Telstra’s Strategic Business Evolution
Introduction
Business organizations take actions as well as decisions depending on their business environment for uplifting their position in the ever-competitive market. The significance of the global business environment lies in the use of advanced technology as well as improvement of the situation of external factors like legal and social changes within the business. In the telecommunication market, the service enterprise market has the benefit in the services of a cloud market that is directly related to the traditional business market. In Telstra, the telecommunication market, new strategies are implemented for improving customer experience by creating new infrastructure business. In order to improve the performance as well as productivity, this above-mentioned strategy is used. The impact of global technology is implemented for the determination of the strategic complexities to operate the global environments. In Australia, Telstra is not shafted, and it is identified that the net present value of this company is $11 billion. In addition to this, the network process of this company is considered as the mixture of nostalgia as well as snarling irritation. The actual money is to be paid the amount and it is identified as $50 billion. According to this report it can be said that the culture of Telstra involves the skill-set along with the scale prerogatives and benefits (abc.net.au, 2018). This company is diversified by the technology that can be considered as the leading communication provider in the entire country. They have the opportunities to use modern software like Python to resolve their problem in their business, where Telstra needs to improve their skill and knowledge according to the use of updated technology. The problem statement of a report is to identify the global business market of Telstra and analyse all key factors such as cost, environment, and competition for driving globalization in the market.
Continue your exploration of Microsoft’s Strategic Framework Analysis with our related content.
Company background
The company under consideration, Telstra Corporation Limited, is, at the current time, the largest telecommunications operator within Australia. The services and products of this company could be determined as telecommunications networks and mobile, internet access and voice facilities as well as paid television services. The headquarter of the organisation is located at Telstra Corporate Centre, Melbourne, Australia. The company was founded in 1975 and the current CEO of the company is Andy Penn and the company employs 32000 personnel currently. The company operates 360 retail stores and has 150 subsidiaries.
Task 1 Analysis of the key factors which drive globalisation
P1 Key factors of cost, market, environment, and competition driving global commerce and trade
Concept of globalization
The world is shrinking in the era of fast transportation and communication. Global business is also changing its shapes and structures accordingly. Globalisation is the umbrella that gives shelter to the fast-changing nature of the global business environment. According to Adegbite (2015, p.45), globalisation refers to the process of increasing interaction among the countries in terms of trade and business, polity, culture, transport and communication, social coordination and overall economic cooperation. The concept of globalisation applies to the business environment and it can be explored through different dimensions of culture, polity, economy, and society. The losses and gains of the globalization can be analyzed in increasing the overall productivity through channels such as wireless and it is related to the economic globalization. According to the viewpoint of Heckmann et al. (2015, p.87), in the international trade, the resource allocation has the competitive advantage as the productivity is increased by specialization. In Telstra, a telecommunication market use globalization to expand their business market by increasing their total profit and sales. Globalisation has both positive and negative effects on the global business players. The positive factors for the global trade and business are the opportunity of expanding markets, reaching out to more consumers, adopting new and advanced technology which, in turn, helps the profit of the company to grow. The negative effect, according to Zhang et al. (2015, p.234), of globalisation is the increase in competition among the rivals. This high competition often leads to the violation of laws and policies and corruption in order to get favour from the government concerned. As for example, the recent case of Facebook's data breach with the help of Cambridge Analytica indicates the negative side of the high competitive market in telecommunication and related fields (gizmodo.com.au, 2018).
The cultural dimension of globalisation and business
The cultural dimension of globalisation covers the cultural factors across the world. There are various cultural aspects all over the world as for example, the business culture in developed and developing countries are different and these differences are kept in mind by the global business leaders while making a decision (Foster and Graham, 2017, p.87). Not only the developed and developing countries but the cultural dimension of globalisation differs from one country to another and from one province to the other province. Telstra, being a global telecommunication company must give equal emphasis on the non-economic factors because they are becoming important determinants of the consumers' preferences. However, globalisation is also leading to the cosmopolitan culture in different countries and the urban regions of those countries reflect a mixed kind of culture with a more inclination towards the Western culture. The cosmopolitan culture helps the global business organisations to capture the market easily with their global image (Boz et al. 2015, p.9). On the other hand, many countries like China, being conservative in nature, prefer local companies. Getting into the markets of such countries becomes a big challenge for global players with the origin in a different country. Telecommunication industry mainly grows in urban regions. According to Volonté (2015, p.43), most of the urban regions across the countries have become cosmopolitan in nature. Urban population does not care about traditional cultural customs and norms. In such countries, the consumers can easily be attracted to the brand image, quality services and nice advertisements of the global telecommunication companies. However, the recruitment of employees in these countries must consider the cultural beliefs and thoughts as most of the workforce, even in the urban area, prefer their way of work culture (Snyder, 2016, p.22). Telstra, while expanding its global market needs to keep in mind that the people in the new countries want high-quality service and prefer local work culture in the workplace.
The economic dimension of globalisation and business
Globalisation helps the economies to grow and experience a multiplier effect in production and profit generation. In the view of Karimi and Walter (2015, p.8), globalisation has helped the global players to reach out to the consumers belonging to different economic backgrounds. As a result, a company encountering issues in one market may have the option to participate in another market and bypass the probability of loss. However, globalisation makes the markets more competitive which may affect the revenue share of a global market (Baldwin and Lopez-Gonzalez, 2015, p.9). Globalisation also forces the companies to better their service and product qualities in order to survive in the highly competitive markets. At present, the telecommunication is one of the flourishing industries in the global context as all the countries irrespective of their economic conditions are eager to grow the telecommunication facility in the county. In turn, it could be said that telecommunication companies like Telstra, are acting as the harbinger of globalisation in the world. Telecommunication industry requires to adopt the economic dimension of globalisation in a different way and it cannot follow that of other traditional industries like iron and steel industry, food and beverage industry, textile industry, retail and pharmaceutical industry and so on (Teece et al. 2016, p.54). The traditional industries have a physical mode of production as for example, the metal industries consider the sources of raw materials like metal ores, water, and energy availability but telecommunication industry does not have any such location factors since it is a footloose industry. Similarly, the demand-and-supply system of the traditional industries playing at the global level largely depends on the market whereas the telecommunication industry does not have a physical location of the market as such and the business could be done from anywhere given the infrastructure is available.
The political dimension of globalisation and business
The political dimension of globalisation is one of the most important factors considered by global business entities. Trade and business policies in one country influence a global company's business strategies. As for example, predatory nature of Chinese business environment is not conducive to the foreign companies whereas the restrictive approach of the US to the foreign companies could become a threat for the global players (Fernández-Mesa and Alegre, 2015, p.8). Political dimension includes the concerns like environmental degradation, employment generation issues, stagnation of production and manufacturing of the domestic organisations that make a nation adverse towards the foreign companies. In addition to these factors, intergovernmental relations affect the countries' trade policies. As for example, Australia has an amicable relation with Asian countries like China, South Korea and European countries like Germany and the US. Export from Australia to China, the topmost export country of Australia, has grown by 8.1% in the last 5 years (aph.gov.au, 2018). Telecommunication has become an essential part of the development of the countries and it is required by not only the developing countries and by the developed ones. The developing countries need the telecommunication industry to grow the communication system in rural areas and utilise the benefit of telecommunication in other areas such as research and development, education, health and defence (Sbia et al. 2014, p.65). On the other hand, developed countries require advanced, faster and better modes of communication. Therefore, Telstra must have different strategies for different countries based on their degree of development. The strategies could be framed by understanding the aims and targets of the governments of the countries concerned. The success of the global telecommunication companies relies upon their excellence in following up the government's' policies and analysing them critically before farming their own business strategies.

The social dimension of globalisation and business
According to Volonté (2015, p.6), the social dimension of globalisation acts as an undercurrent of changes that affect the other dimensions of globalisation namely cultural, political and economic dimensions. Therefore, social dimension is tacit in nature that influences the other factors of globalisation. Social dimension refers to the demographic structure, gender parity, social norms and customs that vary from country to country and from society to society. In the opinion of Shaikh and Karjaluoto (2015, p.65), the global players must consider the age composition of a country while expanding their business there. As for example, the countries like Japan experiencing ageing population and its median age is 46.9 (world.bymap.org, 2018). Therefore, telecommunication companies like Telstra must focus on the innovative and advanced telecommunication facilities in the banking sector which are supposed to flourish in Japan due to its ageing population. Many countries like Sub-Saharan countries are not developed enough to facilitate telecommunication in their societies due to political unrest and social backwardness. These countries are yet to come up in the list of the global business ventures. Telecommunication companies can adopt the social dimensions of globalisation in two directions that is one from the consumers’ side and the other one is from the employees’ side (Nadtochy et al. 2016, p.32). The employees also include those local companies working in the alliance of the telecommunication company supplying the infrastructural equipment and other supports. The social dimension of globalisation on the side of customers includes their taste and preferences. The South Asian countries such as India, China, Middle East countries like Saudi Arabia, Qatar, United Arab Emirates (UAE), have distinct social customs, norms, and structures and the customers in these countries reflect their preferences according to their societies. On the other hand, in the view of Hashem et al. (2015, p.21), the workforce in the countries having strong social traditions, customs and beliefs prefer the global companies that adopt the local mindsets in the workplace. The advertisement is the best mode of communication for a global telecommunication company, with both the customers and potential workers to showcase the respect for their societies and cultures.
Explanation of key driving factors of globalisation
The key driving factors of globalisation could be broadly identified as the technological advancements, trade barriers, and national trade policies and consumers' demand. The cost of production, environmental policies, and international economic integration both environmental and economic aspects are important factors to be studied. The key driving factors of globalisation could be categorised as cost, environment, international economic integration, foreign direct investment, market, competition, and international business and trade. All these factors affect the global business environment of a company. The consistent and rapid expansion of the global business operational activities regarding the goods and services as well as financial transactions have been responsible for the relentless integration of the different economic centres on the international spheres. This could be further elaborated in the manner of the concentration of the operational business activities undertaken by the international multinational corporations and such concentration has been made possible on account of the entire range of multifarious factors which closely correspond to the economic, political as well as the social scenarios which are currently prevalent at the international market. According to Adegbite (2015), one of the factors of the globalisation process drivers is the integration of the markets and permeation of consumerism. This could be better delineated in the manner of merger of the individual markets into a singular global market so that sales and availability of products could be maintained at an optimised extent through the absence of the trade barriers of the transnational and cross-border trading operations. In this regard, another of the various specific drivers of the process of globalisation could be understood to be the cost of of accessing the benefits which could be derived from the process of globalised business and trade could be considered. Under the globalised international commercial dimensions, the assets of any business group could not be the singular determinant regarding the prospects of achievement of the success since the nature of the globalised market ensures that not only the multinational business organisations could get facilitated to reap the benefits from the globalised market spheres. Even smaller organisations could as well benefit from globalised commercial trading prospects through the offering of standardised products to the markets which these companies could target. According to AKPAN (2017), the process of Globalisation could be further characterised through different factors. These could be understood to be the market, environment, competition, international economic integration, foreign direct investment, international business and trade. Expanding international interconnections between various market spaces are influenced by the cost element. The swiftness of the elemental interconnectivity regarding the different multinational as well as national and regional business organisations is determined by the international economic integration. Continuity of changes in the market preference profiles of the companies which could be willing to invest in new and often unchartered market horizons is infeuned by the existing market environment. Increasing number of the market competitors and participants in the differential business disciplines is generally influenced by the elements of competition and foreign direct investment scenarios within the market segment. Ultimately the considerable growth in the complications regarding the business operations which are now incumbent upon a host of different drivers on which the entire process dynamics closely depends could be as well determined by the interanational trade related approaches which could be implemented regarding the global business perspectives. The research of Andrews, Schank and Upward (2017) has outlined that there are four primary drivers of the process of Globalisation. These could be understood to be the Market, Government Policies, the Cost structure and the Market Competition. These are mostly the external drivers of the process of Globalisation and these influence the most significant conditions regarding the potential of success which could be achieved through the process of Globalisation. Such conditionalities are mostly not able to be controlled by the individual business entities. Furthermore, the driving factors of Globalisation involve various aspects such as the changing preferences of the customers, the capabilities of the individual companies to perform the necessary activities to utilise the transferable marketing processes and the emergence of the consumer inclination towards globally compatible and standardised products. These factors have enabled the business entities to cater to the significantly changing demands within the new market spheres with the products which could be already in existence. One major driver of the Globalisation of trade and business could be understood to be the policies and practices of the concerned national governments. The associated government policies could lead to the reductions in previously existing trade barriers and the greater shift towards the open market economy based operational processes could be the definite facilitator concerning the process of Globalisation. The greater access of different and hitherto often inaccessible market horizons as well as human resource capitals could be now facilitated with the integration of different national economic perspectives within the global economic structure. This brings forward the cost advantage related drivers of Globalisation as the multinational organisations could now be enabled to achieve the coveted economies of scale through performing higher quantity based sales of the endorsed goods and services. This could now as well be augmented by the exploring and availing of the low cost based production processes in the format of manufacturing or services outsourcing or through outright import of the goods and products. Ultimately, the competitive drivers of the Globalisation process could be outlined in the form of the exponential growth in the trade processes in between the various national and private sectors which could be enhanced through the infusion of consistent Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). The influence of FDI has been instrumental in helping to enhance the exposure of new competitive entrants in the hitherto secluded and protected or restricted market spaces.
Evaluate how operating in a global market influences an organisation’s structure, culture and functions.
