Innovative Solutions in Waste Management
Introduction
Terracycle is a private US recycling company with headquarters in New Jersey (TerraCycle, 2019). The business operates a volunteer-based recycling platform to collect non-recyclable pre and post-consumer waste while partnering with the corporate donors are municipalities to turn them into raw material for being used in new products. Terracycle is an innovative recycling company that emerges as a global leader in recycling hard to recycle materials offering free programs (TerraCycle, 2019). Scientists around the world work together to find out the end of life challenge in plastic waste calling for new ways to reuse and recycle plastic endlessly in closed-loop systems. Innovation on that level would convert the current disposable linear economy into a circular economy where recycling plastic for eternity will not be perceived as a challenge (Dziallas and Blind, 2019). The aspect of innovation within the industry of waste management needs to gain pace. With limited knowledge among people, the management of waste makes redundant aspects making the whole plan a complete failure. The assignment hence works on underpinning the possible innovational theories embraced by Terracycle in managing the business operations while, ensuring that the theories can help in business development (TerraCycle, 2019). If you are seeking business dissertation help related to environmental innovation and waste management, Terracycle's approach and success can offer valuable insights into sustainable business practices.

The study of innovation has a long history in management research. Still, the literature is not uniform, and the description needs much work. The structure of the paper follows the prime argument as laid above next is a brief review of how differently innovation is conceptualised in regards to the current organisation while making use of the right innovation determinants and contingencies. There are many innovations being developed within the company on a daily basis. Innovation becomes important for a group of people making their life easier. It becomes important to question the factors that lead to change. As stated by Kazadi et al. (2016), a combination of social and cultural factors works on influencing the change. The assignment highlights the maintenance of diffusion theories and models such as innovation diffusion theory, understanding the framework and analysing the real-world cases presented by such theories
Continue your exploration of Waste Management with our related content.
Two innovation theories
The innovation of diffusion theory
Before dividing into models and theory for innovation it is important to understand the actual definition of innovation. Innovation refers to the introduction of something new, which would be ideally a process or product (Davids and Frenken, 2018). In the current context innovation of diffusion theory or IDT has been different several times in case analysis. It creates a scope of the foundation for understanding the need of adopting innovation and the factor that influences choices of an individual about innovation. Kahn (2018), the theory provides a broad scope, allowing flexibility for the business organisations that plan to implement it. There are four main components within the diffusion theory; such as innovation so many channels implemented for broadcast information about the innovation, existing social norms around the non-adopters of innovation and time taken by the individual to move through the process of adoption. The interaction of these components helps in understanding why an individual supports innovation and why some people do not (Vuori and Huy, 2016).
The chosen theory works on seeking five stages of potential adopters for moving through the process. The process of diffusion, in theory, is the innovation-decision leading to rejection or adoption of innovation. The first is seeking knowledge about innovation and function. Second is the perspective when the adopter forms a strong opinion about innovation. The third stage is when the decision is made to reject or adopt the innovation (Meissner and Kotsemir, 2016). Finally, the adopter makes a confirmed decision where they work on seeking reinforcement of the decision they made and work on continuing the implementation of the innovation for the perceived benefits.
Rogers extends beyond the process of adoption by identifying these attributes, whether the innovation adopted has a relative advantage. The aspect of relative advantage refers to the lesser or greater benefit of the innovation as compared to the alternate options. In the case of the chosen company, it becomes important to note that recycling of waste products is of prime importance. The importance is further increased by the increasing level of awareness exhibited by the people about the environment (Gerke et al. 2017). However, due to limited knowledge and options of recycling units, people fail to implement their thoughts into actions. The reluctance of the people can be clearly explained through the complexities, which is perceived to be too high. Potential adopters are likely to accept innovation if there is a scope to experiment with and test out before making the final decision. Observability occurs when innovation is rightly adopted and diffused across the people within a system by changing their mind for considering an adaptation of innovation. For instance, personal technology services smart devices like smartphones have experienced widespread diffusion due to high levels of Observability. This intervention allowed them to perceive the success along with learning from the challenges of early adopters (Thayer et al. 2018).
