Strategic Corporate Social Responsibility Practices in Retail Multinational Organizations
Introduction
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is the practice, of running the organisational operations efficiently by fulfilling the corporate and social responsibilities of the business in the society. It is the responsibility of the firms to manage their responsibilities while operating in the industry or the market and the firms aim to maximise their business objectives by profit maximisation and strengthening their customer’s base, where it is also the responsibility of the corporate firms to create the values for all the stakeholders, engaged with the company (Utgård, 2018). The study aims at discussing the strategic practice of corporate social responsibilities after evaluating the models and theoretical framework of CSR. Through the discussion, it is also possible to identify the challenges faced by the companies in the market in managing their CSR in the market and acknowledging the strategic planning of the retail firms in the market to manage their CSR in doing the operational activities efficiently. The study also provides an opportunity to recommend some suitable suggestions through which the retail brand would be able to manage their responsibility in doing their business efficiently and maximising social values. There are many retail firms, who try to maximise their sustainability in the global retail industry and the firms like Tesco, Wal-Mart and Sainsbury’s are famous retail multinational organisations who aim at securing future sustainable development through sustainable practice, so that the firms can manage their operations across the international markets ethically and legally. This study is going to add value to the field of business dissertation help by evaluating the strategic implementation of CSR practices in the retail sector and providing actionable recommendations for firms who are looking to enhance their social responsibility efforts.

Concept of corporate social responsibility
The major purpose of managing CSR in the industry is to create social values and run the organisations ethically by managing the operations ethically. CSR encompasses the economic, legal, ethical and philanthropic expectations places on the organisations by the society at a given point of time. CSR refers to the capacity and capability of the organisation in responding to the social expectations and thus it is the responsibility of the organisations to maximise the values for all the stakeholders engaged with the company. The major stakeholders are such as employees, managers, suppliers and distributors, producers and manufacturers, customers, government and the social communities, where the firms try to create values for all the stakeholders to run the business ethically. There are different theories and model, through which it is possible to understand the CSR practice which is Carroll’s pyramid of corporate social responsibility, Friedman theory of CSR and triple bottom line. As per the Carroll’s pyramid, there are four stages, which are economic, legal, ethical and philanthropic. For all the organisations, it is necessary to fulfil all the responsibilities so that it would be possible to create values for the social communities as a whole.
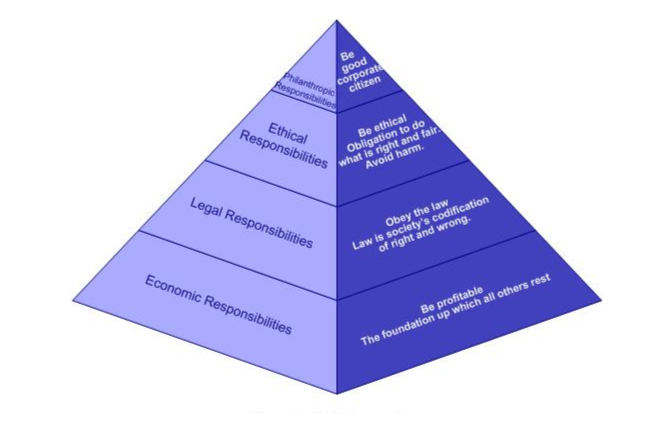
As per the economic responsibility, the firms should be profitable so that the leaders can provide high return on investment and fulfil their commitment on investment purpose. It is effective for the organisations to crate values for the stakeholders like shareholders, employees, distributors and the investors, who can be benefited after investing their capital and expertise in the organisation. In addition to this, the legal responsibility should also be fulfilled where the organisation need to obey all the business laws and the legislations of the society. The employment rules, non-discrimination practice, minimum wage related practice as well as copyright, intellectual property rights are effective to establish the business legally (Schrempf-Stirling, Palazzo and Phillips, 2016). On the other hand, there are the rights of the human being in the society which also need to be maximised while conducting the business operations in the market. Being ethical is also essential to run the organisation sustainably and in this regard, the companies try to maximise the rights of the individuals and avoid harm, while running their business operations. On the other hand, the philanthropic responsibility is related to being good corporate citizens, where the leaders must focus on social developmental activities and invest in charitable programs and educational activities for social sustainable development.
