emphasised on the productive efficacy of AI assisted regression methods in providing the capacity to the accounting organisations to effectively develop data based solutions to recover previous remissions of their clientele. The particular benefit of this system is associated with maximisation of such remission recovery on the basis of differential parameter based measuring of Net Operating Loss (NOL). Bagnoli, Dal Mas and Massaro (2019) have illustrated this factor in the manner that if any business organisation could incur extensive los within a specific duration of the existing financial years, while permissible deductions of cumulative earnings of the company could surpass that of the net income incurrence, then, occurrence of greater expenses within that particular period in comparison to the actual organisational revenue. Thus, this particular period of time could be defined as the duration which had been subjected to NOL (Omoteso, 2012). In this context, Antoniuk et al (2017) have outlined that it remains critical concerning any business organisation to determine the accurate extent to which NOL could occur since every organisation is required to recover previous payment percentages to the maximised extent. However, these payments have to be reimbursable in the context of respective national legal structure of the countries where such companies could operate and under such legal structures such companies are registered as well. To this effect, Pannu (2015) have observed that the combined regression algorithms of ES mechanisms could accurately perform each task concerning the retrospective calculations through which backward tracing of payables could be achieved.
Utilisation of Clustering Algorithms
As per the observations of Dean, Yoon and Susman (1992), different AI assisted accounting systems based approaches utilise clustering mechanisms. The objectives are to properly take into account the available alphanumeric data structures and to effectively define the obtained and evaluated data structures so that these could be grouped into specific clusters through proper determination of points of representation associated with each of the clusters. Furthermore, Drucker (1988) has determined the following as the involved algorithms:
1: Expectation Maximisation (EM). Such an algorithm cluster is utilised for the purpose of determination of search outcomes through various LOGICAL parameters.
2: Hierarchical Clustering (HC).
Interdependence between technology and supervision
Development of interdependence between supervision and technology, according to Pannu (2015), has been spawned by the requirement of maintaining control on particular accounting functionalities. The emphasis is on maintaining proper co-ordination between the technical and supervisory functionalities of accounting firms involving execution of responsibilities. According to O'Callaghan (1995), there are three particular characteristics of any accounting organisation on which such co-ordination is incumbent and these are exertion of power, discretion and interdependence in between the divergent working groups. Meservy, Denna and Hansen (1992) have brought into focus the theoretical observations of Perrow to outline the determinants of functionalities through which this interdependence aspect could be managed in between organisational supervision and AI assisted functionalities. Wagner, Otto and Chung (2002) have indicated towards the contributions of AI systems in the forms of Expert Systems and Independent Systems mechanisms which are oriented towards predictive manner based automation of information exchanges as well as communication analysis pertaining to accounting functionalities. Effective communication could be facilitated, in this context, in between the organisational supervisory management echelons and individual professionals. Kokina and Davenport (2017) have emphasised upon the notion that AI could facilitate the analysis of business flows and issues which could be associated with such discourses and the available not AI technological issues could as well be resolved effectively through application of ES and IS mechanisms. As per the research of Kim (2016), the impacts of AI on the involvement and proficiency of accounting professionals could be considered to be comprehensive regarding the incremental and progressive codification of stupendous measure of information and knowledge which could be generated through differential and existing digital data analysis processes applied within the accounting industry. On the other hand, the research of Li and Zheng (2018) has delineated the increment in efficacy measurers regarding team work based functionalities at the accounting firms to be the prime impact of AI on the accounting industry in general. Furthermore, subsequent changes have taken place within the organisational supervisory structure through betterment of communication measures, facilitated by the AI applications, within employees and organisational managerial echelons.
Original Contributions
The research literature review section has been deliberative of the impact of AI on accounting professionals through extensive emphasis on multidimensional operational procedures pertaining to accounting such as incremental codification of available information and knowledge pertaining to existing processes of accounts management and associated responsibilities which have to be performed by accounting professionals with expanding participation of computer assisted technologies. Thus, the literature review has provided the Researcher with the valued perspective that greater efficacy management could be developed through converging team work initiatives. Furthermore, the Researcher has also been successful in terms of identification of the fact that subsequent transformations in the responsibilities scenario for accounting professionals have occurred within the framework of organisational supervisory hierarchy and the rationale has been greater expansion of communication in between the accounting professionals and their hierarchical supervisors. Furthermore, the clarity of finding has been consistently evaluated by the Researcher through identification of the research gap through reviewed literature. This research gap identification has been the outlined dearth of proper and holistic understanding regarding the comprehensive influence of AI on accounting work procedure management. This has been contextualised through observations performed by the Researcher that auditing through the Expert Systems has been undertaken by most of the previous researches which have been undertaken in this context. Out of the remaining, the Researcher has realised that, most have only focused upon the impact which has been generated by ExperTax automated data management and processing methods involving the accounting organisation of Laybrand and Coopers. Thus, it could be observed that such evaluated and analysed secondary literature has been only responsible for assessment of individual segments of the ES mechanisms. From the perspective of original contributions, it has been complicated for the Researcher to generalise the research findings so as to synthesise proper theoretical means through which credible and empirically authenticated conclusions could be discerned.
Research Methodology
The Researcher has selected to utilise the combination of several specific tools and methods of research for the purpose of performing the forthcoming research process in the most empirical and accurate manner. The significance of such selection of research methodologies has been incumbent upon the evolution of the selected research subject under consideration. Such a combination of research methods formulates the elementary foundation on which the verifiable progress of capture, collection and analysis of research data could be performed. As an integral measure of the overarching research methodological structural process, the Researcher would be implementing the preferred research philosophy of Post Positivism, the Descriptive Research Design and the Deductive Research Approach. The purpose would be to consolidate the entire effort which the Researcher has invested within the research project so far (Jung, 2018). To this effect, it could be observed that the selection of this pertinent research philosophy by the Researcher has been incumbent upon the evaluation of Ontological, Axiological and Epistemological disciplines from an empirical academic perspective. As per the observations of Amani and Fadlalla (2017), the discipline of Epistemology could be utilised to recognise and acknowledge the existing factual reality through scrutinising various direct outcomes of particular interactions in between variegated strands of activities undertaken at the research data collection and analysis related functional levels. Kumar (2019) has observed that such a method depicts the elements of Reality as artificial constructs which could emanate only out of subjective approaches employed by conscious human intelligence. To this effect, the implications of cognitive psychology become significant regarding the evaluation of such interaction between research information sources (both primary and secondary) and the actual research issue resolution processes. In this context, it is always necessary to consolidate the multiplicity of knowledge strands which could generally be obtained from the tangible factors and incidents related to the Epistemological studies, the utilisation of the preferred research philosophical construct of Positivism could be considered by the Researcher (Wiek and Lang, 2016, p.34). The objective would be to consolidate the collection of accurate research data. To this purpose, the Researcher would be opting to utilise the specific subset of the selected research philosophy in the form of Post-Positivist philosophical approach in the overall data collection and analysis approaches. As a side note, it is necessary to acknowledge that Post-Positivism has been an Epistemological evolutionary outcome. The justification of such a preference could be illustrated in the manner of the necessity to achieve the most empiricist observation of the process of evaluation of data collection and analysis through which obtainment of accurate data outcomes could be achieved. To this purpose, the utilisation of the Post-Positivist research philosophy could be considered to be effective in terms of furnishing adequate opportunity to the Researcher to quantify and data analysis outcomes involving the responses generated from the survey of the research participants and to further synthesise accurate, credible and verifiable research conclusions (Kothari, 2004). Furthermore, greater assistance could be accorded to the Researcher through Post-Positivism for the purpose of formulation of differential structural frameworks through which planning and obtainment of study imperatives could be performed. The fundamental reason of this could be contemplated as the inadequacy of measures of proper interpretational themes of collected research data in other research philosophies which could only be rectified through the application of Post-Positivism (Peffers et al. 2007, p.59). The congruent similarities within the differential strands of collected research data could be explored through authentication and verification of such data sets through such research philosophies as well. The purpose would be to generate research findings which could be accurate and able to be validated to extensive measures. The empiricist research approach associated with the research philosophy of Post-Positivism could also be considered to be effective in terms of the selection of this research philosophy in the forthcoming research project (Silverman, 2016).
