Safe Material Storage on Construction Sites
Task 1
As a relatively new member of the team on a new construction site which is being set up to build a combined office, warehouse and manufacturing unit on a brownfield site.
You have been asked to look after the safe storage of building materials, tools and personal protective equipment and the safe disposal of waste.
The site is roughly rectangular located on the junction between two trunk roads with footpaths and cycle ways running alongside of the roads. The other two sides of the site have a small road leading to an infant
school along one side and a residential street on the fourth side.
a) Prepare a sketch of the layout of the site which has a construction fronting onto one of the main roads. The main building under construction is 80m long and 20m deep and occupies about one half of the total area of the site. The main health and safety concerns are the storage of construction materials, their safe use during the construction process and the safe disposal of any waste. Particularly consider asbestos and other hazardous demolition materials On the sketch, locate the building under construction and also locations of various storage areas for materials
Factors to consider in location of various storage areas for materials
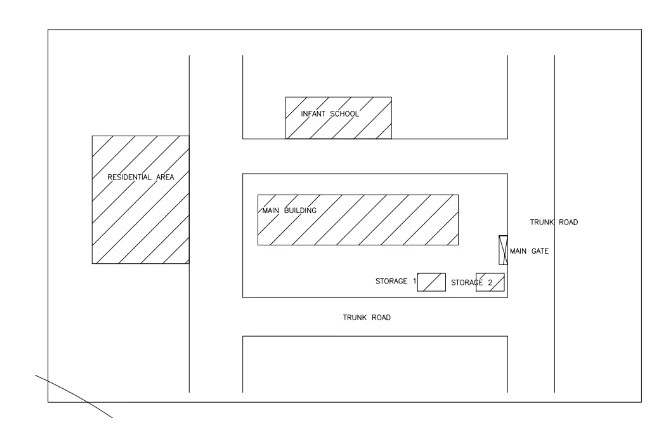
Construction materials can create health and safety risks in the site. The following factors were considered in choosing the locations for the storage areas
1. Should be located away from infant schools. Infants and toddlers are at the greatest risk of being harmed because their immunity system is still developing, thus their caregivers ought to ensure they do not come into contact in any way.
2. Should be located away from residential areas due to the high human traffic as well as vehicles passing frequently.
3. Should be located near the main road for easy transportation. This is highly recommended for hazardous materials like treated timber.
Looking for further insights on Dissertation is the stepping-stone to the Master's Degree? Click here.
4. Should be located near the gate for easy transport. This helps in reducing labor strains and unnecessary fatigue on the workers. This location is also suitable for offloading and loading materials quickly, ensuring that no time is wasted.
b) State what materials would be needed during the preparation of the site including the demolition of existing buildings and in particular outline how the demolition waste is handled and stored before removal off site. Indicate what materials would be needed during the early phases of the construction after the site has been cleared. Also suggest materials involved in the construction of the main structure, what precautions will be needed in their handling and use.
Site clearing involves intense preparation. Strategies of how the site will be demolished need to be communicated to the necessary team.
Materials used during demolition include the following:
- Landscape surveying
Landscape survey is paramount as it will establish if there are plants or trees that need to be salvaged during the demolition. As such, proper legislations regarding the ones to be removed need to have been effected prior to the demolition while the ones to be salvaged need to be protected.
- Mechanical machines like tractors and excavators
These tools are part of demolition itinerary since they have the capacity to bring down complex structures. Legal permit need to be obtained prior to the exercise. Contracts need to be signed by the respective parties. The companies leasing the machines as well as the site owners need to agree on the terms and conditions for leasing the machines.
- Signage for creating awareness
It is required by the law that signs need to be erected during demolition. This serves as a safety procedure, thus they should pass the exact requirements enacted by law in terms of shape, readability and functionality. This will create awareness in passers-by and other citizens who might be affected by the demolition exercise.
- Safety and protective gear for the workers
This is imperative. Construction workers or any laborers are protected by the laws of the land. Any company which fails to meet the safety standards are subjected to legal actions in case injuries occur in the line of duty. These gears ought to be of high quality as well.
