Analyzing Starbucks: A Comprehensive Examination of its Global Presence
Introduction
Starbucks, the coffee industry's powerhouse, now boasts a global client base. Under this well-known brand, over 3000 retail locations can be found in nearly 80 countries, spanning the globe from one end to the other, in collaboration with a few organisations. Starbucks' restaurants and foundations are globally popular with individuals of all ages for social events. Of course, Greggs is a British company that competes with Starbucks; despite serving as bread shops, Gregg's locations have a tremendous offer in the UK market (Richey & Ponte, 2021). This report will attempt to analyse and answer some major, challenging questions about the Starbucks business. As a result, the report will attempt to analyse and comprehend the Starbucks crisis using the 4Vs and 5POs. business dissertation help. the report is going to analyse the company using the 4Ds and the 5 performance objectives that have contributed to its success. Most importantly, the report is going to analyse the most likely supply chain objectives of the company according to the case study given.

The crisis of Starbucks from 4vs and 5POs
According to the 4Vs principles of marketing, Starbucks has been having major and minor problems in management because of its large expansion; according to the 4Vs. Starbucks has different coffee selling facilities/ shops in countries such as Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and a processing plant for its Tazo Tea subsidiary in Portland, Oregon. The company also relies on 24 manufacturers, most of them in Europe, Asia, Latin America, and Canada. However, this larger arm has been cut off or affected by the company’s operating expenses. All task processes operate in the same way; they all take 'inputs' such as raw materials, information, money, equipment, and time and convert them into outputs (labour and goods) (Campbell & Helleloid, 2016). They do this in a variety of methods, the most important of which are known as the four 4V's: volume, variety, variation, and visibility.
Volume
In its multiple facilities across the country and the world at large, the company has witnessed tremendous growth in its branches in the city and outside the world. However, despite its success of giving out a larger volume to its clients all over, the company is continuously faced with one major challenge, the operating expenses. These expenses occur from its transportation distribution and logistics. It ships so many products to its facilities around the world, and this has presented a greater challenge to the supply management teams.
According to Gibbons, the company does 70,000 to 80,000 deliveries per week around the globe, and as a result, they spend a lot of money on these shipments. Therefore, they are trying to source ways in which they can be able to manage these logistics systems. Also, according to the case study, the companies' cost analysis revealed that they spend almost 65 to 70 percent on their supply chain expenses, third party logistics, and contacting manufacturers. As a result, Starbucks was a victim of its success because it was launching new stores around the world rapidly and all at once.
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to Strategic and Operational Challenges at Starbucks.
Variety
Originally, the company was only producing and selling ground coffee and coffee beans to its customers. During those times, the company was doing well as it had the option of concentrating their attention on one service that they were offering at the time. Their main challenges came as a result of adding additional services such as offering prepared coffee, cold blended drinks, Italian style espresso, premium teas, food items, and all beverage accessories and equipment. This variety became a challenge to the company because it had no option but to divide its attention between producing quality services for its consumers. It is true, they achieved greater success because of offering a variety of services, but these success stories have also made them victims in the production market.
Variations
Starbucks' ability to make adaptable changes based on the requirements and expectations of its customers enables effective alterations in both the rate of production and the requests made by its customers. The company faces the challenge of meeting the ever-increasing demands of its customers. On top requires a lot of hard work and Starbucks has the challenge of trying to keep up with it and, of course, trying to be ahead of Gregg's Company, which is their main business rival in the United Kingdom. Starbucks also has several outlet variations in the UK, and they give their clients the option of selecting any shop where they want to spend their good time in. Despite the success of Starbucks, Schultz faced scepticism from investors when he was trying to raise $1.25 million to fund his expansion (Campbell & Helleloid, 2016).
Visibility
This component refers to a client's ability to view, track, or request their way through the task cycle. These include the high coordination associated with the organization. Starbucks is one of the most visible brands in the world. As a result, it has a bigger competitive advantage than other espresso brands. The Starbucks brand is successful in using the arrangement of scattered decision-production among its clients because of its high perceived ability. As a result, the organization faces the challenge of attempting to maintain its image in the eyes of its clients.
