Adapting to Modern Business Challenges
Introduction
In contemporary business environment characterised by intense competition, changing consumer preference and demands, increased diversification, globalisation, and dependent on constantly changing technologies. Akhmetshin et al. (2017) and Domanović (2013) describe modern business environment as a buyers’ market and largely driven by the consumers. As such, organizations have increasingly remodelled respective approaches to align with market demands, consumer preferences, and regulations aimed as road to survival, business success, market share, and advancing stipulated goals. Such elements as distribution channels have changed narrowing in manner that it consumers are access the commodities as well as developing products to meet consumers’ preferences.
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to Exception for Alternative Consideration.
Building on the purview of inevitability of change, organizations irrespective of size, culture, and aims have been forced adopt new approaches such as abandoning ways of doing things that can be termed outdated models for survival and growth especially for traditional established in 20th century. For instances, globalisation have had a significant influence on social consciousness, workplace culture, and consumer culture and behaviour for most if not all businesses that include connecting the socioeconomically disadvantage, those living in extreme poverty, and developed social and economic worlds. Currently, as argued by Camisón and Villar-López (2014), organizations have obligation to address social and economic issues affecting communities they are doing businesses with whether directly or indirectly. Prominently, businesses entities in apparel industry have recently received numerous criticisms on the working conditions of workers in such areas as Indonesia and Philippines or phones manufacturing subjected to questioning on their role in human right violations and child labour in Congo mines even though most do not directly deal with fibre or tantalum mineral core raw materials respectively (Hodal, 2018; Human Right Watch, 2018; Ochab, 2020). This is not to mention the influence of technology ranging from social media and data mining tools in modelling consumers’ need and marketing for any organization. Kovaleva and de Vries (2016) highlighted that heightening competition in the market as well as changing environments demands constant innovative ways of combating and navigating through for organization growth and success. Collectively, changes in the businesses environment highlighted by increase competition, demands, social responsibility, and regulation on business and working environment have forced organisation to seek reform or seek alternative ways for sustainability and business growth.
Looking for further insights on Business Environment? Click here.
Organisational Innovation Framework
Crossan and Apaydin (2010) argued that organizational innovation should not be confused with organizational change, creativity, or knowledge but it incorporate evolution and transformation such as doing things differently resulting in new product, new market, or new source of supply but also venturing to new management domain of adding value in economic and social spheres. According to Laforet (2013) and Camisón & Villar-López (2014), organizational innovation encompasses restructuring such factors as ways in which organizations conducted businesses, changing beliefs held, organization structure, or business model aimed at meeting changing environment and consumer needs while gaining competitive advantage. Building from this, organizational innovation takes several framework largely dependent on need for a firm to innovate that include profit model, network, technology, product performance, distribution channel, or process. Crossan and Apaydin (2010) held that innovation in an organizational culture and structure is widely perceived as subset of organizational change where new products, approaches, technologies, and strategies are introduced to addressing challenges and problems encountered as well as improving effectiveness.

However, as illustrated by Hogan and Coote (2014) and Polder et al. (2010), it is fundamentally stimulated by either opportunities (‘opportunistic surveillance-initiate’) or discrepancies between firm’s performance and goals depending on an organization needs and goals. For an organization in tech industry, constant innovation driven by new technologies, market, and consumer preferences but not limited to regulatory bodies demands. The fall of both Nokia Corporation and Kodak, two of the large tech business entities in 1990s measured by revenue and market share, has been attributed to failure to foresee changing consumer preferences and readjusting it respective business models to address such (Aspara et al., 2013; Laamanen et al., 2016; Gershon, 2013). The Eastman Kodak, for instance, insisted on producing and selling its camera film despite inventing digital camera back in 1975 in fear of hurting then its lucrative sales (Gershon, 2013; Kotter, 2012). The company invented digital camera that currently used in every smartphone and used in cameras but management failed to see a shift from film-based photography to digital technology as a future and disruptive to its business model.
Looking for further insights on Global Business Environment in Focus Click here.
Looking for further insights on Benefits In Multinational? Click here.