How to handle demolition waste
Demolition comes with ample debris in its wake. It is imperative for the site manager to establish clear guidelines on how this waste will be handled. This is because there will be hazardous as well as non-hazardous waste. Each must be handled differently. Waste can include the following: concrete, wood pieces, glass, asbestos, broken tiles, PVC pipes, bricks, plastic as well as bituminous elements like tar. The site manager has to have product knowledge of all types of waste. The manager can involve a few members to separate the waste into different categories. You may find that some of the non-hazardous waste can be recycled and used for the imminent project. The hazardous waste ought to be disposed through the legal way.
Materials needed during early stages of construction
The early construction stages form a crucial aspect of how the final structure will turn out. Thus, it should be handled with utmost care, by utilizing state of the art equipment and durable materials. As such, the basic materials normally depend on the structural design thus whatever works out for one structure may not work for another. The basic materials used include
- Concrete which is poured into the foundation. Concrete is mixed with cement and water to form a solid mass upon drying.
- Sealants which are applied on to the dried concrete to prevent moisture from penetrating into the concrete, resulting in weak foundation.
- Excavators which are used to dig out the soil.

Materials involved in constructing the main structure
These materials are similar to the ones used during early preparation. However, more materials are utilized in this stage as this is where the structure takes its form. It also depends extensively on the design of the structure, thus materials can vary. The basic ones include: Timber; bricks; fabricated steel; fabricated trim; concrete; floor coverings like tiles, wood, granite; roofing; insulation panels; windows; doors; fastenings like nuts, bolts, screws; paint; wallpaper, termite treatment; sewer pipes; plumbing itinerary; landscaping tools and machinery like tractors, cranes, ladders, elevators and drilling machines.
Precautions to take when handling construction materials
- The site manager needs to create awareness on how to handle each type of material.
- All the materials used have to have user guides and manuals which are readable to all.
- The use of protective gears when mixing different chemicals, paints, treatments or when operating the machines.
- Putting up of warning signage in high-traffic areas.
- Ensuring there is ample lighting in the construction site.
c) Prepare a table summarising the main construction materials, what hazards they may present and what measures must be taken to reduce the risks to people working on the site or working moving or living near to the site. Explore, by giving an example, of how a risk assessment on the use of one such material would help to ensure a safe workplace.
A summary of the main construction materials.


A risk assessment on paint involves the following:
Paint is part and parcel of construction. It poses the following risks:

d) Discuss the regulations and ACOPS that would apply to one activity on site during the foundation building.
One activity during building a foundation is the storage of materials. The Approved Codes of Practice (ACOPs) in such a case would entail:
- Ensuring all sections of the site are well maintained and neat.
- There should be no litter or waste lying around.
This is in accordance with the Regulation of Health and Safety at work as well as Occupational Safety and Hazard Acts which state that workplaces must be kept free from potential and recognized hazards.
Task 2
In the past the choice of building materials for the kind of project outlined in task 1 above would have been based on availability, cost and the ability to perform the role that the material has in the structure. Today it is necessary to add further criteria to fulfil the need to protect the environment, to use the minimum of materials that cannot be replaced (non-renewable), to maximise the recycling potential of non-renewable materials that have to be used and produce a waste management plan for the demolition stage of the work. To minimise the amount of embedded energy, use as much renewable material as possible, and minimise the energy needed to keep the internal environment of the new building at a comfortable temperature.
Consider ONE of the following materials to produce the main structure of the building and outline the arguments for and against its use from the environmental and sustainability point of view:
Structural Steel
Construction steel, also known as structural steel has been identified as one of the most popular construction materials for centuries. Its feasibility makes it an outstanding material in the construction industry. This is because it possesses several qualities that make it desirable and on the flip side not quite desirable for certain projects.
Advantages of using construction steel
1. Steel is extremely maintainable
Structural steel is durable. This means it can be reused consistently over a long period of time without compromising on the quality of the structure. It also has the ability to withstand adverse weather conditions. In case a structure is demolished, the scrap parts of the steel used can be remodeled and used in other construction projects.
