Cultural Milk Blend: Pip & Nut's Cross-Border Strategy for UHT Success in Shanghai
Executive summary:
Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) processing can be referred as the process that is associated with sterilising liquid foods such as milk and healthy drinks to kill the germs and spores in these foods. The entire processed is generally used in production of the high-quality health drink such as high-quality milk, that are easily consumed by the infants and older people. UHGT milk is poured in sterile container after production in terms of protecting the milk from the refrigeration which makes this product stay effective as well as ready to use for at least six to nine months if not opened. The UK is considered as the one of the most important and largest UHT milk producers, that sells massive amount of UHT milk to different regions of intentional market. This report is going to discuss the international business strategy of an UK based SME, Pip & Nut, which is going to sell UHT milk in Shanghai city of China for school children of age 3-11 years. In this context, the report will analyse the macro environmental factors in Shanghai which impact on the decision-making process and business operation of thisPip & Nut. In addition to this, the report will also discuss the trade barriers, cultural preference, social and ethical issues that will be experienced by thePip & Nut, while operating its business in Shanghai. Finally, the report will analyse the expansion methods that is going to be implemented by thePip & Nut to grab strong competitive position in the Shanghai market, with a focus on providing business dissertation help.
Introduction:
Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) processing can be referred as the process that is associated with sterilising liquid foods such as milk and healthy drinks to kill the germs and spores in these foods. The UK is considered as the one of the most important and largest UHT milk producers, that sells massive amount of UHT milk to different regions of intentional market in today’s global business world, internationalisation is crucial for any organisation to operate in foreign market successfully. This report is going to discuss the international business strategy of an UK based SME, Pip & Nut, which is going to sell UHT milk in Shanghai city of China for school children of age 3-11 years. This report will discuss the business drivers that are associated with improving the business process and organisational framework of Pip & Nut in order to deal with the current market trend in Shanghai. In this context, the report will analyse the macro environmental factors in Shanghai which impact on the decision-making process and business operation of this Pip & Nut. In addition to this, the report will also discuss the trade barriers, cultural preference, social and ethical issues that will be experienced by the Pip & Nut, while operating its business in Shanghai. Finally, the report will analyse the expansion methods that is going to be implemented by the Pip & Nut to grab strong competitive position in the Shanghai market.

Industry background:
Ultra-High Temperature (UHT) processing can be referred as the process that is associated with sterilising liquid foods such as milk and healthy drinks to kill the germs and spores in these foods. The entire processed is generally used in production of the high-quality health drink such as high-quality milk, that are easily consumed by the infants and older people. UHT milk is poured in sterile container after production in terms of protecting the milk from the refrigeration which makes this product stay effective as well as ready to use for at least six to nine months if not opened. The UK is considered as the one of the most important and largest UHT milk producers, that sells massive amount of UHT milk to different regions of intentional market. whiles it comes to the production of UHT milk, UK comes in the third position after the Germany and France. As the numbers of UHT milk consumers has increased across the world, the UK government support development of SMEs in the local market that are associated with UHT milk manufacturing process. From the ONS report it is seen that, the overall import of UHT milk increased with 139 million litters during 2015 in comparison with 75 million litters during 2014. Addition to this, the report also stated that, overall export of the UHT milk by the Pip & Nut is also increases due to the increasing number of consumers of UHT milk in the international market. From the overall business report from ONS [Office of National Statistics], in the UK, the number of SMEs is more than 5.4 billion during the 2014. The SME business in the UK market accounts for nearly 99% of the entire business sectors. The UK government pose strong financial support to the SME in term of improving overall employment and economic standard in this country. The Goldman Sachs shows that there are more than 10,000 small businesses operating successfully in this country. From the overall report of ONS it is seen that, more than 18,033 tons dairy products such as cheese, milk, UHT milk and yogurt are exported from Pip & Nut to the overseas counties, From the ONS report it is also seen that, majority of the Pip & Nuts are associated with the production of the dairy products which are the largest consumed product in overseas countries such as USA, Shanghai and India. In Shanghai there is high demand of UHT milk, as it is high quality milk that is equally healthy for people of ages ranging from school children to the older people of above 60. On the other hand, in case of children and older people, UHT milk can easily be digested which is one of the most important reason behind preference of this UHT milk in Shanghai.