Technology acceptance model
Continuing as per the theme of opinion attitude in influencing innovation adoption, technology acceptance models make sure that it is the attitude of the adopter of an expectation of innovation that increases chances for adoption. The two focus concepts in the chosen framework state how innovations are perceived by the potential adaptor. In terms of ease of use and how the innovation would be learned and implemented. Of the two elements Dehghannasiri, Esfahani and Dougherty (2017), believe that use of use creates a direct impact on the person's usefulness as easier and adaptable leaves an innovation is flexible then there means a greater chance to use it experiencing a high level of productivity. There is a high correlation between perceived usefulness and adoption of innovation as compared to persuade usefulness and adoption. From the above statement, it could be clearly concluded that it would not matter how easy and innovation is to implement; people are less likely to adopt if they do not understand the usefulness and relation of the innovation to their productivity (Pérez et al. 2019).
The general theory of innovation
The general theory of innovation, instead of using the logic of evolutionary process it allows reversal of the odds and creates successful innovation based on demand. In order to be successful, innovation must be diffused and adopted. The wisdom would be limited for innovation for creating a competitive market and will market share at an increasing profit (Cinar, Trott and Simms, 2019). Administrative innovation aims at improving operational processes; however, there remain certain innovative approaches that work on increasing the level of profit. These days' managers also used to renovate the products and deal with the new demands of the customers. It is important to maximise the success of innovation file managers work on using the right innovation as per the time and place. The dimension of innovation service appeared with the change of industrial society to service society. These days most of the companies are service-based companies while previously it was product-oriented. The chosen theory works by stating that innovation involves more science and technology, then meeting the needs of the customers. As per the perspective put forward by Simmons et al. (2018), customers are important in innovation as they are the one to use the services and give feedback regarding the efficacy of the innovation. As supported by Keum and See (2017), innovation aims at satisfying the customers by improving the company client relation. If the chosen theory stresses that innovation is to be market-oriented disapproving the idea which states that innovation can be motivated by excitement than by economic gain
Application of theories to explain the development
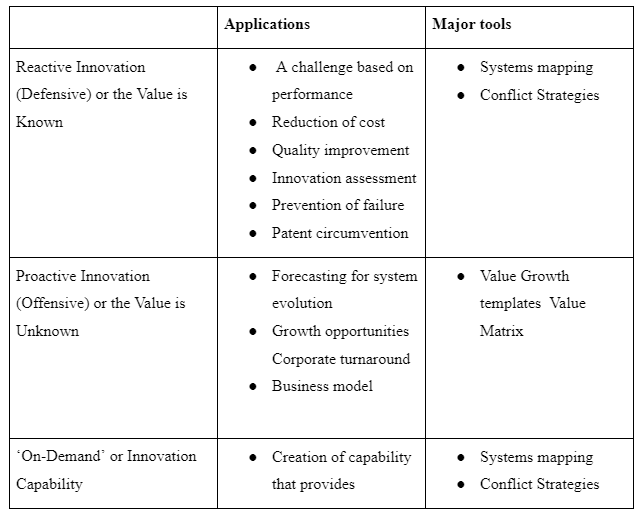

The innovation approach implemented by Terracycle is incremental innovation. As stated by Chen, Liu and Zhu (2018), incremental innovation refers to continuous small but gradually developing improvement towards existing processes and products for maintaining a competitive position within the market over a period of time. The majority of innovations are incremental in nature as these innovations are the easiest and cost-effective to implement (Husain, Dayan and Di Benedetto, 2016). The business conducted by Terracycle is a recycling business where the used materials are recycled for producing raw materials for new products. Terracycle works with a lot of businesses all over the nation, within the approach to social business, eliminating the idea of waste. Terracycle works on producing unique one of kind solutions from recycling the non-recyclable, integrating unique materials in new products and transforming product packaging from disposable to durable with the help of the partners who sponsor the activities.