In technology industry characterised by dynamic business ecosystem and rapid changes, innovation is fundamental for an organization’s growth and success. However, as pointed by Tidd and Bessant (2018), it follow that adopting right innovative tools built around doing in-depth analysis company’s innovation ecosystem and not limited to its internal environment but take into account the demands and preferences of customers and potential consumers, that is, factors moulding business environment. For any organization, aligning innovation, unless it is drastic change, should be informed by company’s portfolio, human resources, and its organizational capabilities aimed at developing a conclusive gap analysis and action plan. According to Naranjo‐Valencia et al. (2011), innovation can incorporate defending core model of an organization, building around emerging approaches, or creating viable options as well as having realistic targets.
Dig deeper into Canadian Tea Consumption Trends with our selection of articles.
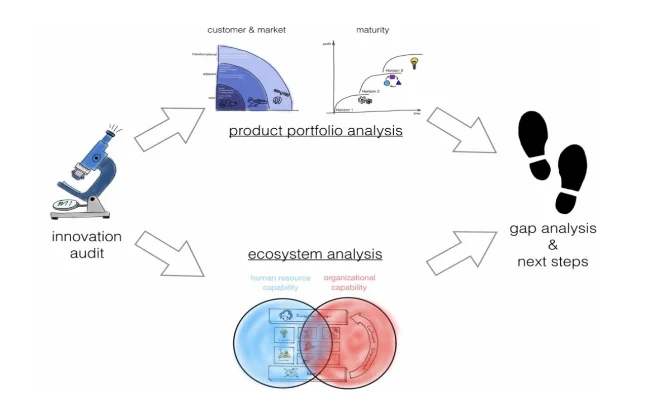
Using above model, companies need to understand their audiences that include current and potential consumers through examining the market and consumer needs then construct a perspective of needs then coming up with solutions. As pointed by Tidd and Bessant (2018), using the premises of the need of innovation, an innovation audit highlights the innovation process and whether the core factors have been incorporate to the satisfaction of the target audience hence avoiding initiating innovation program that are time consuming and wasting resource without foreseeable tangible results. For instance, disruptive innovation such offering virtual computing storage services commonly referred to as cloud computing a shift from traditional hard drives and personalised storage system can completely overhaul organization process that include business strategy, products, target consumers, and organization culture. Recently, artificial intelligence is continuing to reshape business operations by guiding decision-making process.
Continue your exploration of Ultimate Goal of Firms with our related content.

In technology industry morphed by continuous and rapid push for bleeding edge changes affecting not workplace culture and consumption behaviour but also organisations’ core business model, innovating products, as well as organization culture in such environment tend to be complex despite being essential. According to Evangelista and Vezzani (2010) and Azar and Ciabuschi (2017), organization innovation framework is built around creativity and visionary leadership in addition to adopting a crosscutting practices and encouraging it. As pointed out by Camisón and Villar-López (2014), organizational innovation is largely dependent on not only the external factors but also the internal elements driving an organization meaning different firms and there exist no proven formula for innovation success but in technology-driven organisation, as illustrated by Evangelista and Vezzani (2010), elaborate continuous innovation systems.
Continue your exploration of business with our related content.
Nevertheless, the strategic alignment adopted should reflect the business strategy while combining non-traditional fixing the outcome on the long-term opportunities then bridging to present strategies (Pisano, 2015), for instance, future of businesses will be largely data-oriented collecting consumer needs and modelling a product to suit a particular consumers based on the data acquired from them. As such, businesses can adopt such technological advancement as machine learning, artificial intelligence, and virtual reality in understanding the consumer and articulating their needs and enhancing personalised experiences. A belief that consumers are loyal to a brand and organization until a competitor offers a better product and service, has driven the Amazon Inc. pushing for continuous integration of better service delivery and products. Whereas, traditional thinking orients present business activities and projecting to future. Amazon Inc. started by Jeff Bezos as a book selling business but has changed its approach and modelled over the year to multinational conglomerate technology focusing on e-commerce, digital streaming services, cloud computing and recently venturing into artificial intelligence, home automation, and food supermarket chain. In his reasoning on innovation by technology-oriented business, Gerow et al. (2014) argued that firms need to understand emerging trends and looking beyond the obvious while aligning internal and external.Dig deeper into Business Ethics Responsibility with our selection of articles.