Business drivers behind company’s expansion:
Business drivers are the factors that are associated with influencing the business strategies, decision making process; marketing operation, trade process, macro and micro environment analysis of the business. by analysing the macro environmental factors in Shanghai, it is possible to determine the driving forces such as political system, legal system, economic condition, social aspects, technology and environment impact on overall business decision and marketing strategies of thePip & Nut that is operate its business Shanghai to sale high quality UHT m milk. Through Conducting PESTEL analysis, it is possible to understanding the above-mentioned macro environmental factors that are the driving forces for Pip & Nut in the Shanghai market.
PESTEL analysis:


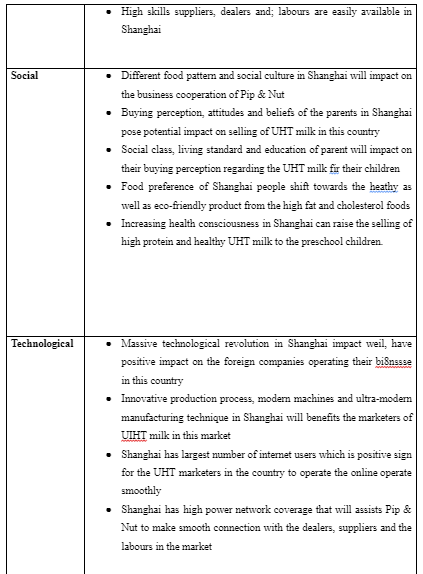
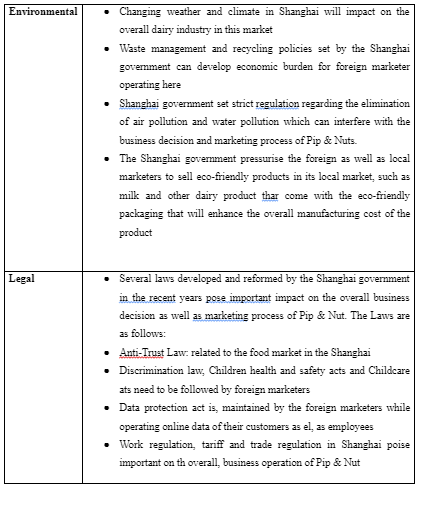
International trade theory:
International trade theories are associated with discussing the marketing strategies as well as business processes that that are taken by any organisation in term of operating the business in the foreign market. There are two important international theories that will be highly relevant to the business operation in of Pip & Nut in Shanghai, in terms of selling UHT milk to school children.
Competitive advantage Theory:
Competitive advantage is important business strategies in modern marketing context, in which firms set the relatively low market price for each product as compared to their trade rivals in the foreign market, in terms id grabbing the customer attention (Amir et al. 2016). Here, the Pip & Nut can use thus strategy in which the company need to research ion the market price of local UH milk in the Shanghai and set a reasonable market price that will be relatively lower than that of the local UHT milk marketers. this process will assist the Pip & Nut to grab strong competitive position in Shanghai dairy market and grab huge customers. In addition to this, through using tis theory, the marketers if UK base SME can target the parents of all middle- and high-class economic background rather than only choosing the high-class people, in terms of convincing them to invest in their firm to buy the high-quality UHT milk.
Absolute advantage Theory:
Based on this theory, in terms of operating a successful international operation, foreign marketers can set lower price for each item per unit in comparison to their rivals in the market, which will assist the marketers to strengthen their customer base (Amato et al. 2017). In this context, the Pip & Nut can set lower price of per litre of UHT milk while selling it Shanghai, by using the small number of inputs such as small number of staffs, labours, manufacturers and sellers. Through using small number of inputs and setting low price of each litre of the UHT milk the marketers of Pip & Nut can grab strong attention of large number of parents who are intended to buy the best quality UHT milk for their children.
Trade barriers:
Trade barriers can be referred as the restriction and obligation that are posed by the government of a country on foreign business in terms of securing the local businesses. Thera are two types of barriers such as informal and formal barriers which are as follows:
Formal trade barriers:
Tariffs:
Tariff can be defined as the tax that the government of any country imposes on the products ass well as services of the foreign companies that are operating in the country in terms of enhancing the market price if these product and service overall product of the local firm (Burns, 2016). In Shanghai, the government has cut the tariff rate on the 187 types of the milk and dairy product that will provide market benefits to marketers of Pip & Nut in terms of selling their UHT milk at reasonable market price in Shanghai. On the other hand, Shanghai has also reduced the overall market prices of the local UHT milk and dairy products. therefore, if the marketers of Pip & Nut is going to grab the market, they need to research on overall market of UHT milk in the Shanghai in terms of setting the justified prices fir each litre of UH milk.
