Fraud Theory Analysis of Volkswagen Scandal
Abstract
This analysis intends to apply a fraud theory to the Volkswagen emissions scandal that experienced a significant fraud within the past five years and develop an anti-fraud mitigation plan. Besides, the paper seeks to investigate the Volkswagen emissions scandal. This case broke up on September 18, 2015, when the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) accused the manufacturer German of equipping several hundred thousand vehicles with software that skewed the emission test results (Crête, 2016). After testing three cars of the German make, the test result show they were voluntarily reducing as much as possible the pollutant emissions of some of his models. The United States authorities opened a judicial procedure. A critical and detailed argumentation is presented forthwith concerning the history baselines of this fraud, how it was propagated, the chief actors involved in the scandal, the strategy used in carrying out the scam, who was the great actor of this fraud in addition, and what was the criterion used to carry out this fraud.
The Volkswagen emissions scandal- fraud risk assessment
Corruption is the perversion or misappropriation of a process, or interaction with one or more persons for the purpose, for the briber, to obtain special benefits or prerogatives or, for the corrupt, to obtain compensation in exchange for his complacency. Corruption generally leads to the personal enrichment of the corrupt or to the enrichment of the corrupting organization (mafia group, company, and club). This is a practice whch is considered unlawful depending on the area in question (trade, business, politics, etc.), but whose ownership is precisely to act in such a way as to make it impossible to detect or denounce (Jung, Chilton, & Valero, 2017). Corruption may concern any person enjoying a decision-making power, be it a political figure, a civil servant, a manager of a private company, a doctor, an arbitrator or an athlete, a trade unionist or the organization to which they belong. Fraud is a serious problem in commercial trade. It generates decisions based on improper grounds and prevents progress and innovation as well as distorting competition and damaging society. Corruption is prohibited. The perpetrators found guilty may incur fines and sanctions under criminal law. In autumn 2015, Volkswagen acknowledged that it had equipped 11 million diesel cars, including about 600,000 in the United States. The companywas found having software able to distort the results of pollution tests and concealing emissions which practically could exceed 40 times the standards. The company was accused of having violated the Clean Air Act (1970) (Nelson, 2016). The scandal has cost the corporation more than $ 20 billion in vehicle recalls and legal proceedings. The analysis of this case presents all aspects of the Volkswagen emissions scandal
The Volkswagen emissions scandal history
Case Volkswagen
The Volkswagen case, also called "Dieselgate N 1”, is an industrial and sanitary scandal related to Volkswagen Group. The company from the year 2009 to 2015, employed different techniques to reduce the pollutants emissions (NOx and CO2) from engine’s exhausts and before it would be certified as per the environmental law. According to the group, more than 11 million brands Volkswagen vehicles, Audi, Seat, Skoda, and Porsche are consumed around the world. The case, untitled in the history of the automobile, unveiled in September 2015 by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the CEO of the group, Martin Winterkorn. Several countries were currently investigating (Oldenkamp, van Zelm, & Huijbregts, 2016).US authorities have sued Martin Winterkorn, the former CEO of Volkswagen, and the other leaders of the German group, accused of agreeing for failing the installation process of software to reduce emissions of certain car brands. The United States authorities maintained they have e-mails disseminated between Volkswagens workers, who impersonated the company’s executives involved. Richard Dorenkamp, Heinz-JakobNeusser, Jens Hadler, Bernd Gottweis and Jürgen Peter constituted the five amongst other leaders indicted by the Department of Justice (Reitze, 2016). Oliver Schmidt, head of VW's regulatory compliance department in the United States from 2014 to March 2015, pleaded guilty in December to cooperate with the United States authorities after his arrest in Miami while on holiday. He was convicted of seven years imprisonments and fined $ 400,000.

What is Volkswagen guilty of?
They were guilty to have voluntarily circumvented the homologation programs to green its notes and to reduce as much as possible the pollutant emissions of some of theirbrands. If we know that the calculation methodologies are very far from the actual figures and that the manufacturers know the techniques to draw the tests to their advantage (over-inflated tires), Volkswagen goes very far since she knowingly manipulated his system to defraud certification cycles and benefit from many powers granted to "green" vehicles, such as the ecological bonus in France (Chossière et al., 2017).
Who discovered the trickery?
