Supply and Demand in Commercial Property
Introduction
Commercial property is a tangible asset, which is subject to supply and demand. The prices of commercial property, similar to shares and bonds, rely extensively on the theory of supply and demand. Every commercial property transaction involves a purchaser and a seller. The purchaser puts a proposal on the property, providing the seller the chance to accept or to reject the bid. A low level of supply can increase the prices of commercial property, which is what it tends to occur with bidding wars. Certain commercial property can be in demand by different parties who intend to outbid each other through enhancing the price of the property. The bidding war finishes by reducing the supply of property when the seller accepts one of the proposals. When there is a high demand for commercial properties in a specific city and a low level of supply of quality properties, the prices of capital tend to increase. On the other hand, when the economy is weak, and there is a low number of purchasers for the property, and there is an oversupply of property, this results in low demand for commercial property and the prices of capital tend to fall.
Supply and Demand Analysis of Commercial Properties
The supplier of commercial property earns a profit by selling the property at a high price than the price of construction. The amount of profit is determined by the factors of demand and by the effectiveness of supplier in constructing the property. Since high rates facilitate earning a high amount of gain and high profit is also subject to the quantity sold, if increased demand for property increases the prices, then the supplier will react by enhancing the supply, as it will permit them to earn a high amount of profit. This is regarded as the law of supply, which states that if all other factors of the price are equal, if the cost of commercial property increases, the quantity that suppliers offer will also increase and vice versa. On the other hand, the law of demand states that if all the factors are static, the price of commercial property increases when the quantity demanded increases and vice versa. This occurs due to diminishing marginal utility.
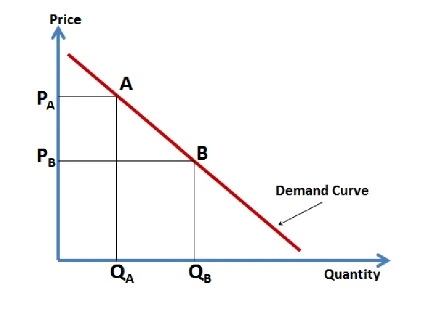

In the above figure, the demand curve is demonstrated in the red line. Based on the high picture, when the prices of the commercial property increase from PB to PA, the quantity demanded of commercial property reduces from QB to QA. The demand curve is downward sloping because if the price of retail property increases, the demand decreases (Kenton, 2019). The market demand for commercial property is demonstrated in the following figure, which is termed as the market demand curve.

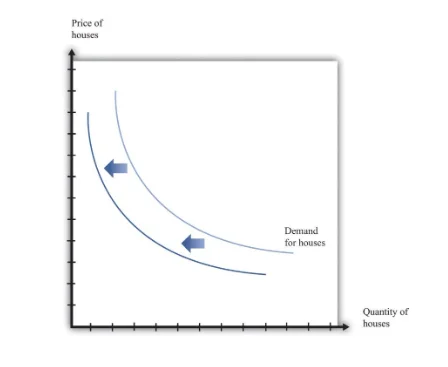
In the real estate market, as the price of property reduces, the quantity demanded enhances. The majority of individuals own either zero commercial property or one commercial property. As the estate becomes inexpensive, more individuals decide that they can afford a property. Hence the quantity demanded enhances when the demand for commercial property reduces; the demand curve shifts to the left (see the following figure).
The supply curve is upward sloping because, through time, suppliers can select the number of their products to produce and bring to the market. At any given point, the supply is fixed, and the seller merely chooses to either sell or withhold the product. Demand help to set the price, and the seller can only change what the market bears (Kenton, 2019). If the demand increases, the amount of product will increase, and then the supplier can select devoted new resources to produce, which enhances the quantity supplied.
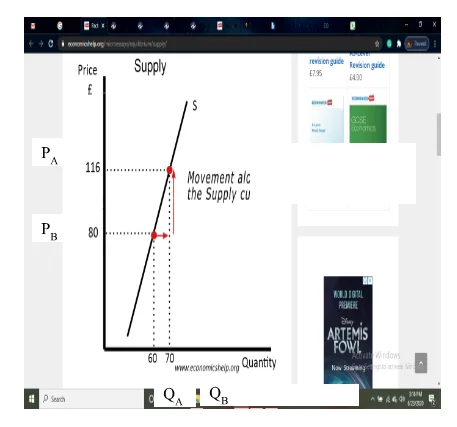
From the above figure, it can be stated that if the price increases from PB to PA, the supplier will get a motivation to supply more as they get more profit, and hence the supply will also increase from QA to QB. If there is a reduction in the supply of commercial property, then fewer features are supplied at a certain price. Then the supply curve shifts to the left side (see the following figure).