Quotas:
Quotas is another important trade barrier in which government poses constraints on the measurement and quantity of imported products (Ayandibu and Houghton, 2017) for indefinite time. the UK base SME will face quotas in Shanghai, in which the Shanghai government can provide the hand out of agreement based on which the marketers of UIK based SME needs to operate their function. Based on the agreement the marketers Pip & Nut can sell the quantity if UHT milk that I mentioned in the agreement. In addition to this, in term of complying with quotas, thePip & Nut needs to follow the addition acts such as Anti-Trust Law, Childcare At, Food Safety At ands Children Health care act.
Informal Barriers:
Logistics:
There are two types logistics such as inbound and outbound logistics that are associated with international business (Burns, 2016). In-bound logistics is associated with process of collecting braw material and manufacture the product and the outbound logistics is associated with delivery of the products to the customers. In Shanghai, Pip & Nut can face issues in logistic operating such as delayed delivery of raw material, high shipping charge, delayed delivery of good to the customers and poor distribution channel.
Lack of Market data:
Lack of market data is important trade barrier that is commonly faced by the international investors and marketers while operating in foreign market (Czarniewski, 2016). As Shanghai government strictly maintains confidentiality regarding its official database, thePip & Nut will face issues in conducting through research on the overall market type and customers presence of Shanghai dairy market. in addition to this, lack official database on the overall marketing operation of the local marketers in Shanghai dairy market, will create issues for the marketers of Pip & Nut in terms of setting effective marketing strategies to deal with new market.
Cultural barriers:
Shanghai has completely different culture as compared to the UK which will pose barriers on overall business operation of Pip & Nut. The food habits, traditional beliefs, customs and social perception in Shanghai is different from the UK, which makes it difficult for marketers of Pip & Nut to understand the changing buying behaviour and preference of the customers in this country.
Language issues:
Most of the consumers in Shanghai can speak only in Chinese language, which creates difficulties for staffs of foreign companies to communicate with them in proper manner (Czarniewski, 2016). In this context, the Pip & Nut will face huge difficulties in interacting ad communicating with local marketers, consumers and suppliers in the Shanghai, which makes the marketers as well as staffs of Pip & Nut unable to understand the preference and interest of Shanghai’s people regarding UHT milk and other dairy product.
Ethical and social issues:
In terms of operating international business operation, organisation can face several ethical and social issues that interferes with business strategies, marketing operating and selling method of overseas marketers (Dugguh, 2017). Ethics and principles of one country can be the irrelevant legal obligations for the marketers of anther countries. In term of marketing the high-quality UHT milk in Shanghai, Pip & Nut is going to face the following ethical as we’ll as social issues:
Ethical issues:
As stated by Epifanova et al. (2015), ethics can be considered as the principles of codes of conduct that impact on the behaviour, activities and perception of people. Pip & Nut will face different ethical issues while marketing UHT milk in the market of Shanghai.
Human rights:
Human rights can be defined as the basic rights as well as freedom of human being, that assists them to get the facilities as well as advantages that are entitled to them (Dugguh, 2017). Human rights in one country can interfere with the business decision and marketing foreign marketers. for example, Shanghai government has set legal obligations on the foreign marketers to consider the legal rights and social rights of labours, dealers, suppliers and staffs in the local market, which can interfere with the business operation of this company. in addition to that, the high labour charges of the local market in Shanghai will enhance the overall expenditure for Pip & Nut which will automatically enhance the market price of UHT milk in Shanghai.
Employment practice:
Employment practices as well as pattern is completely different from one country to the other, which pose potential impact on the overall buisne4ss operation and marketing process of the foreign business (Giaoutzi et al. 2016). Pip & Nut will face issues in implementing the proper factory regulation (Factory Act, 1948), marketing polices and operational instructions in dairy market of Shanghai. In addition to this as the overall employment practices is Shanghai is different from the UK, the marketers of Pip & Nut will face issues in determining the relevant employment process that needs to be implemented by them to grab the market of UHT milk in Shanghai.
