A Comprehensive Overview of Services and Components
Introduction:
The term “special education” is a broad one describing the variety of instructional services needed by children based on their individual demands. According to the definition of the Individual with disabilities education Act (IDEA, 1990), special education denotes the specially designed instructions provided free of cost to the parents who are having children with disabilities. This may include the instruction provided in the classroom, home or hospital setting and in any other institution. The following components of the special education are: the speech language pathology service, training related to travel and vocational education, audiology service, service related to interpretation, physical and other occupational therapies, early identification and assessment of disabilities in the children, counselling services such as rehabilitation services and orientation, mobility services, school nurse and social work service in school, counselling of the parent (Peters, et al, 2003; Turnbull, et al, 1995). For those working on their education dissertation help, understanding these provisions can be crucial in examining how educational support systems adapt to the needs of students with disabilities.
It is a neurological condition which impairs one or more than one basic psychological processes that are required for speaking, reading, writing, understanding languages and solving mathematical calculations. It is considered to be a broad term - an umbrella label that comprises a variety of conditions. Unfortunately, due to lack of awareness among the teachers, school authorities and parents, many children afflicted with this disorder are never identified and are generally classified as an incapable, failure and slow or behind. This particular disorder cannot be cured and therefore considered as a lifelong challenge. Individuals with this disorder fail repeatedly while performing a task which results in the development of poor self-esteem or confidence due to which they often stop trying and learning and ultimately get dropped out of the education system. As a result, these individuals who failed to gain proper education and also lack any support system are at a higher risk of becoming addicted to drugs or illicit substances, tobacco and alcohol. These individuals also get engaged with some illegal activities and are very much prone to teenage pregnancies. About 13 to 14 per cent of all the school children are suffering from learning disorders and they are labelled as “failures” by our society. But in reality, it is the education system that has failed in recognizing these children with special needs (Sawhney, et al, 2014; McDermott, et al, 2001).

Theoretical perspectives on the special education needs:
There are a range of theoretical perspectives regarding the strategies and approaches which are broadly classified as: Behavioural models, Constructivist models and Ecological models.
Behavioural models:
This approach highlights on the learning outcomes which is influenced by the chief principles of reinforcement theory based on the varied learning contexts. The theory includes all the behaviours which are acquired through different rules which help in change and in sustaining it. The cognitive behavioural approaches deal with the individual’s capacity to comprehend and think about their own behaviour. The associated advantages with the models are positivity and practicality in the outlook applied during the teaching process after evaluating the targets and expectations of the individuals. Moreover, this model had been criticised because of its narrow outcomes (Davis, et al, 2004).
Constructivist models
In this model the children are considered as an active participant in the process of seeking knowledge, gaining experiences and the satisfaction obtained after solving the problems. It is considered to be a transformative process which brings new opportunities for further learning newer concepts and gaining knowledge in depth. The theory of social constructivism is related to this theory of learning (Davis, et al, 2004).
Ecological models:
This model focuses more on the interaction of the individual with his/her immediate environment rather on the learning capacity of the individuals. The model works on the concept of “nested system” and deals with levels such as micro, macro, bio, meso, exo and chronosystems. The learner is considered to be situated in the centre and interacting with the various levels which belong to any larger system such as classroom. During teaching the approach focuses on the micro level but involves the activity at broader levels. The mesosystem focuses on the relationship between the varied settings in which the child participates (Davis, et al, 2004).
In the classroom of special education the teachers should apply the following theories so that the students can learn the most which includes: L. Atincronbsch and R. Snow, Component Display Theory, Gestalt, Connection Theory, Gagne’s Conditions of Learning, Sign Learning Theory and Cognitive Load Theory. The Gestalt theory is better as it involves the grouping of the students which makes it easier for them to learn. Some communications have to make verbally and with the help of application as students may not be able to connect the dots independently. The cognitive theory and the sign theory enable the students learn by drawing lines. Connection theory is a special education theory and it helps the students to learn by connecting the dots. This theory is based on the concept of cause effect relationship of response and the stimuli. The conditions of learning and component display theory operate via verbal and hands on approaches. These theories follow a identical structure which will guide the children during the learning process. The theories of inclusion and inclusive education have strong impact upon the special education policies and practices in the developed and the developing countries (Edyburn, et al, 2001).
