Apple’s Internal Environment Analysis
Introduction
A firm’s internal environment comprises all the elements which are endogenous to its operations and, to a great extent, the firm is highly influenced and completely controlled by these elements (Stefan & Popescu, 2011). An internal environment provides solutions to all resource related problems, issues regarding resource management and serves as the first steps towards making of the marketing strategy of an organization. A collection of these elements makes up a value chain, whereby a value chain analysis can be set up using the link between the resources of a business and its competitive state and explores how all the elements result in the profitability of a firm (Stefan & Popescu, 2011). In this paper, an internal environment assessment shall be presented according to Apple, Inc., a technology company in the smartphone industry by discussing the firm’s strategic capabilities using appropriate strategy tools and identifying the firm’s strengths and weaknesses. The strategic tool for internal environment analysis that shall be used is the value chain analysis to discuss Apple’s core competencies, resources and capabilities. This will be followed by recommendations which suggest the strategies which the company ought to implement in order to meet its needs of creating more value in the future by taking advantage of its strengths and working on its weaknesses.
Value Chain Analysis
Any organization can fine-tune the value chain to acquire an edge over its competitors. Fine-tuning can be done using decision-making processes which push the firm further towards being above its competitors and gaining profits. The decision-making processes constitute strategic planning, and the value chain analysis is key towards the development of strategies. Value chain analysis develops an understanding of the interrelationships and linkages that exist or can be possibly developed between the value chain activities regarding core competencies, resources and capabilities (Pakkanen, 2012). The value chain analysis shall be developed in the context of Apple Inc. The analysis identifies the primary and support activities which are crucial elements of Apple’s value chain. The analysis shall also identify the activities which are not in any way adding value to the company’s final products (Pakkanen, 2012). The identification of primary and support activities of Apple will aid in the understanding of their key functions such as core competencies, resources and capabilities, and their economic viability to the company. The primary activities of a value chain include the basic elements of inbound logistics, sales, marketing, operations and outbound logistics in Apple Inc. The supporting activities are those which aid in improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the primary activities (Pakkanen, 2012). The supporting activities have four main divisions, which include technological development, procurement, company infrastructure and human resource management.

Primary Activities for Apple
Inbound Logistics
Apple has a supply chain that is vast with suppliers who present different raw materials to the firm. By having a large number of suppliers, Apple has a higher negotiating power for obtaining its raw materials. As a result, the company’s management can get suppliers to compete against each other in the delivery of material parts and components used in making Apple’s products (Apple, 2019). Eventually, the company can minimize costs incurred during inbound logistics leading it to secure a cost advantage while purchasing its resources. A large number of the company’s suppliers are located in China, the U.S, and nations in Europe and Asia. Companies such as Foxconn and 3M are the largest suppliers of Apple’s raw materials (Apple, 2019). In addition to having a higher bargaining power, Apple has a set of principles and standards of quality where suppliers are mandated to comply with while working with the firm.
Operations
Operation activities for Apple Inc. take place in different nations in different continents, such as China, Japan, and the rest of the Asian Pacific nations, as well as nations in Europe, Africa and the Middle East . However, a larger proportion of its manufacturing and assembly operations are done in China, and this why its products bear the inscriptions ‘Made in China’ (O'Grady, 2009). Apple takes advantage of the lower costs of production in the Asian nations which minimize the operational costs involved with manufacturing. In addition, Apple implements the some of the six sigma principles in the removal of variations in its manufacturing processes by focusing on the reduction of toxic substances during the making and assembly of its products. Outsourcing production not only allows Apple to implement the use of recyclable materials, but also allows the firm to manage its costs of production (O'Grady, 2009).
Outbound logistics
Apple’s channels of distribution are vast and consist both indirect and direct channels. The outbound logistics consist the distribution and warehousing of final products such as MacBook Computers, iPads, iPhones as well as other Apple related products made by the company. The company recognizes E-commerce activities in its outbound logistics as a core source of value for its products. For the company, e-commerce is more cost advantageous and effective compared to making sales through the Apple Store (Apple, 2019). As a result of the implementation of e-commerce as a primary value-adding activity, Apple has grown into the largest retailer in the U.S in the category of e-commerce business, second after Wal-Mart and Amazon. Therefore, e-commerce is a core competency for Apple which is valued at $12 billion, that is equivalent to 5.1% of the firm’s total sales (United States Securities and Excahnge Commision, 2017).
Sales and Marketing
Apple has developed its market position for making smartphone devices and related technology that are known for innovation, quality and design. This market position arises from its inbound logistics capabilities of having a cost advantage by manufacturing in regions where quality and skilled labor can be provided at relatively lower costs (Johnson, 2018). Apple engages in promotional advertising as a way of communicating to its target customers in different market segments which are located internationally. Eventually, this drives the increase in demand for its products through brand loyalty and the use of imagination and creativity in its advertisements. In addition to commercials presented online and on televisions, the company uses print media to promote and market its brands. In 2017, the total net sales for Apple were made up of sales from its international and domestic markets, proportionally at 63% and 37% respectively (United States Securities and Excahnge Commision, 2017).