The research approach
Considerable significance is accorded to the process of examination, evaluation and testing of objective as well as theoretical constructs which could be outlined within the discourse of the research process through the utilisation of the Deductive Research Approach. O'Leary (1993) have emphasised on the purpose of this to be the accurate utilisation of an empirical research process through which better credibility could be infused within the entire research project such as the forthcoming one. Furthermore, this format of research approach is particularly effective in terms of concentrating the required emphasis on effective and extensive evaluation of data, collected through primary and secondary methodical measures, during the data capture phase of the associated research project (Shi, 2019). This could be further illustrated as an ascending format of progression of implemented research procedures through which application of theoretical constructs, which, could be deemed by the Researcher as pertinent ones in terms of the collection of empirical and verifiable research evidence pertaining to the selected research topic, within the entire structural process of the research project, could be undertaken without any procedural errors which generally occur in an unwarranted manner. Selection of comparatively extensive research samples is another significant and integral aspect of this research approach. Finally, the Deductive Approach could further enable the Researcher to synthesise data analysis outcomes in the most credulous and accurate manner.
Research Design
Research methodical frameworks involving integration of differential techniques so as to combine multiplicity of analytical components pertaining to collected research data in the most logical and credible manner, are of vital significance for any empirical research project(Nassaji, 2015). To this effect, the Researcher has concentrated on selection of the Descriptive Research Design since this research design is critical in terms of provisioning of adequate insights of the differential data assessment and outcome analysis processes. Such insights are significant from the perspectives of development of efficacious solutions to existing research problems and to perform assessment of the identified research questions.
Research Sample
The test instrument for the pilot study had been selected by the Researcher to be utilised on the identified research sample encompassing 15 different business organisations. These organisations are mostly the accounting institutions which have implemented the Expert Systems based AI applications and had provided training to their personnel regarding the associated accounting functionalities completely. Furthermore, these are the active accounting institutions which are still undergoing this process. The selection of the particular organisations has been incumbent upon a random selection process involving 90 different organisations which utilise Expert Systems based AI applications. The organisations have been selected from the list of attendees of the conference sponsored by the American Association for Artificial Intelligence pertaining to discussions regarding application of AI assisted systems within the disciplines of the accounting industry. The selection process entailed selection of 1 individual each from the determined numbers of accounting organisations on the basis of purposive sampling. This specific format of sampling is also referred to as sampling procedures based on judgemental methods and involves non-probability sampling procedures. The Researcher has the objective of production of a research respondent sample through which logical assumptions could be developed regarding the representation of the research population. The Researcher has attempted to accomplish this endeavour through application of expert knowledge regarding the accounting industry for the purpose of selecting the non-random sample so as to identify and represent the cross-section of the existing population in the most effective manner (Certo et al. 2016). In terms of the probability sampling technique, each of the involved elements within the population has been ascribed a non-zero opportunity regarding the possibility of selection through the utilisation of any random selection procedure (Silverman, 2016). On the contrary, the Researcher has ensured the application of the non-probability sampling process which does not involve such known nonzero probabilities in terms of the possibility of selection. To this effect, the Researcher has utilised subjective selection methods for the purpose of deciding the respondents who could be included within the sample itself. The non-probability sampling method also involves focusing on the units which could be investigated on the basis of judgemental subjective evaluation. The primary objective is to develop a purposive sampling effort so that focus could be concentrated on the particular characteristics regarding the research population of interest. This has been envisaged by the Researcher to be the method which could be best suited to synthesise proper answers for the existing research questions (Etikan, Musa and Alkassim, 2016). However, the sample selected by the Researcher has not been completely representative of the entire research population since the selected sample of 15 personnel has encompassed mostly the directorial and chief executive positions in terms of work designations of the involved individuals pertaining to the selected active accounting organisations under consideration. In spite of such a fact, it has been demonstrative of the efforts of the Researcher to pursue the mixed methods of research through purposive sampling based research respondent selection for the development of Quantitative questionnaire based response measures for the purpose of collection of accurate data on the selected research topic (Cuddeback et al. 2004). Furthermore, the purpose of this selection could consistently vary regarding the measure and extent of purposive sampling techniques applied within the research process. This could be further illustrated from the perspective of Etikan, Musa and Alkassim (2016), that, the sampling measure involving Homogeneous Sampling processes could encompass the units which are selected on the basis of similarity of characteristics since such characteristics could be of particular significance and interest for the respective Researcher. On the contrary, the measures of Critical Case based Sampling have been considered by the Researcher since this ode of sampling is frequently utilised by the various qualitative, exploratory and quantitative research formats so as to properly asses the possibility of existence of the identified or presumed phenomenon of interest within the research architecture (Raeisi-Gahrooei, Khodabakhshian and Hooshmand, 2018). Thus, it is, therefore, necessary to observe the efficacy of application of Purposive Sampling in this context of research. The emphasis has been on the fact that within the course of Quantitative or Mixed Methods based research design development, the utilisation of a combination of differential purposive sampling techniques could be observed to be effective to bring into context the overall extent of data which could be required to develop fundamental research outcomes. To this effect, the Researcher has carefully considered to utilise the Critical Case evaluation based sampling aspect which could be utilised to investigate the worth of further research concerning the phenomenon of interest in context of the identified variables pertaining to this research prospect. The objective has been to develop the techniques required for instituting the Maximum Variations Sampling (Criscuolo et al. 2019). Furthermore, in addition to the accumulation of information and knowledge, the element of significance concerning the availability of research respondents and their propensity towards cooperating with the Researcher in terms of participating in the research process, also has crucial implications on the overall success achievement prospects for the research project under consideration. Another factor which has influenced the Researcher to take it into cognisance has been the ability of such participants of the research project to properly communicate their experiences and opinions within an articulate, reflective and expressive manner. This aspect could highlight the efficacy of purposive sampling in the form of achievement of specificity as opposed to the generalizability of research findings