Earlier, the products were concentrated on recycling. No intervention was undertaken to develop the existing mode of sustainable packaging. The packaging is anybody cockroach undertaken by the chosen company. This innovation is incremental in nature as it works on modifying the existing products and services where the prime goal is to improve the functionality by keeping the costs to a bare minimum (Ahn et al. 2016). Incremental innovation is of prime importance to companies such as Terracycle; the business is still new in the industry and must keep up with the existing competition and hold a strong position in the market. The incremental type of innovation follows the pathway of the general theory of innovation, highly customer-centric and works as per the demands of the market. The company leverages the interest of customers in sustainability and works on deriving funds from the same.
Rather than working on a traditional pathway of recycling the materials as old companies do, Terracycle approaches the brand of the manufacturer for making the packaging of their products nationally recyclable. Terracycle works on developing custom supply chain processes of collecting, processing and supplying the unique materials that tell a story for integration with the brand's primary packaging. From where the team works with the company to leverage the story to general sales lift and incremental display space allowing the business to earn a positive media reputation and marketing buzz. Terracycle understands the importance of sticking to sustainable approaches to waste management and additionally understands the importance of corporate social responsibility of business towards the environment. An innovative approach of this waste management company is to enhance the reputation of the business partners by making them appear as an environmentally aware business and upgrading their packaging (Akhmetshin et al. 2017). The latest innovation by Terracycle, the loop is a reuse platform that allows a business partner from the world's largest consumer brand to new startup to rethink ok and design out of disability while balancing the affordability and convenience of disposable items. The business is so innovative in nature that it works on amalgamating aesthetics with corporate social responsibility. Innovation takes a step above the normal domains while operational in Terracycle. The business provides upgraded services to the clients where they work on designing the office space with reclaimed or recycled materials as per the budget of the clients (TerraCycle, 2019).
The unique approach to business is not limited to the huge clients; rather, Terracycle health services for the distributors and related too. Terracycle works on creating an emotionally engaging activation for communicating the brand sustainability effort and dry foot traffic while promising positive publicity and consumer engagement. These programs earlier involve mobilising the retail employees to send the collected item back to Terracycle why are shifting of small parcels (Turker and Vural, 2017)
The innovative approach of Terracycle remains in the way they run their business. The chosen company works on combining a series of strategic, scientific logistic and technical interventions for promoting the customer business model that together makes both Terracycle the client's program scalable and profitable business. The innovative process undertaken by Terracycle is dependent on three major interventions. The prime approach to the business of this modern waste recycling company is not only limited to recycling the used waste rather it works on improving the existing business model of the client (Kurpjuweit, Reinerth and Wagner, 2018). The first step is collection done by inspiring and motivating the businesses, community schools, and individuals to collect several wastes on a message scale, especially the ones which cannot be recycled easily. The second step is developing technology and science to determine the exact ways to optimally transform large quantities of non-recyclable into raw materials that can be easily used by manufacturers. Third step designs equation which is profitable for the client from driving the share with the market to the foot traffic and offering a competitive advantage that differentiates the product from the competitors for in terms of a scalable platform (Stefan and Bengtsson, 2017)
Recommendation
Consumers have a clear understanding of the importance of processing waste. However, this understanding is overpowered by the recycling of a specific product. The local recycling companies who are a major threat to the business of TerraCycle. The theory of diffusion can be implemented for removing the potential challenges faced by local recycling units (Jakobsen and Clausen, 2016). The business should work on making the customers aware of how Terracycle is different from local wastage recycling companies. Most consumers assume that a local recycling company pull a lot of material away and salvage it. However, there remains a lot of action to be undertaken for recycling a cream cheese tub or pouch of juice. A lot of planning is implemented coupled with trial and error with different types of machinery and costs that give sustainable recycling intervention to the packaging of consumer goods. All of the waste materials collected from different households cannot be recycled under the same facility due to the different nature of the product packaging. There exist various kinds of processing partners with a varied range of equipment specialising in specific types of material which can be leveraged for getting a used product into a reusable state (Ommen et al. 2016).
