Unilever’s Global Success Strategy
1.0. Introduction
Unilever is a British-Dutch multinational firm that manufactures and sells consumer goods in over 190 countries. Unilever is one of the most successful and most recognized brands in the world, commonly used by people worldwide. The company is supported by the power of its eight international brands: Sun Silk, dove, clear ponds, magnum, Vaseline, Rexona, and lux. Unilever has entered most of the markets and has started competing with other brands worldwide. This report reviews the case study of a United Kingdom-based, multi-billion dollar company known as Unilever. This report reviews how Unilever UK's primary aim is to meet the daily needs and wants of a consumer by providing rich, nutrition, hygiene, and care brands. The analysis of the company will rely on SWOT analysis and PESTLE, which are specifically meant to give us a general overview of the strength and future of the company.
2.0 The business model of the company
According to Cheng, (2021) the business model of the company begins with consumer insights. Their main purpose is to take care of consumer interests through brand innovations, manufacturing, sales, logistics, collaborations, and sourcing sustainability. In the world today, Unilever is the number one supply chain with 306 factories and has invested heavily in inefficiency and eco-production. Unilever uses its centralized operations network with global logistic towers with the intention of improving consumer services, reducing CO2 emissions and cutting costs. The company uses the media as the primary means of advertising its goods and services. They primarily use a digital marketing strategy that has proved very effective because it influences consumer shopping at all stages of their decision-making. Unilever collaborates closely with local and international retailers to gain market share. They make sure that their brands are always available for retailers and properly displayed in all places, from e-commerce to supermarkets. Consumer insights help the company predict consumer trends to maintain its competitive advantage in the market. Their marketing strategies also involve working closely with non-governmental organizations, governments, and other stakeholders to change society and the business.
3.0. Review of Unilever Company
Unilever is an all-around customer merchandise company that produces food, drinks, cleaning items, and individual consideration items. The company was founded in 1929 as a merger of a margarine and cleanser processing plant, and it now has over 400 brands.Knorr, Dove, Axe, and Lipton are a portion of Unilever's most notable brands. As far as deals go, the Unilever Group was named the world's fourth-biggest FMCG company in 2019. Unilever's picture in the worldwide media is to a great extent sure, with the organization being introduced as mindful and inventive (Abubakari and Thuranira, 2021). Personal care is the Unilever Group's biggest item category, with deals of generally 21.1 billion Euros in 2020. That year, the organization acquired around 59.8 billion US dollars in deals. Unilever is headquartered in the Netherlands and the United Kingdom, but the vast majority of its revenue is generated elsewhere on the planet, primarily in the United States (Ahmed, 2019). In 2019, Unilever spent more than 1.36 billion US dollars on advertising in the United States alone. Unilever is a global innovator in FMCG classes like home consideration, fabric care, and skincare (Chernobay, Yasinska, and Malibroda, 2020). Unilever's most important brands, Dove and Axe, both make antiperspirants and antiperspirants. Unilever held 36% of the global antiperspirant market in 2013, but therapists expect this figure to fall to 26% by 2020. In 2019, Dove was the smash hit antiperspirant brand in the United States (Chernobay, Yasinska, and Malibroda, 2020).


3.1. Analysis of the Unilever competitors
The organization is predominantly portioned into four divisions which are Foods and refreshments, beauty and personal care, water purifier and home care. These divisions are in consistent development due to the developing interest because of populace development. Also, the water purifier is outstanding as its developing at a quicker rate since individuals need water purifiers in their homes to stay sound (Cheng, 2021).

Figure 2 shows how multinationals Unilever and Procter and Gamble control the Home Care and Personal Care markets. Since L'Oréal Group doesn't contend in the Home Care industry, note that the French firm has a generous piece of the pie in the Beauty Industry.
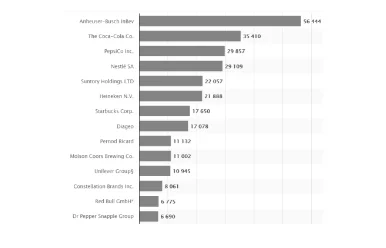
According to the data provided, the world's largest beer producer, Anheuser-Busch InBev is the company that is leading beverage company. The list is followed by two main rival companies The Coca-Cola Company and PepsiCo Inc. Unilever is ranked as the number eleven which means it has the potential to expand further (Nahar & Zayed, 2019). It is ranked number eleven because it is one of the leading companies in terms of beverage sales on the list.