The statement of Salamanca adopted from the World Conference on Special Needs Education: Access and Quality “Reaffirming the right to education of every individual, as enshrined in the 1948 Universal Declaration of Human Rights, and renewing the pledge made by the world community at the 1990 World Conference on Education for All to ensure that right for all regardless of individual differences”. It made an important contribution to the principle of achieving education for all and for the improvement of the schools to make them more educationally effective (Hunt, et al, 2011).
Social and medical models for the SEN children:
The social model of disability is described based on the perception of society about the disability, i.e., it highlights the social barriers which inhibits the individuals with special education needs to function normally and accessing the needs their within the society whereas the medical model of disability is described the impairments or by the differences present within the individuals. It deals with the aspects what the person cannot perform, i.e., what is wrong with the individual rather than what the person requires managing their condition. The social model of disability recognizes all the parameters while identifying the child with special education needs, i.e., the impact of both the physical and social environment and also takes care of the individuals facing problems while interacting with the society. This particular model guides the child in a more holistic manner by considering all the parameters such as the psychological, behavioural, social and physical needs. The medical models approach the person in an absolutely different manner, i.e., it considers the individual as a patient who requires treatment to perform normally within the society. The controversy develops when an individual with disability acquires illness and needs treatment but the clinician tries to treat the disease and also the disability which is not feasible without the intervention of social model of disability. The doctors aim to treat the person with disability to the state of normalcy. The medical model is also referred as “individual model” as it encourages the concept that a disabled individual should try to familiarize with the organisational structure of the society.
The children with the special education needs were guided with the guidelines of the Education Act introduced at 1981. The report prepared by Warnock stressed on the application of social model of disability which replaced the term “handicap” to special education needs (SEN) to encourage them regarding their needs rather than focusing on their disabilities. Before the preparation of this report, the medical model labels the person as disabled and completely ignores the requirements of the individuals. Overall the social model of disability encourages inclusion.
Inclusive education:
It is considered to be a multidimensional concept which consists of both the celebration and the valuing of the diversity and differences, reflection of the human rights, the concept of the social justice and the equity issues. It also includes the social model of disability and the social and the political model of education. The process of school transformation and highlighting the children needs to education and schooling has also been considered in this concept (Kozleski et al., 2011; Loreman et al., 2011; Mitchell, 2005). There are four key principles of inclusive education: all learners are offered with challenging, flexible and engaging general education; the diversity and response to the individuals strengths and challenges are also considered in the process; use of reflective practices and differential instruction; establishment of a community consisting of the teachers, parents, students, families and other professional in the communities. In this way it provides an improved and focused attitude to provide education to the children with SEND.
The major themes of the inclusive educations are:
Overview and rationale: it examines the theories and rationale behind the themes of inclusion.
What this look like in practice: these include the practical application of inclusion under each theme.
Additional Practices: these include the other additional inclusive practice.
Reference: It lists all the reference of the themes (Refer Fig:1) (Mallory, et al, 1994; Kozleski, et al, 2011; Loreman, et al, 2010).
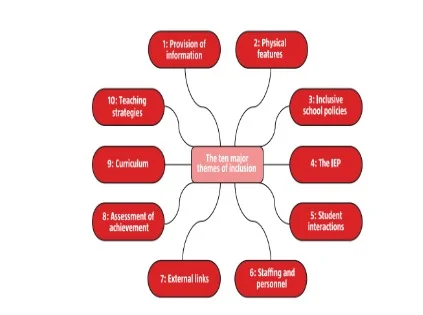
Fig: 1 Themes associated with the inclusive education (Mallory, et al, 1994)
The theory of inclusion concerning the children with SEN highlights that these children should be taught along with their peers in the mainstream education. The schools need to fulfil the needs of the children with both learning disability and physical disability. This approach of education utilises the concept of social model of disability and allows the children to gain access the wide ranging, balanced and relevant form of education. Moreover, the implementation of the cultural practice, management practice and the consumption of resources are formulated in such a way within the settings of school to meet the needs of these children. The believers of the theory of inclusion state that, this is matter of civil right concerning the need of the people with disabilities. The rights highlight the equal opportunity and equal access of these people. The theories of learning related to the special and inclusive education should be applied by the teachers in the SPED classrooms so that the children benefit the most from the education system.