2. The use of Construction steel is time-friendly.
Since the steel pieces are taken to the construction site after being shaped in the factory, the time spent installing them is greatly reduced. This ensures that the construction is accomplished within the given time-frame.
3. Construction steel is budget-friendly
Compared to other construction materials, steel is fairly cheap. This is why it is a popular material in many construction projects. Another aspect of being budget friendly is that its durability means there are fewer maintenance costs incurred in the long run as a result of using this material.
4. Construction steel has aesthetic value
Construction steel is malleable, thus there is no limit into how steel can be shaped into diverse designs. These designs are appealing to the eye therefore it offers architectural beauty to the structures.
Nevertheless, nothing is 100% perfect, thus construction steel can also be undesirable to use in construction.
Disadvantages of using construction steel
1. Rusting
Steel is a component of iron. As we know, iron is corrosive. Therefore, construction steel that has not been fabricated using appropriate proportions of the required ingredients exposes the construction steel to corrosion.
2. It has extraordinary expansion rate
This especially happens in hot weather conditions. The constant expansion and contraction can eventually have harmful effects on the structural layout.
3. Construction steel can pose safety threats
This is because steel is not fire-proof. This means that in cases of a fire break out, structures made from construction steel are at a higher risk of being destroyed.
The advancement of steel as a construction material in the last 50 years
In as much as steel has been in existence for centuries, its usage has varied extensively across diverse sectors.
Steel became vital in the construction of railway stations. This resulted in massive success of those structures thus steel became a highly sought after material in other structures like churches, offices as well as residential homes. Its popularity shot through the roof at the turn of the 20th Century during the Industrial Revolution as well as in the World Wars when it was utilized in constructing protective accommodations as well as storage facilities. The type of steel used in this era was mostly in its natural state of having iron and carbon, thus the steel industry was considered one of the most labor intensive industries due to the amount of skill needed to produce steel. Over the subsequent years, advancement in technology enabled other elements to be mixed in it, resulting in more complex types of construction steel. Elements like manganese became preferable as it produced a more compact form of steel which made it more durable. It became apparent that oxygen played a key role in making the end product more malleable. Currently, the major types of steel have chemical elements that are categorized as follows:
- Carbon-manganese steels: this comprises of carbon, iron as well as manganese. This type has been the most common one. The end product is mostly of average tenacity.
- Intensive, minimal-alloy steels: this is more current compared to the others. It comprises of more chemical elements which increase the steel’s viability.
- Toughened and slaked amalgamated steel: These are used for structural purposes. It can also be combined with various construction materials like spurred items and cold-pressed materials to enhance tenacity.
Automation as well as technological advances and applications have resulted in better quality of steel that can be used in projects deemed impossible previously.
Task 3
Materials choice for a given building taking into consideration the performance properties, sustainability and environmental concerns
The building under consideration is the same as described in task 1. The additional information needed for this part of the assignment is the height of the building. It is 5 story building with a height of 20m to the eves. It has a flat roof which will be available as an outside space for the building’s occupants. The basic structure will be conventional consisting of vertical columns which support each floor above the ground floor. There will be a grid of 17 rows of equally spaced columns across the frontage of the building, each row having 5 columns.
The columns and beams of such a building would often be made from either steel or concrete.
a) Analyse the advantages and disadvantages of these materials for this structure
Advantages of steel as construction material in high rise structures
Steel has over the decades become more and more popular with builders for construction of both low rise and high rise buildings. It is more popular than both wood and concrete because of the following advantages
Durability - Structural steel is know to have very high yield strength. It is not easy for structural steel to age or decay, compared to other structural materials
The use of structural steel results in lighter buildings because of its high strength - to weight ratio. The foundation for such a light-weight building will be subsequently less expensive
Constructability - Structural steel can be fabricated into whatever shape one desires, owing to its strength, toughness, stiffness and ductile properties
Steel structures require only welding and bolting of the pieces together, which is a pretty fast undertaking, as opposed to a material like concrete which takes more than 2 weeks to cure before achieving significant strength
Steel structures are designed in such a way that tension and compression stress is distributed among several steel beams. This is good for the architects as they can play around with the design as much as they want.