It is not always easy to find the partner who can process these waste materials into reusable form as demands and amalgamation of capability and willingness. A great example is those juice pouches which are smelly and sticky containing materials, such as aluminium structures. Apart from having the right kind of equipment, recycling facilities need to be willing to grind or shred, washing dry and searching difficult metal parts using expensive machinery. Most of the processing facilities refrain from the materials that TerraCycle deals with on a regular basis as they are concentrated on cleaning post-industrial waste. The big waste recycling companies perceive that dirty use pouches and wrappers are not worthy of the money and time (Kurpjuweit et al. 2018). However, few processes are more than glad to celebrate such waste materials as long as economics matters. Terracycle works on developing long-standing relationships with their business partner taking time, labour money and patience, for processing the difficult materials and salvaging the right kind of benefits. At this point in time, these initial challenges from the local recycling company and the huge giants can turn into a scope of new business for Terracycle.
It can often take years to innovate and end of life solutions for difficult materials that cannot be easily recycled. However, the chosen company works on developing and working towards a way that can be implemented for eliminating waste on a permanent basis (Dolinska, 2017). The business in the mentioned context works on understanding the possible ways that can be implemented for ensuring that the competitive advantage is rightly maintained. In similar regards, it can be additionally recommended, the innovation of diffusion theory can be implemented for propagating the right kind of knowledge among the consumers. The knowledge should work on explaining the consumers about the importance of working with Terracycle, by exhibiting the environmentally-conscious steps undertaken by the company at their every operational step. The mentioned recommended mode of innovation originated in communication for explaining the exact ways the services provided by Terracycle.

Conclusion
The investigation of development as a long history in the executives examines. Still, the writing isn't uniform, and the portrayal needs a lot of work. The structure of the paper follows the prime contention as laid above next is a short survey of how distinctively advancement is conceptualised with respect to the current association while utilising the correct development determinants and possibilities. There are numerous advancements being created inside the organisation every day. Advancement gets significant for a gathering of individuals making their life simpler. It gets critical to scrutinise the components that lead to change.
The business directed by Terracycle is a reusing business where the pre-owned materials are reused for creating crude materials for new items. Terracycle works with a lot of organisations everywhere throughout the country, inside way to deal with social business taking out the waste. Terracycle chips away at creating interesting stand-out arrangements from reusing the non-recyclable, incorporating one of a kind material in new items and changing item bundling from dispensable to solid with the assistance of the accomplices who supports the exercises.
Reference list
- Ahn, J.M., Ju, Y., Moon, T.H., Minshall, T., Probert, D., Sohn, S.Y. and Mortara, L., 2016. Beyond absorptive capacity in open innovation process: the relationships between openness, capacities and firm performance. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 28(9), pp.1009-1028.
- Akhmetshin, E.M., Vasilev, V.L., Puryaev, A.S., Sharipov, R.R. and Bochkareva, T.N., 2017. Exchange of property rights and control as a condition of the innovation process effectiveness at collaboration between university and enterprise. Academy of Strategic Management Journal.
- Chen, X., Liu, Z. and Zhu, Q., 2018. Performance evaluation of China's high-tech innovation process: Analysis based on the innovation value chain. Technovation, 74, pp.42-53.
- Cinar, E., Trott, P. and Simms, C., 2019. A systematic review of barriers to public sector innovation process. Public Management Review, 21(2), pp.264-290.
- Davids, M. and Frenken, K., 2018. Proximity, knowledge base and the innovation process: Towards an integrated framework. Regional Studies, 52(1), pp.23-34.