Operating in the global markets could entail the organisational culture of any specific business entity to implement certain aspects for the purpose of better adapting to the realities of a Globalised International Market space. This involves the utilisation of inclusive and shared belief systems within the organisational working architecture. The Globalised environment could compel any organisation to invest specific effort towards founding specific strategies to develop and implement successful operative tactical processes within the organisational operational structure. Aquino and de Castro (2017) has observed that the establishment of effective goals and initiatives is key in this regard so that the practical realisation of the organisational strategy could be made into a definite possibility. Inthis respect, the initial step is to infuse adaptability of operational procedures and flexibility of actions and decision formulation processes within the concerned organisational structures for the purpose of better suitability development. This is a vital aspect regarding the necessity of ensuring survivability and profitability of business endeavours in the global market scenario. The second step is the inculcation of the different characteristics of stability within the organisational cultural framework. This systematically supports the implementation of strategic perspectives which could be decided upon and could as well foster the culture of adapting to changes of situations and and utilisation of partnership based ventures. Furthermore, the effective formulation of organisational cultural stability could enhance the cooperation and teamwork based inclinations amongst the employees of the organisation. The emphasis is always on productivity enhancement and production cost control. Another aspect of organisational culture and structural functioning in the globalised environment could be understood to be the unification of goals and objectives through the benefit of fostering unified and strong organisational culture which could further formulate implementation of strategies in tandem with the achievement of the primary mission of the business organisations under consideration. Ultimately, the alignment of organisational culture with the strategy implementation perspectives is another aspect of such globalised multinational organisations. This permits the business process leaders to effectively perform both at the individual levels and at the team level. Instances could be mentioned regarding the formulation of new partnership or rejuvenation of previously formed ones. The emphasis is always on the delivery of the most effective results in terms of profit maximisation.
Evaluate the influence of globalisation on organisational decision-making and strategy
The unpredictability of both domestic and international change generally leads to the consideration of the variable regarding the evaluation of probable impact of the previously experienced effects. However, the consistent awareness of external changes in the political, technological, social, cultural and financial as well as environmental domains is key for any business organisation to remain relevant in the globalised market. Arvis et al (2018) states that changes in national, international and regional policies as well as in the economic trends are the factors which profoundly influence the decision making process of any business entity in globalised market conditions. The determination of strategy is thus completely incumbent upon the delineation of the most effective evaluation of the variables such as differential changing aspects of global conditions. The most important step is to comprehend the variables of change and impact of the same on the global economic and demand cycle performance. Successful anticipation of the same could lead to the efficacy achievement in decision formulation for global multinational organisations such as the one under consideration in the corresponding study.
Impact of digital technology on globalisation
Globalisation has become faster in the present century because of the emergence and diffusion of digital technology. The digitisation of the world has increased the importance of telecommunication sector. Therefore, the telecommunication sector could be regarded as the facilitator as well as the receptor of the benefits of globalisations. According to Sheu and Kundu (2018, p.87), the concept of globalisation has become a common factor and digital globalisation has been appearing in the scene as a new form of it. Globalisation is no more a buzzword rather has become a part of the world trade and business environment. This rapid popularity of globalisation has been possible with the help of digitalisation. In the following section, the impacts of digital technology on globalisation have been investigated.
Impacts of Information system and technology
Information system refers to the arrangement of the methods of data collection, data synchronisation, data analysis, and data storage. All the information system works under the information technology that has made the data transmission swift and error-free. However, as commented by Blanchard and Olney (2017, p.182), the information system is becoming very complex due to the increase in quantity and varieties of data and as a result, the information technology needs to be upgraded so that the speed and quality of data generation and transmission are maintained.
Digital flows of data and information
Analysis of data and information on business factors like production, propensity to consume, demand for a service and so on gives an advantage to the present global organisations. They easily arrive at a conclusion regarding business factors and take measures accordingly. Telstra, being a telecommunication company plays a pivotal role in generating and analysing big and complex data across the countries where it operates. The data could be used by them to find out the issues encountered in the existing markets and potential prosperities in the new markets. However, as commented by Trigeorgis and Reuer (2017, p.74), the flow of data and information leads to the violation of data privacy. Therefore, Telstra must respect the privacy of data as per the acts of the respective countries. As for example, Telstra abides by the Federal Privacy Act 1988 and Australian Privacy Principles for ensuring the privacy of data gathered on digital platforms (oaic.gov.au, 2018).
Efficiency in business operation
Digital globalisation has helped the global players to operate efficiently at the lowest cost and time. Geographical barriers are no more considered as the hindrance for business operations. Offices working in different time zones work coordinating among themselves (Girma et al. 2015, p.23). Telstra also channelizes this advantage of digital globalisation in their business functions. Business units of Telstra spread in different countries coordinate with each other and arrange their operations based on the digital communication facility. However, according to Ho et al. (2015, p.74), the efficiency of digital technology may get hampered due to the issues encountered by the communication lines and technological glitches.
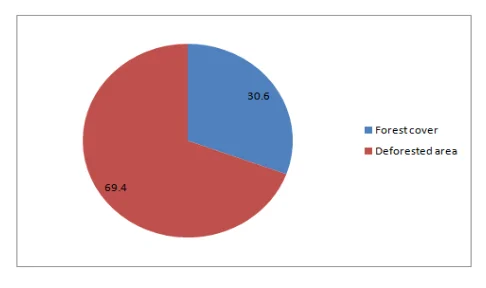
Over-dependence on digital technology in the context of globalisation has the potential to mar the whole information systems in the world if any major technological collapse occurs in the future. The digitalisation of global business also affects the environment since the installation of equipment like telecommunication towers and large equipment causes deforestation. According to the Food and Agricultural Organisation, the world's land area under forest has decreased to 30.6% in 2015 due to rapid industrialisation (fao.org, 2018).
Impacts on the social sectors
Digital technology has a key role to play in the social sectors like health care, education, public governance, and media in the era of globalisation. Telstra must utilise its capability in the field of each sector in order to stand at a better position in the global market. Each and every sector has unique opportunities which have been explored in the following section.
Health: According to Bowen et al. (2015, p.26), the telecommunication industry has a great role to play in the health sector especially in developing countries as they need to connect more people to the local healthcare facility centres through telemedicine facility, video conferencing and alike. For the developed countries Telstra can try to provide the health sector a faster, interruption-free and improved mode of communication at a low cost. However, many countries are getting concerned about the impact of digital communication on their health which may affect the telecommunication industry.
Education: Telstra must venture into the education sector in terms of providing the smart classrooms features like digital aids of teaching, digital boards, and learning platforms. At the time of globalisation, education sector in both the developed and developing countries are going digital (Cheng et al. 2015, p.39). The governments, educators as well as learners prefer digital education facilities. However, the problem of this sector is that it requires a huge amount of investment with a low achievement of profit (Graham et al. 2017, p.147). However, this profit margin could be adjusted if the government subsidies are available for the global telecommunication companies.
Public governance: Public governance is another important social sector in which the telecommunication companies can venture into. Both the developed and developing countries are putting emphasis on people's participation in public governance. Telstra already has collaboration with Australian agencies and it must enter the public governance of other countries as well (telstra.com.au, 2018). In that direction, the developing countries of Asia like India and China, of Africa like Morocco and Ethiopia and of South America such as Brazil and Peru are the potential ones that are ready to hire foreign telecommunication companies for improving their governance (Hotho et al. 2015, p.111).
Media: The field of mass communication and journalism is a flourishing social sector which requires a strong telecommunication system for transmission of news and ensuring the authenticity of news collected. This field could be of both public and private in nature. Telstra can venture into this field by collaborating with different broadcasting media like BBC and the public news emission agencies in the US, Canada, European countries like Germany, the UK, France, and New Zealand.
Production of virtual goods
Digital technology creates a new form of goods that is virtual goods. Prior to the advent of digitisation and digital telecommunication, the physical goods which are produced and consumed physically such as foods, industrial goods, luxury goods and so on covered the maximum share of the global business. At present, virtual commodities like mobile apps, software, and social media platforms are becoming the mode of trade and business (Wirtz et al. 2015, p.78). The mode of transaction is also becoming virtual as the physical monetary transactions are not preferred by the global business players anymore. Bitcoin has been gaining popularity in the global market that puts the national currency generation and monitoring system on a serious threat. Telstra has already achieved a strong ground in producing virtual goods in terms of telecommunication services, broadband, cloud computing and internet of things for enterprises.
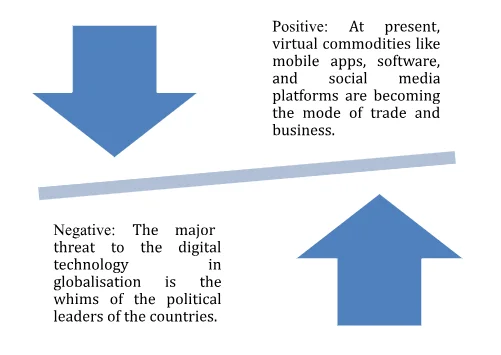
Digital technology has facilitated the globalisation by increasing the economies of scale and the cost of transportation has also decreased all over the world (Pinto and Zhu, 2016, p.74). Raw materials can be sourced from the resource-rich regions to the resource deficit regions. A major benefit of digital globalisation is that the footloose industries like information technology do not need to be concerned about the factors that affect industrial location like the source of raw materials and energy, the location of the market and so on. These industries are able to establish their units in developing countries on the basis of the available workforce working at a low wage rate and an industry-friendly government policy. Telstra also can use this benefit of digital technology by employing skilled workers from different countries who are ready to work at low wage rate. The major threat to the digital technology in globalisation is the whims of the political leaders of the countries (Mi et al. 2018, p.87). As for example, sometimes the digital business platforms like Amazon, social media platforms like Facebook encounter the political rage due to their not following the business ethics in a particular country. This affects the other company’s business performance and fate depending upon the major ones.
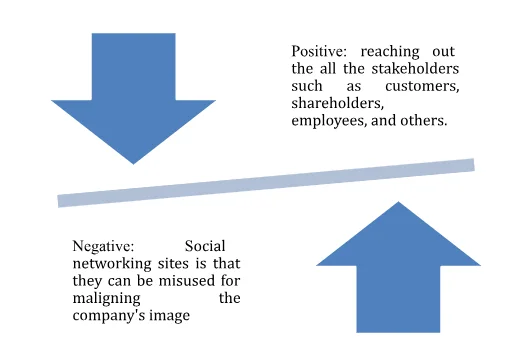
Use of social networking sites
The smart way to reach the customers, as well as employees, is using social networking sites by the global companies. Telstra already has a dedicated platform for reaching out the all the stakeholders such as customers, shareholders, employees, and others. However, the negative side of the social networking sites is that they can be misused for maligning the company's image (Odunukan, 2018, p.231).
M1 Critical analysis of the impact of key factors on the global business environment in terms of benefits and challenges.
The forces of globalisation can be summarised under factors like technological advancement, reduction of trade barriers, increase in demand, and competition.
Technological advancement
Technological advancement especially the progress of digital technology has reduced the time and cost of production in the telecommunication industry (Ramdhani et al. 2017, p.87). However, over dependence on the technology and technology-intensive production method have challenges. As for example, the employment generation capacity of the telecommunication industry has reduced over time. The impact of globalisation has the effect in worldwide societies in social, political, cultural, and economical and so many other aspects. In the technological advancement in telecommunication market, VoIP is used along with the provision of triple play (Snyder et al. 2016, p.21). The gateways of VoIP are identified about $1B according to the market size, where the bandwidth of mobile networks is also increased such as 3G is updated in 5G. The Wi-Fi networks are also transformed from server to any other device. The benefits of the technological advancements could be understood in the form of ease of business in the current age. Technological innovations such as the Internet have offered the benefit of online based businesses and electronic commerce. Web based businesses allude to business directed through methods for electronic correspondence systems . This has achieved new extent of the globalization of organizations. Where virtual business can be set up and conducted worldwide with no obstructions ceasing these. These facilities have changed the manner in which independent business ventures work and have offered chance to even the small and micro companies to enter the global level markets (Baccini, Pinto and Weymouth, 2017).
Reduction of trade barriers
Trade barriers and trade wars between the countries affect the interests of the companies present in those countries as well as the countries themselves. Telstra can venture in those countries like Japan, China, and the US that have a good diplomatic relation with Australia. As a result, they will be provided with a large access to local markets. However, the trade barrier has one positive side. As commented by Roh et al. (2014, p.54), trade barrier between two countries does not affect the country that has an amicable relationship with either of them. It means that the companies belonging to one of the rival countries do not get an entry in the market of the other country and as a result, the market becomes less competitive. The benefits of reduction of the trade and tariff barriers could be understood in the form of reduction in the prices of imported goods and products. The relative reduction in the import prices would benefit the multinational exporters in terms of sales offering prices in the domestic markets of the targeted nations. This would force the domestic producers to reduce their product sales prices as well for them to stay competitive and relevant in comparison to the MNCs. This would then provide the customers the benefit of having multiple and relatively affordable options regarding their product preferences. Increase in consumers’ demand: According to Baccini et al. (2017, p.78), growing consumers' demand is another important factor for globalisation. Increase in demand leads to the more participation of new companies in the market. The globalisation facilitates the foreign telecommunication companies to enter new markets. However, excessive demands of the consumers encourage the new players to enter markets creating the market more competitive. It results in the reduction in the profit margin of each company. Ultimately, the increasing demand cycle of the consumers would be effective to fuel the growth of the respective national economies and would be attracting greater FDIs and would lead to better foreign currency reserves for the concerned national economies.
Task 2 Determination of the strategic complexities operating in a global environment
P2 Explanation of the complexity of strategic challenges faced by organisations operating in a global environment supported by specific examples.
Explanation of the challenges of globalization to enter new markets
Choosing the right countries
The first and foremost challenge faced by a company while entering a market is choosing the right country. A company must do enough research to analyse the right place to expand its market. In the case of telecommunication companies, it must consider the demand, infrastructure, and government’s incentives for the new companies and the availability of the skilled workforce and so on (Clark et al. 2016, p.74).
Distance
Although distance has become a less important factor in the intertwined countries it has not lost its complete importance. Distance still affects the decision of new entrants in the global market based on the analysis of the cost of production, economies of scale and the principle of distance decay in the market (Fenwick and Edwards, 2016, p.87).
