Online Shopping Trends in the UK
CHAPTER 1
Background of the Study
In recent some years the e-commerce companies have performed exceptionally well, and they have now become the most commonly used method of shopping for several people in the UK (Mazzarol, 2015). Online shopping is now very common in the country. Establishment of leading e-commerce companies, effective cyber laws, etc. have contributed significantly to the growth of this sector. 82% of the country’s population uses the internet on a day to day basis. They depend on the internet for almost every aspect of their daily lives. In 2015 total online sales amounted to £157 million (Skeldon, 2018). Figure 1 shows the total number of online shoppers in the UK, along with future projections. Herein it can be observed that there is a constant increase in the number of people that use online mediums to purchase different products. This indicates that online shopping is now the preferred means of shopping for a large section of people in the country (Wang, Wang and Liu, 2016). Through this study, the researcher has analysed and compared the performances of Amazon and Alibaba – two of the leading e-commerce companies. Through this research, the scholar was able to identify and evaluate the business models of the two firms and also compared their performances. In addition, various recommendations to help the companies improve their performance have also been provided in this research.

1.2 The Rationale of the Study
Currently, the UK is the leading e-commerce country in Europe. British people spent nearly €200 billion in the year 2017 (Skeldon, 2018). This shows that a large number of people in the country prefer to use e-commerce companies such as Amazon, Alibaba, etc. for their varied needs. The European B2C E-commerce Report 2018 shows that Amazon was the leading e-retailer in 2017 (European E-commerce Report 2018 Edition, 2018). This shows that companies such as Amazon have captured a majority share of the UK market and also are some of the main contributors to the country’s growth and development. 33.5% of all e-commerce transactions in the UK were made through Amazon (Skeldon, 2018). While on the other hand, Alibaba has only very recently entered the UK market, but it is fast becoming one of the leading e-commerce companies in the country (Lavinga-Lott, 2017). Through this study, the researcher has assessed, and compared business models of both the companies and have analysed their performances as well. Herein tools such as SWOT analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis have been used to evaluate business models of both the firms.
1.3 Aim and Objectives
The aim of the current study is “To Evaluate Performance of E-Commerce Companies: A Case Study of Amazon and Alibaba, UK”. To achieve this aim the following objectives had to be first fulfilled:
To evaluate factors affecting the performance of e-commerce companies. To compare business models of Amazon and Alibaba UK. To analyse performances of Amazon and Alibaba UK. To provide recommendations to improve the performance of Amazon and Alibaba UK.
1.4 Research Questions
By answering the following questions, the researcher was able to fulfil the aim and objectives of the current investigation:
What factors affect the performance of e-commerce companies? How do business models of Amazon and Alibaba UK different from one another? How have Amazon and Alibaba UK performed in recent years? How can Amazon and Alibaba UK improve their performance?
Dig deeper into A case study on GExceptional Comfort with our selection of articles.
1.5 The Scope of the Study
This research can be used by a number of different parties and entities. This study focuses on comparing business models of Amazon and Alibaba in the UK. The two e-commerce giants can use findings obtained through this investigation. Other e-commerce companies in the country can also use them. Moreover, the results can be useful for future students conducting research on a similar topic. This study can be a beneficial starting point for future scholars because this research provides an in-depth analysis and specific detail about the two companies along with a comprehensive analysis of business models followed by them.
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to Solving Traffic with Vehicular Networks.
1.6 Structure of the Study
This research has been divided into five sections. In the first chapter, an introduction to the research topic has been presented. It consists of the aim and objectives of the research paper. As the name suggests, this chapter acts as a beginning point for the study. It provides the main reasons for conducting the research and also a description of who can use the findings of the paper. In the second chapter, a thorough analysis of various past studies has been carried out. Through this section, the researcher has presented a critical analysis of different studies that have been carried out on the topic in the past. The third chapter consists of an evaluation and analysis of the different tools and method that have been used to conduct this research. In the fourth chapter, the data collected through different tools have been analysed and presented; while in the fourth chapter a summary of the study has been presented.