which are fostered through probabilistic sampling methods through randomised selection procedures. This could, however, not ensure the minimisation of research bias potential for the overall selection of the entire research sample and accumulation of proper data from these. Thus, for the Researcher, it has been paramount in terms of the controlling of the potential influence of such identified and unidentified confounders as well while having to formulate the overall research sample and then, determining the most specific and suitable method through which the efficient and accurate mode of data collection, accumulation, collation, analysis and synthesis of the conclusive observations could be achieved. The research of Tongco (2007) has enumerated the fact that, regardless of the procedural specifics associated with the methodology under consideration and employed with the research project, in terms of Quantitative or Qualitative data collection and sampling methods, it is always necessary to maximise the validity and efficiency of the data collection and analysis process so as to ensure that no deviation from the appropriate process of research management could become a possibility. Nevertheless, it is always necessary that sampling processes should be consistently developed in alignment with the aims and objectives as well as the inherent assumptions of the research project under consideration. In terms of development of research data collection processes, the Qualitative method application, in most part, could ensure the achievement of extensive depth of understanding regarding the research problem under consideration (Clougherty, Duso and Muck, 2016). On the other hand, Quantitative methods of research data collection are best suitable for the purpose of measuring the breadth of the achieved research comprehension and understanding to the greatest extent. While Qualitative research methods could impact primary emphasis on the factor of saturation, involving the obtainment of comprehensive understanding through continuation of engagement with the research sample until the scope of obtainment of new and greater substantive information could be exhausted completely, the Quantitative research and data collection methods could be utilised to develop generalizability based emphasis so that properly ensuring of gained knowledge in terms of representation of the engaged research populace in the most accurate manner, could be achieved completely (Certo et al. 2016). To this effect, each of the methodologies, in turn, has been evaluated by the Researcher to determine their efficacy in opposition to the variegated expectations and standards of the research. The obtainment of the research aim has been the primary catalyst which has driven such considerations and evaluations. The Type I and Type II errors could be avoided by the Quantitative methods of research since such research methods generally utilise the formulae which has been established for such purposes. On the other hand, no such formula based approach could be determined from the perspective of Qualitative approaches. Thus, it is always a matter of precedents to determine the number of participants on the basis of whom the analytical type of the data could be determined. This dilemma could be better illustrated from the perspective that 36 to participants of the research could be interviewed for multiplicity of occasions regarding the application of Qualitative research methods through the application of the Grounded Theory or, 20 to 30 personnel could be interviewed either once or twice. Furthermore, the level of detail which could be required to ensure that homogeneity of the sample could be maintained, is another factor which has been taken into consideration by the Researcher. The reason could be understood as the limited time frame which has been available to the Researcher in terms of accessing the research participants and development of the required questionnaire through which the responses of these personnel could be garnered (Tongco, 2007). The time duration restraints have also prompted the researcher to preclude any possibility regarding heterogeneity based sampling processes which could require considerably larger samples of research participants to be engaged with for expanding the data collection procedural horizons.
To this effect, the development and application of a four phase based framework was undertaken by the Researcher regarding sampling the personnel amongst the identified individuals who have been deemed to be eligible for inclusion within the research data synthesis process. The objective has been to enhance the element of data richness to the extent where information could be extracted from individuals who have been prioritised to be included within the research data collection process (Raeisi-Gahrooei, Khodabakhshian and Hooshmand, 2018). The range and setting of such sample extent have been extensive and special emphasis has been placed on the element of relevancy since the review process of the collected data from the identified and engaged participants could become jeopardised if absolute relevancy of the questionnaire and data presentation could not be maintained to the extent which is required.
The four phase based process of sample development


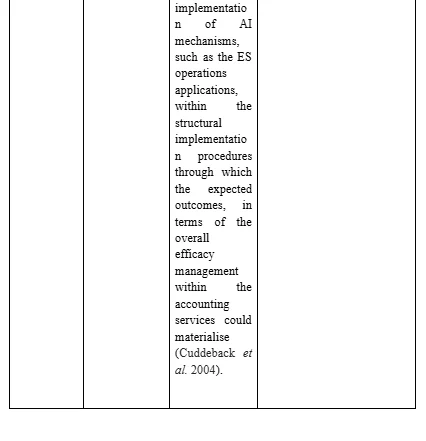
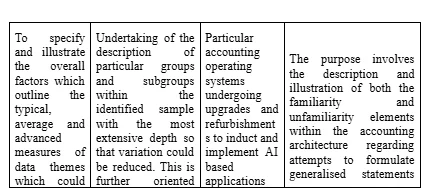
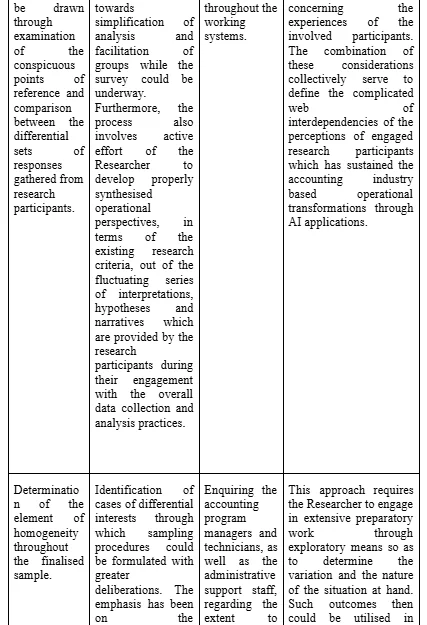
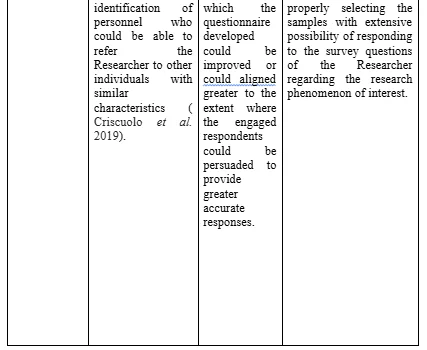
Concerning the overall implications of the accuracy of research data collection, the sampling method employed for this purpose had to take into account the uniqueness and novelty of the assigned responsibilities to the Researcher. Thus, the selection of the research approach and associated methods had to be extensively reliable. In this context, the capturing of major variations has been intended to identify the commonality of different strands of data. The emphasis is on the fact that such commonality could emerge in the due course of time through the analytical process (Clougherty, Duso and Muck, 2016). To this effect, the Researcher has combined the typical case sampling with the maximised variation sampling method through application of the purposeful sample mechanisms to determine the average and below average instances of response possibilities involving the particular questions which have been formulated within the research questionnaire. The selected number of research respondents has not been representative of the entire variation sample. However, the selected sample has appropriately represented the simple typical case sampling measures. Overall, the sampling process has involved tactical case based sampling approaches rather than involvement of complete variations of responses since, that would have required encompassing a lot greater numbers of research respondents, which have not been possible for the Researcher under consideration. Furthermore, the Researcher has undertaken special effort to evaluate confirmatory references which could be comparable to the overall examples of data patterns identified so as to effectively add to the depth and credibility of the identified research outcomes. Disconfirming cases have outlined sources of rival data themes which have not been paid the extent of attention which has been devoted to the analysis of overall data themes since no cross-referencing and cross-validation has been possible in this context. The disconfirming cases could only be employed whenever the possibility of identification of properly representative samples concerning the research population could be diminishing. Thus, the Researcher has realised that at the very outset of the study, it is required to drawn the outline of the research sample. The ethnographic field work involvement, in case of any future research project, could involve such an approach involving the disconfirming cases as well.
Selecting of 15 different members of the 15 randomly selected organisations has involved the application of the systematic stratified sampling process. This process has been completed in two specific phases. The initial phase involved utilisation of systematic sampling methods which divided the entire research population of selected personnel within subgroupings of strata. The basis had been identification of shared characteristics. The shared characteristics have been the following:
1: The personnel were divided as per their association with similar accounting functionalities pertaining to their complete independence from technical advisors/operators within their employer organisations.