Mastering marketing
In the telecommunication market, identifying prospective customer is the important factor to take the entire business in the global market so that customers can attract to their business and their business is increased as well as their profit percentage is also increased. As opined by Blanchard and Olney (2017, p.165), the main key ingredient of the global marketing is the transcription, which allows to adopt the total marketing content so that this company can easily enter in the global business market. The implementation of globalization in the telecommunication business is processed on the long-term period. In Telstra, concentration on efforts is considered as the vast majority in this country Australia, where the total concentration is given on the independent user platform by providing good customer service through the social channels. All social channels like Facebook is considered as the great place, where the customer service is required to facilitate, and it is totally depending on the real time. The overall transparency of social channels helps to facilitate the service for promoting the fact so that customers can get well behaviour from the employees of this company. The good customer service helps to improve the overall communication through the social channels for quick responding. Attractive advertisements are used to find the target audiences so that they can get good services from this company. Effective interactions are required to maintain with the followers so that the customer responses as well as feedback are reached to them for future modification.
Tariffs and the export fees
Most countries have the export as well as tariff fees, which are charged to the companies for bringing goods into the country of Australia. As stated by Boban (2016, p.191), in order to implement these changes, the tariff rates are required to incorporate within this company so that the elements of financial planning such as planning of cash flow, investment and many more with the plans of globalization. Several fees are charged depending on the shopping in the specific country Australia. As Telstra is considered as the leading telecommunications market in Australia, so the Australian tariffs as well as export fees are applicable in this company. The world trade organisation in Australia includes the tariff quotas so that they can export the subsidiaries such as energy and power for supporting their online products. The Free trade agreements in Australia (FTA) mainly contain the legal binding commitments for accessing the market for the service as well as goods and the total investment.
Human resources
A business is taken as the global business and it is required to meet the total manpower requirements that help to operate the entire business in the foreign country like UK. New employees are appointed for maintaining the account. According to the explanation of Bowen et al. (2015, p.25), in the telecommunication market, the human resource is required, who know about the updated technology that are used in telecommunication market. In Telstra, the effective human resource management helps to evaluate the skills of desired potential for all employees. The employee dissatisfaction is considered as the major problem within this company and this issue is solved by conducting training session for the employees. This training session helps to understand them about their respective work culture. The employment needs are also considered so that employees are getting interested about their work in the workplace. The reward is required to given to them for good working along with the monthly or annual incentive (telstra.com.au, 2018).
Adaptation of content and documents to the culture
The proper document is required to understand the instructions, sales materials and other documents that are considered as the important factor in the total business. As opined by Brandenburg and De Wit (2015, p.87), the updated cultures are adopted to increase the capability for translating them, when the new culture is adopted. The cultural differences have the negative effect in the business, so it is required to resolve so that the overall business condition can be improved. In case of Telstra, mobile services are charged at the fixed rates, where the services of mobile phone help to assist the communication in the field of both workers as well as their family members in emergency. In this company, it can be identified that $4.35 million grants are provided among the 790 numbers of community groups, the community development is identified as $3.6 million and the $750,000 fund is required for the 690 projects on the community (telstra.com.au, 2018). These kinds of issues help to meet the total challenges that is presented by taking the entire business globally and it allows to expand the total business that help to reach telecommunication firm in new heights like Telstra, where the opportunities are discovered for the people.
Unfamilier culture
Adopting a new culture in a new country is another challenge for the companies planning to enter a new market. According to Graham et al. (2017, p.74), the companies based on Australia do not face any problem while entering the markets in Europe and North America due to their similar cultural settings. However, the countries in Asia, Africa, and South America have distinct social and cultural traits that must be thoroughly reviewed by the new entrants in order to capture the markets according to the tastes and preferences of the local customers. However, as commented by Lau et al. (2014, p.69), the telecommunication industry is not affected by a cultural underpinning of a country as much as other industries like food and textiles.
Communication among the units
A serious challenge to the new companies in the market could be the lack of communication among their various production and service generation units. New entrants need to be familiar with the local suppliers in order to reduce their input cost. Telecommunication industry is based on its strength in communication (Nawaz, 2018, p.78). Therefore, the challenge of communication must be overcome by the companies as much as possible.
Understanding marketing
A new entrant in the market must be well aware of the small factors which are covered under the ambit of microeconomics such as production cost, profit generation, economies of scale, demand-and-supply mechanism in the market, condition of supply chain management in the country, multiplier effects of production and so on (Blonigen and Piger, 2014, p.25). All these factors need to be analysed in the telecommunication sector before entering a new market.
Understanding the trade policies of the countries
The countries in the world are becoming more restrictive in the case of foreign trade and business. However, some countries like Singapore, Hong Kong, Sweden, and the others are very much conducive to foreign companies (Bauer et al. 2016, p.25). Their trade policies are simple and friendly towards foreign organisations as they allow more FDI and more presence of the companies in the market. In the case of telecommunication companies like Telstra, they need to go through the employment policy and laws, environmental policies and laws, welfare benefit related policies, laws regarding the corporate social responsibilities, taxation and tariff related laws.
Explanation of the key strategic challenges represented by Globalisation
According to Baldwin and Lopez‐Gonzalez (2015), there are four different but interrelated challenges and complications which any business firm has to grapple with while undertaking international business operations. These could be identified as the elements of Change, Complexities, Competition and Conscience. In terms of the first element of Change, the implications are mostly indicative of the problem of the international business organisations to consistently modify and evolve the marketing strategy and tactical product and services development to suit the rapid pace change of customer as well as consumer preferences within the globalised market space. The emphasis is always on the factor of adaptation to involve the new realities concerning the technological, political and economic as well as social dimensions. These are critical in enabling the business organisations under consideration to successfully monitor and adjust to the altered situations and volatile conditions which such corporate entities are bound to encounter within their business disciplines. As has been highlighted by the research of Bauer, Matzler and Wolf (2016), the second element of Complexities is more nuanced from a definitive perspective and thus is required of greater clarity in terms of the academic evaluation based building of better understanding in this regard. According to Bazerman and Sezer (2016) the factor of Complexities could be better determined to be a mechanism of interplay of different internal as well as external forces and the associated effects on the business organisations under consideration over the longer period. The difficulties arise out the challenges of management of the human, material and technical assets of the organisations within the diversified and far flung operational sectors was the market configurations keep on consistently changing throughout the passage of time within the globalised market environment. In this respect, Beugelsdijk, Kostova and Roth (2017) has observed that the technological advances could ensure that the organisational management hierarchy could be enabled to coordinate, direct and control the market based operations within a much expanded and diversified geographic as well as social perspective. In this respect, the management structure of different organisations are required to master the different skill sets and tools of management of the burgeoning responsibility scenario concerning the international infrastructures of the organisations under consideration. Blanchard and Olney (2017) states that additional segments and layers of the multinational organisations are developed to content with such operational complications. From a definitive perspective, the emphasis of the companies is generally concentrated upon the integration of regional markets and on the establishment of region specific management systems which could better coordinate and direct the organisational functions at every phase of the value chain. The global level of complications also require real time based transfer of assets, experiences, resources and information throughout the global scale of operational sectors. . One potent example of it could be found from the operations of Ford Escort which has been launched primarily at the European market. This specific automobile which has been sold widely throughout the world, demonstrates the manufacturing of the components of this vehicle throughout 15 different countries throughout the globe. According to Blonigen and Piger (2014), the dispersal of customer based markets throughout the globe under the ambit of Globalisation has ensured that establishment of proper and effective linkages with the product and service consumers as well as with the various supplier segments has also become more critical and more difficult in a successive manner. Such difficulties have contributed in the necessity to invest increasing effort to remain competitively advantageous within the current hyper competitive market scenario. In this respect, the third element of intensification of competition is necessary to be evaluated. Boban (2016) has observed that the expanding competitive influences of different business organisations within the most lucrative market domains within the global trade scenario is the prime source of the variations of every state of the involvement within the international market by the multinational organisations under consideration. The opening up of the markets has also ensured that the pace of change generally is accelerating with every financial year within the globalised financial context. This generates the shrinkage of geographical distances more effectively and markets become more and more accessible to every business entity which could afford the same. This also contributes in the reduction of the pre-existing the advantages of large business firms which could be previously derived from the large sizes and operational scales of such multinational large companies as well as from the centralised reservoirs of capitals, both the financial as well as human asset based, of such companies. The cumulative effect of such factors could be understood to be the enhancement of the intensity of competition by many folds within the entire length and breadth of the global markets. According to (), the consistent mounting of competitive pressures on the existing and established multinational organisations is a definite outcome of such a complication and challenge based on competition. The established firms operating in different parts of the globe have to be always attentive to the new threats and dangers which emerge from the new entrants in the existing market spaces and from the consistent proliferation of competition. Furthermore, as has been observed by Bolden (2016) the sources and dimensions of competitive strategic challenges faced by all of the organisations which have been operating in the global context are multifarious and often cross-operational in nature. Furthermore, the newly emergent international networks and coalitions of different business groups from diverse origins also pose significant strategic challenges of overwhelming competition from the relatively smaller business entities. The research of Bowen, Baker and Powell (2015) demonstrates that newly invigorated business organisations such as those from the recently industrialised countries such as China or Taiwan have been consistently taking the initiatives to utilise their existing human and material capital to compete intensely within the global market sphere. The opening up of the domestic markets of hitherto restricted and controlled economies such as India, Brazil and Malaysia has contributed in the domestic business organisations of such countries to become increasingly competitive both on the international as well as in the domestic sector. Boz, Bussière and Marsilli (2015) has opined that this has transpired on behalf of the renewed awareness on part of these organisations concerning the necessity of realising the opportunities which could be garnered from the international markets. Thus, the international competitiveness has become the most significant strategic challenge which has to be overcome by any international business operatives. This is especially significant concerning the price sensitive segments of the global markets. According to Bresciani, Thrassou and Vrontis (2015) the legal structure of the international business organisations are completely incumbent upon the international legal perspectives which have been promulgated upon the trade regulation based laws. The legal structure is the primary vehicle on which the entire business operation is conducted. According to Bryson (2018) this implies the entire extent of limited operations and partnership based activities which are integral to the existence of any business operation. According to Cheng, et al (2015) the origin of the international business laws could be traced back to particular customs, multilateral agreements and treaties and international conventions which had been prevalent over the ages and which had been brought together by the leading international legal institutions to formulate the commonality of the legal framework for global trade and market based operations. This has been also another aspect of enhancing the process of Globalisation of the market with the introduction of differential yet imperative legal regulations concerning the global trade and business operations, including the formulation of new business organisations and undertaking financial transactions on a real time basis. Clark et al (2016)has also highlighted the fact that such effects of the international legal systems also lead to the promotion of the regional trade practices. According to Cowin (2018), the most prominent sources of international trading laws could be identified as treaties such as GATT, NAFTA and the political conglomerates of nations such as the European Union. Such entities and international agreements are basis on which the development and the periodical reviews of the standards and regulatory codes and conditions regarding the international trade could be developed so that the nations which are either the members of such groups or are signatories of such international agreements could be directed, controlled and bound by these. The legal stipulations are more or less reflective of the various ethical issues which generally are expected to influence and affect the business proceedings within the entire global business environment. The international laws could as well address the involved processes through which the resolution of different disputes concerning the business conditionalities and clash of interests could be developed. () has stated that it is the prerogative of the international legal systems and associated stipulations to ensure that the determinations of the rights and responsibilities of the involved business parties could be secured and the transactions of economic value could be perfectly conducted as well without any hindrance or any interruption. In this context, the evaluation of the aspect of influence of the international trade laws on a selected global multinational organisation is critical. The selected organisation could be identified as that of McDonald's. Concerning the activities McDonald's on the global scale, consistent changes and evolution of the legal systems and introduction of the new laws introduce profound effect in terms of macro-environmental considerations of the global business discipline within which the selected company operates. According to (),McDonald's Corporation generally considers three aspects of the international trade and civil laws which could influence the overall business activity of such an organisation. These three could be identified as the increase in stringency in the regulations pertaining to health and security maintenance at the workplaces, especially at the sales outlets of McDonald's, the increasing regulations of animal welfare internationally and above all the persistent rise in the minimum wage structure of the employees which could a prime source of concern for the global business operator in this regard. In terms of health regulations, the effect of the international trade laws could impose certain limitations concerning the availability and accessibility to the fast food outlets operated by the organisation under consideration at both critical points of customer congregation such as workplaces and educational institutions where the potential gathering of a large number of existing and prospectus consumers of the food products endorsed and produced by McDonald's could be affected due to the prevailing and under stipulation health regulations. Such legal trends could pose a considerable strategic challenge and complication for the generation of expected revenue from particular market segments. De Mooij (2018) also has also opined that regulations related to animal welfare could be another source of complexity since adherence to the regulations could increase operating costs for McDonald's by many folds. However, as has been comprehended by Clark et al (2016), the regulations regarding the animal welfare prospects could as well be transformed into a significant opportunity by McDonald's. This could be contemplated in the form of the fast food operative becoming more attentive towards implementation of an animal welfare policy which could be comprehensive in nature so that greater number of customers who have inclination towards betterment of animal welfare situations could be as well attracted to the activities of McDonald's Corporation.
