Theoretical Framework
In theory, low minimum wages are associated with positive employment rate, this is due to the reduced burden of wage bill among employers, and therefore, employers can accommodate more workers. However, after a certain extent of the minimum wage, the association is likely to turn out harmful; this means that there is an optimum level of minimum wages that is likely to maximise the employment rate. Besides, there could be a negative association between minimum wages and employment rate, in cases where the market is regulated strictly and when workers are not as productive as employers expect them to be. Therefore, this article would use OECD data, to establish the relationship between unemployment and minimum wages.

Theoretical Framework
From the theoretical perception formed by Brown, Merkl, and Snower (2014), firms would only offer an employment position if the distinctive variation in employees’ appropriateness for the jobs are adequately low. As an outcome, since the job rate in a fixed condition depressingly rest on on the equilibrium wage, any growth experienced in the minimum wage bill is likely to reduce the rate at which jobs are offered, which subsequently leads to higher unemployment. The researchers refer to this situation as the job offer effect.
The researchers also tenet that the job offer effect has a positive relationship on the average worker production and has a negative correlation with wage levels and hiring costs. Contrary, other employees are mostly ready to offer their services for the new (higher) equilibrium wage since it is now more than their arrangement pay. This means that the job acceptance rate is likely to increase, which later leads to higher employment. The researchers referred to this occurrence as the ‘job acceptance effect.’
The methodological forecasts of Brown et al. (2014), allows the readers to frame propositions concerning the signs of the impact of the precise labour market on employment trends. Since the occurrence of the job acceptance effect could control job proposition effect for lesser remunerations, and the contrary could be correct in situations of higher minimum wages.
OECD Data
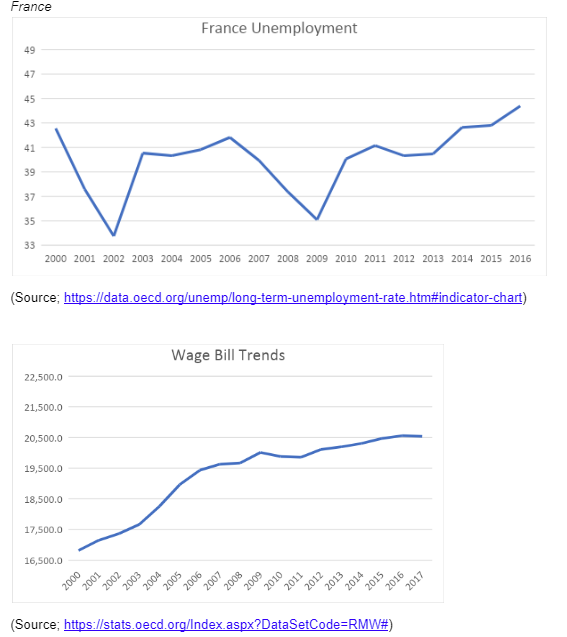
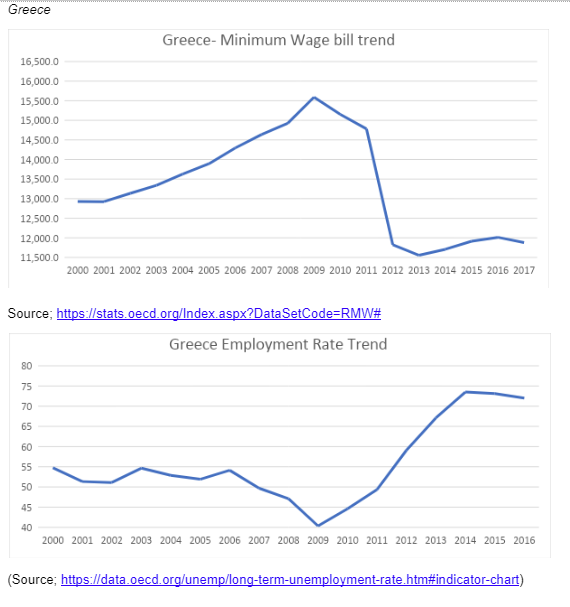
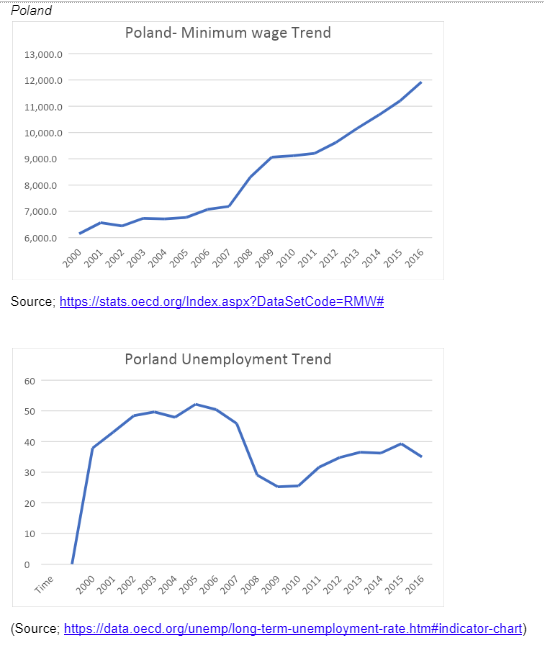
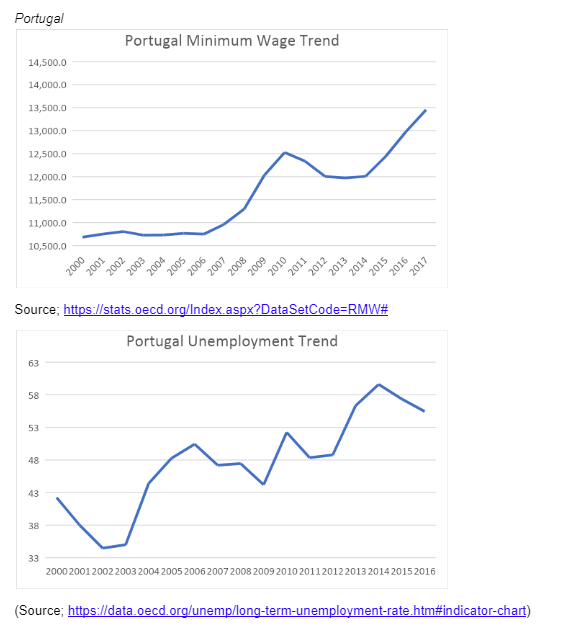
Using the OECD data, this paper will prove the hypothetical frameworks of Brown et al. (2004). The data will be collected in 5 different European countries, which are Poland, Portugal, Greece, the United Kingdom, and France. From minimum wage trends, it is evident that almost all countries have a similar trend when it comes to the minimum wage. In all the states the period between 2012-2013, is characterised by a sharp decline in the minimum wage bills, probably this could be due to the economic recession experienced at this time. Generally, it can be concluded that since 2000 up to date, the minimum wage bill has been gradually increasing, in all the five countries sampled in Europe.