As per the Friedman CSR model, the organisations must focus on managing the business ethically and legally so that the organisation can maximise the values for the social communities. As per the theory, it is essential to manage the responsibility of the organisations for maximising the environment impacts (Lins, Servaes and Tamayo, 2017). Creating values for the customers and employees, managing the value of social communities, satisfying the shareholders and other stakeholders, engaged with the operational activities of the business. Freidman focuses on managing the people, who are engaged with the business through people development and involvement, where the organisations need to develop strong corporate relationship with all the stakeholders including the social communities as a whole. As per the theory, it is necessary to focus on customers and identify their preferences to satisfy them in long and additionally, leadership and management strategy of the firm must be developed properly through which it would be possible for the companies to manage their operations and fulfil their commitment towards all the stakeholders.

In addition to this, the triple bottom line theory of CSR is also effective to understand the ways the corporate firms can run their activities across the international markets ethically and sustainably. As per the theory, there are three factors which are people, planet and profit, which provide scope to the organisations to restructure their activities and develop proper strategic planning of creating the values for the social communities as a whole. People management is mandatory for the organisations, where education and training program, managing equality and diversity, health and wellbeing of the people and helping the people to maximise their standard of living are effective to manage the people, engaged with the organisation (Edinger-Schons et al., 2019). On the other hand, the firm needs to be profitable, in the market in doing their business sustainably, and economic variables are necessary to be managed to deal with the bottom line and cash flows. Additionally, it is necessary to manage planet, where environmental sustainably needs to be manage well and in this regard, the organisations try to protect the natural resources and aim at providing green environmental footprint so that the social values can be maximised well.

Hereby, the theories and models of CSR are effective to provide proper strategic planning and suggestions to the corporate firms to run their operational activities efficiently. The multinational corporate firms in the recent era of globalisation try to manage their sustainability in long run to establish the brand and secure future development.
Key challenges related to corporate social responsibility
In the recent era of globalisation, the corporate retail firms face difficulties to manage the CSR activities which in turn deteriorate the performance of the business sustainably. It is the responsibility of all the retail firms to run their operations sustainably by developing effective approached to provide positive impacts on the society and in this regard, the major challenge of the firms is lack of financial stability and less capital investment. Without having proper capital investment, it is not possible for the organisations to manage their CSR practice and creates social values. The firms need to be profitable to create values for the societies, and in this regard, some of the retail firms fail to manage their financial stability and it becomes difficult for them to invest on CSR practice in running their business ethically. In addition to this, lack of management and leadership planning is another major mistake, for which the retail organisations such as Wal-Mart and Lidl and Aldi face difficulties to establish their brand in the market. The leader sometimes fail to develop proper strategic planning to run the organisations properly and sustainably which raise difficulties of the retailers to run their business by providing green environmental footprints (Hopkins, 2016). Moreover, the firms face difficulties to manage the business sustainability due to failure of CSR innovation. Lack of investment or social developmental project, lack of fulfilment of the organisational commitment and lack of proper organisational vision are the major changes of which the retail firms fail to fulfil their CSR objective and it further deteriorates the performance of the companies in long run.
Corporate social practices of the retail organisations
The retail organisations in the recent era of globalisation focus on managing CSR to create values in the society. In this regard, Tesco as a famous and largest supermarket chain in the UK focuses on CSR practice, where the leader develops the strategy to create values for the customers and the strategy of customer focus is fruitful for the organisation to establish the brand and run their operations efficiently. The company is successful to manage over 6 million customers, and the company also have around 60000 colleagues with them to support the activities (Jamali and Karam, 2018). In this regard, Tesco focuses on delivering high quality products including grocery, food and beverages electronics and furniture and other daily use products to the customers at effective price so that the customer can afford the products, thus the company is successful to manage their customers and create values for them in long run. As per the Carroll’s pyramid, it is the responsibility of the organisation to maximise the profitability of the organisation, and in this regard, Tesco is also successful to fulfil the responsibility, by generating revenue in each year. In the last year, the company has generated over £63,911 million, which enhance the performance of the firm in long run. Financial stability and proper capital investment further helps the organisation to provide high return on investment o the stakeholders including the shareholders. Hereby, the company is efficient to fulfil the economic responsibility as well as create values for all the customers in the market around the globe.