Ultimately, the complication regarding the higher minimum wage related international trading legal regulations could lead to greater cost of production and undertaking of sales and communication operations for the McDonald's Corporations. Globalisation process involves the consistently enhancing integration of diverging national economic sectors and the expansion of interdependence on part of such integrated economies. Aquino and de Castro (2017) states that this is the indication of the absolute significance of the entire international economy through multiplication of international trade, forward investment and subsequent significance of multinational business organisations such as that of the McDonald's Corporations. This could be also the source of another strategic challenge for the business organisation under consideration. To elaborate upon this, as per the research of Adegbite (2015) it is necessary to consider specific aspect regarding the globalisation of economies and the direct outcomes which such a process could entail. This aspect is that the process of globalisation is responsible for making the national economies becoming consistently absorbed and integrated within the overarching structure of singular global economy the components of which are highly interdependent upon the fortunes and performance of each other in a collective manner. One instance could be outlined in the manner of the common market in the erstwhile undivided European Union, the harmonisation of individual monetary policies and closer integration with third world economies such as those of the Southern America, Africa and Southern Asia. In this context, the strategic challenge could be understood from the perspective that economies generally progress in trade cycles where the onset of economic depression or slow down in the economic sector of any particular nation such as that of the United States of America could lead to the detrimental impact on the entire global economy since the interdependence of international and globalised economic structure could enhance the cumulative effect which could be better described in the form of a domino effect where the displacement of any singular component jeopardises the structural integrity of the entire structure. In terms of the operational activities of McDonald's Corporations, the globalisation of economies have become particular sources of strategic challenges regarding the 2008 onwards global economic slowdown and the subsequent slow pace of recovery of the specific market segments where the majority of the fast food outlets of the McDonald's Corporations are situated such as that of the United States of America and the markets where the majority of the consumers of products of the company could be found, such as that of China. The effects of such economic slowdowns on the business prospects of McDonald's Corporations could be understood to be the sources of the most intractable strategic challenges. According to Baldwin and Lopez‐Gonzalez (2015) the extensive effects of globalisation could be comprehended to have considerable impacts regarding the changes which have set in on the global as well as regional climate systems and on the environment in a cumulative manner. According to Baccini, Pinto and Weymouth (2017) the most prominent aspect of it could be outlined to be the often mentioned aspect of Global Warming. The inequitable risk and responsibility distribution of greenhouse gas emission amongst the developed and the developing world have emanated from the highly globalised international trade and production systems where environmental regulations have been regularly disregarded by the leading multinational corporations operating at various parts of the globe. In this respect, renewed focus on the environmental regulation formulations on behalf of organisations such as the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and on part of United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), has gained precedence through the legal agreements which had been finalised in Kyoto Protocol of 1995 and which were ratified in the Paris Agreement of 2015. According to Andrews, Schank and Upward (2017) Globalisation could be contended to be responsible, at least partially, for the issues related to environmental degradations and increase in the global warming gases such as the CO2. This could be better comprehended in the format of increment in industrial products and in the surge of the global trade since the process of Globalisation has resulted in the enhancement of global consumption to a great extent. Primarily, extensive accounts of human activities proscribing to sectors such as transportation, industrial operations and manufacturing as well as consumption and the waste generate out of such consumption, both on the individual as well as on the industrial or organisational levels, have contributed to the upsurge in the emission of the CO2. Regarding the operations of McDonald's Corporations, the environmental issues could have significant impact upon the macro-environmental considerations regarding the business prospects of McDonald's Corporations. The emphasis is primarily on the ecological trends and the environmental policy based considerations while having to contend with the newer regulations which have been put in place by the United Nations as well as concerned national government agencies to better protect the environment. It is thus necessary for McDonald's Corporations to increase the effort and resources for the improvement of the existing environmental as well as the sustainability programs which it endorses to strengthen the performance of business activities of the company. The changes in the climactic conditions at various parts of the world could as well lead to shortages in food supply and this could have grave effects on the supply chain management prospects of the company under consideration. Thus, investment towards fostering greater sustainability of practices could be the only solution for the company under consideration. Concerning the challenges emanating from supply chain management operations for the overall activities of globalised economic structures, the primary complication could be comprehended in the manner of political disputes which could jeopardise the unhindered flow of material an supplies, the accessibility of local markets and utilisation of local labour and transportation assets and finally the prospects of promotion of new products and services within these regions since the state of political disturbances could jeopardise the inclination of the targeted customers to purchase new products and services. According to Bauer, Matzler and Wolf (2016) the next strategic risk to the global supply chain management could be the incidences of natural disasters which could jeopardise the communication possibilities which are vital regarding the entire prospect of accessibility of the comprehensive markets within any national or geographic region. Furthermore, the inadequate availability of proper human resources could be understood to be another serious strategic risk for any supply chain management process. All of these factors could have serious cumulative effects concerning the activity scenario of the McDonald's Corporations since the existence of any of such factors could prove to be the source of a considerable problem in terms of effective supply chain management performance on part of the fast food retail giant under consideration. However, the two most significant factors in this regard could be identified to be the inadequate manpower and the lack of local resources for the production of the goods endorsed by the company under consideration.
Recommendations to Telstra to overcome challenges
Concerning the recommendations to overcome the complications and challenges which Telstra could encounter as direct effects of Globalisation Bazerman and Sezer (2016) has observed that the emphasis has to be concentrated on the strategy of pricing and product standardisation, from the perspective of overcoming of global competitive pressure. Apart from this, the considerable effort investment concerning the promotion of the products and service endorsed by the company could be understood to be another of the most effective methods to overcome the competitive challenges from the domestic as well as global competitors, both within and outside of the Australian markets. Concerning the pricing strategy for Telstra, the point of significance could be the effectiveness of controlling of production costs. Concerning the problems of entry into new market horizons, Beugelsdijk, Kostova and Roth (2017) has observed that there are three particular processes through which Telstra could formulate the most effective growth strategy which could enable the organisation to overcome such strategic challenges. These are to be identified as the increasing of the products and services, including the handset, the maximisation of profit from sales operations through controlling of the forward expenditure and ultimately through improvement of the operational shelf-life of the quality of the goods produced by the company. The controlling of costs for the purpose of achievement of economies of scale could be a definite recommendation for Telstra and this could be achieved through instituting localised management systems. Selection of different modes of operation through diversification of entry strategy and competitive tactical applications could be another recommendation. This could be augmented through the utilisation of particular business models which could enable Telstra to integrate environmental considerations in the products of the company and could as well commence joint ventures with local companies so as to have effective franchisees to support itself when any of the supply chain management related challenge or complication could be encountered.
M2 Critical analysis of strategic challenges in the context of risk and diversification strategies and the supply chain flow
In the strategic challenges in the telecommunication market, climate change is considered as the important factor in the telecommunication market. The climate change drivers are included for reducing risk in the supply chain management that has the negative effect in the telecommunication business market such as risks in core operational management, risks in the entire value chain and risks are raised in the total infrastructure. The supply chain is depended on the manufacturing, transportation, storing as well as warehousing, trading and the effective customer service as well as consumption. In manufacturing, climate change has the effect in changing the efficiency as well as effectiveness in the production process, plants and production line can be disrupted and it has the effect on the cost of upstream operations that is increased if the overall quality can be same. The consumer demand can be increased for the sector of pharmaceuticals (Yawar and Seuring, 2017, p.54). In Telstra, risk assessment is performed by implementing several stages such as the front line management includes the management team as well as staffs in business operations. In the second line management, it is managed by the Chief Risk officer for providing the effective methodologies that are embedded in the risks management. In the last stage, risk assessment is completed by identifying risks like technological risk and infrastructural risks.
The risk assessment in supply chain mainly includes these steps such as risk identification, assessment, mitigation and the risk control. The risks of any organisation are mainly combined with actions to mitigate as well as minimize risks. The effective supply chain management helps to increase the total market share in organization.
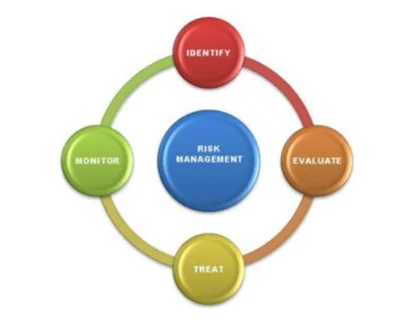
According to the viewpoint of Yawar and Seuring (2017, p.621), all risks are required to control as well as monitor effectively so that the probability of risk occurrence can be reduced. The effective risk management helps to take right decision in any circumstances so that the overall efficiency of employees can be improved and overall operating cost can be reduced. The risk can be minimized by the effective risk management along with the effective plan and the execution of that plan.
D1 Evaluation of the global business environment including the opportunities and challenges faced by the organizations.
The global business environment has the effect in the organization for reaching new clients as well as customers along with potential profits in boosting. As stated by Nadtochy et al. (2016, p.87), the opportunities of the global business market in telecommunication market to apply advanced technologies as well as improve the economic growth in the business market. In order to produce new products in the telecommunication market, global business market helps to identify the relative productivity in the competitive market. Some challenges are faced by telecommunication organizations in the global business market in making good relations with their customer. Leadership quality is required to improve by recruiting new managers (Mi et al. 2017, p.87). As opined by Teece et al. (2016, p.15), in the telecommunication a market, new communication technologies such as the internet are created that is related to the connection with networks so that the total digital world helps to meet the challenges in technology in the field of connectivity. On the other hand, Tasavor et al. (2018, p. 361) disagrees with their opinion and said that in the telecommunication market of Telstra, the overall energy efficiency is required to improve so that the environmental impact is reduced, and it helps to improve the supply chain management. It is also related to the development of the greener services as well as products. In Telstra, the sustainability performance involves factors such as global initiative and moderate assurance, which includes the reliability evaluation along with the information on sustainability performance. According to the sustainability report, this company includes 1.4 million numbers of the shareholders. This company is engaged with the 8000 number of suppliers, where the total spends is calculated as $6 billion (telstra.com.au, 2018). Telstra is the telecommunication company in Australia, who offers a broad range of telecommunication market in the entire country of Australia along with other countries like China. The markets of Telstra mainly operate the market with significant liberalization in the competitive market. According to the market research of previous years, the overall telecommunication market in Australia involves the open-market environment. This is the leading telecommunication company in Australia; updated telecommunication technology is used such as GSM-based internet connection (telstra.com.au, 2018). This connection is also can be accessed from a mobile or any smart devices. The operating processes are getting simple by applying updated technologies and it reduces the total workforce within the entire company. In order to improve the leadership quality, they open their opportunities for the recruitment of a new manager and training sessions are conducted so that other employees are trained from the new members so that their challenges are resolved. In this company, organizational structure is changed, and the operations of customer service are improved so that the challenges can be solved. New appointments are taken in many departments so that the new strategies can be implemented in their business. It helps to improve the business position of this company in the international business of telecommunication market.
Task 3 Evaluation of operation in a global market and its influences on an organization's structure, culture, and functions
P3 Evaluation of the influences of globalization on organizational governance and leadership, structure, culture, and functions
Influence of global markets and operations on an organization
The McKinsey 7s model is used in the organization to facilitate the total organizational change in management and many more. It helps to implement new strategies for identifying the effective area that can change in future. It also helps to facilitate the merger process of organizations. According to this model, there are 7 factors such as 3 hard actors like strategy, systems, and structure as well as 4 soft factors such as style, staff, shared values, and skills.
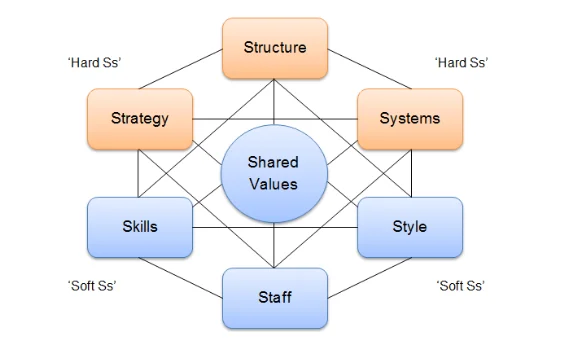
Strategy
In this factor, a plan is required to be develop by an organization so that the short-term strategy is the poor choice of organizations that are aligned with the other factors as mentioned below. Telstra is noted to be mainly influenced by the changing technology in the global market. This has resulted into implement the use of shared values when implementing the red ocean strategy in the market. It seeks to fulfil the purpose of transforming the market through bringing changes in social, cultural and economic context (Telstra.com.au, 2018).
Structure
It helps to represent the way of the business ways as well as divisions are organized, and it includes the account information such as which person is accountable to whom. Systems area are considered as the total firm area, where the determinants such as buyers’ income and many more. Organizational change is based on the changing structure.
Telstra has been noted to have a divisional organisational structure. According to Jenkins and Poole (2017, p.34), a divisional organisational structure is one in which the company is divided into various departments based on location. Telstra has been seen to already have expanded to other countries, leading it to have such an organisational structure. Despite this, it has a centralised hierarchy, which leads the company to have a shared vision, which it implements in its global operations.
Systems
Telstra has been known to use mobile base stations in its system (Telstra.com.au, 2018). This has resulted in it to implement the use of technology and innovation in its organizational system to simplify communication procedure used for providing information in tasks. It helps to reveal the daily activities of business along with the process of decision making.
The soft factors are discussed below like
Skills
Skill is the factor that identifies the competencies as well as capabilities, where new strategy, as well as new structures, can be reinforced with the existing ones. According to Blanchard and Olney (2017, p.166), it has been understood that an organisation applies the use of competency skills to excel in marketing and operational management functions. This leads it to diversify and expand in the market arena. It has been understood from the case of Telstra that the company hires employees with competent skills. Moreover, they are promoted based on a collection of skills acquired on the job in the company. This is applied in marketing operations so as to retain employees who would prove to be assets in human capital invested in by the company (Telstra.com.au, 2018).
Staff
This element is mainly concerned with employees, who are recruited, motivated, trained as well as rewarded. According to Cowin (2018, p.72), companies having a divisional organisational structure tend to have a lot of staff members. This often results in diversity in staffing and an increase in the scope of labour in the organisational staff. However, Telstra has been seen to show a contrasting result. The company of Telstra involves the use of a small staff size in each of its regions (Telstra.com.au, 2018). This lets it follow instructions and be trained properly by the company. The result is the use of competent staff in marketing operations, leading it to expand in the global market.
Style
It helps to determine the design of an organizational structure that is identified in a straightforward way. The organisational style is representative of the manner in which the management hierarchy of the concerned organisation under consideration could operate.
Shared values
The shared values are implemented in the changing of an organization, where the changes are based on the other six elements also. Telstra aims to expand further in the global market to achieve its goal of transforming the community with its simpler technology. It has undertaken this goal to bring social, economic and cultural change in its operations (Telstra.com.au, 2018). This has been done by the company with the help of its values - care, togetherness, trust, simplicity, courage along with humility and responsibility in its global operations. As opined by Trigeorgis and Reuer (2017, p.98), it can be said that the global market, as well as global operations, are influencing the Telstra organizations along with the implementation of the factors of McKinsey 7S model of an organizational structure. On the other hand, Nadtochy et al. (2016, p.87), in order to use this model, organizations can change their positions so that they can be operating their functions in the international global market. The strategy of Telstra helps to make position in the market penetration, whereas systems are totally concerned with the total processing of orders along with the business generation systems.