How Starbucks was turned around using the 4DS
Discover
According to the case study in 1982, Starbucks was doing progressively well because it had five retail outlets in different parts of the country that are was successfully selling beans and supplies people with the beans to brew coffee at home it had also roosted facilities and wholesales. This growth attracted the attention of Schultz, who was the president of the American Subsidiary of Hammarplast (Gupta et al., 2019). He wanted to find out why Starbucks, a small company, ordered more filters from their shops. His discovery impressed him and joined the company and later in the same year was made the director of the company. After one year Schultz went to Italy for a business trip and was attacked by the city's ubiquitous espresso bars. The bars featured well-prepared espresso and brewed coffee and were significant meeting and gathering spots. Schultz recognized a gap in the market for comparable establishments that serve high-quality coffee in a welcoming environment for meeting and resting. He departed Milan, determined to start a similar organization in America. Discovery is about understanding how a particular product could change your organization and how it can fit the market and competition when you introduce a product that can add value to the company and its clients.
Define
This process is very important for organizations as they practise very important things that challenge them and deal with them. The growth of the company exposed some of its weaknesses and as a result, Schultz discovered that their supply chain management was very weak and that they were opening so many brands that were making them spend a lot of money only on its supply chain management. Also, they realized they could use information and technology, but there were not enough that was done to improve the score so that the company could have incorporated the use of 5POs. In 2008, gibbons reorganized the supply chain management problem of the company and they planned out how to deliver the best for their consumers by improving on the supply chain of the business. According to Gibbons, before solving out any issue that affects an organization, it was very important to first define the problem before trying to implement strategies on how to solve it. As a result, they had to take a complicated structure and simplify it such that every task fit into one of four core supply chain functions: plan, source, make and deliver. For example, everybody involved in planning, whether it was production planning, restocking, or new product releases, was assigned to the planning group.
Development
By conceptualizing, sourcing activities were divided into two categories: coffee and "non-espresso" acquisition. The purchase of various commodities, such as dairy products, prepared food, shop equipment, and paper products, total the US $2.5 billion every year.), all workers involved in transportation, allocation, and client service were assigned to the "supply" group. The key features of these strategies were to change/improve the organization's efficiency. After the inventory network capacities were redesigned, the various offices focused their attention on the second part of the production network modification. Here, the organization concentrated on lowering expenditures, as it was the fundamental point that was affecting the company yield. The gaining group was tasked with identifying the expense drivers that were driving up expenses as part of that job.
Delivery
This stage is where the company implemented its strategies to change the image of Starbucks and also improve its performance. And as results Gibbons says. "We built more effective 'should cost' models, including benchmarking ingredients and processes, which showed that we could negotiate better prices." Meanwhile, the manufacturing business developed a more effective method of getting coffee beans to its processing plants, intending to make the product in the region where it is sold. Starbucks already had three coffee plants in the United States, in Kent, Washington, Minden, Nevada, and York, Pennsylvania. The company launched its fourth manufacturing in the United States in 2009, in Columbia, South Carolina. The benefits of this strategy, according to Gibbons, were immediately apparent: by regionalizing its coffee manufacture, Starbucks was able to reduce transportation costs and lead times. Once the new plant was up and running, all the coffee companies in the United States could switch from seven-day to five-day operations (Kumaresan, 2019). The company relayed on the 4Ds to improve the 5 POs aspects to produce effectively.
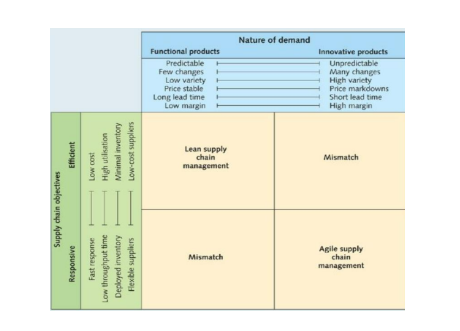
Supply chain objectives for Starbucks
Starbucks' in-store customer service is an attempt to enhance customer loyalty. Starbucks' retail mission has always been to provide customers with a one-of-a-kind Starbucks Experience. Service training is a critical component of the value chain that adds to the distinctiveness of its goods. The most likely supply chain of Starbucks based on the case study is to lower cost while producing quality to its consumers. Starbucks' aims at supply chain are also too fast respond to consumer demands and requests through fast response and introducing low costs to put time. They also aim to be flexible and minimize the cost associated with their suppliers. Starbucks has reduced expenses globally without affecting service performance since launching its supply chain reform initiative. "As a corporation," Gibbons continues, "we have publicly said that we have saved over $500 million in the previous two years, and the supply chain has been a key contribution to that." The presence of middlemen in Starbucks item sales is minimal to non-existent. The majority of the things are available in shops. Stockpiling and appropriation to retail outlets are crucial in any circumstance (Azriuddin et al., 2020).