CHAPTER 2: LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Introduction
The following paragraphs present a critical analysis of the various past investigations that have been carried out on the research topic. This section has helped in identifying loopholes in the past studies and an evaluation of how they can be filled by the current study.
2.2 Business Model of Amazon
Amazon is the world’s leading e-commerce company. Since its establishment, the company has grown by leaps and bounds. One of the main reasons for the firm’s exceptional growth is the large product selection and low prices (Cuofano, 2017). The business model of the company is primarily based on customer satisfaction. Herein the firm pays attention to maintaining low prices, fast delivery speed and a vast selection of products. These have been the mainstay of Amazon’s operations. By focusing on customer satisfaction, Amazon has been able to develop a strong image in the market and maintain it. Zhang and Wen (2017) stated that such a business model has been the central aspect of Amazon’s operations and acts as a unique selling point (USP) for the company. Figure 2 shows the business model canvas of Amazon.
Under the key partner tab, there are four elements that the company considers – logistics partners, affiliates, authors and publishers and sellers. Herein Amazon has tied up with different logistics partners for shipping the products; even so that it has established its own logistics system as well. In addition, the company also provides affiliate links to influencers who can sell more of the products. Amazon Kindle and publishing is another key aspect of a firm’s operations (Cuofano, 2017). Herein the firm provides opportunities to authors to publish their books and sell them online. Apart from this, the company also allows different retailers and sellers to list and sell their products through Amazon. Merchandising and production and design are some of the key activities of the company. Over the years the company has been able to amass a significant amount of resources. For instance, it has developed numerous warehouses all around the world. Amazon is also one of the largest employers in the country (Rouibah, Lowry and Almutairi, 2015). Therefore, it can be said that the company has developed a strong base of human resources. Value is provided to customers through four key areas – convenience, low prices, fast delivery (through Amazon Prime) and virtually endless products. Low cost and economies of scale form the key part of the cost structure of the company (Cuofano, 2017). There are five main revenue streams of the company – sale of assets, e-books and content, acquisition and investment, commission on resale, prime monthly subscriptions.

2.3 Business Model of Alibaba
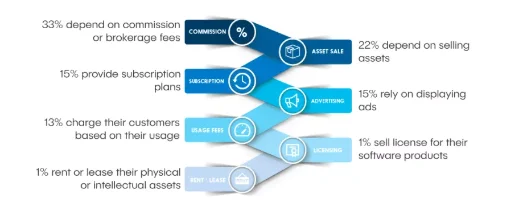
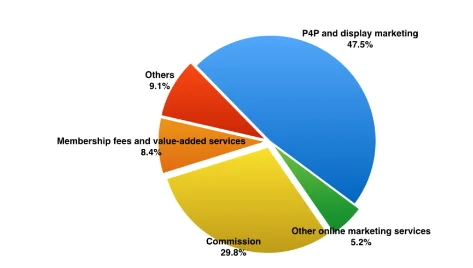
It took nearly 20 years to bring the Chinese e-commerce giant to the UK. Although the company was founded in 1999, it officially started operating in the country only very recently. To establish its operations in the UK, the company two data centres in London (Morrison, 2018). Figure 7 shows the revenue share of the company based on different types of services that it provides. There is a lot of difference in the business model of Alibaba with that of other e-commerce firms such as Amazon. It is focused more on the trade between businesses. Alibaba does not focus on B2C transactions; rather it operates as a platform for suppliers to sell their products in bulk at wholesale prices to small and medium-sized businesses in the country (Company Overview, 2018). The company makes money by charging a small commission from the sellers for every product sold through the website. Thus Akter and Wamba (2016) rightly stated that the business model of Alibaba is very simple. Commissions form the majority of Alibaba’s source of revenue. Figure 5 shows a business model of the company.
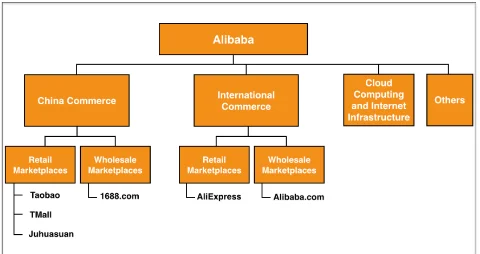