2: The personnel were categorised on the basis of their official designations as knowledge engineers as per their familiarity measures regarding the information and knowledge acquisition procedures which are integral to the operations systems of their accounting functionalities. To this effect, the Researcher has only approached and enlisted the services of directorial and managerial personnel of the 15 selected accounting institutions.
3: The personnel were categorised on the basis of their familiarity with the specialised applications computer software. This was deemed essential since constituting and maintaining the ES based AI applications required minute familiarity with software applications.
The justification of this categorisation could be explained as the logical expectation that the measurement of survey generated data solutions to vary extensively between different strata and this requires ensuring of representation of every subgroup. Furthermore, the next phase involved utilisation of regular intervals from the frame of sampling so as to utilise the intervals to ensure adequate size of the final sample. The intervals were determined through selection of every x/nth individual from the total number of research populace involving each stratum. Proportionality was ensured through this approach.
Data capture
As has been delineated earlier, the numbers of research respondents contacted and responses received were 15. From the entire research population, the generated rate of response was 100% and specific effort was invested by the Researcher to analyse the timing of reception of such responses so as to determine the response bias measures. The culmination of data capture effort did not yield any such response bias. The exclusion criteria were applied to 15 responses. The Researcher was left with only 15 effective responses regarding provisioning of appropriate information concerning accounting functionalities and management of data in the associated processes.
Research Questionnaire
1: What could be the approximation concerning the extent of ES mechanisms based operational frame of rules within your work systems?
0. 0-20
1.21-50
2. 51-100
3. 100-500
4. >500
Responses
2: What could be the extent to which the application of ES mechanisms could control the utilisation of alternative strategies of search and identification within the accounting systems?
0.0
1.1-25%
2.26-50%
3.51-75%
4. 76-100%
Responses

3: What could be the percentage based extent of differential options which have been developed so as to provide assistance to exceptions of searches and in cases of situations which do not conform to standard measures of operations experienced by the accountants?
0.0
1. 1-25%
2.26-50%
3.51-75%
4. 76-100%
Responses

4: Do such operatives of ES functionalities involve all of the organisational employees or do only departmental accountant professionals could access the systems?
0. No
1. Yes
Responses
5: What could be the extent to which new rules could be inducted and old ones could be excluded from search and analysis procedures within the ES mechanisms based accounting framework?
4 3 2 1 0
Daily Every Week Every Month Every Year Never
Responses

6: What could be the increment or decrease in proficiency of accounting professionals due to the application of ES processes?
Very much Somewhat No Somewhat Very Much
Increased Increased Decreased Decreased
Responses


7: Are there professionals who are provided access to such services who do not belong to the same accounting departments and could be associated with other accounting groups?
1. Yes
0. No
Responses

8: What could be the status of either increment or decrease of the required managerial, functional and technical supervisions involving occurrences which could not be standardised in terms of managing the accounting functionalities?
1 2 3 4 5
Considerable Some No Some Decrease Considerable Decrease
Responses


9: What are the workability extents within which the operatives could either partially alter or completely disregard the ES mechanisms based conclusions?
0.0
1.1-25%
2. 26-50%
3.51-75%
4. 76-100%
Responses


10: Can the wider and narrow accounting complications be managed through engagement with user based ES applications within your organisations?
0: Much Wider
1: Somewhat Wider
2: Wider
3: Not Wider
4: Narrower
Responses
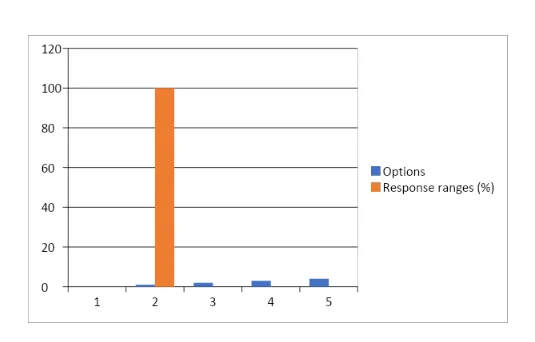
11: What could be the measures to which immediacy and speed of operational decision formulation has been increased in comparison to the previous methods?
0:Much More
1: More
2: The Same
3: Less
4: Much Less
Responses
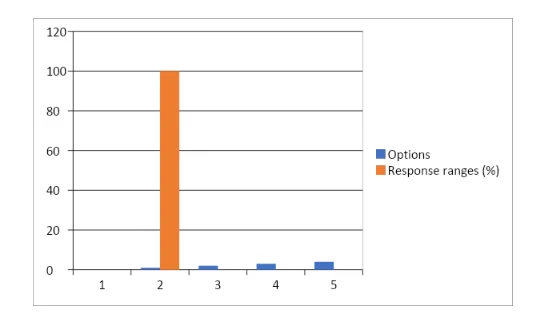
12: How much efficacy improvement has been achieved in terms of handling of greater workloads without having to undertake particular supervisions in comparison to the previously utilised systems of accounting functionalities management?
Much More
More
The Same
Less
Much Less
Responses

Findings and Analysis
Observations for data findings from Question 1
The response data provided by the engaged respondents have specified the propensity of greater utilisation of Expert Systems based operational frame of rules in the accounting functionalities of organisations under consideration regarding the data collection based research process. The measure of standard deviation assessed has attested to the fact that the data accuracy deviation has not been that of a concern.
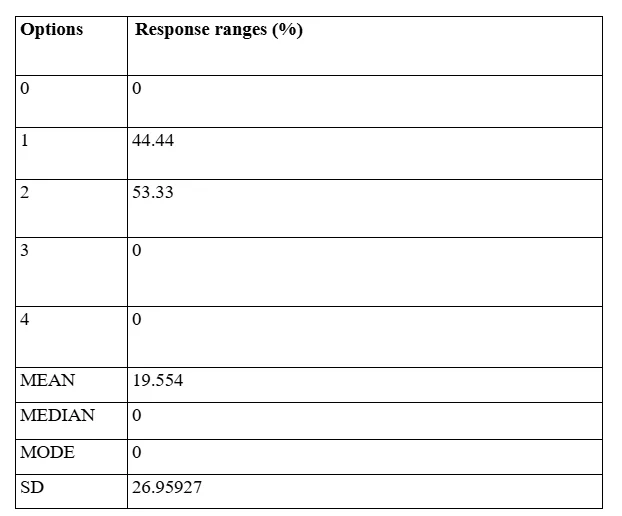
Observations for data findings from Question 2
Application of the above demonstrated question has been of vital significance from the perspective of the Researcher since the alternative strategies of search and optional functionality identification have been fundamental in terms of development of AI assisted ES mechanism based accounting operations within the two particular accounting organisations selected by the Researcher for the purpose of the research project under consideration. To this effect, the data collection effort based pilot study has demonstrated the gathered responses from the active research respondents, as has been illustrated in the above demonstrated data exhibition and categorisation table. Out of the gathered responses, the relatively constricted Standard Deviation has attested to the fact that the data accuracy sequence has been maintained to a credible extent and the variation of responses has not caused any data bias. The evaluation could outline the fact that this process of ES applications based alternative calculations and data search strategies in the discourse of accounting functionalities is under consistent practice at the two selected organisations although this approach remains at a nascent and fledgling phase.