Amazon Inc. has remodelled and built its business strategy by embracing machine learning based systems and supported by AI aimed at improving consumer experiences and selection process in addition to optimizing its service quality and logistic processes. Machine learning in combination with AI and big data enables businesses to predict consumer consumption behaviour based on region and particular demographic pointing to businesses sales and profit margins, feasibility of a product, as well as consumer satisfaction levels. The company launched the Amazon Web Services (AWS) to take advantage of the growing dependence on data in decision making by business entities such as consumer preferences and market direction. Given that AI is estimated to inject $13 trillion to the global economy by 2030 (Fountaine et al., 2019). According to Harracá and Coriat (2017), through such products and services as business analytics, artificial reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), Blockchain, and application integration, AI based approach aids in solve pragmatic business problems and machine learning platforms for other business entities as customers.
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to Ethical, Sustainable, and Responsible Business Practices.
Although organization management may be fully committed to implementing new approaches and changing core aims of a firm, such changes occasionally faces resistance change by organization. As pointed by Tidd and Bessant (2018), managing innovation process encompasses several steps such as initiation, implementation, consumer, market trends, and competitive analyses while thinking and coming up with new products. However, according to Guisado-González et al. (2017) and Cap et al. (2019), diversifying thinking allows exploration of different and alternative approaches such as partnering with external partners and adopting faster time-to-market approaches. Considering organizational readiness, consumer perception, and following a disciplined implementation driven by path management including Amazon’s innovations shift to integrate innovative measures and change way of doing business has led to being recognised as a leading products innovative business entity as well as innovation-friendly workplace.
Dig deeper into Globalisation upon a Tourism with our selection of articles.
Morgan (2018) described Amazon reorganisation around machine learning and AI as cutting edge in not only products it offers but also management strategies called the Flywheel while boosting consumer experiences, it core business culture. Additionally, the company adopted AI to learn what consumers and potential customers look for on Amazon website then recommend similar product or what other consumers who were interested with the product search. Amazon has not only restructured search experiences and offering analytics products using AI and machine learning but interconnected entire company and departments to enhance coordination and cooperation within and among department (Shaughnessy, 2015; Vickery, 2020). As pointed by the move to incorporate interactive approach with consumer through products recommendation founded on search behaviour and pattern of consumers has been attributed to heighten consumer experiences and ultimately competitive advantage for the company. More so, AI and machine learning power products such as Alexa and Amazon Go store, the company’s products. It is worth noting that, the company faced several setbacks initially while introducing and adopting the approach since such emerging trends as voice-powered virtual assistant in developing innovation approaches had not been adopted before. In addition to recommendation products, Amazon through its amazon Go store tracks consumers buying behaviour.
Take a deeper dive into Role and Duties in Foragers with our additional resources.

The company’s motto of putting consumer’s experiences first is driving factor of continuous adoption of new ways and ultimately leading to preventing customers from defecting to rivals and keeping them in an ecosystem. The company has, over the years, emphasised a platform built around an ecosystem serving consumer in a fastest manner possible while maintaining efficiency. Essentially, coining consumer-oriented products through customer-partnering strategy is one approach that upholds an organizations’ competitive advantage over its competitors but cushion need to be taken to prevent them from incurring switching cost that many cause deflection.
Continue your exploration of Exploring Various Business Functions with our related content.
Addressing Areas of Weakness
Despite it’s largely genius innovative capacity including the use of AI and Machine Learning, effective use of these machines and innovation is key to success, failure of which they can be significantly exploited by upcoming competitors in terms of capturing and retaining market share and sales revenue. One major weakness experienced in Amazons innovative capacity and strategies include the development of an easily imitable business model and tech (Greenspan, 2019). Despite the company being at the forefront in innovative capacity within the retail industry as well as the leading online retailer globally, various aspects of innovation including the use of Artificial intelligence and Machine learning can be effectively imitated by other developing retail companies and even perfected to increased competitive advantage over Amazon.
Dig deeper into valuating the Road to Global Net Zero with our selection of articles.