Herein it can be observed that the company offers a wide variety of products and services. The e-commerce business consists of three major web portals – Alibaba, Tmall and Taobao. Tmall targets middle-class customers who want to purchase branded products, while Taobao is a trading platform for customers. However, there are six more subsidiaries through which the company makes money – Aliexpress, 1688, Alimama, Alibaba cloud, Ant Financial and Cainiao Network (Our Businesses, 2018). All these companies collectively make Alibaba group a big ecosystem. Apart from being an online marketplace for global trade, Alibaba provides a number of other services as well, such as customs clearance, VAT refund, trade financing and logistics services. These are some of the key components of the firms’ operations. Alibaba’s e-commerce portal essentially is an intermediary that charges commission from sellers. Although this is one of the main sources of revenue for the firm, there are other ways as well through which the company earns money (Al-Somali, Gholami and Clegg, 2015). It offers two types of memberships to suppliers – free supplier membership and premium gold supplier membership. Under the free membership, suppliers do not have to pay any fees to the company, but they are limited in terms that they cannot list more than 50 products on the site. Moreover, they are not verified suppliers, which then have a significant impact on the buyer’s trust. On the other hand, to obtain the gold membership suppliers have to undergo intense authentication process (Wirtz, Ullrich and Göttel, 2016). Taobao does not charge any fees from the merchants. The website functions like Google and thus acts as a place where customers can search for different products. However, the merchants are required to pay a certain amount to stand out from other merchants (Taran and Paolone, 2016). This just like the search engine optimisation function, since Taobao has a special ranking system where the merchants are ranked according to ratings they receive from customers, along with package they have selected for SEO, as argued by Wu and Wu (2015). There are three sources through which Tmall ears revenue – commission on the price of goods sold, service fees (one time fixed deposit and annual technology and service fees) and marketing services provided to the merchants. Alibaba’s revenue is dependent on ads displayed on the site; while Aliexpress makes money by charging a commission between 5-8% of the transaction value (Rahayu and Day, 2015).
2.4 E-commerce in the UK
The UK is the largest country in Europe in terms of online shopping. More than 82% of the UK population uses the internet on a daily basis (Skeldon, 2018). This indicates that a large chunk of the population uses the internet for their varied needs. Online shopping has become the key platform through which people purchase different products. In 2018 almost 17% of the total retail sales were made through online channels, indicating a considerable rise from the figures of 2016 where online retail sales accounted for 14% of the total sales. The B2C e-commerce turnover grew to over 13,000 million GBP indicating a growth of 13.65%. The most purchased products in the country were clothing items (European E-commerce Report 2018 Edition, 2018). Figure 8 shows the divided internet usage according to different age groups. Herein it can be observed that the majority of the customers who do online shopping on a daily basis is done by 16-24-year-olds.

Figure 9 shows the projected e-commerce revenue in the coming few years. It can be seen that fashion is the leading product category accounting for $25 billion market share. Further, it is expected that by 2021 fashion will be the most purchased online category with an estimated value of USD 34 billion, followed by Toys, Hobby & DIY worth USD 22 billion.

Debit and credit cards are the preferred mode of payment for the UK customers, followed closely by Paypal. Figure 10 shows different payment options used by UK online shoppers.

2.5 E-commerce trends in the UK
Wilson (2018) states that despite the economic uncertainties due to Brexit and the unstable nature of the economic environment in general, consumers in the UK continue to spend. The retail sales increased by 4.7% in 2017 to reach £466.15 billion, while online retail sales grew by almost 15% in the same year (Wilson, 2018). This indicates that online shopping is the most preferred way of shopping for the majority of the UK population, as they rely on it even for their daily requirements. According to Wilson (2018), mobile commerce or m-commerce has a significant impact on online shopping. Wilson (2018) states that this is one of the key trends that affect the e-commerce sector. However, Kalia (2015) contradicts by stating that many high street retailers have not felt any pressure from such digital mediums. Hua, Morosan and DeFranco (2015) further supported this by stating that physical retailing has not put too much pressure on such digital channels as well. Fisher (2018) believes that e-commerce companies should pay attention to six particular trends – buyer behaviour, platform performance, abandoned basket, email marketing, e-commerce personalisation and customer lifetime value. It is expected that 18% of all retail sales in the country will be done online; and this number will rise to 95% by 2040 (Fisher, 2018). In this regard Baesens, Vanthienen and Zhao (2016) stated that if the customers do not like the layout of the website they will leave. A study by Deng and Wang (2016) indicates that 56% of the customers abandon their carts because of unexpected costs at the checkout page. Email marketing will continue to be the primary form of marketing for e-commerce companies.
2.6 Pros and Cons of SWOT Analysis
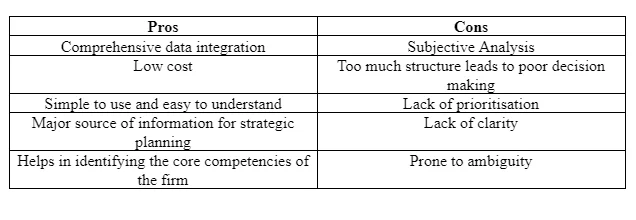
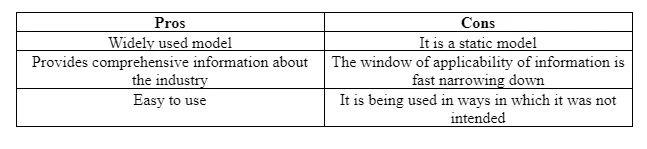
Sevkli and Delen (2012) stated in their researcher that conducting a SWOT analysis can be immensely helpful for companies. According to Yuan (2013), such analysis can help forms in understanding their internal and external environment in a better and more effective manner. One of the biggest advantages of such an analysis is that it can be used in almost every type of situation. This means that the management of a company can use it at any point in time, get a better understanding of their operations, and determine ways to improve firms’ operations. According to Wijngaarden, Scholten and Wijk (2012), by using such a tool, the authorities can obtain more information about four different aspects of business operations. However, Kajanus, Kurttila and Kangas (2012) stated that SWOT analysis’ major disadvantage is that it is only one stage of business planning. In managing any business organisation, it is imperative for companies to identify and analyse different areas of operations. By conducting a SWOT analysis, the management can obtain information only about these aspects, but not in other areas. Advantages and disadvantages of SWOT analysis are shown in the following table.
2.7 Pros and Cons of Porter Five Forces Analysis
One of the biggest strengths of this model is that it is a widely used method in effective strategic planning. Dobbs (2014) stated that through the Porter Five Forces model, companies could perform the function of strategic planning easily and effectively. This is due to the reason that they can collect more information about the external environment of the company. Today almost every company and individual at the managerial position and above uses a porter five forces model. Through such analysis, the company can identify and learn about its competitors. The information obtained through such analysis can be used in dealing with customers and suppliers. However, on the other hand, this model is not useful for analysing ‘alike’ industries, as stated by Mathooko and Ogutu (2015). The following table shows the strengths and weaknesses of the model.
2.8 Financial Ratios of Alibaba
The following table shows the financial ratios of Amazon during the year 2016-17.