Cost effectiveness - Structural steel components now enjoy an all time ease of erection due to the improving standardization and regulatory policies. This saves both time and money.
Steel structures are therefore constructed within relatively short periods. The neighbourhood suffers less disruption from the construction activities. The purchase price of steel has also significantly dropped, meaning less construction costs
Safety - Structural steel is not porous and therefore mold and mildew find it difficult to grow on steel, making it an ideal choice for residential buildings
Steel can be fabricated off site and then assembled on site. This makes the construction site even safer.
The recyclable nature of steel makes it beneficial to the environment.
Disadvantages of steel as construction material in high rise structures
Though steel is a non-combustible material, its strength and integrity may be considerably affected in case of fire.
Steel is prone to corrosion if not coated well with water resistant coatings
Steel may be a bit expensive to maintain in the long run because it has to be painted time after time to keep it corrosion-resistant
Steel columns are susceptible to buckling when their length increases
Advantages of Concrete as construction material in high rise structures
Concrete is normally reinforced with high yield steel for construction purposes. Here are the advantages of reinforced concrete structures.
Reinforced concrete has a relatively higher compressive strength compared to other building materials
Reinforced concrete ca also withstand a great deal of tensile stress
Reinforced concrete is fairly resistant to both fire and weather elements
Reinforced concrete buildings are the most durable compared to those made from other materials
Reinforced concrete is fluid and thus can be molded into whatever shape desired
Reinforced concrete requires very little maintenance
Reinforced concrete can be used to manufacture precast structural components, which are very difficult to undergo deflection
Erection of reinforced concrete buildings requires less skilled labour than erection of structural steel
Disadvantages of concrete as construction material in high rise structures
Outlined below are the disadvantages of reinforced concrete construction
At a ratio of 1:10, the tensile strength of reinforced concrete is significantly low compared to the compressive strength
The production steps of reinforced concrete - mixing, casting, curing - are known to affect the final strength of the concrete. The strength of reinforced concrete can therefore be compromised if care is not taken during the preparation of the mix.
Reinforced concrete structures incur the extra cost of formworking
The cross section of reinforced concrete columns is generally bigger than that of steel because reinforced concrete has lower compressive strength than steel
Reinforced concrete is prone to shrinkage immediately after casting, which forms cracks and compromises the strength.
b) Suggest an alternative material that has a smaller environmental impact which would could be used and compare its performance in use and its environmental impact compared to the conventional materials mentioned in part a.
Timber
A better alternative would be timber. Timber is a widely used building material which has been in use since time immemorial. A timber frame comprises of panelised structural walls and floors assembled from timber studs and clad with timber boards. A timber building can also be in the form of timber posts and beams. Outlined below are the advantages of timber as a construction material.
Renewability - Timber can be obtained from thousands of tree types. By planting more trees every time you cut down one, timber remains a renewable construction material.
Insulation properties - Timber has excellent insulation properties considering both heat and electricity. It can prevent the room temperature from escaping, thus the occupants won’t have to suffer cold. It also protects the occupants from electrical components. It is therefore widely popular for use on ceilings and wall covers.
Tensile strength - Timber has a high strength to weight ratio, meaning it is both light and strong. Timber exhibits good tensile strength, and thus it can bend significantly before breaking. This makes it usable for structural beams
Versatility - You can bend timber into several shapes, nail different pieces together, bolt timber to another material, etc. On top of these, timber is also easy to move and store.
c) Discuss the standards that would apply.