Demand Elasticity
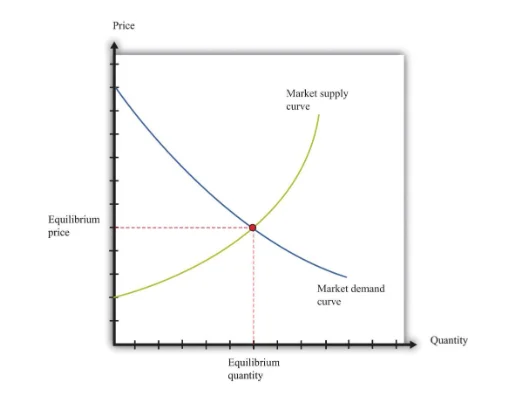
The level to which increasing-price results in a reduction of demand is the demand elasticity. Concerning commercial property, the demand curve is not much elastic in nature, i.e., even if the prices of the commercial property enhances, the demand for commercial property may not reduce. However, after a limit of price increases, the order of commercial property may reach an equilibrium price (Hall, 2020). The point at which the supply and demand of property meet is the equilibrium (see the following figure). If a factor apart from price and supply changes, a new demand curve is created, and a new equilibrium point is made. In this context, there are various factors which can make the equilibrium point of commercial property to shift.
Supply Elasticity
Supply elasticity is a measure of reactiveness of any industry or supplier towards the changes in demand of the product. The level to which increases in price interprets to a rise in supply is termed as supply elasticity (Chappelow, 2019). If an increase in product price results in a reduction of amount, than the supply curve will shift to the left and vice versa.
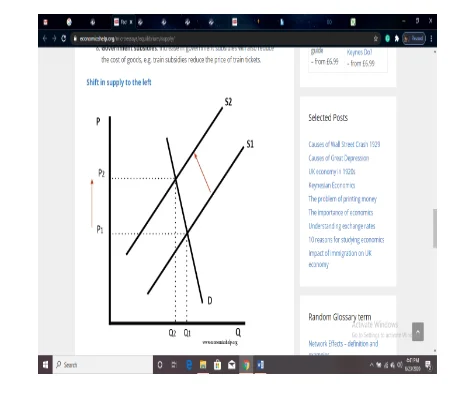
For example, in the above figure, when the prices increase from P1 to P2, the supply reduces from Q1 to Q2.
Factors of Demand and Supply Equilibrium in Commercial Property
Demand Factors
Commercial property demand is income and price inelastic and seems to fall with property size. The elasticity of demand for commercial property is subject to various factors, comprising the necessity of the product, the availability of suitable substitutes and the period in which the elasticity is evaluated. Since the commercial property has no alternative, it tends to have a low elasticity of demand. In the short run, the need for commercial property is more possibly to be inelastic due to limited options to compensate for changes in price (Kenton, 2020). In the long term, individuals have more time to pay for differences in rates. Therefore, the demand for the commercial property becomes is much elastic. There are various factors, which impact the changes in demand for commercial property; for example, one crucial factor is the income of people. If the income of people reduces, then their purchasing power for buying the commercial property also reduces. This can result in a reduction of demand for commercial property. Concerns about the future health of the economy also lessen the need for commercial property. If people have grave concerns over the health of the economy, they will intend to save more money and spend less on purchasing commercial property. Apart from that, the interest rate is also a key factor of change in demand for commercial properties. When the interest rate reduces, individuals typically become enthusiastic about taking more debts. In this way, they will be able to finance the purchase of commercial property as the amount of interest reduces. Furthermore, if there is a low supply of commercial property, that will make individuals purchase even more commercial properties.
Supply Factors
The price elasticity of supply differs extensively, depending not only on the product but also on whether the price change happens through a short or long period. In this context, it can be stated that concerning commercial property; it is regarded as highly inelastic. Various factors can influence the supply elasticity for commercial property. The first factor is the availability of critical resources. The construction of the commercial property is subject to many resources and raw materials. If the supplier of commercial property or producer of commercial property depends growingly on specific resources to construct the property, it will be unable to increase the construction of commercial property even if when the demand increases (Ross, 2020). Furthermore, in such a scenario, the particular resource or raw material will become growingly costly, forcing a corresponding growth in the price of commercial property. Another critical factor for the supply elasticity of commercial property is technology innovation. Any kind of change in technology can make the construction industry much efficient. Therefore, the construction companies will be able to produce the commercial properties with comparatively low expenses and with a larger quantity. This can increase the supply of commercial property. Growth in the cost of production of commercial property, for example, an increase in wages and growth in interest rate, can reduce the supply of commercial property, as fewer suppliers will be able to produce the features in such an environment. Apart from changes in regulation, that makes property challenging to create can also impact on the supply of commercial property.
Factors Determining the Price of Commercial Property in the UK
Interest Rates
The interest rate plays a vital part in determining the cost of borrowing and repayment of debt. Most of the UK people prefer to take out variable mortgage rates. Therefore, any changes in the base interest rate by the Bank of England will instantly influence the interest payments. This is a vital factor in determining the affordability of commercial properties in the UK. Mortgage payments consume a significant proportion of an individual’s disposable income. Even small changes in the interest rate can deter individuals from purchasing commercial property. Following is the base interest rate and inflation rate in the UK from 2003 to 2015.