Support Activities for Apple
Technological Development
Apple has made considerable investments in its research and development activities which have resulted in technology which has revolutionized the world. Apple has evolved from the concentrating its production of personal computers, to the making of iPhones and iPods, all running on Apple’s iOS operating software. The company’s iOS is regarded as the most secure in the world and this is particularly due to its close-ended administration where only Apple has the potential to incorporate improvements and changes in the software. Investment in technology research and development gives the company an edge over its competitors and this is evident through its reputable high-tech and uniquely designed products (O'Grady, 2009). In 2016, Apple spent over $10 billion in research and development; in 2017, it spent $11.6 billion for the same purpose. From 2014, Apple’s expenditure on research and development has increased by more than $5 billion (Business Insider Intelligence, 2017). Thus, investment in research and development is one of Apple’s capabilities which boosts its core competencies to increase its profitability by adding technical value to its products.
Procurement
This supporting activity has been effectively managed by Apple to reap benefits resulting from increased demand for its products in different markets (Wallace & Hill, 2011). For instance, under Steve Job’s reign, Apple reworked its procurement activities for critical services and goods in a manner which is still being used in its current supply chain (Wallace & Hill, 2011). Apple’s supply chain activities are broad as they stretch overseas, and alike any other smartphone manufacturer, it transports its products through sea, instead of the more expensive alternative of air freight. Therefore, Apple’s procurement-supply chain strategy consists a procurement reality where high costs are incurred in purchasing and inward shipping of products in order to reap benefits of greater sales emanating from the supply of its products to its respective markets (Wallace & Hill, 2011).
Company Infrastructure
Apple’s infrastructure development is done according to four core philosophies which include direct sales model of business, Apple brand power, the spirit of continuous innovation (“Think Different”) and provision of services which are focused on the customer. The spirit of continuous development causes Apple to engage innovation in making consistent upgrades to its products and infrastructure inexhaustibly (Jinjin, 2013). The company has sufficient infrastructure to facilitate its sale of products directly to customers via Apple stores, the web, and even via phone calls. Its infrastructure is developed with a focus on customers through activities such as the “Switcher” campaign, and the Apple World population. As Apple’s management of infrastructure becomes better, its profitability increases.
Human Resource Management (HRM)
This support activity is of significance in Apple’s value chain. Apple recruitment goals are to hire the best skilled and talented personnel and reward them with good salaries. Since Apple’s founder, Steve Jobs, Apple has had the same approach towards its human resources. Although, some of the HR practices have changed during Tim Cook’s management as a way of changing the firm’s reputation in terms of diversity of its employees and the protection of their rights .
Apple’s Financial Position
To determine the financial position of Apple Inc., a ratio analysis shall be carried out. The ratio analysis evaluates a firm’s financial and operating performance in terms of its profitability, solvency, liquidity and efficiency. Regular reference to these trends is done as a way to determine whether or not a firm’s financial position is improving. In this context, the ratio analysis shall also be used to point out the weaknesses and strengths of Apple Inc. in financial terms. Some of the ratios that will be used include the ROCE, gearing ratio and current ratio.
Return on Capital Employed (ROCE)
This financial ratio will evaluate Apple’s profitability and investors can use this information in scanning for suitable opportunities for investment. The ROCE is calculated by dividing the earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by the total capital employed. The total capital employed consists the difference between the total assets and total current liabilities (Anon., 2011).
The details financial information that shall be used to calculate the ROCE are retrieved from the reports of the year 2017. The EBIT for Apple in 2017 was $64,089,000,000. The total assets were valued at $375,319,000,000. The total current liabilities for the same financial year was $100,814,000,000. Therefore, to acquire the ROCE, the formula shall be applied as follows.
ROCE= 64,089,000,000 / (375,319,000,000 – 100,814,000,000)
= 64,089,000,000 / 274,505,000,000
= 0.2334
This reflects that for every $100 of capital employed by Apple, $23.34 is earned by the firm.
Universal Electronics Inc.’s ROCE shall also be computed to develop a comparison of Apple’s financial position in this case. The EBIT for Universal Electronics Inc. in 2017 was $7,288,000. The total assets were valued at $608,430,000. The total current liabilities were valued at $332,935,000 (Universla Electronics Inc., 2017).
ROCE=EBIT/Total capital employed
= 7,288,000/ (608,430,000-332,935,000)
=7288000/ 275495000
=0.02645
This reflects that for every $100 of capital employed by Universal Electronics Inc., $2 is earned by the firm.
From this analysis, it can be derived that Apple’s return on capital employed is nearly ten times that of Universal Electronics Inc..
Gearing Ratio
This financial ratio compares the owner’s equity or capital with the debt acquired by the company . The following is a calculation of Apple’s gearing ratio for the financial year 2017.