Influence of governance and leadership on the organization's functions
According to Willich and Worthington (2016, p.594), proper governance in an organisation, sees the direction and control of management functions in the company to ensure ethical decision-making in various business situations. This control of functions in the company is only possible with the use of communication within the firm. Telstra has been seen to implement the use of governance to support various business functions, playing a major role in the multinational organisation. It has been noted from the annual report of 2018, that governance is applied in organizational functions of Telstra (Telstra.com.au, 2018). This leads the company to implement the use of corporate governance, accountability and transparency in global business functions. It has been supported by the study of Hulme et al. (2015, p.86), transparency is implemented in governance to ensure better communication of business functions with stakeholders. Telstra has been noted to policy framework, Code of Conduct to take decisions in business. This use of governance in business leads Telstra to use clear delegation in their decision-making process. This results in the company of Telstra to put the skilled board members in the company, to implement the use of clear communications to communicate the progress of the business with the shareholders (Telstra.com.au, 2018). This could further indicate the measures applied by the top level managerial personnel while undertaking their responsibility execution and the extent as well as the methods of interaction between such organisational personnel. Furthermore, the organisational governance also involves the actions which the managerial personnel of the concerned organisations undertake and the symbolic value which could be associated with the outcomes of such actions. The governance prospects of the business organisations generally utilise the management style to better operate within any specific business environment, either laterally or horizontally. From a generalised perspective, the governance of any organisation and the influence of it on the structural integrity and functioning of the organisation could be outlined as multiplicity of factors. These could be outlined as the performance management board formulation under the ambit of corporate governance, establishment of co-ordination committee between the executive council and the broad of directors, the formulation of operations committee for the purpose of responsibility management amongst the board members, development of the budgetary committees for the proper allocation of resources and reporting of finances and finally the board of conformation and compliance management through which the internal control could be exercised by the company hierarchy within any definite organisation such as the one under consideration. As opined by Foster and Graham (2017, p.89), the governance as well as the leadership of a multinational of Telstra, which is a telecommunication organization within the international context that helps to improve the leadership situation. Each and every organization has consisted of some elements such as management, time of people, and performance in tasks. All elements are internally related so that leadership objectives, as well as goals, can be achieved within the organization. On the other hand, Fernández-Mesa and Alegre (2015, p.87) disagree along with their opinion that an autocratic leader within telecommunication organization analyses emergency situations, where the homogenous workforces are involved. As a leader, he has the quality to identify the overall inability of subordinators for the development of pride of accomplishments. As opined by Foster and Graham (2017, p.98), as a democratic leader, effective decisions are made by him based on the current situation so that the overall organizational situation can be improved and it helps to improve their position in the international business market. On the contrary, Fernández-Mesa and Alegre, (2015, p.69) opine that as a laissez-faire leader, the responsibility of him is to take decisions for making process within the group. The overall structure of groups is loose, where the ability of leadership is increased so that decision is made effectively. On the other hand, Fenwick and Edwards (2016, p.98) commented that all leaders have the influence the organizational functions along with their strategy and decisions so that they can use legitimate power, reward power, export as well as coercive power for the organization to improve the overall condition of the organization. In case of Telstra, leaders can have the total commitment on their work, good communication skill, effective decision-making power, clear view about their work so that they can execute all plans very effectively based on the international market situations. Expert opinion is also required to take effective decision along with having knowledge’s, where knowledge helps to solve most problems that are faced by the organization. The quality of eldership is improved by the improvement of all of these factors. The personality is improved by developing knowledge based on the physical as well as mental effort (telstra.com.au, 2018). According to Bolden (2016, p.145), leadership is important for directing an entire team towards the achievement of a goal. This has been supported by Deresky (2014, p.10) as per whom, leadership is the reason behind which a company undertakes specific goals like market penetration. These result in the marketing and departmental teams to collaborate and work together in order to increase productive output and performance outcome. This results in better efficiency of organisation functions. Telstra has been seen to implement the use of its own leadership team to operate its business. This has led it to undergo expansion in the global market. According to Pendleton and Furnham (2016, p.67), appropriate usage of leadership technique can uplift organisational position in market. Telstra has implemented the use of T22 strategy in its marketing operations. This has been implemented to improve the performance of the marketing department. This has been further implemented in the telecommunications business of Telstra by the establishment of standalone business along with control of assets (Telstra.com.au, 2018). Moreover, leadership has been put in use in case of Telstra to simplify the structure into a more top line-oriented structure. This has resulted in more leaders and experts to cater to the needs of the clients to increase organizational functional output.
Influence of national cultural differences on an organization
There are several dimensions in cultures such as power distance index, masculinity vs. femininity, uncertainty avoidance index, restraint vs. indulgence and the orientation in long term vs. the short-term representation. It helps to demonstrate the process of national cultural differences has an influence upon Telstra that is a telecommunication organization. According to Jippes et al. (2015, p.922), it has been understood that with differences in culture of various nations, a diversity of culture is created in the organisation. This diversity in culture has an impact on the organisational culture of Telstra.
Power distance index (PDI)
The power distance index refers to the degree of the total inequality, where the high score of PDI helps to indicate the social acceptance in an unequal, hierarchical power distribution. It is applied in centralized organizations along with more complex hierarchies, where the large gaps are present in authority, compensation as well as respect (Nawaz, 2018, p.87). The low score of PDI is related to share power that is dispersed widely. The society members are not accepting situations, where unequal power distribution is performed. The low PDI is applied in the flatter organizations, where employees and supervisors are equally considered. In the case of Telstra, as the PDI score is 1, it is identified as the flatter organization. In the case of Telstra, it helps to identify the total cultural differences based on the score. It was noted from the study of Beugelsdijk et al. (2017, p.31) that, power gap in an organisation is mainly created by the presence of a centralised hierarchy in a divisional structure. Telstra has been noted to have a divisional organisation structure. Moreover, the power gap index between the workers and the management of Telstra has been noted to be high. This has led to be a major gap in organisational functions of the company. This, in turn, has resulted in the organisation to expand, however, not expand to every market in the world.
Restraint vs. indulgence (IDV)
IDV refers to the overall strength that helps to ties people along with the other persons within the community. A high score IDV helps to indicate the interpersonal connection that includes the part of a family, where each people take less responsibility for the outcomes as well as other's actions. According to the viewpoint of Odunukan et al. (2017, p.65), high IDV score is placed in the trine of people and their privacy needs so that they can get free. The low IDV helps to emphasis in the skis building to become master of the specific field. It also helps to maintain the overall harmony among the group members that overrides moral issues, where wisdom is considered as the important factor. In the case of Telstra, it helps to identify the total cultural differences based on the score. According to Deresky (2014, p.16), restraint is understood to be control of desires while indulgence value is the freedom to do various tasks in an organisation. Telstra has been seen to have more restraint in its organisational culture. This is due to the imposition of Code of Conduct along with policy framework implemented in the company.
Masculinity vs. femininity (MAS)
MAS refer the overall distribution of roles between women and men in the masculine society to demonstrate the success within the organization. In order to identify the MAS score, a high MAS score is included in the important achievements that are related to money. A low MAS score is identified to concentrate on the overall quality of life (Clark et al. 2016, p.78). In the case of Telstra, it helps to identify the total cultural differences based on the score. According to Beugelsdijk et al. (2017, p.32), it has been understood that high masculinity index indicates the presence of masculinity in the organisational culture. Such a culture has the presence of gender roles and little to no benevolence. On the other hand, Telstra has been noted to have a low masculinity index in its culture. This shows the presence of femininity in the culture of the company where benevolent means of management are applied. Moreover, it was noted that Telstra implements moral management through its Code of Conduct which uses benevolence in the management of resources.
Long-Term vs. Short Team Orientation
Most Asian countries and Australia are known to follow a short-term orientation. However, the organisation of Telstra follows a long-term organisational culture. This has been noted especially in the application of governance by the company sees to the long-term performance (Telstra.com.au, 2018). This has resulted in Telstra to have a positive implication on the company resulting it to protect and improve the experience of the shareholders. This has resulted in it to experience a positive result with respect to economic growth, thereby expand over the global market.
Individualism vs. Collectivism
According to De Mooij (2018, p.78), individualism entails to working along as compared to collectivism where a group of people work towards a common goal. The company of Telstra has been noted to work together of becoming one of the best technology-based companies which empower its customers to keep connected with each other. This has resulted in it to apply a common platform of technology and work as a team towards the achievement of this goal (Telstra.com.au, 2018).
Uncertainty avoidance index (UAI)
The high score of UAI (uncertainty avoidance index) is implemented in the social conventions such as social norms, where people are rigid, conservative as well as structured and it requires the attitude that is more flexible. As opined by Epstein (2018, p.78), a high energy society is considered, where people are feeling normal and it means that the control is present in their emotion and they are not overwhelmed in their life at the time of taking decisions. In the case of Telstra, it helps to identify the total cultural differences based on the score. The other important factor is identified as the orientation of long versus short-term and it reflected on the importance on the brains of the statement including profit and loss, where the nationalism is involved in the social standards. According to Minkov (2018, p.233), the concept of uncertainty avoidance is the extent to which the individual is able to avoid the risks in business activities. It has been noted from the case of Telstra that, the company has a high uncertainty avoidance index value. This clearly entrails the organisational culture believes in the identification and mitigation of the risk. It helps to overcome any such uncertainties which arise in their business activities (Telstra.com.au, 2018).
P4 Evaluation of influences of ethical and sustainable globalisation on organisational functions
Ethical and sustainable factors of globalization
Business ethics calls for the morals and the principles that are required to govern the organisation’s effective conduction in the group. However, these factors play an effective role based on the other factors that call for the individual along with social factors such as the values, morals. As commented by Cheng et al. (2015, p.74), it can be said that the ethical and sustainable factors are the most important factors for the development of the organisation. There are many ethical challenges that are required in the role of promoting sustainable development in the global market. The main operational ethics generally covers the values that are required to be adopted for an organisation such as equality, solidarity, justice, protection of the environment and promoting human rights by providing required regard. These factors are generally incorporated in the organisational values however these are the most important factors that are quite hard to be implemented in the developmental stages. The proper addressing of the gap that is among the conceptualising and effective actions required critical evaluation in order to resolve it. However, establishing an effective global framework will help in mitigating such issues that need to be addressed as an organisational factor for enhancing the sustainability in the global market. As commented by Lau et al. (2014, p.45), it can be stated that a genuinely democratic and the global framework need to be evaluated based on the meaningful policies in order to encounter with the effective and enforcement mechanism of the ethics in the global market. Integration and the partnership will help in giving innovative partnerships ideas to facilitate with the sustainability in the global market in order to identify the challenges that are being faced in the global market. Since there are the factors that have generally put an emphasis on the global market will help in resolving the issues that are seen to be faced in the global market.
Ethical Factors:
Ethical codes that guide towards the sustainability
The employers and all the concerned employees in the organisation generally struggle with all the new challenges that rejuvenate on the progressive basis. This also plays a factor of reconciliation of the ethical codes and practices of the employees over the corporate ethics and the practices. The business ethics model in the global market generally calls for the corporation of the ethical codes in the business practices. This generally resolves the involvement of cutting expenses and costs, as a solution to mitigate the unsustainable business practices along with unethical practices.
The business ethics model generally emphasizes the need for effective business policies in order to meet with the effective ethical factors required for the effective business codes practices. This generally involves the factors of the virtue ethics along with the factors responsible for the utilization (Wirtz et al. 2015, p.55). This also includes certain factors that include the utilization based on the working environment and effective service delivery to outstanding with the performance in the global market. Apart from this, the factor also works as a motivational factor required for the increase in the self-determination model acts as a suitable ethical practice and area.
Professional Accountability
Professional accountability is one of the highest factors responsible for the ethical practices of the organisation. This takes a proper strength involving the action of meeting deadlines, meeting the dedicated target and also relies on inputting cognitive effort in working with the organisational behaviour. As commented by Karimi and Walter (2015, p.78), it can be stated that this generally implies the betterment of the scope of the organisation required for the effect. An Organisation that acquires the requirement of its own factors generally involves the establishment of ethical accountability in the global market.
Dedication and Commitment
As commented by Girma et al. (2017, p.74), it can be stated that the ethical factor in the organisation generally involves the factors for the guidelines of the ethical along with the behaviour based on the high amount of the importance based on the dedication and the work commitment of the employees. However, possessing the essential and required necessary skills in the strong ethics towards the work and having the optimistic attitude in the workplace carries way long in the establishment of the highest position in the global market.
Sustainable Factors:
Sustainable factors are often considered in order to make the organisation stable and effective to enhance its production in the longer run. These are often observed as the factors triggering efficient growth in the economy too. As commented by Steger (2017, p.320), it can be clearly noted that the globalisation as a factor can be processed through an organisation possessing maximum internationalisation over the national beliefs and factors. This also calls for certain structural reforms in the interface of the consumption pattern. However, the government can also play a factor in determining the pace and direction towards the pattern of the globalisation. However, there are certain tools that can facilitate the growth accepting the internationalisation such as international transportation, and telecommunications.
As per the organisation, Telstra is concerned the factor implementing several growths can be identified as a global source, that is becoming an acceptance in cheaper, quicker along with higher quality rate. As commented by Nadtochy et al.(2016, p.37), it can be said that the sustainable development of the organisation generally encounters for the sustainability that lasts for the longer duration that helps in holding positions of the organisation in the global market. The basic features that are required and responsible for sustainable development are:
Strengthening the process of decision making
Implementing and supporting the latest technologies for organisational up-gradation
Make wider and thick usage of the market
Identifying and managing links to the section including the global economy
In order to grow the sustainability of all the business along with the implementation of all the types of organisational measures, there are few elements that needed to identify and need to ensure such as:
With the policy of the organisational change, the human resource needs to be improved
Improvement in the relationships with the suppliers along with the quality of its services
Implementation of the organisational changes triggering certain business sustainability will need to be considered in terms of performing certain activities and human resource training.