Nestlé, a Swiss firm, has a significant piece of the pie in the food business. Unilever is put 10th and, as recently said, can develop in the beverage sector, despite the industry's toughness and competition. The overall water purifier market is at present esteemed at around 10800 million US dollars and is relied upon to be worth 15000 million US dollars by 2025. Since this industry is as yet in its beginning stages, organizations are laying down a good foundation for themselves in the worldwide market. Aquasana, Brita, PUR, Unilever Pureit, and Philips are instances of organizations that stick out (Sar, 2018).
3.2. The major competitors of the company
Unilever's principle rivals are other Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) organizations with similar construction and scale. For instance, Procter and Gamble, the world's biggest food organization Nestlé, the British Reckitt Benckiser Group, which makes cleanliness, wellbeing, and home items, the worldwide maker Mars, the New York organization Colgate-Palmolive, the American shopper products and drug global Johnson and Johnson, the Kraft Heinz Company (a new consolidation), and the German substance and purchaser merchandise Henkel. They all capacity on a worldwide scale; however they put forth an attempt to comprehend the requirements of clients in every country in which they work (Gichuki, 2017).
3.3. FMCG companies global sales ranking

With 60531 million US dollars in net deals in 2017, Unilever has ascended to fourth place among FMCG organizations (Couto, 2019). Just Nestlé, Procter and Gamble, and PepsiCo outflank Unilever in the FMCG market. Recall that www.statista.com's positioning just joins information from organizations that have given it. Organizations like Oetker and Mars are excluded (Shadaya, 2018).
3.5. Product and services offered
As stated earlier the products of the company can be classified into four divisions namely, water purifier, home care, beauty and personal care, food and refreshments.




Unilever's income has moved by 40% during the most recent 12 years, as found in the past diagram. The individual consideration business, which more than quadrupled its pay, the reward business, which expanded by 35%, and the home consideration industry, which expanded by half, were the areas that enabled this gigantic ascent. The food business, then again, declined by 8%, which is minimal in contrast with the upgrades in different regions. Note that working edges have expanded in all businesses during the past couple of years (Mahalle, Yong, and Tao, 2021).
3.5. Customer distribution
"We are devoted to fostering trust via ethical actions and open communication." According to Unilever's website, their mission is to build consumer loyalty; hence their image and advertising are highly essential to them. Unilever's beauty and personal care, Home Care, and food brands sell their products in supermarkets and grocery shops. On the other hand, Trivia and Pure it, on the other hand, sells their water purifiers online (Ravindran & Krishnan, 2020).
4.0 Key success factors
To begin, Unilever's R&D department employs around 6000 researchers, engineers, chefs, and technicians who endeavour to enhance existing goods and innovate new ones. Another important component is their variety; they have a wide range of products, which helps them to mitigate risks. Also, important is their commitment to marketing and advertising; Unilever was named the Most Awarded Advertiser at the 60th Cannes International Festival of Creativity. Furthermore, Unilever's CEO, Paul Polman, is worried about climate change and other social concerns that give Unilever a positive image. Furthermore, he has earned several prizes and plaudits for his ethical business practices, and he is the Chair of the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC), ensuring the company's good management (Appel-Meulenbroek et al., 2019).
Unilever’s marketing strategy
The company performs marketing activities to deliver value to the FMCG consumers globally. The marketing mix in FMCG is the combination of the price, product, distribution network, and promotion.