Reflective Comments
The data reveals that the minimum wage in Europe are always increasing, apart from in Greece where the recent developments in their economy have led to a decreasing wage bill. In the case of Greece, the growth in the minimum wage has attracted employment. As per the tenets of Brown et al. (2004), the situation in Greece can be described as the job acceptance rate effect, which implies that an increase in the minimum remuneration is likely to attract more people to the labour market and therefore resulting in high levels of employment. At the same time, lowered minimum wages deter employees from joining the labour market. This is evident in Greece between 2006 to 2009, in this period Greece the minimum wage was at its peak, and at the same time, unemployment was at its lowest. On the same note, the period between 2012 to 2016 was characterised by a reduced minimum wage bill, which leads to higher unemployment rates. The same phenomena can also be explained by the fact that the minimum wage in Greece is not as high as in other states such as France and the United Kingdom, and therefore, even when the minimum wage increases, employers are still willing to employ since the cost of employment is relatively low. The same can also be said in the case of France in the period between 2000 to 2005.
Portugal on the other hand, depicts a contrary revelation, as much as the minimum wage is always gradually growing, unemployment also takes a similar trend. This occurrence is what Brown et al. (2014) referred to as the job offer effect, meaning that increase in the wage rate is likely to reduce the number of jobs given, which ultimately lead to high rates of unemployment. The same is clear in the period between 2010 to 2011, where Portugal recorded the highest annual minimum wage since 2000 up to date, in the same period, it also recorded the highest rates of unemployment.
Dig deeper into The Significance of Auditing in the UK Economy with our selection of articles.
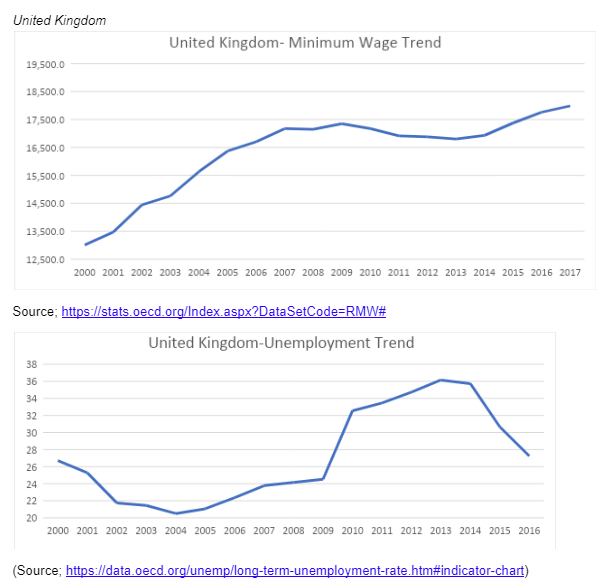
Brown et al. (2014), also argued that in cases, where employees are very productive, the employers are likely to offer jobs even if there is an increase in the minimum wage bill. However, in cases where the minimum wage bill suppresses the employee output, the fewer jobs are likely to offer. The same can be seen in the case of the United Kingdom. Since 2000, the United Kingdom has been continuously recording a rise in the annual lowest wage paid. However, the unemployment has not been recording a constant rather it has been inconsistent. This can be explained by the fact that at equilibrium (when employee output is equal to the minimum wage), employees will hire even if the minimum wage rises. Though, any further growth in the wage bill, upsets the existing status quo leading to high unemployment, despite the fact that the minimum wage bill is always on the rise.

References
- Brown, A. J., C. Merkl, and D. J. Snower. (2014). The minimum wage from a two-sided perspective. Economics Letters 124 (3), 389–391.
- OECD Data. (2018). Long-term unemployment rate. [Online] Retrieved at; https://data.oecd.org/unemp/long-term-unemployment-rate.htm#indicator-chart
- OECD Stat. (2017). Real minimum wages. [Online] Retrieved at; https://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=RMW#
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