The International Council for Clean Transportation (ICCT), an NGO specializing in clean transport, had been testing certain diesel cars since 2013 to check their actual emissions. In the absence of sufficiently precise measuring instruments, the association utilized the University of West Virginia's, Alternative Emissions, Engines and Fuels Center for research and found disturbing discrepancies between homologation data and actual data on some Volkswagen models. Recorded in a report published in May 2014, the results are rather significant. For example, the Nox issued by a Jetta is 15 to 35 times higher than the American standards those of the Passat 20 times higher (Rhodes, 2016). Alerted by the association, the EPA and the CARB, two US environmental agencies, carry out their investigation and start mediation with the German group which leads to the recall, in December 2014, of all the diesel models of the product manufacturer between 2009 and 2014. If the story could have ended in this way, the EPA and CARB decided to carry out new tests in May 2015, which again confirm significant differences. Pressured by the US authorities, the manufacturers finally admitted to having introduced a device to bypass the emissions and officially received a violation notice from the EPA on September 18, 2015.
Looking for further insights on Restoring Volkswagen? Click here.
How did Volkswagen cheat?
It's an algorithm that allowed Volkswagen to do its trickery. Integrated into the computer, which analyzes in real time all the parameters of the vehicle, it proves to be able to identify test protocols to trigger a series of actions to minimize emissions to the detriment of other performance not evaluated. According to professionals, these test phases would be very easily detectable through software. "During a test, the steering wheel does not rotate; the hood is open. We can set up software that recognizes these phases,” said an equipment manufacturer in the Les Echosnewspaper. Once the test is complete, the engine returns to "normal" operation with pollution levels much higher than those found (Siano et al., 2017).
Analysis of the fraud
The EPA test protocol
The methodology adopted by the ICCT and the Center for Alternative Fuels Engines and Emissions CAFEE is also indisputable. Not only the number of vehicles tested is unusually low, but several aspects can raise legitimate questions. To understand the EPA test protocol, you first need to present the test protocol. These tests are performed in a laboratory, using a standard test procedure specified by federal law. The automotive inspectors test their vehicles, usually the prototype version of pre-production, and report the results of the EPA. The EPA reviews the results and performs a second opinion on approximately 10% to 15% of the manufacturer's tests at the National vehicle Sand Fuel Emissions Laboratory (Zhang et al., 2016).

The test protocols use accelerations and decelerations as well as steady speed bearings. The speed must be maintained within a certain tolerance range around the reference value. These tests are carried out in laboratories, the vehicles being positioned on rollers.

The test cycles are different between the United States (FTP-75 & US06) and Europe (NEDC)
In Europe, the vehicles are all tested and homologated by the approved laboratories before their commercialization.
Vehicles tested
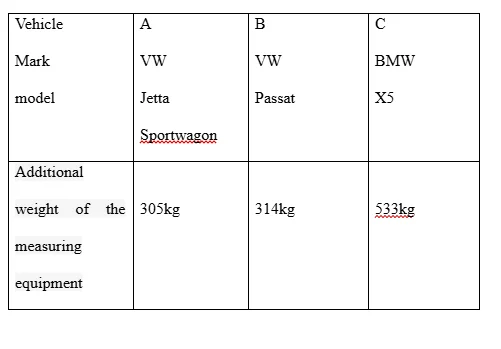
ICCT has selected 3 vehicles to test:vehicle A (VW) and vehicle C (BMW X5) were leased from two separate agencies and the vehicles (VW Passat) were acquired from private individuals.

The above tabulatedvehicles were all used. At the beginning of the test, thekilometer was 7580Kms for the vehicles A (VW Jetta), 24503 Kms for the vehicle B (VW Passat) and 24190 Kms for the vehicles (BMW X5).

Test tracks in real conditions
Five test routes were in California's three main population centers, namely Los Angeles, San Diego, and San Francisco, to reflect a rich diversity of topological characteristics, driving habits and environmental conditions, which are representative of the normal operation of the vehicle in the areas indicated. The itineraries can be divided into four categories:
Highway operation: high-speed highway driving during business hours, with frequent stop and go.
Urban driving: urban driving, characterized by low-speed vehicles and frequent stop and go.
Rural driving: Driving in rural areas at medium speed with occasional stops in the suburbs of metropolitan areas.
Uphill / downhill driving: Driving on roads with a positive or negative elevation higher than usual at intermediate and high speeds each was the subject of his main road map.