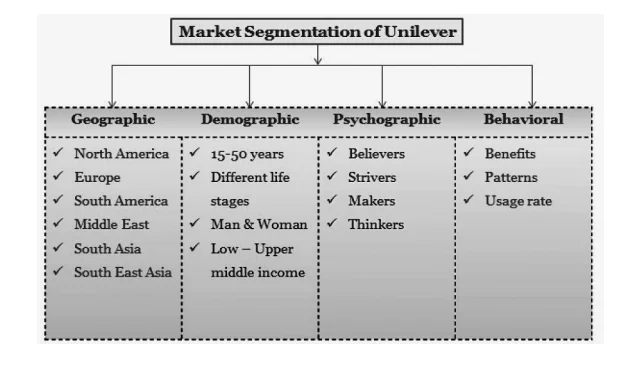
4.1 Marketing Mix
Unilever's brands have diverse promoting division dependent on the arrangement of their highlights and worth. The organization uses all the accessible showcasing devices accessible to work on its business. This is the reason their items are found in practically north of 190 nations and every one of the brands have a different brand system with a Unilever logo and a message. Its logo contains 25 images that mirror the worth of every one of Unilever's 400 brands. Unilever utilizes around 165000 individuals worldwide and has a wide organization of retailers and merchants (Unilever, 2021). Most of Unilever products are bundled in plastic packs or containers. They can be bought in a retail location, a shopping center, or on the web, among different spots (Đại, 2019).

Unilever's clients or consumers may be split into numerous categories based on their ages, income, and what they desire from Unilever. Unilever's clients are of all ages. The personal and home care market contains a demographic of 14-50-year-olds with a medium to high income. The food segment's age group begins at 5 and has a penchant for good flavour and healthful meals. Unilever's product costs include production, packaging, marketing, distribution, and other costs that are factored into the product pricing (Rahman, 2020). Unilever employs a variety of communication channels and is always looking for new ways to communicate with customers (Kartawinata et al., 2020). Unilever consumers buy products from retail stores, supermarkets, and online stores, among other places, and Unilever aggressively competes for better store placement than competitors (Shadaya, 2018).

5.0 Theoretical framework
A theoretical framework is an assortment of formal theories. When a review is worked around a theoretical framework, the theory fills in as the essential method of comprehension and exploration of the exploration subject. Although hypothetical structures are regularly utilized in quantitative investigations, they are likewise utilized in subjective examinations (Braidotti, 2019). To comprehend the current circumstance and the issues that face Unilever Company, this report has chosen to embrace the utilization of SWOT examination and PESTLE speculation to attempt to explore and comprehend the circumstances in the organization (Sohir, 2021). The reason for SWOT examination for Unilever is to assess the situation with an organization in the cut-throat world. It permits organizations to more readily appreciate and perceive inward and outer factors, just as the positive and adverse results they have on their activities. This information can assist firms with being more proactive by supporting them in settling on the fundamental choices in a powerful market to keep up with energy (Varpio, Paradis, Uijtdehaage, and Young, 2020). A PESTLE study is a structure for breaking down the significant outer components affecting an association (Political, Economic, Sociological, Technological, Legal, and Environmental). It provides human resource professionals with insight into the external issues affecting their organization. Since the examination is versatile, associations might use it in an assortment of settings. Individuals specialists and senior leaders can use the discoveries to assist with impacting key navigation. These two farmworkers compare with the current status of the organization, and they are the best in regard to breaking down and tracking down the answer for Unilever Company.
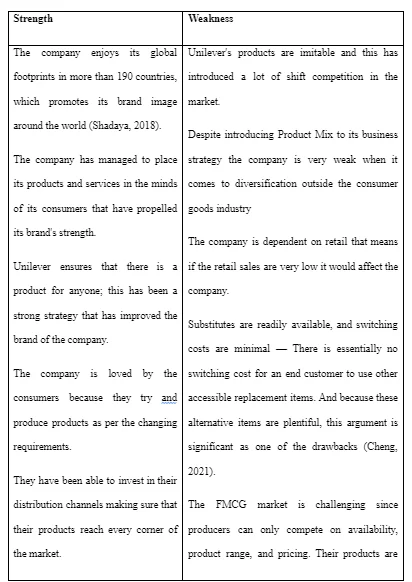
5.1 SWOT analysis
Unilever is a Dutch-British multinational consumer goods firm headquartered in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, and London, England. It sells food, drinks, cleaning supplies, and personal care things. It is one of the world's largest consumer goods companies. It is Europe's seventh most valued company. Unilever is one of the world's oldest multinational conglomerates, with products marketed in over 190 countries. The SWOT Analysis of Unilever is provided below.