According to Amazon.com (2018), Amazon has developed a lot of its business strategies and models around machine learning and the possible use of Artificial intelligence. It utilizes machine learning to evaluate consumer activities, engagement, and feedback and as such effectively improve its customer experience and selection, and optimize its logistic speed and quality. However, the company allows other similar retail businesses to imitate as well as use similar IT infrastructure with agility as well as cost benefits (Terdiman, 2018). Democratizing its innovation capabilities to other retailers who are competing in the same market represents a significant weakness for which other businesses might capitalize on and gain competitive advantage. The structure of Amazon.com development teams, and the focus on Machine Learning to solve hard pragmatic business problems, drives Amazon.com and AWS to develop simple-to-use and powerful Machine Learning tools and services (Amazon.com, 2018). These tools are first tested in the scale and mission critical environment of Amazon.com, before they are exposed as AWS services for every business to use, similar to other IT services (Terdiman, 2018). While the democratizing of these innovative technology significantly adds on to the company’s revenue, copyrighting them as well as privatization of the specific development steps and phases is critical to ensure the monopolization of these AI and ML strategies. Through effectively regulating the number of companies privy to these innovations as well as their use within these companies, Amazon can effectively manage the innovation capacity to not only inspire success within the organization, but also gain and maintain competitive advantage that will see them maintain a top spot in retail brands even in the future.
Dastin (2018) also premises that Amazon has developed Artificial Intelligence recruiting tools, which can be used in Human resource management as well as inventory control. However, multiple sources confirm that the AI exhibited biasness against women thereby presenting a weakness in its innovation strategies and techniques (Terdiman, 2018). While computer programs and AI cannot be quite accurate in employee evaluation, effective upgrades in programming to influence increased accuracy in recruitment impact a significant process in effectively upgrading the AI to limit resource usage in recruitment of employee. The negative reports related to employee treatment and workplace conditions such as poor air conditioning, timed bathroom breaks, and constant video surveillance can be solved using AI and ML to ensure effective working environment as well as satisfied personnel. This significantly increased their performance measurers and impact growth and profitability at Amazon.

Addressing opportunities
One of the major disadvantages experienced by Amazon currently as highlighted by Terdiman, 2018; Amazon.com, 2018 and Robles, 2018) includes the scarcity of traditional brick and mortar stores to which a significant amount of consumers in the market still prefer compared to online buying. Development of these brick and mortar stores has been minimal based in the number of personnel required for its management and operations (Robles, 2018). However, with innovative capacities involving Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, effective management techniques can be developed to ensure inventory control and management. For instance, installation of Machine learning capabilities in the robots used within the companies warehouses would not only enable the robots to manage inventory effectively, but also to significantly forecast required inventory for various developed brick and mortar stores and as such ensure optimum operations of these stores leading to increased sales and a competitive advantage over all other retailers globally. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence can also be significantly utilized in enhancing consumer experience within these brick and mortar stores through guiding shoppers on different shelves where their desired products of choice are. This overlay enhances consumer engagement and experience thereby enhancing the sharpness of the ML and AI overtime to afford Amazon a competitive advantage. According to D’Onfro (2019), the company has also developed drone delivery services dubbed Amazon Prime Air which enables the company to deliver products to specific clients with Amazon landing pads. This further creates an opportunity for infusion and use of AI and ML to further impact efficient deliveries. Through the installation of AI and ML in these drones, the machines can be able to conduct multiple deliveries adequately without the engagement of human beings in the process. Evaluating the various consumer preferences in terms of products as well as delivery location and places, Machine Learning enables automated deliveries by the company to their various clients thereby influencing effective consumer satisfactions and experience increasing their competitive advantage and market share.
Conclusion
Amazon is indeed one of the most innovative companies when it comes to technology infusion in business processes and they have made significant strides in ensuring they maintain their competitive advantage through consistent innovation strategies. Eventually maintaining their innovative capacity and differentiating it from competitors significantly ensures the maintenance further lead in the retail industry ensuring profitability and increased market share.
Reference
Akhmetshin, E., Danchikov, E., Polyanskaya, T., Plaskova, N., Prodanova, N. and Zhiltsov, S., 2017. Analysis of innovation activity of enterprises in modern business environment. Journal of Advanced Research in Law and Economics, 8(8 (30)), pp.2311-2323.