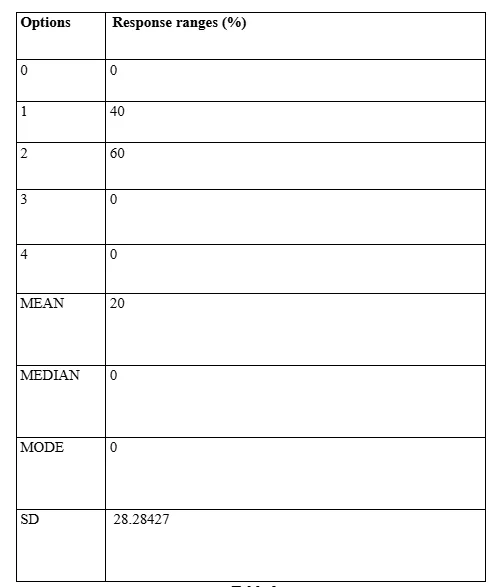
Observations for data findings from Question 3
The data outcome demonstrated within the Table 3 has outlined that, differential optional applications based accounting operations, have been developed to a sustainable measure though the percentage is primarily of limited extent. Involving the introduction of ES mechanisms within the accounting industry, the associated question was incumbent upon determination of the progression scale of AI assisted technologies within such discourses. The outcome has specified the fact that, in spite of sustainable progress which has been verified in terms of alternative technology application in this context, the AI application measures are still at the nascent phase which requires greater time and effort for such practices to effectively evolve into mainstream accounting practices throughout the entire spectrum of accounting operations. The limited Standard Deviation extent also attests to the actualities deduced by the evaluation of such data by the Researcher.
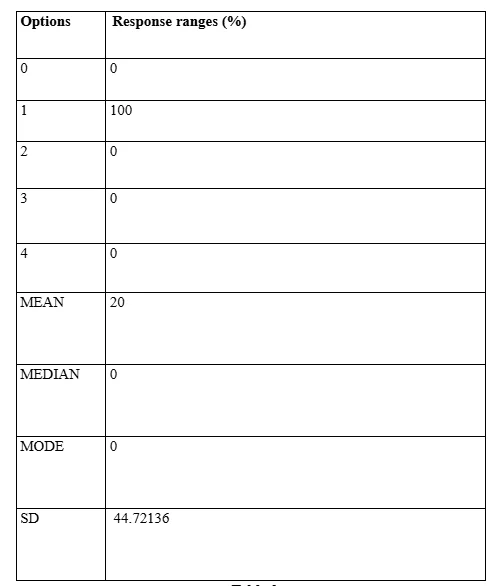
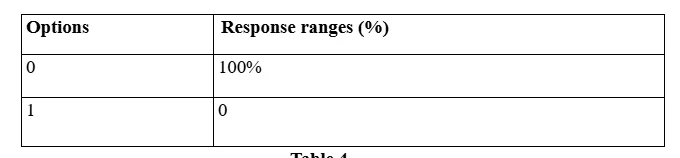
Observations for data findings from Question 4
The fourth question in the developed questionnaire has been constituted by the Researcher for the Pilot Study to determine the accessibility and, accordingly, the familiarity extent of the employees of the two selected accounting organisations to the applied ES mechanisms. The response data accumulated by the Researcher in this context has confirmed the initial assumption developed by the data evaluation outcomes from the previous questions based assessment that utilisation of ES and other AI applications assisted functionality automation has been constricted primarily to the domains of accountant professionals and the familiarisation measure has not been entrusted to have undertaken by the organisational management strata since the AI based operations are primarily technically demanding ones and only professionals with adequate training and experiences could be assorted to operate such processes.
Observations for data findings from Question 5
The question associated with the responses generated by the respondents, demonstrated in the Table 5, has been formulated by the Researcher to evaluate the most vital perspective concerning the initiation of the Pilot Study. This has been to determine the extent to which the selected accounting institutions have been investing effort in terms of inducting and upgrading their AI assisted accounting automation functionality mechanisms. The time bound sequential assessment process and the associated enquiry levelled by the Researcher has been both intended to establish such procedural particularities. The extent of Standard Deviation has been below the threshold of variation which could cause serious fluctuation in data response sequences. Thus, the data accuracy has been ensured through such an observation.
Observations for data findings from Question 6
Table 6 has demonstrated the response data derived from 15 respondents to the research process regarding the fundamental inquest concerning the overall efficiency measure transformation of the accounting professionals who have been utilising ES mechanisms. The perceptions of the respondents have categorically attested to the positive assumptions regarding enhancement of operational efficacy of such professionals, though, not to any considerable extent. The consistent Standard Deviation has been representative of the stability of received responses in terms of data variability. This could be further illustrated as, that, it is the average distance which exists in between the data value and the standard mean of such data. In terms of the existing Standard Deviation, it suggests that data variability is extended over a medium range of differential values.
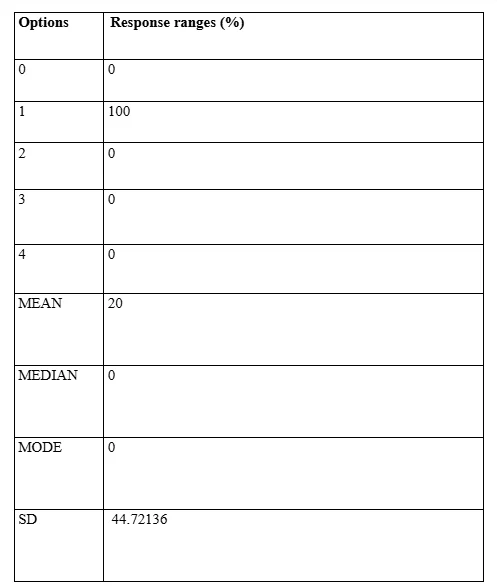
Observations for data findings from Question 7
The question associated with the data responses received and demonstrated in the Table 7, had been formulated by the Researcher as an extension of the inquest concerning the proliferation of AI assisted ES mechanisms within the selected organisations. The objective of the associated inquest was to determine the extent to which inclusivity measures have been implemented within the organisations under consideration concerning differential operation of accounting functionalities conducted through ES processes. In this context, the data was of significance concerning inter-departmental access of professionals to the instilled ES applications. The demonstrated data responses attested to the unanimous affirmative acclamation that such inter-departmental accessibility is an observed practice within the selected organisation under consideration. However, this finding has to be put in perspective as it directly contradicts the conclusive findings of question 4 where the accessibility of AI systems to personnel across the organisational spectrum has been claimed by the respondents to have been constricted only to the accounting personnel. Thus, this finding is primarily a self-contradictory one within the research process which has contributed to the requirement of directing further effort by the Researcher towards validations of such antithetical data findings. The requirement, in this context, is to ensure the proper synthesis of data analysis conclusions so that variability coefficients in the data themes could be successfully precluded with associated deviations in accurate responses.