IDEA special education Act of the United States was first formulated in the year 1975 and has been revised several times by the process called reauthorization. It is a law that offers free education to the public and eligible children within the age of 3 and 21 suffering from disabilities throughout the nation, to identify and locate the children with disabilities, can develop an individualised educational programme for individual patients, educating the children with disabilities within their least restricted environment, those students who are enrolled into an early-intervention programme should be provided with a positive and effective transition into an preschool program, also provides special education services to the children of the private schools, the teachers are adequately trained and certified to offer special education service, the children with learning disabilities are dealt with compassion and care so that they do not suffer from any psychological problems by comparing themselves to their peers (Lipkin, et al, 2015).
The following guidelines have to be followed in the institution of the special education need:
Every division should organise a special education centre that can meet up the needs of the disable children. The programmes organised should also include the special education concept and the different SPED programmes to meet up the needs of the children. This particular centre should act as resource centre by providing teaching materials to the children with special needs, they conducts continuous assessment of the children with special needs and also provides in service training to those children. During the early years of development of the child they may require help in the following aspects such as: for solving their school homework, during reading and writing, evaluating the information, while expressing them, while making friends, cannot behave properly and organising. As the early years of development of the child are very critical for the emotional, social, intellectual and physical development they may require different forms of help. They might require help from clinicians, educational psychologists and speech language therapists. The therapeutic activities related to communication, play, development of the language and specially training the parents. The family also plays a major role while providing education to the children with special needs. Research based evidence have shown that the inclusion of the family in the school markedly improves the achievement level of the student by diminishing the behaviour of absenteeism. This also helps to retain the confidence of the parent’s about the educational capacity of the children. Children with involved caregivers and parents can help them to earn higher grades, improved social skills and better behaviour (Peters, et al, 2003; Lipkin, et al, 2015).
Safeguarding Acts:
There are several laws that safeguard the children with special needs such as Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, 2004, Americans with Disabilities Act, 1990, section 504 of the rehabilitation act of 1973, anti-bullying laws and school policies (Rothstein, et al, 2009).
The teaching strategies for approaching students with special education needs:
The concept of good practice approach showing promising aspect in the field of teaching includes the following:
a) The early identification and intervention: It is considered to be a key principle for implementing successful teaching strategies.
b) The involvement of parents and families in a collaborative approach towards teaching.
c) The collaborative working with other agencies in a child centred approach: this is an important aspect because the different support systems may focus on the different aspects of interventions.
d) Teaching approaches that adopts the visual reinforcement strategies complementing the verbal instruction and it should be conducted along typically developing the peers.
e) Stress should be given concerning the teaching of language, cognitive processes and on the implementation of the strategies ensuring the effective generalisation of the structures formulated to meet the requirements of the children.
Mainstream education for special education need children involves a school where children with the special needs are kept with children with normal abilities. By using this approach of education the children get the exposure of mainstream education where they participate both in the regular class room and their special needs are considered in the special education classroom so that they get the specific attention to fight with the challenges of life. The approach promotes the concept of inclusive society which is rewarded with countless benefits (Peters, et al, 2004).
The concept of social constructionism changed the approach to teaching:
This particular theory of sociology had a huge impact concerning the improvement of the education prevailing in our modern society. The concept of the social constructionism or constructivism had evolved from the ideas of the Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky who had contributed in this particular field at the end of 19th century and early of the 20th century. His contribution became famous after his death but it highly influenced the formulation of the approach of classroom teaching in the 21st century. Therefore, in the latter half of the 20 th century the educators had started applying this concept to teach at schools. the concept of Vygotsky highlighted on the fact that learning concept can be defined as a process of social interaction due to which the children are able to develop notion about the world and also about them. The teachers also started to understand the concept that it is very essential to read the minds of the students and the knowledge can be developed only by a collaborative approach. The teachers should change the concept about the children as “empty vessels” to “active participants” in the learning process. When this approach was adopted by the teachers the concept of the student directed learning initiated to materialize. The present concept of learning includes several aspects based on interactive lessons such as the assignments based on interaction with each other, project oriented approach, conducting research as a team and the learning based on the concept of real world (Silvers, et al, 2009; UKEssays 2018; Lloyd, et al, 1999).