Operating margin of the company has improved during the one-year period along with return on assets and return on equity. On the other hand, the current ratio, quick ratio have decreased considerably while financial leverage and bet/equity ratio also has increased. Increase in financial leverage indicates that the majority of funding has increased. In comparison, the capital Alibaba had from debt has now shifted towards finding through equity. On this basis, it can be said that the performance of the company in terms of its financial position has improved during the said time period.
2.9 Financial Ratios of Amazon

The following table shows the financial ratios of Amazon during the years 2015-16 and 2016-17. Herein it can be observed that while operating margin has improved from the year 2015-16 to 2016-17, return on assets and return on equity have declined considerably. On the other hand, the current ratio has not changed during the time period, but the quick ratio has decreased while financial leverage and debt/equity ratio have increased. The decline in the return on assets ratio indicates that the amount of return that the company got from its assets have decreased along with a significant decrease in the return on equity as well.
CHAPTER 3: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Data Collection
Lewis (2015) stated that data collection is the spine or central aspect of any research investigation. By properly carrying out the data collection process, the researcher can obtain a substantial amount of data pertaining to the research topic. There are two main methods and sources from where data can be collected. In this research, only secondary sources have been used (Smith, 2015). This is due to the reason that plenty of information is available regarding differences and comparison between the performance of Amazon and Alibaba. Therefore, the researcher has used already available articles, research studies, books and annual reports of both the companies. By using such data, the credibility and reliability of the research were enhanced (Flick, 2015). Through the secondary sources, the researcher was able to get access to detailed information pertaining to both the companies. This helped in carrying out the study effectively. The biggest advantage of using secondary data in the context of the current study is that a wide variety of information is available on the subject matter. There is plenty of information in the form of articles and reports available through which the researcher was able to collect data about the current research topic (Vaioleti, 2016). Further, it is an economical approach to collecting the data, thereby saving time and effort for the researcher, which then is used in analysing the data. However, its biggest weakness is that sometimes, the data is outdated and inaccurate. Since such sources are not updated on a regular basis, the information available through such sources can be unreliable. In addition, the researcher did not have any control over the quality of the data (Mackey and Gass, 2015).
CHAPTER 4: DATA ANALYSIS
4.1 Introduction
In the following paragraphs, performances of the two companies have been analysed. Herein the researcher has also conducted SWOT and Porter Five Forces Analysis in addition to using various other key performance indicators to analyse performances of Amazon and Alibaba.
4.2 SWOT Analysis of Amazon
Amazon is one of the largest e-commerce companies in the world. Since its establishment, the company has grown at a very healthy pace and now is also one of the most valuable brands in the world. One of the biggest strengths of the company is its brand value and market position. Today Amazon is ranked near the top in every list related to ranking the e-commerce companies. There are three main factors that helped the company become a leader in the e-commerce industry (Akter and Wamba, 2016). They are cost leadership, differentiation and focus. Jeff Bezos, the founder of Amazon, gave emphasis to these aspects along with customer satisfaction. High recall from the customers is another major strength of the company. Since e-commerce is such a competitive market, the company enjoys having superior recall among the customers. This means that more customers tend to search for products on Amazon. Moreover, Amazon has become the equivalent of Google, as almost every kind of product is available on Amazon and can be bought (Cui and Pan, 2015). Although the company enjoys having a superior brand image and recall among the customers, in recent some years Amazon’s focus has shifted from its core area of operations. Amazon has been criticised on many occasions as it is now paying less attention to retailing books online and is now venturing into other areas. One of the main aspects of its operations is the fact that Amazon ships the products free of cost to the customers. This can be very dangerous for the company in the long run because it might reduce the margins and hence the firm might not be able to optimise on its costs (Kalia, 2015). There are several opportunities that the company can benefit from. One of the biggest opportunities for the firm is that it should sell more products with its own branding. Although Amazon is a marketplace and a platform for buyers and sellers to meet, the firm should also products with its own brand name. Amazon is already selling products with the Amazon Basics, but currently, it is operating in very few categories. Therefore, the company should expand in other areas as well (Rahayu and Day, 2015). This way the company can cater to a wider customer base and enhance its performance. In addition to this, the firm should also open more physical stores outside the US. Through such brick and mortar based operations, the company will improve engagement with the customers, and this could also result in more repeat purchases and an increase in the loyal customer base. The low entry barrier is one of the biggest threats to the company. As the market has expanded at a very rapid pace, it has now become very easy for new firms to enter and establish their operations. The required investment in the industry has also declined very quickly (Smith, 2015). This means any new company can establish its operations quickly and if they properly maintained and managed, then the new firm could even rival Amazon. Apart from this, increasing cases of data and identity thefts have left the consumers on online shopping sites such as Amazon very vulnerable.