Environmental policies:
According to Guo et al. (2016), foreign marketers can face ethical issues in complying with environmental policies in host country, when the environmental laws and practices are inferior in the host country the that in the home country. During marketing the UHT milk in Shanghai, Pip & Nut will, face ethical issues regarding using the recycling raw material, eco-friendly packaging and pollution free manufacturing process. In addition to this, Shanghai government imposed the strict environment regulation on the overseas companies operating here, in term of using natural resources and fuel in lower amount which interfere with the manufacturing process of the UHT milk and enhance the overall expenditure if this company. In this context, the marketers of Pip & Nut face the ethical issues that whether they will comply with entire environmental regulation in Shanghai or they will strict to their own principles of business operation and marketing processes.
Social issues:
While operating the international business, foreign marketers can face social issues in host country (Jones et al. 2018). As Shanghai has completely different social values, perception, shared beliefs, customers, tradition and attitudes as compared to the UK based society, Pip & Nut will face issues in adapting to this new social context. In addition to this, marketers of Pip & Nut will face issues in adapting to different social trend and culture of Shanghai, which will make them unable to understand the actual preference and taste of the consumer in this market. in Shanghai, although the economy is strong and people have string income level, due over population the number of people residing in the below poverty level increases day-by-day. Therefore, the marketing opportunities to sell costly UHT milk to most of the consumers in Shanghai is reduces for Pip & Nut. On the other hand, social perception of the many older people poses barriers on marketing of the UHT milk by Pip & Nut, as they prefers to buy the UHT milk for their grandchildren from the brand of their home country rather than choosing the other international brand.
Cultural preference:
Culture plays important roles in buying behaviour, preference and interest of the customer on particular products and service (Julien, 2018). the clutter and tradition of Shanghai is completely different from the UK, which makes the marketers of Pip & Nut face issues in determining the actual taste and buying behaviour choosing UHT milk for their children. on the other hand, Shanghai is now more health conscious than earlier that makes the citizen to chose healthy and eco-friendly dairy product over the fat-enriches milk product such as yogurt and card. In this context, the marketers of Pip & Nut need to make proper standardisation and modification on their manufacturing and packaging process of UHT milk in terms of meeting the needs to consumers in the Shanghai.
Expansion method:
Trade agreement:
Through using this formal document, the government of the host country allow the foreign company to market their product and service here (Karadag, 2015). In this context, Pip & Nut can use trade agreement with Shanghai government in terms of marketing the UHT milk in this country. here the marketers of UK based SMNE need to comply with all the laws and business policies in terms of operating the business successfully.
Licencing:
This is the process, through which the government of the host country provide legal permission to trade their goods and services in this country (Miles et al. 2017). Through using t licencing process, Pip & Nut can be allowed by the Shanghai government to market the UHT milk in this country. in this context, the marketers of Pip & Nut need to comply with the legislation regarding the marketing and business operation in n dairy market of Shanghai.
Joint venture:
The Pip & Nut can use this internationalisation process in which the firm can merge with the local marketer in Shanghai in order to market its UHT milk to the target customers. In this context, Pip & Nut can merge with Shanghai Dairy Corporation Ltd, in terms of getting advantages to have local suppliers, raw materials and dealers and international investors.

Conclusion:
From m the above-mentioned discussion, it can be concluded that, internationalisation is process of extending th business operation beyond the national boundary. Before conducting the international operation, an organisation needs to conduct the macro environmental analysis on the market in which it is going to operate to understand that how the political, legal, social, technological and economic factors in the host country will impact on the business operation of the organisation. The organisation can have different market expansion method such as licencing, joint venture and trade agreement in term operating the business in foreign market smoothly. In addition to this, the organisation needs to consider the trade barriers such as cultural, ethical and social barriers while operating in the market to set proper market strategies to maintain sustainability of the business in the foreign market.
Reference list:
Ahmad, S.Z., 2015. Entrepreneurship in the small and medium-sized hotel sector. Current Issues in Tourism, 18(4), pp.328-349.
Akhmetshin, R.M. and Shafigullina, A.V., 2015. Government regulation of small and medium entrepreneurship under the influence of value-time benchmarks. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 6(1 S3), p.151.
Alaref, J., Brodmann, S. and Premand, P., 2019. The Medium-Term Impact of Entrepreneurship Education on Labor Market Outcomes: Experimental Evidence from University Graduates in Tunisia.
Amato, C., Baron, R.A., Barbieri, B., Bélanger, J.J. and Pierro, A., 2017. Regulatory modes and entrepreneurship: the mediational role of alertness in small business success. Journal of Small Business Management, 55, pp.27-42.
Amir, A., Auzair, S.M. and Amiruddin, R., 2016. Cost management, entrepreneurship and competitiveness of strategic priorities for small and medium enterprises. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 219, pp.84-90.