5.2 PESTLE analysis
The limit of Unilever's ability to address outer elements in It's far off or full-scale climate serves the organization's situation in the worldwide shopper products industry. Such outside impacts are recognized in this PESTEL/PESTLE examination (Christodoulou & Cullinane, 2019). The PESTEL/PESTLE Analysis model is a strategy that supervisors might use to survey what the outside climate means for their organizations. Given the overall construction of the organization, Unilever's outside impacts shift broadly. Regardless, the organization should zero in on expanding its monetary achievement. Unilever can further develop its organizational execution by carrying out procedures that address the most genuine dangers and gain from the main chances distinguished in this PESTEL/PESTLE research (Thomas et al., 2020).
5.3 Political factors
Unilever is dependent upon the European Commission's administrative imperatives and proposals, just like the Food and Drug Administration in the United States of America. Assuming that they couldn't consent, the enterprise would face common and criminal accusations, as well as fines (Birahim, 2020). It may even prompt the detainment of individuals in power (Shadaya, 2018). The company is also bound by all local and provincial laws (within Europe) as well as any international regulations enacted in any country where its products are sold. Among them are India, South Africa, Russia, China, and a few different nations. Import, commodity, or exchange limitations may upset Unilever's future turn of events (Ullah, 2021).
5.4 Economic factors
The exhibition relies upon the monetary circumstances of the world. That implies that the current pandemic contrarily affects the development and improvement of Unilever (Fitchuk, 2021). The accompanying monetary elements can prevent Unilever from performing better in the business climate; increasing wages in emerging nations (opportunity and danger), agricultural nations' high development, and the economic security of created nations (Ahmed, 2021). All regional and local regulations (within Europe), as well as any overall norms established in the area where its products are promoted, are similarly stifling to the organization. India, South Africa, Russia, China, and a few different nations are among them. Import, product, or exchange limitations may obstruct Unilever's future development (Christo, 2021).
5.5 Social Factors
With so many brands, Unilever has focused on establishing a solid reputation. They place a premium on social and environmental issues. Given that many of Unilever's products are geared toward personal care and well-being, the company has a strong desire to help people feel and look attractive while also living the life they deserve. Even their marketing, especially with Dove, is focused on supporting women to feel their best from the inside out. Sociocultural trends and concerns influenced Unilever's company success and the distant or macro-environment (Cools & Terry, 2018).
5.6 Technological factors
Unilever is always developing new items and selling them online in the locations of their brands. The organization is working hard to improve its digital marketing and sales tactics. Unilever also has a higher level of automation than its competitors, allowing it to provide products to retail outlets more quickly (Sroufe, 2018). Otherwise, they risk experiencing negative cash flow, a loss of profit, or harm to their reputation, which they have spent so much time and money building. Rising business automation offers Unilever the opportunity to increase operational efficiency (Shadaya, 2018). New business processing equipment, for example, can increase inventory management while also increasing supply chain and distribution efficiency (See Unilever's Operations Management) (Sammi, 2021). However, the same external technology aspect poses a risk since it increases the competitiveness of other businesses, particularly small businesses, in local marketplaces. Rising R&D investments represent a risk to Unilever since they increase rival businesses' competitive edge in the consumer products industry (Sammi, 2021).
5.7 Legal factors
As a purchaser of products, Unilever is dependent upon an assortment of laws and guidelines. They own around 400 brand names in classifications, like food, wellbeing, and individual consideration, among others (Sammi, 2021). Copyright, item wellbeing, staff wellbeing, security laws, and worldwide and territorial charges apply to each brand and store area. Unilever improves its corporate picture by interfacing its corporate social obligation technique with natural rules (Rekhoum, 2019). Bettering unfamiliar patent principles can help the association's development. For instance, new patent laws in non-industrial nations assist Unilever with decreasing patent-related issues in its remote or full scale climate. A harder buyer's insurance law permits the organization to further develop client care and item quality principles (Robertson, 2020).
5.8 Environmental factors
Unilever advances the utilization of inexhaustible and long haul assets. Their items are OK for customers in whatever area they are advertised. All materials are biologically cordial, from the bundling to the plan. They need to be viewed as an earth principled association, and they've endeavoured to achieve that throughout the last decade (Robertson, 2020). Unilever might exploit the expanded interest in corporate environmentalism by fostering its natural projects to draw in ecologically concerned customers. In such a manner, the organization can foster its manageability drives to contend all the more successfully with different partnerships in the buyer item market (Leinonen et al., 2019). Unilever's corporate social responsibility plan must ensure that it properly implements these programs throughout the firm. To decrease the environmental effect of the firm, for example, the plan must address product innovation and internal business operations. These approaches should also help Unilever meet the demands of more complicated environmental programs. Such an external issue represents a chance for the firm to increase its competitive advantage through corporate responsibility (ZHUKEVYCH, 2021).