Observations for data findings from Question 8
The associated research inquest has been formulated on the predominance axiom of human resources over supervision functionalities involving technical, managerial and functional sectors. The objective has been to determine the implications of decisive combination of human and technical resources (in the form of ES mechanisms and other AI applications) through the Pilot Study based research process. The obtained Standard Deviation has been below than 0 and this could be interpreted as the data response points have been mostly clustered at a closer statistical proximity to the data mean. The acquired data findings have been indicative of the outcome which has been so far speculated by the Researcher. The Standard Deviation has outlined that the application of the Trimmean method has become required since Standard Deviation could never be an actual negative one. The subsequent method applied by the Researcher has involved calculations through exclusion of data point percentages from the initial and final portions of the data set so as to exclude the outlying data from the analytical approaches. When Standard Deviation is less than 0, then, it actually indicates that the data points and interquartile range of data mean are overlapping with each other. Thus, the Researcher has paired the SD with the determined mean to quantify the data spread completely. The approach has proved to be effective in terms of comparison of multiple data sets.
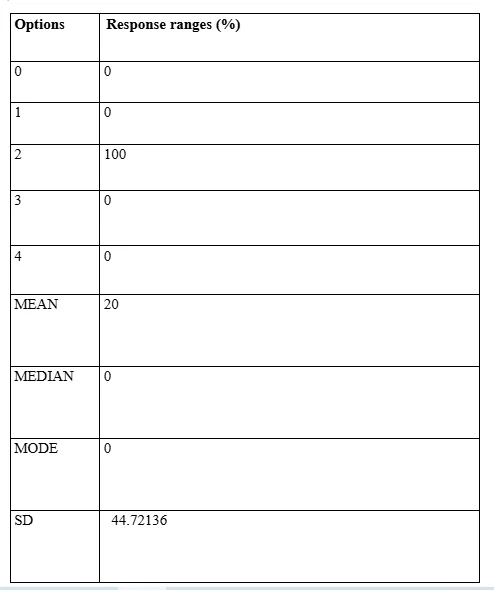
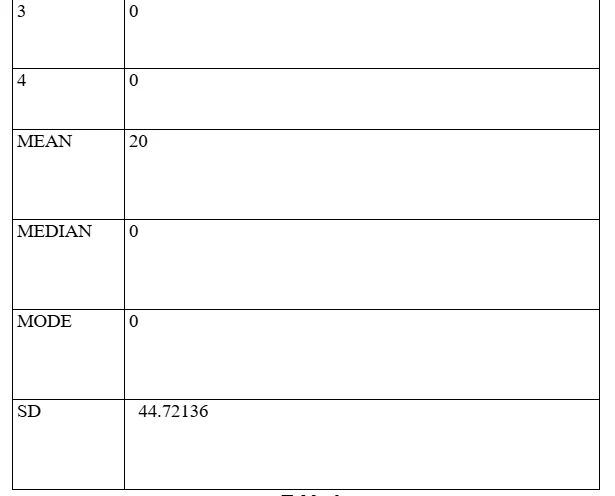
Observations for data findings from Question 9
The question under consideration has been formulated by the Researcher on the perspective of evaluation of the element of flexibility and autonomy of accounting professionals concerning exertion of control and manipulation of outcomes of accounting functionality processes involving ES mechanisms. The response value has outlined, again, the relative close proximity of the data mean value and that of the SD. However, the spread of data value has been comparatively greater since the SD value is of greater extent (almost 50%). The data finding has determined that the extent of multidirectional application of ES mechanisms, involving operations and rectifications of the accounting processes, has not managed to be dominant in terms of comparative operability with the conventional accounting processes which are not assisted by AI intervention based technologies related to accounting services.
Observations for data findings from Question 10
The question associated with the data responses demonstrated in the Table 11 has been indicative of the particularities of the versatility element which is expected of ES applications. The SD value has been that of the previous data findings and could thus be contended that, the data values indicate medium measures of dispersion from that of the determined mean. Thus, the expected variability measure could be countenanced to be a manageable one which does not negatively impinge upon the overall data value accuracy.
Observations for data findings from Question 11
The Table 11 demonstrates the sequential measure of the value of gathered response data which has been provided by the research respondents involved in the Pilot Study. The objective had been to determine the actual efficacy measure of the application of such AI assisted applications regarding the accounting functionality management processes which are practiced within the two selected business organisations under consideration. The relatively moderate SD has been indicative of the overall composite nature of the data response values with the data mean determined so far. The unanimity of responses outlined the fact that the respondents are on the same page, so to speak, from the perspective of their assumptions regarding advancement of the swiftness of accounting solutions development related decision formulation capabilities introduced by the ES mechanisms.
Observations for data findings from Question 12
The Table 12 has been associated with demonstration of response values gathered from 15 respondents to the Pilot Study with the specific purpose of determination of the fundamental benefit associated with application of AI assisted automated work management procedures within any business organisation in the form of progressive workload management. In spite of the limited variability of the responses, outlined by the relatively small SD value, the responses have been contradictory in the most measure. In this context, the Researcher has utilised the mathematical approach under the perceptual description that all the initial values of the gathered response sequences could be equal. Thus, it was supposed that there have been n values which are equal to that of x. The mean of this has been determined through the following formula:
x=(x+x+x+………….+x)/n=nx/n=x.
Furthermore, the sample variation (s2) has been considered equal to that of the mean value of the response data. The following equation has been utilised in this context:
0 = (1/(n - 1)) ∑ (xi - x )2
The value of n-1 has been utilised to multiply both of the sides of the above equation to determine the proximity of individual response clusters to that of the overall data mean. The sum of this squared deviation has been researched to be that of 0. The Researcher has managed to understand that this outcome could be validated only through the perspective that each one of the squared deviations would be required to have a value comparable either to 0 or less. This could be illustrated as the following:
(xi - x )2 = 0.
Furthermore, the Researcher has taken the square root of the above demonstrated equation to demonstrate the every deviation from the acquired mean has to be equal to 0 in terms of value. This has been obtained from the fact that since for all of the denominations of i, xi - x = 0 stands to be the value, thus, every data value could be demonstrated to be equal to the obtained mean.
At this phase of data capture and analysis, it has been deemed required by the Researcher too evaluate the findings from an aggregate perspective. In this context, the aggregate outcomes could be effectively outline that ES mechanisms could be efficaciously utilised for the purpose of enabling the accounting personnel to exercise the required measures of control regarding development of search options and solutions regarding the accounting procedures under consideration. Furthermore, the data analysis findings also confirm the fact that greater discretion could be achieved through implementation of ES mechanisms recommended solutions. This has been critical in terms of availing consequential discretion for the ES application operators. This benefit has been further responsible for enabling the accounting professionals to not be in requirement of supervision control from the higher echelons of management. The AI mechanisms have enabled the accounting professionals currently working within the two organisations selected for the pilot study to develop the capability to solve greater complications with extensive range of operations and greater frequency of accuracy management. Such findings also determine that greater multitasking span could be achieved in terms of accounting roles management within the business organisations. The added benefit to such application of AI operational applications within the accounting industry has been outlined by the data research and analysis process in the manner of garnering better control over various search and data entry processes through the ES mechanisms application within the accounting auditing processes. This could further be illustrated as requirement of lesser measures of supervision as the autonomy aspect associated with functionality management and decision formulation could improve regarding the roles and capabilities of accounting professionals. The integration of AI mechanisms with those of the decisional range of accounting professionals has been the most significant outcome of the data capture and analysis exercise pertaining to the research pilot study.
However, in spite of such integral properties of AI assisted accounting operations with the overall functionality disciplines of both of the accounting organisations under consideration, the differential and noticeable divergences within such functionalities are also required to be taken into consideration. To this effect, the ordinal summarisation scale has been utilised by the Researcher to manage the obtained data. The outcomes have been detailed in the following as it could be deduced from the Pilot Study:
1: It has become apparent that accounting professionals have greater control on the processes of search in comparison to the AI mechanisms. This attests to the determination of greater control potential for accounting professionals on the search options.