As commented by Kolk (2016, p.32), it can be said that apart from this, an organisation needs to re-escalate its every dimension in order to identify certain problems and factors to rebuild its structure in order to serve the modern and the cooperation aspects to meet globalisation. Generally, there are the companies that are identified for facing loss in terms for the customer having more choices and options. On a larger note, the better service will generally ensure strong customer loyalty along with the repetitive business with them. These generally involve certain factors such as the:
NGO activities
NGO's plays an effective part in better sustainability. These factors draw the efficiency in the development of the societal factors to enhance the reasons of the sustainability (Wirtz et al. 2015, p.87). These are also helpful for the effective coherence approach towards the project development. The organisation needs to perform many activities encircled as a part of the CSR activity as the primitive factor for the development of the organisational trust and belief on the people.
Media management
Media organisations play a very important part in the establishment of the codes and practices in referring to the position and the importance of the globalization organisation in the global market. Steger (2017, p.57) suggested that while reporting the sustainable development issues media need to be coherent about the factual presentation of the organisations it reaches out to the global market scenario and also plays a vital role emphasising the policy of the company.
Transparency
Transparency is the most affluent factors that are responsible for efficient transparency in the global market. As commented by Sbia et al. (2014, p.78), it can be stated that business operations and customer choice play a very significant part in the facilitation of efficient business ethics in the global market. The labelling of the transparency will identify the several factors of labelling the sustainable factors require for the certification. The reliability of the auditing procedure must be assured in order to maintain with the availability of the resources that are generally encountered to meet with the profitability.
Influence of ethical and sustainable factors on an organisation's functions
The influence of ethical and sustainable factors plays a very vital part in the development of the organisation in the global market. As commented by Graham et al. (2017, p.67), it can be stated that growth strategies play an effective part in translating the course of sustainability in the global market that will increase the pursuit of the revenue generation along with the profit growth effectively. The sustainability of the organisation possessing globalization generally found on the basis of the internationalisation that might cause a bit pace divergent than the national policy and the cause. There are certain organisations that may identify the changed and improved work environment as a result of the process of the globalisation. As commented by Kentikelenis and Seabrooke (2017, p. 1087), it can be said that sustainability has become a major trend in the recent years as a result of the economy blast in certain sectors. Though organisational sustainability relies on maximum over the sustainability based on the finances of the organisation however other factors can easily help in identifying the need for sustainability as a prime factor for sustainability. As commented by Hotho et al. (2017, p. 110), it can be said that the impact of the globalisation need to be fully understood however on a term it is confirmed that the companies need to also require certain collaboration based on the efficiency of increasing sustainability in a fixed environment. In order to ensure success in this section companies needs to identify a certain situation of effective collaboration. As per the concerned organisation, it can be identified that the having teamed up with the exactly specified partners helps in organisational benefits such as Telstra acquired VMtech as Sydney based service provider in order to enlarge and enhance the business and accelerate its growth accordingly (telstra.com.au, 2018). It was also identified that the VMtechs's overall approach for managing as well as designing hybrid cloud solutions generally identified as an existing section of the technology as Telstra works at public interest causing them certain benefits. As per identification market analysis, it can be said that the cloud services in countries like Australia and Asia are generally identified as a rapidly growing market. In this case, it can also be an adaptation of the hybrid cloud solutions as an effective platform for expanding its business. One of the biggest ventures that are identified as a huge opportunity for the Telstra is the integration with the hybrid cloud solution required for the mange solutions depending on the unified platform. This organisation has also given a platform of the sustainability base on TELSTRA programmable Network providing connectivity to the entire consumer's cloud environment (telstra.com.au, 2018). This acquisition will certainly help in the identification of the factors of the VMtech organisation in order to cater innovative ideas and solutions to all the customers. The company responding to efficient flexibility to their customer demands needs to be listed in terms of the market leaders. This will generally help in the expansion of the organisation in the global rate. Since the company is the functional unit in the section of the telecommunication, needs to be ethically supportive in order to provide effective strategies in the global market. This will also help in the faster-growing economy that will be fuelled by the all type of economic users as a part of the consumer.
However, it can be also said that the organisational behaviour in promoting such ethics calls for a certain standard that is required for the effective ethical behaviour of the organisation in the highest global market that often works as a barrier between the professional work environment and the personal ethics (Mansfield and Reinhardt, 2015, p.74). These factors generally affect individual characteristics that emphasize personal traditional value. Since the organisation is the result of conduction of the group activities these factors play an effective role in it. The business ethics also required to identify the organisational strength in withstanding with the globalisation in the market. The ethics in the organisation generally includes the factors for the effective relationship with the corporate entities. As commented by Girma et al. (2017, p.35), it can be stated that the consumers generally put suspicion focussing on the media and its influence over the general public that are governed by the corporate entities. These play a vital part and as an ethical challenge that is required to determine the level of the responsibility requires to shape the consumers attitude that droves towards the organisational sustainability, Ethical and the sustainable factors are required to function the organisational role effectively that delivers efficient service delivery to the consumers in gaining information about the organisation.
M3 Critical evaluation global market’s influences in application to appropriate theories and models relating to organizational structure and culture
As commented by Baccini et al. (2017, p. 34), the utilisation of Mckinsey 7s framework is primarily utilised for the purpose of effective organisational design and performance management in respect to the influence of the external business environment. The involved processes are to be identified as the Strategy, Structure, Systems, Style, Staff, Skills and Shared Values which could be applied within any particular organisation. In this context, the initial step is to identify the various areas within the organisational working architecture which could have been not properly aligned with the organisational culture and mission. This involves the evaluation of all of the 7 elements of such a theoretical construct. This could be effective in terms of the determination and designing of the strategy which could better assist any organisation to introduce products swiftly by avoiding any internecine conflict of the organisational fold. The next step involves the determination of the optimised design of the concerned organisation in respect to the influences emerging from the existing globalised markets. The emphasis has to be on the outlining of the bestst possible alignment strategy of the imperatives and that of the organisational culture. The next step is about formulating of the decision regarding the actual changes which could be made within the cultural and structural operational framework of the concerned organisation. This could be followed with the implementation of the changes so as to better accommodate the influences of the globalised market disciplines and the organisational reactions to such influences in the according manner(Blonigen and Piger, 2014). . In terms of the influence of the global market on organisational culture and structure, the utilisation of the model Hofstede’s cultural dimensions to evaluate such the propensity and extent of such influences could be effective. This could be effective from the perspective of the cultural influence of any society on the values which are cherished by the members of the society. These values are, in turn, perfect determinants of the behavioural attributes of such societal members. According to (), the dimensions of any national culture could be discerned as six in number. These are Power Distance Index, which could be understood as the extent of acceptance and tolerance of unequal power distribution of power within any societal structure, the extents of individualism as opposed to collectivism, avoidance of uncertainty through differential ambiguity tolerance levels, determination of extent of masculinity and femininity prospects within the behavioural aspects and assertiveness of the members of any society, the difference between the long and short term based orientations of perspectives and the inclination towards indulgence in satisfaction of base human instincts as opposed to observation of restraint. These dimensions are reflective of the value extents of any society and these could as well be instrumental regarding the evaluation of customer preferences by various multinational organisations in the process of market evaluation and analysis. The value dimensions outlined in the theoretical construct of Hofstede are generally utilised by the global market based business organisations to build a better understanding regarding the services and product specifications which could garner better appeal for the targeted customer segments, in respect to the dominant and prevalent value dimension. The determination of such preferences and inclinations also permit the global market based multinational corporations to introduce changes and new policies to better accommodate the transformational influences of the market space where the companies could be operating.
Task 4 Evaluation of the influence of globalisation on organisational decision-making and strategy
P5 Different decision-making methods in global business environment
Evaluation of decision making of the leaders in a global context
Decision making is one of the most important phenomena in order to evaluate and initiate effective leadership and enhance the organisational position in the global market. In context to the global market and it influence strategic management is the most important feature can be adopted while making the decisions that the substantial condition provides the factorial ranges that are adapted to enhance the organisational policy in the given market. These are often made under uncertainty, volatility to mitigate the complex issues. The complexity of all the decision making is often rendered during the financial cycles of the organisation while budget deficits and also during the entitlement of the taxes. However, the effective decision making needs to be taken and addressed in the most complex issues in case of the telecommunications and services that require revisited and upgraded.
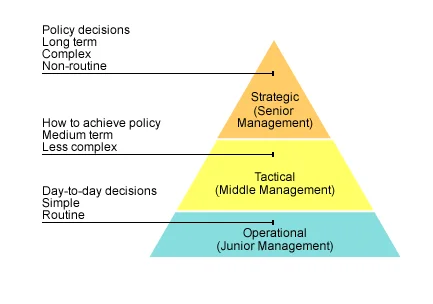
Decision making can be identified based on certain factors like effective decision making based on the certain requirements that are needed to be identified based on the effective model of the enhancement in the effective business policies. These certain decisions are based on the affectivity of the principle that is required based on the sustainability of an organisation such as:
Strategic decision: This type of decision is generally taken to facilitate the long-term and very complex decision that is generally taken by the senior management (Hollander et al. 2016, p.19).
Operational decisions: This decision generally signifies the factors that are responsible to operate in day to day life for implementing and assuring certain operations.
Tactical decisions: This type of decisions is generally less complex and made by medium grade managers. This is for the medium term only. There are designed in order to follow certain strategic norms and tries to meet the objectives that are generally being stated in order to stick to any kind of decision.
The strategic decision making is generally based on the volatility, ambiguity, complexity, and uncertainty respectively. On accounting, the leadership management based on the changes the complexity of any issues can be observed and mitigated. The general adaptation of the steps needs to be accessed based on the:
1. Identification of the complexities: Since change management is the systematic process. The confidentiality generally increases the indication of the team where the layout over the requirement of the change is given along with the reasons for the need for the change. The data analysis about the organisational complexes and the issues must be done and identified in order to mark the demonstration for the need of the change. As commented by Hollander et al. (2016, p.19), it can be said that after identification of the complexities and the issues a decision must be taken in order to identify some kind of the strategies that are required for the general adaptability of the change. Based on the complexity of the matters, the plan delivers a presentation that is required to guide the route of change explaining certain decisions over plans.
2. Identification and embracing the changes:The adaptation of the changes underlines certain principles that are required in order to process certain changes that are essential as a part of the decision-making team. The new approach that is taken by the management needs to be embraced as a direction that is taken as a point of the effective evidence in terms of the changes within the organisational structures. As commented by Quarshie et al. (2016, p.90), it can be stated that the optimistic approach is most important in order to identify and accept these kinds of changes. The acceptance of the change needs to be embraced equally among all the team members in order to ascertain the decisions that are taken as a part of the organisational benefits. In accordance with it, the acceptance of such endeavours increases the affectivity of certain decision making.
3. Seeking feedback from the employees
In order to maintain a certain harmonious organisational environment, all decisions must be embraced equally as in accordance to the organisational elite. As a key responsible person for certain acceptance changes, every team member must be equally feeling responsive and accepted as a team member while assuring the change acceptance. Equal feedbacks must be observed as an important in order to escalate further issues and problems. As commented by Kujawińska et al. (2015, p.200), it can be noted that the changes also involve certain layers of the problems in every sector of these layers containing certain employees and workers. For instance, in order to generate efficient productivity in consumer goods such as purchasing connections and goods may involve different sections of a team with the manager to grounded employees. All level work satisfactory must be acknowledged after finding out the changes. This will also be benefitted as the implementation of the structured plan that is equally organised and addressed.
4. Proving proprietorship
As the transitional period is established the organisation along with its employees undergoes a various type of the challenging task that is generally escalated while working seems in the progress in order to identify such issues and have a quick resolution about it a position for owner ship is required. As commented by Andrews et al. (2017, p.1773), it can be noted that the assigned team must have a team manager or owner to commence the task efficiently. In some of the situation, it can be observed as an overall progress in the task with all kind of steps and process that are involved calls for accountability. Generally, the decision making helps in working out of the issues that are assigned and governed in order to identify such problems and find effective resolutions for it. Apparently, the changes are results of increasing efficiency in the process and productivity in the organisation.
5. Accountability based on the subtle changes
The transition of all the angles is very important to efficiently impose such changes in the organisation for effective working. As commented by Disterheft et al. (2015, p.20), it can be noted that there are the instances where the bigger issues are identified and smaller issues are often seen escalated out without being addressed. In such a situation, it often becomes loopholes in the part of effective decision making as it generally governs the bigger over the smaller ones. However, the addressing of small transitional issues may be working more affecting issues in smooth work, that are often need to be addressed in order to identify the aspects of the decision making and work accordingly.
6. Management based on transitions (global context)
The effective management of the transitions is very important in order to identify certain types of the changes based on the decision making to increase the organisational affectivity in providing the customer satisfaction in the terms of holding a certain position in the global market. In order to maintain the required decision-making impositions on the organisation, sudden assessment is often required in order to maintain with the impact of the changes in the organisation. In order to resolve certain minor issues or the major one, there can be again the requirement of the decision making. As commented by Teece et al. (2016, p.34), it can be noted that the flexibility based on this needs to be identified and escalated so that affectivity in the implementation of the decisions needs to be identified and worked accordingly. The acceptability of any kind of the changes is never easy, however, it’s a part of evolution based on the individual, organisational or the team level. The proper outline of the transitions including the involvement of everyone, planning, and preparing makes this task smoothly deliverable.
Accepting changes based on the global context are never easy but these are an important part of the organisational benefits. Involving effective planning and establishing strategies in context to global terms are very important to make the enhancement of the organisation in the global market position. As commented by Disterheft et al. (2015, p.20), it can be noted that the decision making will help in the evolution of the individual team in the organisation, preparing the layout of the groundwork, consideration of the parties that are involved in organisational enhancement and preparations and planning based on the certain transitions escalating certain shortcomings in the global market. According to Nagle and Müller (2017, p.28), globalisation in a business environment has mainly impacted the decision-making activities in telecommunications companies like Telstra. The use of collaboration of resources through those available all over the globe has resulted in the company to be able to deal effectively with the demand for communication services by customer all over the globe. This has resulted in the use of a common SMART platform. This use of technology and innovation strategy in globalisation has resulted in Telstra to provide 2406 devices to 297 client enterprises all over the globe. Another decision-making method implemented in global business is using ethical decision-making. According to Ferrell and Fraedrich (2015, p.20), it has been understood that the application of ethical decision-making in business has become very important in cases of business. This has been done using trade regulations, Labour rights imposed by the ILO (International Labour Organisation) and the trade centres all over the world and more. It has helped to reduce chances of lack of proper distribution of tasks, promoted training of staff through a CDP leadership programme at Telstra. This has resulted in Telstra to raise awareness about ethical decision-making by spreading awareness. This has resulted in an increase of decision-making at the company.