In addition to this, Tesco is also efficient to manage their people, where the company is successful to strengthen their employee base with more than 450000 employees across the international market. For people management, the company aims at creating values for them by providing them proper structured salary, high incentives and rewards. This further helps the firm to fulfil the monetary requirements of the employees and on the other hand, the company is also efficient to fulfil the nonmonetary requirements of the employees. The company is efficient to manage safety and security of the people at the workplace, where Tesco provide insurance coverage to the employees, as well as they also get discounts and purchase and loyalty cards are there which create value for the employees at the workplace. Tesco is also efficient to manage their suppliers and distributors which help the firm to strengthen their distribution network. The company ties to give high return on investment to the suppliers and develop strong bonding with them, for future. The organisational culture is also effective, where the company provides freedom to work, harmony, cooperative workplace, managing diversity and equality at the organisation which create values for the people. Hereby, the company also fulfils their commitment towards their people who are major stakeholders in running the retail operations across the UK and the global markets (Tesco, 2020).

On the other hand, the company focuses on ethical and legal perspective, where the copyright and licensing of the company as well as the implement rules are effective from the firm to manage their operations ethically. Tesco is also efficient to manage philanthropic responsibility, where the company aims at creating social values and be a good citizen through providing green environmental footprint. In this regard, sustainable planning of Tesco is effective, where as per the Carroll’s pyramid, the philanthropic responsibility can be fulfilled in the company is also efficient to fulfil he triple bottom line to run their business sustainably by managing planet, profit and people. For managing the planet, the company focuses on providing positive environmental footprint by reducing the greenhouse gas emission and in this regard. Tesco utilises electric cars for distributing the raw materials to the organisational prediction sites, so that the green house gas can be minimised in the environment. Additionally, the company aims at waste management where the management team is concerned about transferring the wastage to the landfills and on the other hand, the company took new initiatives for minimising food waste, where Tesco opens refrigerator on the road side, where the excess food will be stored, from where the needy people can access the food at free of cost. This is a great initiative, taken by the company to improve social values and manage food waste in a positive way. On the other hand, the company is also efficient to invest in charitable and educational program to create values for the social communities, which in turn helps the business to run their operations sustainably in long run (Tesco, 2020).
On the other hand, Sainsbury’s is also another famous retail chain in the UK and it operates only in the UK. The company has the second largest supermarket chain where it also focuses on sustainable development by creating effective strategic planning. In this regard, the company focuses on creating values for the customers and the mission of the company is to deliver quality retail products at lower price, so that the customers can make effective purchase decision as per their preferences and budget constraint (Yakovleva, 2017). The tagline ‘lives well for less’ is also effective where the leader aims at creating values for the customers. Economic profitability and financial stability of the firm ensure organisational position in the market and it also fulfilled the commitment towards each stakeholders engaged with the business. The values of the company are delivering great products and services at fair price, creating values for the customers and managing the colleagues, who are the major stakeholders to run their operations sustainably. The major five strategy of the company to make the business sustainable are health and wellbeing management, sourcing, environment, community and our colleagues. Hereby, the company focuses on managing their operations in a sustainable way, where Sainsbury’s focuses on reducing negative environmental footprint and greenhouse gas emission in the environment so that the social communities will be safe (Sainsbury’s, 2020a).
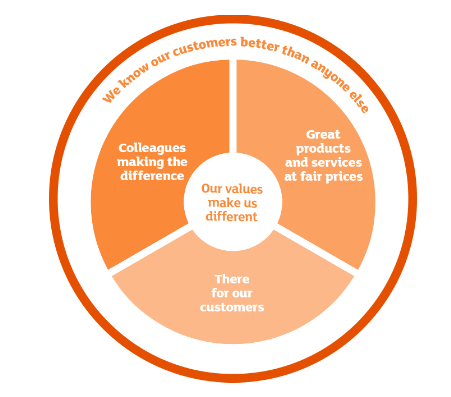
Additionally, there are other retail organisation and restaurant which are focusing on managing the sustainability of the business in securing future sustainable development. The retail firms such as Lidl and Aldi also operates in the retail industry, where the brands focus on managing their operations sustainably by creating values for the stakeholders. The companies try to provide structure salary and the incentives and rewards to the employees in order to create values for them and retain the experienced staff for long run (Sainsbury’s, 2020b). On the other hand, the companies also focused on creating values for the shareholders, so that the business can be operated successfully with proper capital investment, where the companies fulfil their economic, commitment and make the business profitable by operating in the market, which in turn provides a scope to the retail firms to provide high return on investment and satisfy the stakeholders including the shareholders, employees and suppliers in long run (Sainsbury’s, 2020c).