The main standard used for structural design of timber if Eurocode 5 (EC5). the related loading standards are detailed in EN 1991 “Actions on Structures”. This is divided into three parts as follows
Part 1-1 - densities, self-weight and live loads
Part 1-3 - Snow loads
Part 1-4 - Wind Loads
EN 1990 “Basis of structural design” outlines the principles of limited state design and lists vital requirements for design, including partial safety factors, durability and load combinations for serviceability limit state.
d) Give an example of the testing procedure that would be used to check that the material would be able to support such a structure
The most obvious reason for testing wood is to tell its ultimate strength in compression, tension and flexure. Structural timber is normally subjected to these 3 forces depending on what element we are looking at. For tensile testing, the timber should be placed in the universal testing machine and then loaded so as to pull the timber apart. This simulates what happens in tension failure. For compression testing, the load will be applied opposite to how it was done in tension testing. The ends of the timber ought to be pushed together. Compression testing normally takes two forms - 1. Parallel to the grain and 2. Perpendicular to the grain. Both of these yield different results which show timber exhibits different properties for the different planes. For flexural testing, the load is exerted perpendicular to the grain at the middle of the timber, which is supported underneath at 2 points, so as to make the timber bend in half.
e) Show how the standard ensures that wherever the test is conducted the results can be compared to other materials in a completely different part of the world
The standard uses service class to cater for timber grown in whatever part of the world. Different parts of the world have different climates and this affects the moisture content of the timber. Moisture has a considerable effect on the mechanical properties of timber.. The standard allocates service class designations to cater for this. Service Class 1 - the moisture content in the timber corresponds to a temperature of 200C and a relative humidity exceedingly 65% only for a few weeks in the year. Timber growing in such conditions attains moisture content less than 12%. Service Class 2 - The moisture content in the timber corresponds to a temperature of 200C and a relative humidity exceeding 85% only for a few weeks in the year. Timber growing in such conditions attains a moisture content not more than 20%. Service Class 3 - Timber in this class has higher moisture content
f) Examine any one of the case studies of projects approved under the BREAM scheme given in the following web site https://www.breeam.com/case-studies/ and show how use of sustainable practices and considerations for material choice can improve the environmental rating of the completed building
Organic Building Ergodom (Office Unit)
This building makes use of the passive house technology, where solar energy is used to the maximum for heating, and heat losses are minimized by using organic materials such reed, sand, clay, wood and lime. The building was designed and constructed in accordance to the principles of sustainable development. Its negative impact on the environment was reduced and the consumption of natural resources such as water reduced. The building envelope and wooden windows encourage air microcirculation in the rooms and therefore no need for air conditioning systems. Each room has windows and window blinds that prevent too much sunlight from entering the rooms. Natural finishing materials have been used in the offices, which impacts the employees positively as regards health and wel being. The building has no refrigerants. It instead uses a gas boiler which has low NOx emissions. The building is easily accessible, with ample parking spaces for bicycles. There are facilities for separate collection of solid waste outside the building. The flush toilet systems, showers and other appliances are designed to consume as little water as possible.
g) Look at the maximum load that one of the columns made of reinforced concrete with a diameter of 0.5m could withstand. Use the following information Young’s Modulus, 35GPa, Free length of the column 4m the column is effectively fixed at each end. The Euler Bending Equation is given in https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/euler-column-formula-d_1813.html
Euler buckling load is given by
F = 𝝅2EI/(kL)2
Young’s Modulus of elasticity = 35GPa = 35 x 109 Pa
For n 2, k = 0.7
L = 4m
I = 𝝅d4/64 = 3.068 x 10-3 m4
F = 𝝅2 x 35 x 109 x 3.068 x 10-3/(0.7 x 4)2
= 135.2 MN
Task 4
Evaluate the performance of a given building in respect to its human comfort requirements.
Analyse the factors which will affect the internal environment of the building described in tasks 1,2 and 3.
Good indoor environment at home and in the workplace normally improves the well being and minimizes health risks. Passive design is used in buildings to save energy. Outlined below are the main factors that affect the internal environment of the building:
Light - The building should be constructed in such a way that it receives enough daylight throughout the day
External views - The building should allow the occupants to gaze into the distance, so as to have that connection with the environment
Air Quality - The building should have enough oxygen and minimal pollutants
Ventilation - Each room should be naturally ventilated to provide the dwellers with abundant fresh air.