Models and vehicles involved
While the EPA advanced a figure of 482,000 cars in the United States, the group finally announced that 11 million diesel vehicles were concerned around the world. All cars were equipped with diesel engine type EA189. If we do not know precisely the breakdown by country, we know that several brands of the group are concerned: Audi, Volkswagen, Seat, Skoda, and Porsche. In the United States, five models are criminalized by the EPA and have already been withdrawn from the sale (Golf, Passat, Beetle, Jetta, and Audi A3).
Consequences for the manufacturer
Beyond a sharp deterioration of its image on the international scene, the main effects are financial for Volkswagen. If it has already lost a third of its value on the stock market, about 27 billion euros, the manufacturer also risks high penalties. In the United States, where 482,000 vehicles are involved, the bill could reach $ 18 billion, not counting the ongoing criminal investigation, the possible cost of a recall of cars and the many class actions that are in the process of being put in place. On the old continent, several states, including France and Germany, have formalized the establishment of investigations against the manufacturer. A study by the European Commission could follow these, but we know very little about the sanctions that the manufacturer could incur. From a structural point of view, the case will have serious consequences for the organization.
The FBI arrested Volkswagen's German engineer at the Miami airport as he prepared to embark on his return flight to Germany. The 48-year-old man was sentenced on Wednesday, Dec. 6, by a Detroit federal court, to seven years in prison and $ 400,000 (339,000 Euros) in fines for Volkswagen's diesel emissions fraud. After six months, in prison and unsuccessful bail applications, Schmidt pleaded guilty to lying to the federal government and violating the air law. In exchange, the judge had renounced nine other charges, which could have amounted to a total of one hundred and sixty-nine years in prison. In sentencing him to the maximum sentence, Justice Sean Cox accused him of committing "a serious crime against [the] economic system," based on trust, and of wanting to please his superiors for 'advancement. One of the prosecutors, Benjamin Singer, described Schmidt as one of the key elements in Volkswagen's strategy of lying to justice: "It's not as if the scenario was given to Mr. Schmidt. He helped write this scenario“(Utz, 2018). Mr. Schmidt testified that he obeyed the orders but assumed his responsibilities before the judge. "I made some bad decisions, and I'm sorry. An employee of the German manufacturer since 1996, Mr. Schmidt was appointed, in 2013, director of the Environmental Compliance Office of Volkswagen, Michigan. He was then responsible for relations with the federal and Californian regulatory agencies (Tuttle, 2015). When Schmidt first learned in 2014 that the University of West Virginia had reported on a discrepancy between the actual emissions of toxic gases and those calculated in laboratories, he had alerted his superiors. "We must first decide if we are honest. If we are not honest, nothing changes,"he wrote to his superiors in Germany by e-mail, which, according to the US authorities, indicates that he already knew about cheating software. And, back in Germany from March 2015, he has unquestionably pursued this strategy of lying, hiding the existence of the software to US regulatory authorities increasingly suspicious.
Last convict
Mr. Schmidt will undoubtedly be the previous German leader of Volkswagen to be condemned in the United States, in this scandal that led to the resignation of the CEO, Martin Winterkorn. The five other German officials prosecuted by American justice are in their country, which does not extradite its nationals. The US file was able to advance thanks to a German engineer of Volkswagen, James Liang, co-inventor of the software which allowed minimizing up to forty times the polluting emissions. The latter has agreed to cooperate with the courts, which did not prevent him from being sentenced this summer to forty months in prison. He appealed. Volkswagen pleaded guilty in March and agreed to pay $ 4.3 billion in fines in addition to recalling and repairing the 600,000 vehicles involved in the rigging software. Cost of the acquisition, higher than 20 billion dollars.
Application of Jesuit Value
The application of Jesuit values is crucial in combating ill practices in the context of office. The values are critical in guiding and spear-heading forth individuals in the domain of leadership. In the realm of Volkswagen fraud scandal, the cognition and accommodation of Jesuits value would have inspired those in leadership thresholds to be responsible and accountable in doing goodness to one another, and to the planet we are sharing life with. Jesuits value is a construction of six values and for the interest of the Volkswagen fraud; three are granted way and consideration. The first value is Cura Personalis which is build on the determination and will to care for life. As business firms engage in production of goods and services; they ought to perform this based on the desire to achieve excellently; with less harm induced to the sustainability pillars (economy, political, social-cultural and environmental pillars). The second value refers to Magis which constitutes of the challenge to attain excellence. The business enterprises should continually find inspiration in producing quality goods and services, and attain an excellent brand name amidst the competitive business world. Moreover, the value of Unity of Heart, Mind and Soul should have been harnessed by those in leadership transect to is discover themselves, and get to understand their place in influencing the wellbeing of the planet; and the society at large.