Reduction of impacts of barriers on international trade by decision-making
Trade barriers are generally criticised based on the effect required for developing the work efficiency in the global market. Trade barriers generally include certain places such as the imports, subsidies for all the farmers in the developed economies, taxes on the food that leads to dumping on the world markets and overproduction reasoning to the lowering of the costs. On the other hand, Tariffs are also empowered towards the anti-poor showing low rates for all the raw commodities and high rates required for labour processing in goods. The decision making based on the reduction rate of international trade generally encounters the increased employment ability and the division of the labour that is required to provide output based on the economic scale, employees working based on their specialization, often responsible for the better production and certain comparative advantage and all the involving firms and employees working based on the specialised training program to increase their productivity influentially. According to Fawcett and Parag (2017, p.330), one of the major trade barriers is the aspect of carbon emission policy. The aspect carbon emissions have been a major issue which has been coming up with the rise of trade activities all over the world. Telstra has been seen to be mainly influenced by the policy to implement the same in its decision making resulting in the company to execute the environment solutions in its trade practices. This has resulted in Telstra to successfully reduce carbon emissions by 24% in the production and marketing of mobile phones in its global market (Telstra.com.au, 2018). Telstra has been noted to undertake the use of a sustainable strategy as a means of reducing the impact of trade barriers created through electronic wastage in business decisions of the company. According to Deandrade et al. (2015, p.216), electronic wastage in international trade often is a result of complex technology used in communication. This often leads to the formation of communication gap and loss of time in decision-making by the management. Telstra has implemented the use of Telstra 2022 to implement a simpler technology platform in its business activities. This has been done to reduce all competitions by improving customer services. The management combined sustainability strategy along with technology strategy to reduce customer pain points, thereby reducing time wasted in decision-making and increasing profit outcome (Telstra.com.au, 2018). Moreover, it has been seen to implement the use of ethical decision-making practices to reduce the risks in business. This has resulted in Telstra to engage in responsible business. The use of this approach in decision-making has resulted in the said company to establish a strong value-based culture in its business operations. The application of such a value-based culture framework a and moral management in decision-making resulted in an increase of transparency in communication with stakeholders and shareholder. It is even expected that it was brought about certain changes in the structure of the company, reducing the power distance between members in the organisation (Telstra.com.au, 2018). Telstra was seen to implement the use of ASX Corporate Governance Principles in its business operations. The application of such resulted in the company to reduce barriers created in trade activities of Telstra. According to Bazerman and Sezer (2016, p.97), implementation of both ethical decision-making along with technology strategy in making decisions in respect to the business environment, enhances chances of quicker decisions being taken by the management at the appropriate timing. This leads to an improvement in services and earnings. The very results were seen when Telstra combined sustainability and technology strategies in ethical decision-making. The use of customer service points for checking the effectiveness in business. This led Telstra to experience not only a major reduction in barriers in the trade by even reap an increase in profits from 1.5 billion AUD to 2.5 billion AUD. Not only this, it even experienced a reduction in loss of costs in wastage by 1 billion AUD per year (Telstra.com.au, 2018).
P6 Determination and articulate the various routes to internationalization an organization may adopt, including key barriers.
Strategic international expansion routes
The routes to expand in the global markets need to be adopted strategically so that the risk of the loss of the company could be avoided. The strategies to expand the global business must be systematically framed based on the analysis of the company’s current market position, financial health and the degree of competition with other countries in the same area of interests (Mansfield and Reinhardt, 2015, p.70). The telecommunication companies adopt the strategies in order to avoid risk and accept the benefits of diversification. Every business wants to be globalized in this modern world. Every business wants to enter a market where there are no barriers to carry on the business smoothly. Globalization refers to the idea of making the business globally so that the company can expand the business and can also achieve its goal.
Franchising the brand
Telecommunication companies have a better option of franchising the brand in the new global markets as it helps the company to ally with the local companies so that the customers can be reached easily (Mansfield and Reinhardt, 2015, p.71). This strategy is very useful while expanding the market in developing countries and the countries with diversified social and cultural backgrounds. Franchising with the local companies help the global company to understand the local demands and expectations on which the business decisions can be made. This is also useful in the diversification of the business in different sectors like health, education and public governance. However, the telecommunication companies must deal with the healthy local entities so that no financial burdens are placed on the. In the case of Telstra, it can franchise with the Chinese’s telecommunication companies such as China Mobile Company in order to survive in the Chinese markets.
Franchising of the brands is a way that can enable a company to enter into the new markets. Company can take its existing business model which is successful then make an agreement in the target market with a franchise and then the door of internalization will be opened. If the brand of the company is not recognized in the country, then the company should be used the process of franchising that means putting the company brand in the hand of others which is quite risky (Nadtochy et al. 2016, p.36).
Direct exporting
In the view of Boban (2016, p.191), direct exporting by a global company to the new markets in order to expand the market in new countries is a beneficial route as the cost of production in terms of equipment, cost borne on the human resource could be avoided. Telecommunication companies can direct export their service to the developed countries as the expenditure in these countries is very high. Developed countries like the US, the UK and Australia itself have infrastructure and equipment required for telecommunication system. Therefore, Telstra does not need to develop infrastructure in these countries rather it can easily export its services to these countries from Australia. However, exporting to developing countries would not be a good decision as the developing countries lack infrastructure and therefore, installation of infrastructure must be done at first at cost. As opined by Arvis et al. (2018, p.74), the second route is direct exporting which is the most common strategy adopted by the business to makes its business global. The company sells its product directly into the target market in which the company plans to enter. Direct exporting is done through distributors and agents of the company. These are the most important people of the company because they bring the products of the company into the international markets. According to Baccini, Pinto, and Weymouth (2017, p.78), direct exporting is same as selling the products of the company in the domestic market through appointing agents and intermediaries.
Partnership with a foreign company
Blanchard and Olney (2017, p.98) commented that the third strategy for internationalization for a telecommunication organization is to develop partnerships. This is a strategy which is adopted by the company to go global so that it can expand its area of market of doing business. This is a strategy of making partnership with a foreign company who has investment in all the dimension of the business. As commented by Baldwin and Lopez-Gonzalez (2015, p.69), by doing partnership with a good partner can help the company to know more about the market in which the company is trying to enter.
Acquisition of other companies
The other approaches are acquiring the business of foreign company, venturing the business. By acquiring the business of the foreign country Telstra can expand its business in new markets. Acquisition can help to know the policies adopted by the other company to go global. Acquisition can also help to expand the market of business product. Acquisition of other company can result in profit for the company and is not so expensive (Bryson, 2018, p.44). It is also not very risky to expand the business as offers many advantages to the company as the company can get another company supplier, customers, investors, technology used by other company. Company can also get the market power and goodwill of the other business which has been acquired by the business. Another approach is merging with a foreign business which has reputation in the market. Merging also offers different advantage to the company. Company can increase the dimension of the products in different market. Company can also get new technology for its products and can also enhance the market area of the products.
Use of foreign direct investment
Prior to expanding in the market, the governmental policies of trade tariffs and foreign direct investment need to be understood by the company very well. Countries like Singapore, Malaysia, the UK, Hong Kong and Japan are friendly to the foreign companies as they have good FDI policies (Bryson, 2018, p.43). Telecommunication industry depends on the governmental intervention for its expansion and therefore, it requires a good FDI policy to expand its market. Telstra must focus on those countries which provide better trade facilities. In addition to that, Telstra also need to see if a country having a good FDI portfolio is politically stable or not. Political unrest of a country and subsequent changes in the government may affect its FDI policy. As a result, it may become rigid to the foreign companies in the following FDI policies. Telstra also take consideration of those economies which are not susceptible for the growth of foreign companies. According to Kentikelenis and Seabrooke (2017, p.1066) some countries like China encourage the foreign companies to enter their markets but keep their domestic companies at a privileged position with the help of trade restrictions and hindrances. As a result, the foreign companies cannot manage to expand their business and increase their profits. Telstra needs a strategic management group taking participation in the decision-making process to avoid the risks and achieve the benefits of the routes to expansion. As commented by Fenwick and Edwards (2016, p.87), foreign direct investment is also another approach of going global. Foreign direct investment refers to investing in another company market of its products. Company products are sold in different company market as per the policies of foreign direct investment. Different company has different policies of foreign direct investment.
Key barriers to expansion routes
The following factors have been identified as the key barriers to the expansion routes of Telecommunication companies, in general, and Telstra in particular.

High cost of entry
Telecommunication industry requires high grade infrastructure before beginning its actual operations which requires high cost and high expenditure on the part of the company (Harb, 2017, p.98). Therefore, Telstra must enter such markets which already have infrastructure or the cost of installing the infrastructure is ignorable and it can produce enough profit margins by doing business in those countries. The impact of this factor on the strategic operations of Telstra could be comprehended in the manner of renewed emphasis on reduction of gross production costs and formulation of joint ventures and new partnerships to utilise local resources so that the forward investment cost could be kept to a minimum. Furthermore, the services of the company of Telstra would be generally influenced by the uptick in the cost structure since the greater could be the forward investment regarding the achievement of the cost parity with the leading market competitors, the greater would the sales price and offered costs regarding the entire range of services and products which could be offered to the customers. In this context, Telstra could employ high cost of entry opposing strategy which could effectively negate the pressure from high pricing. The strategic components could be undertaking of short terms based actions and the reorientation and repositioning of the entire organisational marketing and sales performance so as to develop effective action plans to modify the pricing pressures to gain the best possible advantages. The high cost of entry would thus be necessitated to be negated through the performance of total cost analysis under the ambit of determination of the potential scenarios. The relative attractiveness of services advantage process could be utilised by Telstra to highlight the trade-offs which the customers could make in between the offers which could be available. This could permit Telstra to deliver the greatest measurfe ofo benefits to the customers under the smallest increases of comparable costs.
International trade and business tariffs and political instability
Trade war and trade barriers are the worst barriers to the expansion of the telecommunication company including Telstra. The current global political scenario is quite unstable as various nations are engaging into the trade wars with each other and the global trade organisations like World Trade Organisations are unable to tackle the situations (Kolk, 2016, p.26). As a result, the global trade and business is also becoming unstable. In this situation, the impact of this factor on the global business strategy of Telstra is that the company must focus on those countries like China, Japan, the US, Germany and others that have bilateral partnership with Australia to stay on the safe side in the global business environment. Regarding the strategic implications of trade tariffs on the policies of Telstra, negotiations could be utilised by the company under consideration to improve the prospects of gaining greater leeway from the national governmental organisations which could be controlling the telecommunication regulatory frameworks of the various respective national regions. Furthermore, the company of Telstra needs to focus on determination of the appropriate national engagement regions throughout the world through evaluation of the respective tariff policies of different nations so as to determine the best possible approaches regarding the investment of efforts in terms of market penetration. On the other hand, the factor of political instability could jeopardise the efforts of Telstra to a considerable extent and this could only be managed through the adoption of the strategic policy to completely avoid such political clash points where instability could emerge. In this context, the careful evaluation of the global political trend by the company hierarchy and public relations department of Telstra could be one of the strategic approaches which could prove to be effective in negation of the effects of such problems on the strategic progression efforts of the company under consideration.
Unavailability of skilled workforce and technological barriers
Telecommunication industry depends on the skilled workforce and, hence, the availability of the skilled workforce in the country of trade is very essential to source the local workers in the business operation. Another barrier would be certain technological barriers. These barriers are often identified as factorial changes for the global international market. This problem could be overcome with the strategy of direct export from one country to the others. However, this is not a feasible strategy in the case of doing business in the developing countries and sourcing the skilled labour in those countries locally is very essential. The overcoming of these barriers could be made possible by Telstra on account of the implementation of two specific approaches. The first one could be envisaged as transfer of experiences and gained knowledge from the country of origin to the country of operations to train and enhance the skill measures of the existing and available localised workforces. The next approach could be considered to be the outsourcing of talented and skilled professionals through third party based operational elements where Telstra could come into agreement with various third party companies and institutions which could provide the organisation with adequately skilled and appropriately experienced human resource personnel. In terms of the overcoming of the technological barriers, the strategy of the company under consideration could be influenced through the consistent updations which could be available in the global market regarding the technological innovative applications which could be under development and could be getting launched withn short notices. The access to trade fairs and technological novelty based business exhibitions could prove to be effective for Telstra to formulate the most effective research and development bases for the R&D department of the company. This could further enable Telstra to equip itself with the latest technological assets and to keep abreast about the different technological developments in the telecommunication and entertainment arena on a global scenario. Another impact would be appointing skilled labour and employees and highly qualified professionals in foreign country to successfully run the business.
Quality of living of population
Developing countries are a great destination for the global telecommunication companies as these countries are always ready to expand their communication infrastructure ensuring the growing market. However, in the view of Boz et al. (2015, p.57), telecommunication companies must determine whether the consumers in the country can meet the cost. In the case of Telstra, it can collaborate with the governments in the developing countries so that the issue of purchasing power of the populace does not affect its growth. The barriers could be per capita income. Thus the Company under consideration, regarding the changes such a factor could introduce concerning the strategic considerations, should make a survey of the population of the country it intends to perform the future business operations. That country where the per capita income is not as per the expectation, company should not expand its business in that market. The sectors of health and education are the important sectors that the governments emphasise, and Telstra must take venture in these sectors to expand its presence at the global level.
Language barriers and unfamiliarity with new cultures
Another barrier would be language because the firm does not the knowledge of other country which could create problems to run the business successfully. Telstra can also face the barriers of setting the business in the new market. According to Boz et al. (2015, p.87), the impact of the linguistic barrier on the operational capability of Telstra could be understood from dual perspectives. The first one is related to the unfamiliarity prospects regarding establishment of direct communication with the targeted customer segments and the next one could be understood to be the uptick of market evaluation costs since hiring of translators and interpreters would be paramount for the company. Thus, the company would have to be cognizant regarding hiring of localised personnel with the knowledge of local and regional linguistic dialects to formulate the direct communication strategic considerations in tandem with the organisational objectives.