6.0. Theory application
6.1SWOT and PESTLE
According to SWOT, the company has invested its footprints in around 190 countries and more. This strategy sound has great strength, as the company can reach its products to most of their clients globally. Investing in more than 100 countries was the greatest strategy for the company; however, one factor that will reduce the income generation of the company is depending on retailers to sell their goods (Shadaya, 2018). The company should consider opening their stores so that they can not only increase their sales but also remain top in terms of completion in the present competitive world. Also, they should invest in technology and come up with new products that cannot be replaced easily by other markets. Besides, Unilever should introduce and offer more products in the market to bit its rivals such as Nestle and P&G (ZHUKEVYCH, 2021).
The external component of rising customer health consciousness must be considered in the company's objectives. Unilever may utilize this aspect to improve its food products. It is also recommended that the firm develop its sustainability activities to fulfil business sustainability prospects (Malaniia, 2020). Another option is to see increased business automation as a major threat that empowers Unilever's competitors, particularly smaller ones in local markets. Local enterprises, for example, may gain a competitive advantage by automating their manufacturing processes. Given these obstacles, Unilever's worldwide development through innovation and corporate sustainability needs a strategic emphasis, according to this PESTEL/PESTLE study (ZHUKEVYCH, 2021).
7.0 Conclusion
The report has analysed and described the operational strategies by utilizing SWOT analysis and PESTLE to understand the current state of Unilever and how it operates. In addition, the report has also managed to address the business model of the company. According to the business model, the report found that the number one interest and concern of Unilever are their consumers. The company begins with consumer insights. There, the main purpose is to take care of consumer interests through brand innovations, manufacturing, sales, logistics, collaborations, and sourcing sustainability. According to the review, the company was formed in 1929 as a merger between one company that produced margarine and another that made soap. Through the report, we found out that Knorr, Dove, Axe, and Lipton are the most popular brands in the Unilever Company. In conclusion, the report has found that one of the major weaknesses of the company that can cause its underperformance is relying only on retailers to sell its products. Unilever's corporate social responsibility plan must ensure that it properly implements these programs throughout the firm. As a recommendation, the company should open their stores worldwide to aid in selling and promoting their products and services.
8.0 Reference
Abubakari, M., & Thuranira, B. (2021). The consumer goods sector and the sustainability agenda in Ghana: a review of sustainability commitments. Discover Sustainability, 2(1), 1-17.
Ahmed, M. R. (2019). The RACI Matrix and its implications: a case of Unilever.
Chernobay, L., Yasinska, T., & Malibroda, S. (2020). APPLIED ASPECT OF CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY IMPACT ON COMPANY COMPETITIVENESS (UNILEVER EXAMPLE). Entrepreneurship, 8(1), 32-44.
Razmochaeva, N. V., Semenov, V. P., & Bezrukov, A. A. (2019, January). Role of process Automation in quality management of Enterprises in Perfumery and cosmetic industry. In 2019 IEEE Conference of Russian Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EIConRus) (pp. 1449-1452). IEEE.
Cheng, Y. (2021, February). Analysis on the Opportunities and Challenges of Unilever’s Differentiated Competition by Using SWOT and PEST. In 6th International Conference on Economics, Management, Law and Education (EMLE 2020) (pp. 280-284). Atlantis Press.
Nahar, S., & Zayed, N. M. (2019). An Analysis of the Impact of Remuneration on Employee Motivation: A Case Study on Unilever, Bangladesh. International Journal Fam Busi Manag, 3(2), 1-5.
Sar, A. K. (2018). Competitive advantage and performance: An analysis of Indian FMCG industry. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 22(1), 1-8.
Gichuki, C. M. (2017). Effect of Agile Supply Chain Strategy on Competitive Advantage of Firms in the Fast Moving Consumer Goods Industry: A Case of Unilever Kenya (Doctoral dissertation, United States International University-Africa).
Couto, C. A. (2019). Robijn vs. Lenor Megabrand: what can Lenor learn from their competitor Robijn to scale up their megabrand strategy in Europe? (Doctoral dissertation).