It is evident from Piaget's (1936) theory which is on cognitive development elucidates on the matter that how a child can create a model of the world based on their own imagination. He did not agree with the fact that intelligence can be considered as a predetermined trait, and also stated that the process which results due to the maturation of the biological parts and by interacting with the environment is termed as cognitive development. Therefore, Piaget (1936) was thought to be the first psychologist who conducted a methodical study on aspects of cognitive development. After going through his contributions, it can be said that designed a platform theory on cognitive development of children, made a in depth analytical study on mental capabilities of acquiring knowledge among children and conducted a list of effortless but creative tests to focus on the difference in cognitive abilities of children (McLeod, 2018).
The learning outcomes in relation to the special education needs of the children addressing the following issues:
In the area of leadership and planning the administrator should have the capacity to evaluate and deal with the change process related to the special education needs of the children, organising group for the achievements of the objectives, efficient planning and re-examine of the implementation, dealing with the human resource responsibility and understanding the theories, models and philosophies. When the area of laws and regulations are considered the administrator should take decisions based on the current laws for the students with special needs, evaluating the policy of the local school and its applications for the children with special needs, implementation of the educational policy based on the evidence practice. They should also make use of and evaluate the tools to identify the student’s achievement, application of the best practice theory for the development of the child, application of the plan to make use of the assistive technologies, implementation of the program to augment the social and emotional well being of the child (Boscardin, et al, 2007).

Conclusion:
The detailed aspects of the needs of the children with special needs have been thoroughly examined in this report. The several laws for the protection of these children were also mentioned. The needs of the disable children during their early years of development were analysed and the role of the practitioner were discussed in regard to that. The various theories concerning the special education needs of the children were discussed and how it helps in the development of the children were also included in this report.
Take a deeper dive into A Comprehensive Exploration of Study Skills for Higher Education Success and Beyond with our additional resources.
References:
Davis, P., Florian, L. and Ainscow, M., 2004. Teaching strategies and approaches for pupils with special educational needs: A scoping study. Nottingham: DfES Publications.
Hunt, P.F., 2011. Salamanca Statement and IDEA 2004: possibilities of practice for inclusive education. International Journal of Inclusive Education, 15(4), pp.461-476.
Peters, S.J., 2004. Inclusive education: An EFA strategy for all children. Washington, DC: World Bank, Human Development Network.
Silvers, A., 2009. An essay on modeling: The social model of disability. In Philosophical reflections on disability (pp. 19-36). Springer, Dordrecht.
UKEssays. November 2018. Social Model Of Disability Education Essay. [online]. Available from:
https://www.ukessays.com/essays/education/social-model-of-disability-education-essay.php?vref=1 [Accessed 22 February 2020].
McLeod, S., 2018. Theories of selective attention.
Lloyd, P. and Fernyhough, C. eds., 1999. Lev Vygotsky: critical assessments (Vol. 4). Taylor & Francis.
Peters, S.J., 2003. Inclusive education: Achieving education for all by including those with disabilities and special education needs. Washington, The World Bank.
Lipkin, P.H. and Okamoto, J., 2015. The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) for children with special educational needs. Pediatrics, 136(6), pp.e1650-e1662.
Turnbull, A.P., 1995. Exceptional lives: Special education in today's schools. Merrill/Prentice Hall, Order Department, 200 Old Tappan Rd., Old Tappan, NJ 07675.
Sawhney, N. and Bansal, S., 2014. Study of awareness of learning disabilities among elementary school teachers. In Conference: International Education Confer'Education as a Right across the Levels: Challenges, Opportunities and Strategies, New Delhi.
McDermott, R., 2001. The acquisition of a child by a learning disability. Understanding learning: Influences and outcomes, 2, pp.60-70.
Edyburn, D.L., 2001. Models, theories, and frameworks: Contributions to understanding special education technology. Special Education Technology Practice, 4(2), pp.16-24.
Mallory, B.L. and New, R.S., 1994. Social constructivist theory and principles of inclusion: Challenges for early childhood special education. The Journal of Special Education, 28(3), pp.322-337.
Kozleski, E.B., Artiles, A.J. and Waitoller, F.R., 2011. Introduction: Equity in inclusive education: Historical trajectories and theoretical commitments. Inclusive education. Examining equity on five continents, pp.1-14.
Loreman, T.J., Deppeler, J.M. and Harvey, D.H., 2010. Inclusive education. Supporting diversity in the classroom. Routledge.
Rothstein, L. and Johnson, S.F., 2009. Special education law. Sage.
Boscardin, M.L., 2007. What is special about special education administration? Considerations for school leadership. Exceptionality, 15(3), pp.189-200.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