According to the data given and the case study, Starbucks' in-store customer service is an attempt to enhance customer loyalty. Starbucks' retail mission has always been to provide customers with a one-of-a-kind Starbucks Experience. Service training is a critical component of the value chain that adds to the distinctiveness of its goods. When baristas make drinks for customers, they generate a lot of value (Valuiskaya, 2019). Additionally, the company intends to use supply chain management to improve on its infrastructures such as management department, legal aspects, and finances. These aspects are very important for the company because they help to keep Starbucks stores operations across the country and globally. And as a result, it has employed business managers, store managers, whose main mandate is to help in overseeing that all the stores are well designed and completed with goods and services provided are of significant benefits to the company (Wittmann, 2019).
Technology is another important aspect that is targeted by the company Starbucks is well-known for its use of innovation, not just in espresso-related technologies (to keep up consistency in flavour and quality while saving money), but also in interacting with its consumers. Because of the free and unlimited Wi-Fi, many customers use Starbucks locations as a quick workplace or social event location (Alwaleed et al., 2019).
Starbucks has organized several events where customers may ask questions, make comments, freely express their opinions, and share their experiences (Wittmann, 2019). Innovation facilitates the implementation of this information, particularly through its reward program. Starbucks also makes use of Apple's iBeacon invention, which enables customers to order a beverage using the Starbucks phone app and receive a notification when it is ready when they enter the store (Tsai et al., 2020).
Moreover, the supply chain management system would help the company to also advance and improve its procurement management system. As a result, by improving on their supply management systems they have seen some changes and through the management, their main aim is to maintain using supply chain in improving their procurement strategies. Procurement is intertwined with several parts of the supply chain. Porter classifies procurement as a support activity (Flamholtz & Randle, 2020). Many companies will establish broad terms, requirements, and standards for all procurement agreements (Khushman, 2019). Procurement relationships usually differ significantly. Starbucks oversees all of its coffee bean procurement, which it sees as a competitive advantage.
Since care is at their office in Swansea branch they Drive-Thru at a rate of 25 per hour and only. Only one drive-thru till is open. The average number of customers arriving will be equal to the average of the driveway. To get to know the time the cars wait before the existing Starbucks drive-through, the following is the calculation of the scenario:
Arrival rate (ra) = 25 per hour
So the average time between arrivals (ta) = 1 hour or 60 minutes
Average service time (ts) = 5 minutes
ra/rs = 60mins that represents one hour /25 = 2.4

Therefore, the average time that the cars have to wait before they are given a pass through the drive-through is 2.4
Reference
Alwaleed, N., Al Huwail, N. H., Singh, S., & AlMejhem, A. (2019). A case study on Starbucks. Journal of the Community Development in Asia (JCDA), 2(2).
Azriuddin, M., Kee, D. M. H., Hafizzudin, M., Fitri, M., Zakwan, M. A., AlSanousi, D., ... & Kurniawan, O. (2020). Becoming an international brand: A case study of Starbucks. Journal of the Community Development in Asia (JCDA), 3(1), 33-43.
Campbell, K., & Helleloid, D. (2016). Starbucks: Social responsibility and tax avoidance. Journal of Accounting Education, 37, 38-60.
Chowdhury, R. The Impact of Business Environmental Factors on Organization’s Change Management Process-A Study on a Multinational Company “Starbucks Corporation”.
Flamholtz, E., & Randle, Y. (2020). 5. Managing the People Orientation Dimension of Culture. In Corporate Culture (pp. 92-108). Stanford University Press.
Gupta, P., Nagpal, A., & Malik, D. (2018). Starbucks: global brand in emerging markets. Emerald Emerging Markets Case Studies.
Khushman, A. (2019). An Evaluation of Entrepreneurial Activities and Growth Strategies–The Case of Starbucks Coffee House. Available at SSRN 3594916.
Kumaresan, R. (2019). The Effects of Macroeconomics Factors towards the Starbucks Corporation.
Richey, L. A., & Ponte, S. (2021). Brand Aid and coffee value chain development interventions: Is Starbucks working aid out of business?. World Development, 143, 105193.
Tsai, P. H., Lin, G. Y., Zheng, Y. L., Chen, Y. C., Chen, P. Z., & Su, Z. C. (2020). Exploring the effect of Starbucks' green marketing on consumers' purchase decisions from consumers’ perspective. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 56, 102162.
Valuiskaya, E. (2019). Corporate Social Responsibility in Business-to-Business and Business-to-Consumer Companies: Nucor Corporation and Starbucks Corporation Case Studies (Doctoral dissertation, University Honors College Middle Tennessee State University).
Wittmann, X. (2019). Starbucks: Managing a Racism Scandal. University of Zurich.
Looking for further insights on Analyzing Power Dynamics and Influence Factors in International Football Player Transfers? Click here.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