4.3 Porter Five Forces Analysis of Amazon
Through this tool, a better understanding of the firm’s position in the market can be obtained, along with analysing its external environment. The intensity of competition in the e-commerce industry in the country is very high. Currently, there are numerous organisations operating in this market space. The level and intensity of competition are extremely high, while the market share is very low among all the companies. The companies aggressively promote their services while the availability of substitutes is very high, while the switching cost for customers is low (Wirtz, Ullrich and Göttel, 2016). This indicates that the market is extremely competitive and the customers can easily switch between different companies based on their requirements. The bargaining power of customers is very high. This is due to high-quality information is readily available to the customers, along with substitutability and low switching costs. This gives customers immense power, and they can pretty much dictate the terms and conditions that the e-commerce companies have to follow (Yu and Huang, 2016). It may be right to say that the customer is the king in this market. If the firms are not able to satisfy the customers, then they will go to other company. Low switching cost means that the customers will have to suffer relatively lower losses and they can still buy the products they want to. However, on the other hand, the bargaining power of suppliers is only moderate. This is due to the reason that there are only a few suppliers while there are virtually endless customers. Herein it was observed that more than 80% of the population in the UK uses the internet on a daily basis to fulfil their varied needs and demands. It is also clear that the internet is mostly used by people between the age group of 16-24-year-olds (Baesens, Vanthienen and Zhao, 2016). Since there are only a few suppliers associated with Amazon in comparison to the number of customers that the company caters to, it can be said that the suppliers have very limited power, and they have to fulfil the demands of the customers, because if they will not then the customers will purchase the same product from some other merchant. The threat of substitutes is very high in the market. This is because of the low switching cost for the customer and low cost of substitutes along with high availability of substitutes. The customers have plenty of options through which their needs and demands can be fulfilled (Deng and Wang, 2016). If they are not satisfied with a product sold by a merchant, then they can always easily find the same product with some other supplier, albeit with a little difference in the prices. The low switching cost indicates that the customers can easily transfer from Amazon to other e-commerce companies. Further, the threat of new entrants is also very high in the market. This is due to low switching costs, low cost of brand development and low economies of scale. Since it is very easy for the customers to switch between brands with relatively non-existent costs, it provides an opportunity for other e-commerce companies to establish their operations (Kalia, 2015). If there are more customers who are switching from Amazon, then this would indicate that they are not satisfied with the company and are searching for better alternatives. Therefore, other e-commerce firms can consider this as an opportunity to fill the void.