Mahalle, A., Yong, J., & Tao, X. (2021, May). Regulatory Challenges and Mitigation for Account Services Offered by FinTech. In 2021 IEEE 24th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD) (pp. 280-287). IEEE.
Ravindran, D., & Krishnan, G. (2020). Measurement of Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction Towards Various Products and Services offered by Reliance Supermarket. AMBER–ABBS Management Business and Entrepreneurship Review, 11(1), 39-59.
Appel-Meulenbroek, R., van de Kar, M., van den Berg, P., & Arentze, T. (2019). Employees’ preferences for services and facilities offered in serviced offices. Facilities.
Đại, Đ. N. (2019). Giải pháp hoàn thiện hoạt động Marketing Mix dòng sản phẩm nước xả vải Comfort của Công ty Unilever Việt Nam.
Rahman, A., Rizky, D. A., Rosalia, D., & Azzahra, D. (2020). MARKETING COST ANALYSIS OF PROFIT OF PT. UNILEVER 2014-2018. Journal of Islamic Economic Scholar, 1(1).
Kartawinata, B. R., Maharani, D., Pradana, M., & Amani, H. M. (2020, August). The Role of Customer Attitude in Mediating the Effect of Green Marketing Mix on Green Product Purchase Intention in Love Beauty and Planet Products in Indonesia. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management (Vol. 1, pp. 3023-3033).
Braidotti, R. (2019). A theoretical framework for the critical posthumanities. Theory, culture & society, 36(6), 31-61.
Varpio, L., Paradis, E., Uijtdehaage, S., & Young, M. (2020). The distinctions between theory, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework. Academic Medicine, 95(7), 989-994.
Sohir, Y. (2021). Analyse SWOT-Unilever. Publications Études & Analyses.
Cheng, Y. (2021, February). Analysis on the Opportunities and Challenges of Unilever’s Differentiated Competition by Using SWOT and PEST. In 6th International Conference on Economics, Management, Law and Education (EMLE 2020) (pp. 280-284). Atlantis Press.
Christodoulou, A., & Cullinane, K. (2019). Identifying the main opportunities and challenges from the implementation of a port energy management system: A SWOT/PESTLE analysis. Sustainability, 11(21), 6046.
Thomas, P. J. M., Sandwell, P., Williamson, S. J., & Harper, P. W. (2021). A PESTLE analysis of solar home systems in refugee camps in Rwanda. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 143, 110872.
Ullah, N. (2021). A Comparative Analysis between Unilever and Johnson & Johnsons.
Birahim, S. A. (2020). Internal and external factors of Nestle and comparison with Unilever.
Ahmed, A. A. (2021). Incentive program for sales representatives of GSK Bangladesh Private Ltd.
Christo, I. (2021). Special Economic Zone: a path to foster Chinese FDI in Brazil. Journal of Special Jurisdictions, 1(2), 252-281.
Fitchuk, C. (2021). Creating a Sustainable Business Strategy for a SME.
Cools, K., & Terry, L. A. (2018). The effect of processing on the glucosinolate profile in mustard seed. Food chemistry, 252, 343-348.
Sroufe, R. P. (2018). Enterprise Systems–Operational and Strategic Assessment. In Integrated Management. Emerald Publishing Limited.
Sammi, T. (2021). Employee satisfaction and digitalization of working method in National Bank Limited: A study on Agrabad branch employees.
Rekhoum, I. S. M. B. (2019). Increasing the market share of the company “Europe Language Jobs” in Portugal (Doctoral dissertation).
Robertson, P. W. (2020). Supply Chain Analytics: Using Data to Optimise Supply Chain Processes. Routledge.
Leinonen, I., Eory, V., MacLeod, M., Sykes, A. S., Glenk, K., & Rees, R. M. (2019). Comparative analysis of farm-based carbon audits.
ZHUKEVYCH, S. (2021). Strategic Aspects of TNCs Entry into the Markets of Central and Eastern Europe (Doctoral dissertation, Masarykova univerzita, Ekonomicko-správní fakulta).
Shadaya, B. (2018). An evaluation of the strategic planning model used by manufacturing company in Zimbabwe: The case of Nelsport Pvt. Ltd.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