Gearing ratio = (Long term liabilities / Capital Employed) *100
= (97,207,000 / 274,505,000,000) *100
= 35.41%
This means that Apple has a gearing of 35.41%.
The gearing ratio for Universal Electronics Inc. is calculated below.
Gearing ratio= (354,881,000 / 275495000)*100
= 128.8%
This means that, in 2017, Universal Electronics Inc. had a higher gearing ratio of long term liabilities than that of Apple.
Current Ratio
The current ratio is computed by dividing the current assets by the current liabilities of a company (Seth, 2019). The current ratio for Apple in 2017 was:
Current ratio= Current assets / Current liabilities
= $128,645,000,000 / 100,814,000,000
= 1.276
The current ratio for Universal Electronics Inc. in 2017 was:
Current ratio = $407,297,000 / 332,935,000
= 1.223
The current ratios of both organizations reflect that Apple had a higher chance of converting its assets to cash than Universal Electronics Inc. within the financial year 2017.

Recommendations
Considering that the ROCE is a profitability ratio, Apple can improve its current ROCE using any other means it would adopt to increase its profitability. First, Apple needs to cut down on its costs and increase its number of sales. Cutting down costs would be of great benefit to the company, because in addition to the low costs of production it acquires by setting up its manufacturing and assembly activities in China, Apple would acquire more economies of scale by localizing its production (Anon., 2011). For instance, Apple could set up a plant for assembly of its products and delivery of customer-related services in a nation in each continent so that it would acquire raw materials cheaply (Maverick, 2019). As an added advantage, Apple will have cheaper resources and its core competencies will grow by increasing the number of diverse employees who are best suited to working in Apple’s localized markets in the international arena. Apple can increase its number of sales by engaging in heavy and specific advertisements which will appeal to the target customers and catch the attention of new potential buyers of its electronics in new markets (Anon., 2011). This will require that the company engages in market development activities for its already existing products and engage in market penetration for the new versions of technology devices that it will roll out. As a way of decreasing its gearing ratio, Apple will have to attract investors. If the firm’s capital is highly geared, it will be difficult for investors to place their money on the company. Apple should also follow the perpetuity principle such that it will be mindful of reducing its gearing ratio. If the gearing ratio remains high for an extended period, it will be hard for Apple to pay off its debt and the firm may end up filing for bankruptcy. Another way that the company can reduce its gearing ratio is by converting its loans into shares rather than cash. This will be advantageous in two ways; first, Apple would not have to seek for cash generating activities so as to pay off debts, and; second, even though the company will have more cash, they shall be able to use it in handling other activities and the debt would be converted to shares. Observing the perpetuity principle will ensure the company minimizes the gearing ratio so that Apple continues operating into the foreseeable future.
Looking for further insights on John Lewis's Effective Promotional Strategies ? Click here.
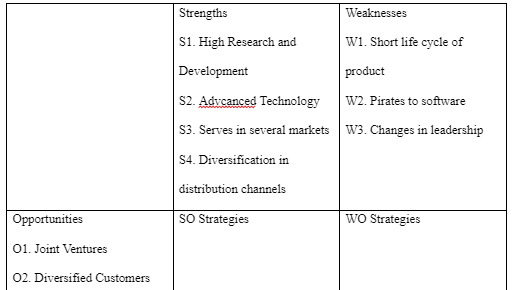
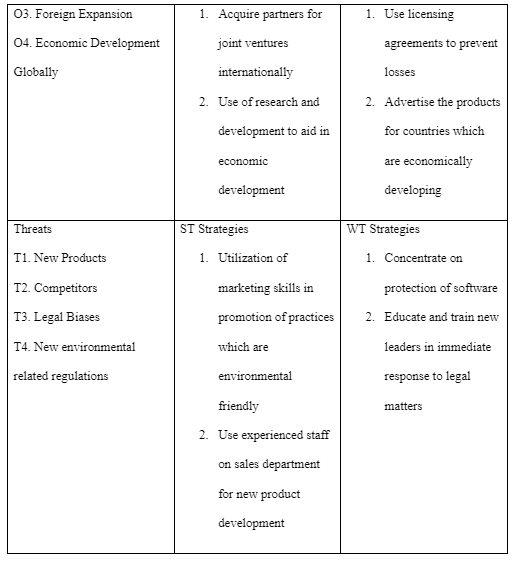
TOWS Matrix
Bibliography
Jinjin, T., 2013. A Strategic Analysis of Apple Computer Inc. & Recommendations for the Future. Management Science and Engineering, 7(2), pp. 94-103.
O'Grady, J. D., 2009. Apple Inc. Post Road West: Greenwood Press.
Pakkanen, T.-M., 2012. Internal and External Analysis, s.l.: ARCADA.
Universla Electronics Inc., 2017. 17 Annual Report, s.l.: s.n.
Wallace, W. & Hill, C., 2011. Insights into the Strategic Sourcing Decision:Understanding Buyer- Supplier Relationships. Operations Management Education Review, Volume 5.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