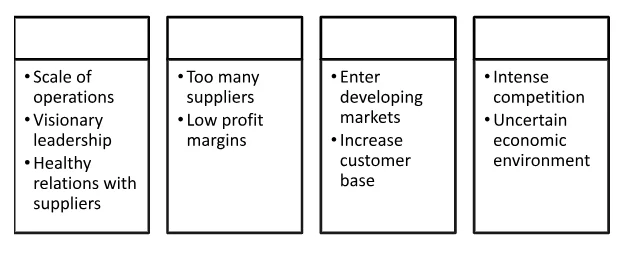
4.4 SWOT Analysis of Alibaba
A SWOT analysis is a very useful tool and helps in understanding both the internal and external environment of an organisation. Many experts and researchers believe it to be an effective methodology that helps in the decision-making process for the management. The scale of operations is one of the main strengths of Alibaba (Sevkli and Delen, 2012). The company operates at massive scales, and this has helped it to become one of the leading firms in the e-commerce industry. Apart from this, approaches used by Jack Ma, the founder and his visionary leadership have propelled the company into the limelight and near the top in the e-commerce industry. The company gives emphasis on maintaining healthy relations with its suppliers. This has further helped the company to gain a leadership position and establish itself as one of the leading players in the industry. One of the major weaknesses of the company is the fact that it has a very low customer base but too many suppliers. Although it was established in the most populated country on the planet, Alibaba has failed to attract the customers, but it has developed a very strong supplier base (Wijngaarden, Scholten and Wijk, 2012). This is further augmented by the fact that the company does not put any limit on the number of suppliers that can register at the Alibaba’s website. In addition to this, the company also provides the option of free membership to the suppliers; this further helps in attracting more customers. Since the company provides very high discounts, its profit margins further decline. It is believed that just like Amazon, Alibaba also operates at nearly zero margins. This, in the end, puts a lot of pressure on the firm and therefore adversely affects its operations and ability to achieve its goals and objectives. The experience and in-depth understanding of the e-commerce industry have helped the company to acquire a leadership position in the market. The management can translate this into a major opportunity, as the company can enter new markets and further increase its customer base (Lavinga-Lott, 2017). In the wake of the current trends in the industry and the rapidly changing economic environment, this opportunity can be of great use to the company. Herein the company can use its various businesses to enter and establish its operations in different markets. This way Alibaba as a whole group can move forward and be able to gain a superior position in the industry. Rising competition is the biggest threats to the company. Due to low barriers in the industry, it is now very easy and simple for new enterprises to firmly establish their operations in the industry. There are many companies operating in the e-commerce industry. This negatively affects overall performance and growth chances. The uncertain economic environment is another major threat to the company. It was observed that world economies are getting destabilised and share markets are not performing optimally (Rodionova, 2015). All these factors increase the chances of a financial calamity. This could have a substantial negative impact on Alibaba’s operations. Similar to Amazon, internet or cyber security is also a significant threat for Alibaba. Rising cases of identity thefts, card frauds, etc. endanger economic operations because if Alibaba is not able to maintain the security protocols, then it would start losing customers at a very rapid pace. This could jeopardise its operations and its existence as well.
4.5 Porter Five Forces Analysis of Alibaba
In order to better understand about Alibaba’s performance, its external environment has been evaluated. Herein Porter’s Five Forces has been used. The threat of new entrants is very high. This is similar to that of Amazon. The modern-day e-commerce marketplace has very few barriers to entry. Since firms have to invest very less capital in managing their operations, they find fewer difficulties in establishing their operations in the industry. Due to this reason, there is a major threat of new entrants establishing their operations relatively easily in the industry (Dobbs, 2014). Even the threat of increasing issues related to cybersecurity does not deter them from establishing their operations in the market. Since there are many companies in the e-commerce industry, the threat of substitutes is very high. There are several e-commerce firms that can easily replace Alibaba. There is virtually no cost of switching for the customers. If they are not satisfied with the services of Alibaba, they can easily buy the same product from another e-commerce company (Mathooko and Ogutu, 2015). Therefore, it may be said that the customers will be able to fulfil their demand and requirement anyhow. The low barriers to entry further add to this. The bargaining power of buyers is moderate. This is due to the reason that Alibaba has failed to attract many customers, rather it has developed a very strong base of suppliers. However, even then the company has to work according to the needs and demands of the customers. If it is unable to satisfy the customers, then its performance will decline rapidly, due to which its very existence could be jeopardised (Wirtz, Ullrich and Göttel, 2016). Furthermore, the buyers still dictate the policies and norms of Alibaba. On this basis, it can be said that the company needs to focus on maximum customer satisfaction. During the study, it was observed that this would be the most effective way for the company to sustain in the market. Similarly, the bargaining power of suppliers is low. This is even after the fact that Alibaba has a very strong supplier base. For every category of products, there are large numbers of suppliers available to the company. Since the company has a very strong presence in China, almost every Chinese manufacturer is willing to list its products on Alibaba. Moreover, Alibaba provides the opportunity for suppliers to register for free, thereby attracting more suppliers (Yu and Huang, 2016). Therefore, if any of the suppliers try to increase their prices will not be successful. In such instances, the customers will switch to other suppliers. There is no switching cost for suppliers for Alibaba. The intensity of competition for Alibaba is very high. As shown above, there are numerous companies that can replace Alibaba. The level and intensity of competition in the market are so high that it can force other companies to change their strategies and rethink about their decisions (Fisher, 2018). Amazon and e-Bay are some of the main rivals of Alibaba. During the study, it was observed that even though Alibaba has a very simple business model, it has not helped the company to gain a superior position in the international e-commerce market. The firm has only been able to build a strong image in the Chinese e-commerce industry.