Astini, R. and Tafiprios, T., 2017. The Application of Three Orientation (Market, Technology and Entrepreneurship Orientation) and Global Mindset as Efforts to Increase the Growth and Export Performance: Evidence from Micro, Small and Medium Sized Industries of Teak Furniture in JAVA Island. Journal of Economic & Management Perspectives, 11(1), pp.1731-1742.
Audretsch, D.B., Belitski, M. and Desai, S., 2015. Entrepreneurship and economic development in cities. The Annals of Regional Science, 55(1), pp.33-60.
Ayandibu, A.O. and Houghton, J., 2017. The role of Small and Medium Scale Enterprise in local economic development (LED). Journal of Business and Retail Management Research, 11(2).
Burch, S., Andrachuk, M., Carey, D., Frantzeskaki, N., Schroeder, H., Mischkowski, N. and Loorbach, D., 2016. Governing and accelerating transformative entrepreneurship: exploring the potential for small business innovation on urban sustainability transitions. Current opinion in environmental sustainability, 22, pp.26-32.
Burns, P., 2016. Entrepreneurship and small business. Palgrave Macmillan Limited.
Czarniewski, S., 2016. Small and medium-sized enterprises in the context of innovation and entrepreneurship in the economy. Polish Journal of Management Studies, 13.
Dugguh, S.I., 2017. Entrepreneurship and small business: Strategic approach to alleviating poverty and corruption in Nigeria. GSTF Journal on Business Review (GBR), 3(1).
Epifanova, T., Romanenko, N., Mosienko, T., Skvortsova, T. and Kupchinskiy, A., 2015. Modernization of institutional environment of entrepreneurship in Russia for development of innovation initiative in small business structures. European Research Studies, 18(3), p.137.
Eze, F.J., Odigbo, B.E. and Bassey, A.E., 2018. Small and Medium-Scale Agro-Produce Entrepreneurship and Promotion of Non-Oil Exports from Nigeria. International Business Research, 11(11), pp.164-175.
Giaoutzi, M., Storey, D.J. and Nijkamp, P., 2016. Small and medium size enterprises and regional development. Routledge.
Guo, Q., He, C. and Li, D., 2016. Entrepreneurship in Shanghai: The role of localisation and urbanisation economies. Urban Studies, 53(12), pp.2584-2606.
Jones, P., Maas, G., Dobson, S., Newbery, R., Agyapong, D. and Matlay, H., 2018. Entrepreneurship in Africa, Part 3: Conclusions on African Entrepreneurship. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 25(5), pp.706-709.
Julien, P.A., 2018. The state of the art in small business and entrepreneurship. Routledge.
Karadag, H., 2015. Financial management challenges in small and medium-sized enterprises: A strategic management approach. EMAJ: Emerging Markets Journal, 5(1), pp.26-40.
Miles, M.P., Battisti, M., Lau, A. and Terziovski, M., 2017. Economic Gardening: Entrepreneurship, Innovation and Small Business Ecosystems in Regional, Rural and International Development.
Pansiri, J. and Yalala, A.T., 2017. The Evolution of Entrepreneurship and Small-to-Medium Business Development in Botswana. Botswana Journal of Business, 10(1), p.50th.
Piperopoulos, P.G., 2016. Entrepreneurship, innovation and business clusters. Routledge.
Ribeiro-Soriano, D., 2017. Small business and entrepreneurship: their role in economic and social development.
Singh, S.K. and Gaur, S.S., 2018. Entrepreneurship and innovation management in emerging economies. Management Decision, 56(1), pp.2-5.
Staniewski, M.W., Nowacki, R. and Awruk, K., 2016. Entrepreneurship and innovativeness of small and medium-sized construction enterprises. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 12(3), pp.861-877.
Valdivia, M., 2015. Business training plus for female entrepreneurship? Short and medium-term experimental evidence from Peru. Journal of Development Economics, 113, pp.33-51.
Volery, T. and Mazzarol, T., 2015. The evolution of the small business and entrepreneurship field: A bibliometric investigation of articles published in the International Small Business Journal. International Small Business Journal, 33(4), pp.374-396.
Wapshott, R. and Mallett, O., 2015. Managing human resources in small and medium-sized enterprises: entrepreneurship and the employment relationship. Routledge.
Take a deeper dive into Critically Assess The Potential Benefits To An Organization with our additional resources.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