Aspara, J., Lamberg, J.A., Laukia, A. and Tikkanen, H., 2013. Corporate business model transformation and inter-organizational cognition: The case of Nokia. Long Range Planning, 46(6), pp.459-474.
Azar, G. and Ciabuschi, F., 2017. Organizational innovation, technological innovation, and export performance: The effects of innovation radicalness and extensiveness. International Business Review, 26(2), pp.324-336.
Camisón, C. and Villar-López, A., 2014. Organizational innovation as an enabler of technological innovation capabilities and firm performance. Journal of business research, 67(1), pp.2891-2902.
Camisón, C. and Villar-López, A., 2014. Organizational innovation as an enabler of technological innovation capabilities and firm performance. Journal of business research, 67(1), pp.2
Cap, J.P., Blaich, E., Kohl, H., von Raesfeld, A., Harms, R. and Will, M., 2019. Multi level network management–A method for managing inter-organizational innovation networks. Journal of engineering and technology management, 51, pp.21-32.
Crossan, M.M. and Apaydin, M., 2010. A multi‐dimensional framework of organizational innovation: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of management studies, 47(6), pp.1154-1191.
Domanović, V., 2013. The effectiveness of the performance measurement in terms of contemporary business environment. Ekonomski horizonti, 15(1), pp.31-44.
Evangelista, R. and Vezzani, A., 2010. The economic impact of technological and organizational innovations. A firm-level analysis. Research Policy, 39(10), pp.1253-1263.
Evangelista, R. and Vezzani, A., 2010. The economic impact of technological and organizational innovations. A firm-level analysis. Research Policy, 39(10), pp.1253-1263.
Gershon, R.A., 2013. Innovation Failure: A Case Study Analysis of Eastman Kodak and Blockbuster Inc. In Media management and economics research in a transmedia environment (pp. 62-84). Routledge.
Guisado-González, M., González-Blanco, J. and Coca-Pérez, J.L., 2017. Analyzing the relationship between exploration, exploitation and organizational innovation. Journal of Knowledge Management.
Harracá, M. and Coriat, B., 2017. Business models and organizational forms: searching the edge of innovation in Google and Amazon (Doctoral dissertation, Master Thesis).
Hogan, S.J. and Coote, L.V., 2014. Organizational culture, innovation, and performance: A test of Schein's model. Journal of Business Research, 67(8), pp.1609-1621.
Khan, M. and Khalique, M., 2014. Strategic planning and reality of external environment of organizations in contemporary business environments. Business Management and Strategy, 5(2).
Kimble, C. and Bourdon, I., 2013. The link among information technology, business models, and strategic breakthroughs: Examples from Amazon, Dell, and eBay. Global Business and Organizational Excellence, 33(1), pp.58-68.
Kovaleva, S. and de Vries, N., 2016. Competitive strategies, perceived competition and firm performance of micro firms: The case of Trento. In Contemporary Entrepreneurship (pp. 75-93). Springer, Cham.
Laamanen, T., Lamberg, J.A. and Vaara, E., 2016. Explanations of success and failure in management learning: What can we learn from Nokia’s rise and fall?. Academy of Management Learning & Education, 15(1), pp.2-25.
Laforet, S. (2013). Organizational innovation outcomes in SMEs: Effects of age, size, and sector. Journal of World business, 48(4), 490-502.
Naranjo‐Valencia, J.C., Jiménez‐Jiménez, D. and Sanz‐Valle, R., 2011. Innovation or imitation? The role of organizational culture. Management decision.
Pisano, G.P., 2015. You need an innovation strategy. Harvard Business Review, 93(6), pp.44-54.
Polder, M., Leeuwen, G.V., Mohnen, P. and Raymond, W., 2010. Product, process and organizational innovation: drivers, complementarity and productivity effects. CIRANO-scientific publications 2010s-28.
Tidd, J. and Bessant, J.R., 2018. Managing innovation: integrating technological, market and organizational change. John Wiley & Sons.
Tidd, J. and Bessant, J.R., 2018. Managing innovation: integrating technological, market and organizational change. John Wiley & Sons.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