Anti-fraud mitigation plan and Recommendations
In an Anti-fraud mitigation plan it is essential ‘to reflect and decide on the allocation of the responsibility for fraud prevention, fraud detection and fraud case management’ Patrick Risch, CFE, CIA, and CCSAHead of Fraud Prevention & Detection BNP Paribas Fortis Belgium stated in the article ‘Setting up an Antifraud Control Plan.’ In the Volkswagen case, this entitles closer and more often supervision by the quality governing authorities, and by governmental bodies, since the CEO of the company was involved in the scandal. EPA can conduct periodic investigations. Creating and implementing a better Code of Conduct that regulates all employee relationships and relationships with authorities is also very important (Utz, 2018). Appropriate oversight processes were the cause of the fraud case at Volkswagen. A governmental employee can be part of the board of directors at Volkswagen, therefore overseeing all decisions and having the opportunity to observe the environment. The Code of Conduct at Volkswagen does not identify possible misconduct schemes, fraud scenarios, fraud categories, and applicable business activity or process and this is another because that made the Volkswagen emissions scandal possible. This paper recommends for the revision of the Code of Conduct and approval of this code and its implementation by the quality governing authorities is necessary. Fraud can also be mitigated through comprehensive training and awareness programs emancipating employees on the structures of fraud, integrity and corruption. The sensitization should instill the staff members with the knowledge about ethical conduct which is compatible with the company’s standards, mission and vision. The recruited employees also ought to be familiarized with their expectations during the orientation process. Fraud Risk Management Policies and Procedures are also instrumental during the induction of awareness programs, for the purpose of fraud detection, investigation, prevention, resolution and communication and reporting.
Quality control is vital in identifying probable fraudulent trends, for further remedy applications. In the process of quality control, relevant training and knowledge can be commissioned to the staff and solid reporting laid for identified trends. All this will promote the opportunity and ability to insinuate impending cases of fraud for further corrective measures. The company management also ought to cultivate strong internal policies addressing issues such as conflicts of interest, transparent procurement, and transparent operations which will invoke accountability and openness on the part of employees and the company; and elevate the external company image.
Conclusion
The concept of fraud encompasses different aspects such as theft, bribery, hacking information, obtaining something through deception or unlawful utilization of company property. As revealed above, fraud can be perpetrated by anyone; and its impacts are deleterious to both the company and individuals doing the act. The Volkswagen fraud came into the limelight of the public; and significantly helped to cut shot the environmental degradation the car emissions were releasing. There is a need for corporate responsibility to ensure their production processes are compliant with the law of land, for the purpose of sustainable development and wellbeing.
References
Chossière, G. P., Malina, R., Ashok, A., Dedoussi, I. C., Eastham, S. D., Speth, R. L., & Barrett, S. R. (2017). Public health impacts of excess NOx emissions from Volkswagen diesel passenger vehicles in Germany. Environmental Research Letters, 12(3), 034014.
Jung, K., Chilton, K., & Valero, J. N. (2017). Uncovering stakeholders in public–private relations on social media: a case study of the 2015 Volkswagen scandal. Quality & Quantity, 51(3), 1113-1131.
Nelson, J. S. (2016). The Criminal Bug: Volkswagen's Middle Management. Available at SSRN 2767255.
Oldenkamp, R., van Zelm, R., & Huijbregts, M. A. (2016). Valuing the human health damage caused by the fraud of Volkswagen. Environmental Pollution, 212, 121-127.
Reitze, A. W. (2016). The volkswagen air pollution emissions litigation. Environmental Law Reporter, 46.
Siano, A., Vollero, A., Conte, F., & Amabile, S. (2017). “More than words”: Expanding the taxonomy of greenwashing after the Volkswagen scandal. Journal of Business Research, 71, 27-37.
Tuttle, H. (2015). Volkswagen rocked by emissions fraud scandal. Risk Management, 62(10), 4-7.
Utz, S. (2018). Corporate scandals and the reliability of ESG assessments: Evidence from an international sample. Review of Managerial Science, 1-29.
Zhang, B., Marita, V., Veijalainen, J., Wang, S., &Kotkov, D. (2016). The issue arena of a corporate social responsibility crisis–The Volkswagen case in Twitter. Studies in Media and Communication, 4(2), 32-43.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