- Dehghannasiri, R., Esfahani, M.S. and Dougherty, E.R., 2017. Intrinsically Bayesian robust Kalman filter: An innovation process approach. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 65(10), pp.2531-2546.
- Dolinska, A., 2017. Bringing farmers into the game. Strengthening farmers' role in the innovation process through a simulation game, a case from Tunisia. Agricultural Systems, 157, pp.129-139.
- Dziallas, M. and Blind, K., 2019. Innovation indicators throughout the innovation process: An extensive literature analysis. Technovation, 80, pp.3-29.
- Geissdoerfer, M., Savaget, P. and Evans, S., 2017. The Cambridge business model innovation process. Procedia Manufacturing, 8, pp.262-269.
- Gerke, A., Dickson, G., Desbordes, M. and Gates, S., 2017. The role of interorganizational citizenship behaviors in the innovation process. Journal of Business Research, 73, pp.55-64.
- Husain, Z., Dayan, M. and Di Benedetto, C.A., 2016. The impact of networking on competitiveness via organizational learning, employee innovativeness, and innovation process: A mediation model. Journal of Engineering and Technology Management, 40, pp.15-28.
- Jakobsen, S. and Clausen, T.H., 2016. Innovating for a greener future: the direct and indirect effects of firms' environmental objectives on the innovation process. Journal of Cleaner Production, 128, pp.131-141.
- Kahn, K.B., 2018. Understanding innovation. Business Horizons, 61(3), pp.453-460.
- Kazadi, K., Lievens, A. and Mahr, D., 2016. Stakeholder co-creation during the innovation process: Identifying capabilities for knowledge creation among multiple stakeholders. Journal of business research, 69(2), pp.525-540.
- Keum, D.D. and See, K.E., 2017. The influence of hierarchy on idea generation and selection in the innovation process. Organization Science, 28(4), pp.653-669.
- Kurpjuweit, S., Reinerth, D. and Wagner, S.M., 2018. Supplier Innovation Push: Timing Strategies and Best Practices A number of motivating and moderating factors influence suppliers’ decisions to involve customers in the innovation process. Research-Technology Management, 61(2), pp.47-55.
- Meissner, D. and Kotsemir, M., 2016. Conceptualizing the innovation process towards the ‘active innovation paradigm’—trends and outlook. Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 5(1), p.14.
- Ommen, N.O., Blut, M., Backhaus, C. and Woisetschläger, D.M., 2016. Toward a better understanding of stakeholder participation in the service innovation process: More than one path to success. Journal of Business Research, 69(7), pp.2409-2416.
- Pérez, J.A.H., Geldes, C., Kunc, M.H. and Flores, A., 2019. New approach to the innovation process in emerging economies: The manufacturing sector case in Chile and Peru. Technovation, 79, pp.35-55.
- Simmons, G., Giraldo, J.E.D., Truong, Y. and Palmer, M., 2018. Uncovering the link between governance as an innovation process and socio-economic regime transition in cities. Research Policy, 47(1), pp.241-251.
- Stefan, I. and Bengtsson, L., 2017. Unravelling appropriability mechanisms and openness depth effects on firm performance across stages in the innovation process. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 120, pp.252-260.
- Thayer, A.L., Petruzzelli, A. and McClurg, C.E., 2018. Addressing the paradox of the team innovation process: A review and practical considerations. American Psychologist, 73(4), p.363.
- Turker, D. and Vural, C.A., 2017. Embedding social innovation process into the institutional context: Voids or supports. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 119, pp.98-113.
- Vuori, T.O. and Huy, Q.N., 2016. Distributed attention and shared emotions in the innovation process: How Nokia lost the smartphone battle. Administrative Science Quarterly, 61(1), pp.9-51.
- Zimmermann, R., Ferreira, L.M.D. and Moreira, A.C., 2016. The influence of supply chain on the innovation process: a systematic literature review. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal.
Take a deeper dive into Innovation Management in Marks and Spencer with our additional resources.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