4.6 Customer Satisfaction
According to the ForSee’s annual Holiday E-Retailer Satisfaction Index, in 2018 Amazon sold the most. More than 26.5 million products were ordered through the website worldwide. The company scored 88 points on a 100 point scale. This has been its highest score since 2005. ForSee surveyed more than 24,000 customers and asked them to rate their satisfaction levels with the top 100 e-retailers. This indicates that the majority of the customers were happy and satisfied with the services provided by Amazon. Similarly, Alibaba too gives emphasis on maximising customer satisfaction. In this regard, the company scored 14 points on the Net Promoter Score. NPS measures customer loyalty. This score indicates that the customers are not only willing to avail services to Alibaba for their own, but they are also likely to recommend it to their friends and family members (Rouibah, Lowry and Almutairi, 2015).


4.7 Gross Profit
Amazon is among one of the fastest growing companies. In the first quarter of 2018, the company had net income of $1.6 billion, double of 2017’s income. Further, Amazon’s gross profit also have increased significantly. Its gross profit was $7 billion in the first quarter, significantly higher than any other top 5 e-retailers in the world. Amazon’s gross profit margins have increased steadily over the past few years. Alibaba, on the other hand, experienced an increase in its gross profits by nearly 40% (Kim, 2018). This indicates that the company performed very well and was one of the leading retailing companies around the world.

4.8 Conversion Rate
This is considered as one of the key ways through which the performance of an e-commerce company can be evaluated and assessed. Amazon’s conversion rate is among the highest. The data shows that Amazon has a conversion rate of 74% for Prime members and 13% for non-Prime members. This means that 74% of all prime members will purchase a product from the company. On this basis, it can be said that such a high conversion rate is the reason for superior performance by Amazon in the international market. However, on the other hand, Alibaba’s conversion rate is only 2.88% (Smith, 2018). This indicates that the company is not able to convert the majority of the searches into sales. Such low conversion rates could be due to the fact that Alibaba has only very recently started operating in the UK and therefore it has not been able to capture a significant share of the market.

4.9 Cart abandonment rate
It is a key figure in measuring the performance of e-commerce companies because it sheds light on how many customers left their shopping carts. This could be due to various reasons, but unexpected price changes are considered as one of the main reasons for customers to abandon their shopping carts. The data suggest that the cart abandonment rate at Amazon is 67%. This shows that a vast majority of the customers shopping with Amazon leave their shopping carts without finalising their purchase (Youderian, 2017). Similarly, this data is even worse for Alibaba. 75% of customers abandon their shopping carts. Out of these customers, the majority do not even leave their emails. This means a large section of the customers has not made an account on the website.
4.10 Website traffic
Amazon is the leading e-commerce company, and it is visited by nearly 3 billion customers every day. This shows that almost every person visits the website. The data suggests that Amazon has become the equivalent of Google when searching for different products. People first search for the product on Amazon, even though they might just want to know the prices and they might purchase the product from another website or through a physical store. In contrast to it, Amazon is visited by 109 million customers every day (Kim, 2018). The main reason for such vast difference could be the fact that Amazon has already established its operations in almost every market around the world, while Alibaba has started expanding its operations at a global level only very recently.
4.11 Time spent
Amazon has the largest customer base, and its customers in 2017 spent 22.6 billion minutes. It is significantly higher than the combined total time spent by the customers on any other e-commerce site. This further indicates that people first search for a product on Amazon and then on other sites. Low cost is one of the main reasons behind this. The average time spent by the 100 million customers in 2017 was 4 minutes. This could be because of the fact that Alibaba has a strong customer base only in China where companies such as Amazon do not operate (Clarke, 2018). However, in the rest parts of the world, Amazon is the very first site that customers go to before buying a product.
4.12 Mobile App Traffic
The data shows that companies are now using smartphones as the primary way of selling products to customers. A majority of Amazon’s customers are through smartphone applications. Shopping through mobile phones is far more convenient for the customers, as they can move around and still be able to purchase, as opposed to shopping through a desktop where the customers have to sit and search. Nearly 56% of the total customers of Amazon do their shopping through their mobile phones (Weib, 2016). Similarly, 59% of the customers of Alibaba use their mobile phones to purchase products based on their requirements (Rodionova, 2015).