Demographic barrier
Age demographics can be another issue that a company can face while making its business globally. As opined by Brandenburg and De Wit (2015, p.98), company must understand the demographics of that country where they want to do their business. Telstra must understand the taste and preferences of different age groups of the country. In this context, the prevalent impact on the strategic considerations of Telstra could be noticed in the manner of formulation of age based product preference profiles and to utilise the data to perform changes in the existing goods and services of the company as well as to formulate new and better appealing products for the prevailing demographic groups.
M4 Critical analysis of key barriers
According to Boz, Bussière and Marsilli (2015), the problems of control and complications regarding operating within a global market environment are multifarious. One such problem could be outlined as the factor of clash of interest which remains to be the most intractable complication regarding operational aspects of multinational organisations in the global business perspective. Under such a complication, concerning the selected organisation of Telstra, the point of inflection could be noticed in the form of the financial policies of the global firms which are mostly designed to garner the maximum profit and benefit of themselves and these policies are not designed to pay any attention to the benefits of the host countries. According to Blanchard and Olney (2017). this is a form of inherent bias regarding the corporate policies. There are three dimensions to the conflict which arises out such complications. The first dimension of conflict takes place in between the various departments of the corporate organisations which could be operating internationally. The second dimension of conflict arises out of the clash between competing multinational organisations within any definite market sphere and the final dimension of conflict could be observed, as per the research of Bowen, Baker and Powell (2015), in between the organisations and the host country. Bryson (2018) has highlighted the fact that such conflict is generally accentuated through the utilisation of different corporate schemes and plans through which the gross earnings accumulated from the host country based markets could be shifted to other operating destinations such as other host nations where the prospects of Foreign Direct Investment could be more lucrative in terms of investment within particularly promising sectors from where the maximisation of profit earning could be achieved. This shifting of earning could be further encouraged through the considerations such as taxation avoidance, risk minimisation possibilities and to avail better competitive prospects. This could contribute in the fostering of successful global collaboration for the purpose of achievement of accurate coordination in international ventures The engagement in operations of globalised market environment leads to the emergence of a host of other challenges and complications for any business organisation under consideration. Such challenges generally influence the competitive capability and the associated advantage or disadvantage which any such organisation could have within the globalised market scenario. Apart from this, the prevalent complications and challenges are also reflective of the determination of the achievement of economies of scale and realisation of the scope of development regarding the improvement of business prospects. The primary challenge in this regard is to ensure proper synergistic operational cohesion within the globalised market environment where different national scenarios could present unique challenges such as impacts of international trade and commerce regulations as well as legal stipulations in this regard, management of the environmental effects of globalisation and the previously mentioned necessity to realise the economies of scale and finally, the proper management of international supply chains so that products and services could be provided to the targeted customer segments within the determined time limit as well as the prevention of acquisition or production related cost overshoots could be definitely ensured. The key barriers which Telstra has to undergo when doing business internationally are the power distance in the organisational structure along with the trade policies it experiences in import and export of goods (Deresky, 2014, p.56). The shipping activities often result in carbon emissions and production leads to loss of electronic wastes (Telstra.com.au, 2018). It would be recommended in such circumstances to implement recycling of electronic wires and batteries in making phones and data chips for providing connection services to the customers in global trade. Moreover, Telstra should keep practising ethical decision-making to overcome any legal risks involved in the import of materials for its global business.
D2 Strategies adopted by organisations operating in a global business environment
Every business is necessary to be constructed on the basis of the most suitable set of frameworks which could be defined from a realistic perspective. This involves the nature and the point of conductance of such a process of development of the business operation. This specific set of frameworks is primarily structured on the legal stipulations which could entitle the proprietors of such businesses to undertake specific approaches regarding fulfilment of particular business necessities. These necessities could be related to various issues such as the management of flexibility within the organised business operations, the maintenance of the confidentiality related to the data and information of the business processes, the proper management of taxations as well as finance generation. Strategic global business techniques are completely incumbent on two mainstays of institutionalization of standards of products and services and adjustment which have been indicative of the prospects of inculcation of the effects of change regarding the ebbs and flows of the existing market conditions. () has observed that the global conditions related to the functioning of businesses are comprised of unique sets of circumstances which delineate different criticalities of strategic considerations which any business organisation such as the Telstra could utilise to better the prospects of profit maximisation within the globally competitive market scenario. The variables of product diversification and differentiation are pertinent on account of both national and global strategic business methodologies in the wake of rising rivalry in both the national and international markets. Global strategic business methodologies have been developed because of globalization and internationalization of the hitherto domestic business organisations and new entrants within the current global market have to experience extensive and tough competition from the previously established multinational business firms as well as from the domestic business organisations which had previously been entrenched within the entire national market sphere prior to the opening up of the markets under the effects of Globalisation process. Such competition based challenges could be outlined to extend in both the product as well as the service markets within the respective regional and national sectors. These national and regional markets involve the countries which have been industrialised recently as well as those markets which could have been protected by different national customs and legal barriers prior to the advent of Globalisation. According to Cowin (2018), the primary strategic considerations are two in number. The first one could be identified as the incidence of Foreign Direct Investment method through which organisations could gain access to the internal markets of any specific and targeted nation. This comes within the long term based operational planning which could be a understood to be the direct outcome of consistently changing market landscape and the volatility in the global trading scenario. The second one could be comprehended to be the networks of physical and social kind through which the entire range of goods and services could proliferate throughout the intended international market spaces. Bresciani, Thrassou and Vrontis (2015) has outlined the necessity of application of various techniques of rational action which could be effective for the analysis of the strategic complications which emerge as outcomes of uncertainties in the global economic and market based scenarios. According to Boban (2016), the most accurate theoretical constructs regarding the international business processes could be directly based on the approaches of evaluating the global networks of intra-organisational communications through which the proliferation of both information and products could be achieved.
Conclusion
This project is concluded based on analysing the key factors driving the globalisation in the entire world. This section has covered the area of all the factors affecting cost, markets, commercialization, and trading. Several concepts of the globalisation including certain cultural, political, social and economic dimensions are concluded here. The explanation based on the impact of the digitalisation on the global market has been also concluded here. Several strategic complexities are also discussed here that are being faced by the organisation while operating the plans in the global market. The challenges faced based on entering the global business as a fresher organisation has been also concluded here. The explanation of the strategic challenges is also mentioned here. Recommendations to overcome certain challenges are also discussed here.
The resultant of the evaluation of the global business management is also discussed here explaining the opportunities and the challenges that are faced by it. Evaluation based on the influence of the globalisation in the organisation has been also discussed here explaining the organisational governance and the structure based on effective leadership and the business ethical policies for increasing the sustainability in the global market. Many challenges and barriers resulting in strategic management are also discussed and concluded here while maintaining with the operational management globally. It has been concluded from the above report that, Telstra is mainly influenced by the changing technology in the global business market. This changing technology influences its business operations. Moreover, it has a divisional organisational structure with a centralised hierarchy system. This results it has chances of experiencing a power gap when taking decisions. Along with this, Telstra shared common goals and values and has a competent staff who perform well to let the company be positively influenced by the global economic environment, leading to global expansion of the company. It has been further concluded from above that, Telstra implements the use of corporate governance along with Code of Conduct and leadership in its operations. This results in it to follow its goal of becoming a technology-based company empowering its customers with connection and technology. Moreover, the company has a high-power index, low masculinity index, high uncertainty avoidance, restraint, collectivism and long-term orientation in its culture. This results in it to experience complications in the communication of instructions in the business operations. Furthermore, it uses the approaches to ethical decision making along with technology and sustainability. However, it would be advisable to find greener ways of production to reduce electronic wastes in trade which could act as a barrier for Telstra in the global business environment.
References
Adegbite, E., (2015). Good corporate governance in Nigeria: Antecedents, propositions and peculiarities. International Business Review, 24(2), pp.319-330.
AKPAN, C.S., (2017). The impact of the new communication technologies on the broadcast industry. International Journal of Communication, 1(1), pp.25-100.
Andrews, M., Schank, T. and Upward, R., (2017). Do foreign workers reduce trade barriers? Microeconomic evidence. The world economy, 40(9), pp.1750-1774.
Aquino, H. and de Castro, J.M., (2017). Knowledge internalization as a measure of results for organizational knowledge transfer: proposition of a theoretical framework. Tourism & Management Studies, 13(2), pp.83-91.
Arvis, J.F., Ojala, L., Wiederer, C., Shepherd, B., Raj, A., Dairabayeva, K. and Kiiski, T., (2018). Connecting to Compete 2018: Trade Logistics in the Global Economy. World Bank, 54(2), pp.87-100.
Baccini, L., Pinto, P.M. and Weymouth, S., (2017). The distributional consequences of preferential trade liberalization: firm-level evidence. International Organization, 71(2), pp.373-395.
Baldwin, R. and Lopez‐Gonzalez, J., (2015). Supply‐chain trade: A portrait of global patterns and several testable hypotheses. The World Economy, 38(11), pp.1682-1721.
Bauer, F., Matzler, K. and Wolf, S., (2016). M&A and innovation: The role of integration and cultural differences—A central European targets perspective. International Business Review, 25(1), pp.76-86.
Bazerman, M.H. and Sezer, O., (2016). Bounded awareness: Implications for ethical decision making. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 136, pp.95-105.
Blanchard, E.J. and Olney, W.W., (2017). Globalization and human capital investment: Export composition drives educational attainment. Journal of International Economics, 106, pp.165-183.
Boban, M., (2016). Digital single market and EU data protection reform with regard to the processing of personal data as the challenge of the modern world. Economic and social development: book of proceedings, p.191.
Bresciani, S., Thrassou, A. and Vrontis, D. (2015). Strategic R&D internationalisation in developing Asian countries??? the Italian experience. World Review of Entrepreneurship, Management and Sustainable Development, 11(2/3), pp.200-216.
Clark, W.C., Tomich, T.P., Van Noordwijk, M., Guston, D., Catacutan, D., Dickson, N.M. and McNie, E., (2016). Boundary work for sustainable development: Natural resource management at the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(17), pp.4615-4622.
Deresky, H., (2014). International management: Managing across borders and cultures. London: Pearson.
Epstein, M.J., (2018). Making sustainability work: Best practices in managing and measuring corporate social, environmental and economic impacts. Abingdon: Routledge.
Foster, C. and Graham, M., (2017). Reconsidering the role of the digital in global production networks. Global Networks, 17(1), pp.68-88.
Graham, M., Hjorth, I. and Lehdonvirta, V., (2017). Digital labour and development: impacts of global digital labour platforms and the gig economy on worker livelihoods. Transfer: European Review of Labour and Research, 23(2), pp.135-162.
Heckmann, I., Comes, T. and Nickel, S., (2015). A critical review on supply chain risk–Definition, measure and modeling. Omega, 52, pp.119-132.
Hollander, R., Amekudzi-Kennedy, A., Bell, S., Benya, F., Davidson, C., Farkos, C., Fasenfest, D., Guyer, R., Hjarding, A., Lizotte, M. and Quigley, D., (2016). Network priorities for social sustainability research and education: Memorandum of the Integrated Network on Social Sustainability Research Group. Sustainability: Science, Practice and Policy, 12(1), pp.16-21.
Jippes, M., Driessen, E.W., Broers, N.J., Majoor, G.D., Gijselaers, W.H. and van der Vleuten, C.P., (2015). Culture matters in successful curriculum change: an international study of the influence of national and organizational culture tested with multilevel structural equation modeling. Academic Medicine, 90(7), pp.921-929.
Kujawińska, A., Vogt, K. and Wachowiak, F., (2015). Ergonomics as significant factor of sustainable production. In Technology Management for Sustainable Production and Logistics (pp. 193-203). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Nadtochy, Y.V., Klochko, E.N., Danilina, M.V., Gurieva, L.K., Bazhenov, R.I. and Bakharev, V.V., (2016). Economic factors and conditions for the transformation of the education services market in the context of globalization. International Review of Management and Marketing, 6(1S), pp.33-39.
Neubert, M., (2016). Significance of the speed of internationalisation for born global firms–A multiple case study approach. International Journal of Teaching and Case Studies, 7(1), pp.66-81.
Pinto, P.M. and Zhu, B., (2016). Fortune or Evil? The Effect of Inward Foreign Direct Investment on Corruption. International Studies Quarterly, 60(4), pp.693-705.
Rajesh, R., Ravi, V. and Venkata Rao, R., (2015). Selection of risk mitigation strategy in electronic supply chains using grey theory and digraph-matrix approaches. International Journal of Production Research, 53(1), pp.238-257.
Ribau, C.P., Moreira, A.C. and Raposo, M. (2015). Internationalisation of the firm theories: a schematic synthesis. International Journal of Business and Globalisation, 15(4), pp.528-554.
Sbia, R., Shahbaz, M. and Hamdi, H., (2014). A contribution of foreign direct investment, clean energy, trade openness, carbon emissions and economic growth to energy demand in UAE. Economic Modelling, 36, pp.191-197.
Snyder, L.V., Atan, Z., Peng, P., Rong, Y., Schmitt, A.J. and Sinsoysal, B., (2016). OR/MS models for supply chain disruptions: A review. IIE Transactions, 48(2), pp.89-109.
Trigeorgis, L. and Reuer, J.J., (2017). Real options theory in strategic management. Strategic Management Journal, 38(1), pp.42-63.
Wirtz, J., Tuzovic, S. and Ehret, M., (2015). Global business services: Increasing specialization and integration of the world economy as drivers of economic growth. Journal of Service Management, 26(4), pp.565-587.
Yawar, S.A. and Seuring, S., (2017). Management of social issues in supply chains: a literature review exploring social issues, actions and performance outcomes. Journal of Business Ethics, 141(3), pp.621-643.
Zhang, Y., Jin, Y. and Tang, Y., (2015). Framing depression: Cultural and organizational influences on coverage of a public health threat and attribution of responsibilities in Chinese news media, 2000-2012. Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly, 92(1), pp.99-120.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