Thermal comfort - The room should be properly insulated and shaded to provide comfortable temperatures to the users throughout the years.
Noise - The building should be properly shielded from external noise. Internal reverberations should also be minimised to reduce noise.
Materials - the building materials and finishes should have minimum Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) and other dangerous substances.
b) Estimate the rate in kilowatts at which heat needs to be generated in the building to maintain an inside temperature of 200C when the outside temperature is at 00C assuming that the windows make up 30% of the outside wall area. That the walls are insulated to a U value of 0.23 watts m-2 0C-1 the roof and floor to a U value of 0.23 watts m-2 0C-1 and the windows (triple glazed have a U value of 0.9 watts m-2 0C-1
Total fabric heat loss flow rate
Qf = (∑UxAx) x ΔT watts
House fabric elements and heat loss


Therefore, Qf = 2460 (20 - 0) = 49,200 = 49.2 kW
c) If the building is designed for 150 occupants some of whom are sitting most of the time but some are quite active assume that the average need for fresh air averages out at 8 litres per second per person. Calculate how much heat would be lost supplying this amount of cold fresh air when the outside air is at 00C assuming that the specific heat capacity of the air is 1kJm-3 oC-1
We will need to calculate the ventilation contribution to the overall heat loss coefficient
Qv/ΔT = 0.33 x n x V
Where n is the number of air changes per hour and V is the volume of the house in m3.
Qv/ΔT = 0.33 x (8 x 10-3 x 150 x 3600) x (80 x 20 x 20) = 45,619,200
Now sum the fabric and ventillation contributions to give a total whole house heat loss coefficient
(Qf + Qv)/ΔT = 2460 + 45,619,200 = 45,621,660
Therefore Qf + Qv = 45,621,660 x 20 = 912.4 MW

d) One of the spaces inside the building is used for meetings and can hold up to 200 people if needed. The dimensions of this space are 17m x 30mx8m high. The walls of this are 30% glass with an absorption coefficient of (double glazing with 10mm gap) at 500Hz = 0.03, the walls of acoustic timber wall panelling 0.42, the floor as carpeted over concrete is 0.25 and the ceiling is covered with perforated plaster board with an absorption coefficient of 0.85. Calculate the reverberation time of this space.
Reverberation time is the time required for the sound to fade away in the room. The sound will repeatedly bounce off the surfaces within the room until it decays.
Reverberation time is the time it takes for the noise to fade by 60dB
We will use the Sabine formula to calculate approximate reverberation time
RT60 = (0.16 s/m)V/Se
a-glass walls = 0.03; a-walls = 0.42; a-floor = 0.25; a-ceiling = 0.85
a-average = 0.3875
Total surface area of room = (17 x 30 x 2) + (30 x 8 x 2) + (17 x 8 x 2) = 1772
Effective absorbing area Se = (1772 x 0.3875) = 686.65 m2
Volume of room = 30 x 17 x 8 = 4080 m3
Thus RT60 = 0.16(4080/686.65) = 0.950702687 seconds
e) What would you expect to happen to the reverberation time if the hall contained the maximum audience of 200?
If the hall contained the maximum audience of 200 persons, the reverberation time would significantly decrease. The clothes worn by these people will increase absorption coefficient. This will in turn increase the effective absorbing area, and thus the sound will tend to fade away quickly.
f) What design considerations are needed to minimise the energy and other resources in use of this building?
To minimize the use of energy in this building, the following measures should be taken:
Reduce cooling, heating and light demands by employing passive strategies, including climate-responsive design, conservation practices, daylighting
The building should be fitted with efficient HVAC and lighting systems, which use part-load conditions and utility interface requirements
Renewable sources of energy should be used in the building, including solar heaters, photovoltaic cells, groundwater cooling
Use energy modelling programs during the design stage of the building to come up with an optimized design
Incorporate water saving technologies to reduce the use of energy in providing potable water
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