2: With the relatively small mean value demonstrated regarding the percentage between the search rules and procedural exceptions, it could be understood that ES mechanisms have been effectively incorporated within the accounting process to effectively manage the exceptions which could be encountered.
3: The responses provided by the research participants have been converging in most of the occasions in spite of the fact that the respondents have been selected from differential groups of accountants from within the two organisations under consideration. In all practical purposes, the convergence/overlapping of functionalities of operators of AI systems at the selected organisation could attest to the fact that such accounting professionals had gained direct influence on the functionalities of coordination of tasks and effective execution of responsibilities within the accounting institutions concerned.
4: The relative stability of the frequency at which ES mechanisms have been consistently updated, is a significant feature concerning the per annum based performance of such updating efforts. The time bound processes of assessment and the concerned enquiry performed by the Researcher in such contexts have been specific in outlining such data findings and in development of such particular outcomes. Furthermore, the significant convergence of responses with stable mean value has been also indicative of the fact that ES management and facilitation, at the functional and operative levels, have been mostly constricted to the personnel executing the accounting responsibilities (auditing and other functionalities).
5: The most significant aggregate finding has been that this research has indicated that requirements of supervisions have been curtailed to certain extents through the application of such ES applications since the obtained benefits permit the accounting professionals to operate in an independent and self-reliant manner since they could obtain assistance from automated artificial intelligence based software applications (Expert Systems).
Finally, it could as well be observed that ES applications have managed to favourably empower the accounting professionals to execute greater measures of assigned workloads with maximisation of diversification even while the extent of required supervision could be minimal. The factor of automated and self-evolving learning software application through AI systems has been responsible for provisioning of service assistance.
Conclusion
At the conclusive stage, it could be observed that the finalisation of the entire Pilot Study instrument has been the requirement to balance and adjust availability of time and accessibility to research respondents. The relatively short research sample has been responsible for the dearth of proper and diversified data accumulation as far as the overall research accuracy and empirical approach is concerned. The concepts of correlation and causation could be understood to be the natural factors which constitute the outcomes of any probability and statistical investigation based research Pilot Study. However, a considerable or even sizable sample of research participants could be the requirement for constitution of the basis on which empirical and verifiable outcomes could be achieved. This further requires the natural gradient of methodical application of research techniques which could be illustrated in the format of questionnaire based information accumulation in the form of responses generated from research participants. With the sample size of research respondents which has been available to the Researcher, the element of cognitive variation in terms of opinions regarding the research topic and fundamental elements of inquests formulated by the presented questionnaire, have so far been unable to be managed to the extent which had been necessitated for a research process of this particular magnitude. The problem has remained that the Research process has not been able to completely sort out the anchor bias element which could influence a fundamental shift in cognitive preferences of research respondents since the research questions are mostly semi-structured. The limitations explained in this context have brought into focus the requirement of development or acquisition of a comparative structure through which the actual value attached to this empirical process of data collection based research could be compared and contrasted with similar outcomes of differential researches, or, with differential and often contrasting segments of the same research project, to actually judge the overall worth of investment of such efforts in research data collection. This is the required method through which the future research could be progressed further.
Reflective narrative assessment
At the reflective assessment phase, certain particularities have become apparent concerning the purpose of this research. These could be explained from the perspective of the requirement of determination of the functionalities of accounting profession and the associated impacts of Artificial Intelligence based Expert Systems. In this context, the application of the Cycle of Reflection, propounded by Graham Gibbs, has been sought at for the purpose of development of an appropriate reflective assessment of the entire course of the performed research pilot study.

The initial phase of this reflective cycle framework requires the elaboration of the performed actions. From an academic perspective, it could be considered to have been an effort to involve every factor associated with the impartation of differential influences by AI assisted work processes on accounting personnel of the selected organisations under consideration. Such factors have been the influence imparted by ES mechanisms on the supervisory format of accounting functionality management, the enhancement and expansion of accessibility of personnel to such services ( an implicit effect has been the variation in capability matrix of such accounting professionals since they have had to experience considerable transformations in their working conditions as far as the procedural aspects are concerned since self-learning software suits have been introduced under the purview of ES mechanisms) and, the ranges of transformation which have so far occurred in the decisional cycles prevalent at the selected accounting organisations. In this context, the Pilot Study has been concentrated on the singular domain of accounting functionalities such as auditing and others. This entire Pilot Study based research performance initiative has been also oriented towards assessment of collected empirical evidence regarding impact of AI assisted technologies on multiplicity of operational factors associated with accounting functionalities of particular institutions/organisations. The most significant emphasis within the Pilot Study based evaluative instrument has been concentrated on the element of supervision of accounting operations since the introduction of AI based technologies could impact the decision formulation processes associated with such functionalities to an extensive measure and this transformation could either become necessary to be controlled with greater supervision or, the automation of repetitive functionalities of accounting discourses through AI could drastically reduce the required measures of human intervention in the form of supervision. Furthermore, the research has also attempted to gather information regarding the possible negative impacts on job prospects of accounting personnel since the requirement of human intervention based operational performance could be supplanted through AI applications. The second phase necessitated analysis of personal emotive responses. In this context, the Researcher has observed that reflective assessment of the pilot study has also been comparable to a crucial as well as formative cognitive practice within the overall field of research. The commencement of such a reflective assessment of personal emotive factors had involved the interpretive juncture of differential experiences which the Researcher had gathered while having to strive for selection of the research population sample. Furthermore, the overall reflective endeavour progressed through application of reflexive cognitive practices. This is a crucial approach in terms of quantitative research processes since this format of analytical practices could be utilised with credible extent of accuracy to legitimise and validate procedures of data collection and analysis. The Researcher has considered this reflexive approach to be associated with the post-structural approaches and the selection of such a reflective method has been prompted by the fact that the reflexive approach could make the procedures associated with quantitative findings greater transparent. The most significant benefit of reflexive reflection, undertaken by the Researcher, has been that merely reporting the research findings has to be expanded to a certain degree by the Researcher under such propositions to the extent that questioning and explanation of constructing the findings and analytical procedures would be required to be thoroughly undertaken by the finalised research report. In terms of subjective judgement based third phase of the reflective cycle, it could be observed that, within the frame of postmodernist paradigm of reflection based assessment approaches, the most significant effort has to be attached to analysis of heuristic experiences, regardless of subject matters of such research inquiries. The Researcher has deemed this to be essential to validate the research pilot study from differential research perspectives as well. In this discourse of reflection, it has been apparent for the Researcher that identification of latent data themes within the entire collection of opinionative information received from the research respondents, completely is incumbent upon the constructivist research propositions since absolute absence of interpretative frame of references could not be a possibility as far as the quantitative data collection based pilot study instrument utilisation could be concerned. Thus, the Researcher is of the opinion that preconditioning of interpretive propensities of the human mind is required to be subjected to an objective reasoning process when such critical research undertakings are to be executed.