Taxation
The tax has a significant impact on the equilibrium of commercial property. If tax is imposed on the supplier of property, then at any given price p, and charge, t every supplier will gain p – t and hence supplies the park with the amount related to the net price. This is the amount that encompasses the marginal value of the last unit, along with providing for tax (Pettinger, 2017). In other words, at a lower price, the supplier will reduce the supply of property (see the following figure).
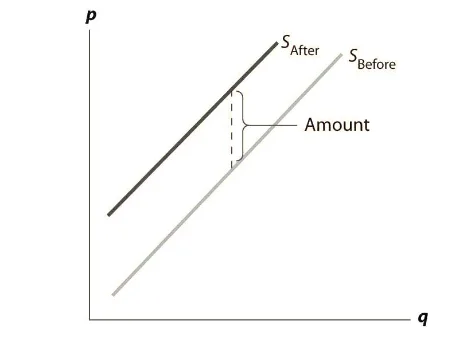
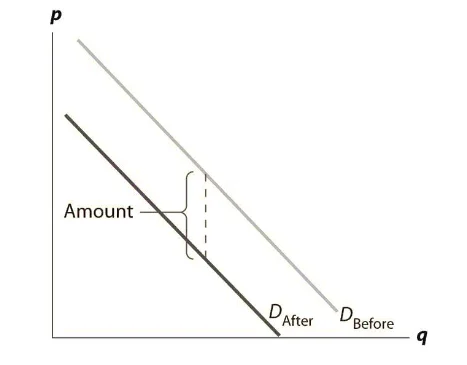
In the above figure, it can be observed that before tax, the supply curve is SBefore, which shifts backward to SAfter after imposing the burden on the supplier. Concerning purchasers, in case of imposing more tax, they will pay the price of the property p along with tax t. this minimizes the enthusiasm to pay for any given property by the amount of tax, hence shifting down the demand curve from DBefore to DAfter (see the following figure).
Population
The population is another crucial factor, which can impact on the demand and supply equilibrium for commercial property. The more community a country has, the higher will be the demand for commercial property. This demand is also mediated by the average salary and salary structure of the population of the country. In the UK the population is increasing (see the following table).
Building New Commercial Properties
The creation of new commercial properties can also influence the demand and supply equilibrium for commercial property. If new commercial properties are created, generally, it will enhance the supply of commercial property. When it comes to the law of supply, prices will reduce when there is a growth in the amount of product in the market. Therefore, in such a scenario, if the number of commercial properties increases, it will shift the supply curve will move to the right. Hence, if the demand for commercial property remains the same, then the equilibrium point will also change.
The Wider Macroeconomy
The broader macroeconomy is another critical factor that can impact the demand and supply equilibrium of the commercial property market. For example, one such factor is economic growth. In a high economic growth, the demand for commercial properties grows. Furthermore, during economic boom times, the income of people also increases. Increasing revenue of people empowers them to afford more jumbo mortgages and hence inspire the demand for commercial property.
Accessibility of Finance
Another important macroeconomic factor is the accessibility of loans. If banks and financial institutions give loans to people with more significant income multiples, then efficient demand for the commercial property becomes better. The readiness of banks and financial institutions to lend loans can depend based on the power of the interbank lending segment. For example, during the recession in the year 2008, there was a sharp increase in the cost of bank lending and reduction in the accessibility of loans, making it challenging for people to get the property ladder. Credits, for example, 125% and 100% mortgages, have been withdrawn. Banks and financial institutions growingly were demanding a higher amount of deposit before lending loans. This can make accessibility of finance harder for people to purchase commercial property.
Cost of Renting
The cost of renting commercial property is another factor that can impact supply and demand. If the value of renting increases, then people will make higher efforts to try and to purchase a commercial property because buying a property by mortgage relatively inexpensive. The market of the UK has been buoyed by expensive renting expenditures, which inspires people to stretch their budget as much as possible to get on the property ladder (Pettinger, 2019).
Affordability
Affordability is another crucial factor that influences on the demand and supply equilibrium for the UK commercial property market. Throughout economic progress, demand for commercial property tends to increase because of the income of customers increases, and their affordability increases. However, the prices of commercial property and hence the demand for capital can increase much quicker in comparison with earnings of people.
Brexit
Brexit is undoubetdly generating uncertainty in the property market in the UK. This uncertainty is infleuing the decision making of people to purchase commercial property. This uncertainty, laed to reduction of demand for property and the supply of property also reduces simultaneously.

COVID-19
The COVID-19 also has significant impact on demand and supply equilibrium for commercail property. The supply side will be reduced due to low level of cobtsruction activities anfd the deamdn side will also be reduced due to loss of income of people. This will have liutttle impact to offset the reduction in property price.
Conclusion
Supply and demand is always a hard task to evaluate in the commercial property market. This is because various factors can impact on the supply and demand equilibrium in the industry. In a similar context, commercial property is not like other industries in that it consumes significant time to purchase and to sell than other products of the economy. From the theory of supply and demand, it can be concluded that in the UK, the key factors which can determine the market and hence the price of the commercial property are, interest rates, taxation, population, creation of new commercial properties, the broader macroeconomy, accessibility of finance, cost of renting and affordability. The bottom line is that the retail property market in the UK and the economic factors subject to supply and demand. The principles of supply and demand generate situations in which customers and suppliers interact and decide the equilibrium price on which both parties communicate.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