CHAPTER 5: CONCLUSION
In recent some years the e-commerce companies have performed exceptionally well, and they have now become the most commonly used method of shopping for several people in the UK. Online shopping is now very common in the country. Currently, the UK is the leading e-commerce country in Europe. British people spent nearly €200 billion in the year 2017. This shows that a large number of people in the country prefer to use e-commerce companies such as Amazon, Alibaba, etc. for their varied needs. The European B2C E-commerce Report 2018 shows that Amazon was the leading e-retailer in 2017. This shows that companies such as Amazon have captured a majority share of the UK market and also are some of the main contributors to the country’s growth and development. 33.5% of all e-commerce transactions in the UK were made through Amazon. Through this study, the researcher has assessed, and compared business models of both the companies and have analysed their performances as well. Herein tools such as SWOT analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis have been used to evaluate business models of both the firms. There is a lot of difference in the business model of Alibaba with that of other e-commerce firms such as Amazon. It is focused more on the trade between businesses. Alibaba does not focus on B2C transactions; rather it operates as a platform for suppliers to sell their products in bulk at wholesale prices to small and medium-sized businesses in the country. In this research, only secondary sources have been used. This is due to the reason that plenty of information is available regarding differences and comparison between the performance of Amazon and Alibaba. Therefore, the researcher has used already available articles, research studies, books and annual reports of both the companies. Different themes were developed to analyse aspects including customer satisfaction, gross profit, conversion rate, shopping cart abandonment rate, website traffic, time spent on site, and mobile site traffic. The low entry barrier is one of the biggest threats to the company. As the market has expanded at a very rapid pace, it has now become very easy for new firms to enter and establish their operations. The required investment in the industry has also declined very quickly. This means any new company can establish its operations quickly and if they properly maintained and managed, then the new firm could even rival Amazon. Apart from this, increasing cases of data and identity thefts have left the consumers on online shopping sites such as Amazon very vulnerable. One of the major flaws for the company is the fact that it has a very low customer base but too many suppliers. Although it was established in the most populated country on the planet, Alibaba has failed to attract the customers, but it has developed a very strong supplier base.
REFERENCES
Akter, S. and Wamba, S.F., 2016. Big data analytics in E-commerce: a systematic review and agenda for future research. Electronic Markets, 26(2), pp.173-194.
Al-Somali, S.A., Gholami, R. and Clegg, B., 2015. A stage-oriented model (SOM) for e-commerce adoption: a study of Saudi Arabian organisations. Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management, 26(1), pp.2-35.
Cui, M. and Pan, S.L., 2015. Developing focal capabilities for e-commerce adoption: A resource orchestration perspective. Information & Management, 52(2), pp.200-209..
Hua, N., Morosan, C. and DeFranco, A., 2015. The other side of technology adoption: examining the relationships between e-commerce expenses and hotel performance. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 45, pp.109-120.
Lewis, S., 2015. Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches. Health promotion practice, 16(4), pp.473-475.
Mathooko, F.M. and Ogutu, M., 2015. Porter’s five competitive forces framework and other factors that influence the choice of response strategies adopted by public universities in Kenya. International Journal of Educational Management, 29(3), pp.334-354.
Rahayu, R. and Day, J., 2015. Determinant factors of e-commerce adoption by SMEs in developing country: evidence from Indonesia. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 195, pp.142-150.
Rouibah, K., Lowry, P.B. and Almutairi, L., 2015. Dimensions of business-to-consumer (B2C) systems success in Kuwait: Testing a modified DeLone and McLean IS success model in an e-commerce context. Journal of Global Information Management (JGIM), 23(3), pp.41-71.
Wang, W.T., Wang, Y.S. and Liu, E.R., 2016. The stickiness intention of group-buying websites: The integration of the commitment–trust theory and e-commerce success model. Information & Management, 53(5), pp.625-642.
Yang, Z., Shi, Y. and Wang, B., 2015. Search engine marketing, financing ability and firm performance in E-commerce. Procedia Computer Science, 55, pp.1106-1112.
Zhang, Y. and Wen, J., 2017. The IoT electric business model: Using blockchain technology for the internet of things. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 10(4), pp.983-994.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