Concerning the fourth phase of the above demonstrated reflective cycle, a collection of extensive arrays of differential realisations could be brought forth to outline the core dynamics of the entire pilot study. These involve an amalgamation of a constructionist and constructivist approaches. It has been also realised that it is not possible to obtain specific knowledge about any research environment in the most objective manner since the inquiry process always formulates the objective perception through various questions which are presented by the Researcher to the research participants/respondents. Thus, the significance lies in the tools, methods and procedures which the research process could be accomplished since the cultural ethos of the research project, including the pilot study, involves constructing and organising the process which could be most suitable in terms of fulfilment of the research objectives. Furthermore, the cross-dynamist in between the anchor bias and confirmation propensities of the Researcher under consideration also become a vital factor which could determine the extent to which certain data collection and their interpretation could be achieved in the most accurate manner. The general observation, in this context, it that AI assisted technology based upgrading of accounting operations and the associated implications on the professional acumen as well as discourses of future progression in this direction could be expected to have an upward increment as time could progress. The trend observed in this regard through the pilot study based data collection and analysis is that various administrative tasks are increasingly performed through AI based technical applications within the working functionality structures of the various evaluated organisations under consideration. The outcome has been that various structural changes have occurred regarding the methods which are utilised by accounting industries in their work responsibility management. Through an individual perspective, the specific determinant of research pilot study based outcomes could be the fact that, notwithstanding the extent of conscious analysis of the obtained experiences, any research process in topics such as the one under consideration, requires extensive material and human resource utilisation so as to realise the probabilities which could exist in terms of research procedures to obtain coveted success. The ultimate objective is to resolve the research issue completely and the pilot study has been oriented towards development of professional guidance through which the future research processes, concerning this topic, could be further developed. Furthermore, the reflection in practice method has been also outlined to be of greater efficiency in terms of utilisation of the same as the foundational practice for prospective research based purposes. Finally, it has to be acknowledged that, students of such research literature, would be required to undertake greater detailing of their efforts for future research projects. The prospective research undertakings in future, involving the implications of AI assisted technology application in accounting functionalities and in overall job prospect security of accounting professionals, would be required to include the following:
1: The researchers/students of such prospective research projects would require to either modify or to alter the required activities associated with both Qualitative and Quantitative research process execution so as to attach greater empirical inquiry effort with the entire research process.
2: The pilot study has not managed to perform any Qualitative research process which has been a serious shortcoming. The reason has been dearth of time and accessibility to high level professionals within the selected accounting organisations. This drawback of the pilot study would be required to be completely redressed by the future research projects performed in this direction.
3: The professional research practices, such as inquiry, both Primary and Secondary in nature, would require to be formulated on a balanced approach combining the survey and interview based data collection and collation methods. Incorporation of acquired knowledge, in this context, could be utilised by the students, to formulate the academic learning methods through which multi-dimensional transformations of the accounting industry could be also perceived in a cross-referential and verifiable manner.
Specific details regarding addressing of research issues in future
The requirement of detailing of efforts of research concerning future research work involves analysis of the communication levels which would be required to be investigated between the accounting professionals and their hierarchical superiors. This could outline the nature and complications pertaining to various accounting services. The considerably greater complicated issues pertaining to determination of extensive accounting responsibilities would require combined efforts of different research teams through overlapping of finding reportage. Such team work would require teams constituted with 11 to 15 different field researchers/research assistants with proper guidance from managerial personnel and supervisors. Focus would be required to be concentrated on investigation of the methods through which reinforcement of working roles of auditors and accountants could be achieved and interpersonal as well as intrapersonal activities between different audit and accounting specialists could be facilitated. Furthermore, greater emphasis would have to be required to be concentrated on selection of larger Quantitative and Qualitative sample sizes for the future pilot studies and associated researches.
Reference List
- Amani, F.A. and Fadlalla, A.M., 2017. Data mining applications in accounting: A review of the literature and organizing framework. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems, 24, pp.32-58.
- Antoniuk, L., Gernego, I., Dyba, V., Polishchuk, Y. and Sybirianska, Y., 2017. Barriers and opportunities for hi-tech innovative small and medium enterprises development in the 4th industrial revolution era. Problems and Perspectives in Management, 15(4), pp.100-113.
- Bagnoli, C., Dal Mas, F. and Massaro, M., 2019. The 4th industrial revolution: Business models and evidence from the field. International Journal of E-Services and Mobile Applications (IJESMA), 11(3), pp.34-47.
- Bloem, J., Van Doorn, M., Duivestein, S., Excoffier, D., Maas, R. and Van Ommeren, E., 2014. The fourth industrial revolution. Things Tighten, 8.
- Brynjolfsson, E., Rock, D. and Syverson, C., 2017. Artificial intelligence and the modern productivity paradox: A clash of expectations and statistics (No. w24001). National Bureau of Economic Research.
- Brynjolfsson, E., Rock, D. and Syverson, C., 2017. Artificial intelligence and the modern productivity paradox: A clash of expectations and statistics (No. w24001). National Bureau of Economic Research.
- Daft, R., and Maclntosh, N.1978. A new approach to the design and use of management information, California Management Review. XXI: 1, 82-92.
- Gordon, L.A., 2018. The Impact of Technology on Contemporary Accounting: An ABCD Perspective. Transactions on Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence, 6(5), pp.10-10.
- Issa, H., Sun, T. and Vasarhelyi, M.A., 2016. Research ideas for artificial intelligence in auditing: The formalization of audit and workforce supplementation. Journal of Emerging Technologies in Accounting, 13(2), pp.1-20.
- Jung, E.S., 2018, December. 4 th Industrial Revolution and Boundry: Challenges and Opportunities. In 2018 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) (pp. 1-1). IEEE.
- Kokina, J. and Davenport, T.H., 2017. The emergence of artificial intelligence: How automation is changing auditing. Journal of Emerging Technologies in Accounting, 14(1), pp.115-122.
- Luo, J., Meng, Q. and Cai, Y., 2018. Analysis of the Impact of Artificial Intelligence application on the Development of Accounting Industry. Open Journal of Business and Management, 6(4), pp.850-856.
- Mirzaey, M., Jamshidi, M.B. and Hojatpour, Y., 2017.Applications of artificial neural networks in information system of management accounting.International Journal of Mechatronics, Electrical and Computer Technology, 7, pp.3523-3530.
- O'Callaghan, S., 1995. An artificial intelligence application of backpropagation neural networks to simulate accountants' assessments of internal control systems using COSO guidelines.
- Pannu, A., 2015. Artificial intelligence and its application in different areas.Artificial Intelligence, 4(10), pp.79-84.
- Peffers, K., Tuunanen, T., Rothenberger, M.A. and Chatterjee, S., 2007. A design science research methodology for information systems research. Journal of management information systems, 24(3), pp.45-77.
- Sutton, S.G., Holt, M. and Arnold, V., 2016. “The reports of my death are greatly exaggerated”—Artificial intelligence research in accounting. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems, 22, pp.60-73.
- Potter, C., 2015. Leadership development: an applied comparison of Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle and Scharmer’s Theory U. Industrial and Commercial Training.
- Cuddeback, G., Wilson, E., Orme, J.G. and Combs-Orme, T., 2004. Detecting and statistically correcting sample selection bias. Journal of Social Service Research, 30(3), pp.19-33.
- Criscuolo, P., Alexy, O., Sharapov, D. and Salter, A., 2019. Lifting the veil: Using a quasi‐replication approach to assess sample selection bias in patent‐based studies. Strategic Management Journal, 40(2), pp.230-252.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