Other than the retail organisations, the restaurants in the UK are also efficient to manage their CSR in running their business ethically and sustainably. The restaurants such as the park, fat duck, Casamia, Moor Hall, and Waterside Inn, are efficient to manage their CSR in the industry, where they also focus on creating values or the customers. They try to provide efficient services to the customers at effective price as well as manage their people, including shareholders, suppliers, staff and employees to run the restaurant chain successfully. As per the Triple bottom line theory, the restaurants and the retail supermarkets also focus on managing their people through arranging effective training and development program, improve employee wellbeing and good health, creating values for the them through managing safety and security at the workplace as well as giving them monetary rewards which help the firm to fulfil their responsibility towards the organisational people. On the other hand, the restaurant and retail firms also focus on generating revenue and maximise profitability through product diversification and cost leadership strategy, maximising innovation and brand creativity in running their business sustainably. On the other hand, for managing sustainability, the firms try to improve social investment for sustainable social development as well as providing green environmental footprint in long run (Crane, Matten and Spence, 2019).

Conclusion and recommendations
In the recent business world, it is essential of the organisations across the globe to manage corporate and social responsibility for securing future sustainable development. It is necessary for all the organisations to be profitable and secure financial stability in long run which further helps he firms to manage their stakeholders and provide positive investment for social charitable program. The retail companies recently aim at providing high quality products and services at lower price by managing product diversification strategy and cost leadership practice which helps to create vales for the customers and influences the organisational sales volume. In order to make the business sustainable, the brands need to utilise electric cars to reduce greenhouse gas emission as well as implement solar panel system at the roof top in order to use the renewable resources and protect the natural resources. Additionally, the retail organisations also need to reduce waste and water use in long run through waste management as well as use paper packaging system rather than plastic packaging to provide green environmental footprint. For running the business efficiently, the companies also need to be transparent and accountable and manage the oversee workforce by enhancing diversity and equality at the workplace. The retail firms must focus on social development and invest more in charitable programs to create values for the social communities which in turn provide a scope to the firms to be responsible citizen and run the business operational activities sustainably.
Reference List
- Crane, A., Matten, D. and Spence, L., 2019. Corporate social responsibility: Readings and cases in a global context. London: Routledge.
- Edinger-Schons, L.M., Lengler-Graiff, L., Scheidler, S. and Wieseke, J., 2019. Frontline employees as corporate social responsibility (CSR) ambassadors: A quasi-field experiment. Journal of Business Ethics, 157(2), pp.359-373.
- Grayson, D. and Hodges, A., 2017. Corporate social opportunity!: Seven steps to make corporate social responsibility work for your business. London: Routledge.
- Hopkins, M., 2016. The planetary bargain: corporate social responsibility comes of age. Berlin: Springer.
- Jamali, D. and Karam, C., 2018. Corporate social responsibility in developing countries as an emerging field of study. International Journal of Management Reviews, 20(1), pp.32-61.
- Liang, H. and Renneboog, L., 2017. On the foundations of corporate social responsibility. The Journal of Finance, 72(2), pp.853-910.
- Lins, K.V., Servaes, H. and Tamayo, A., 2017. Social capital, trust, and firm performance: The value of corporate social responsibility during the financial crisis. The Journal of Finance, 72(4), pp.1785-1824.
- Utgård, J., 2018. Retail chains’ corporate social responsibility communication. Journal of business Ethics, 147(2), pp.385-400.
- Yakovleva, N., 2017. Corporate social responsibility in the mining industries. London: Routledge.
Continue your exploration of Strategic Business Plan for Fresh Feast with our related content.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



