Clinical Experience in Diverse Healthcare Settings as a Physiotherapist
1. Summary of Practice Placement
My practice placements included neurology ward, musculoskeletal medicine ward, oncology ward and community rehabilitation centres. In the neurological ward, the stroke inpatients are analysed to determine the nature and severity of stroke affecting their nervous system, focusing on education dissertation help. I was entrusted to care for stroke inpatient where they are to be provided physiotherapeutic assistance in collaboration with the neurological nurses and experienced neurologists to resolve their health issues. This is because as a result of stroke many of the inpatients develop neurological complication and in worst cases paralysis that interferes with their mobility and effectiveness to execute everyday tasks. In the musculoskeletal medicine ward, as a physiotherapist, I required to work in collaboration with nurses and physicians to determine the intervention to be provided for nature of musculoskeletal difficulty faced by patients. In this ward, I was entrusted to care mainly for the outpatients which included children, elderly people, sportsmen and others who regularly visits the ward but do not require hospital admission for helping them cope with the musculoskeletal difficulties that are interfering with their mobility.
In the oncology ward, patients suffering from cancer and accessing treatment for the health issue are seen to be present where I as the physiotherapist is entrusted to work in collaboration with oncologist, physicians, occupational therapist and others to ensure well-being of the patient. In the ward, I was entrusted to care for the inpatients who are suffering from emotional distress as a result of physical symptoms of extreme pain and other associated physical issues due to side-effects of cancer treatment such as chemotherapy, pharmacological intervention and others provided to them. In the community rehabilitation centres, I was entrusted to provide physical therapy for the disabled people so that they are able to have empowerment and enhanced physical efficiency to be rehabilitated in the community.

2. Inter-professional Learning Activities
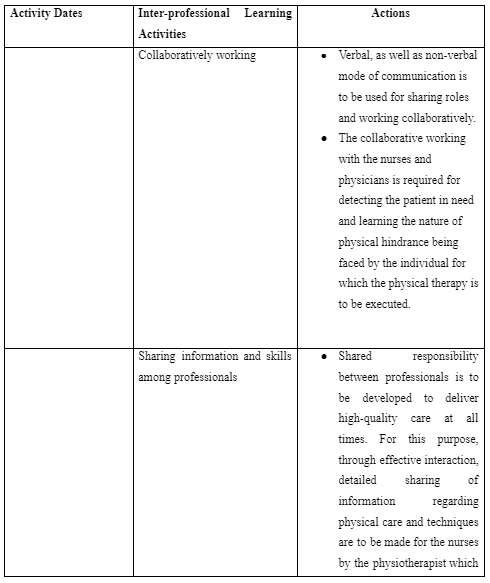
The inter-professional practice is referred to collaborative approach taken by the healthcare providers where the patients are treated through collective involvement of expertise and knowledge from the physicians, nurses, physiotherapist, occupational therapist and pharmacists (Leary et al. 2019). In the neurology ward, the initial inter-professional learning activity included the way I as a physiotherapist is to collaboratively work with the nurses and neurologist in determining the patients who require immediate physical assistance for their improved physical health. For this purpose, the activity mentioned that verbal, as well as non-verbal mode of communication, is to be used for sharing roles and working collaboratively. As mentioned by Lee and Kim (2018), stroke leads people to lose muscle control and balance of their body. This is because stroke affects the part of the brain which manages and delivers the nerve impulses required for making movement and balancing the body.
The physicians and nurses are able to determine the extent of mobility and neurological efficiency of the stroke patients as they perform diagnosis of their health and evaluate the results (Gandolfi et al. 2019). Thus, as a physiotherapist collaboratively working with the nurses and physicians is required for detecting the patient in need and learning the nature of physical hindrance being faced by the individual for which the physical therapy is to be executed. The collaborative working policy among professionals is also suggested in the NMC Code of Practice so that appropriate information can be shared and used in delivering proper care plan (NMC, 2018). In this process, I learned that effective communication with nurses and physicians in the neurological ward is to be maintained. This is because even after the physical therapy provided by me as the physiotherapist for the patients; the coordinated care by the nurses is also to be established so that physical care for the stroke patient in my absence is effectively maintained.
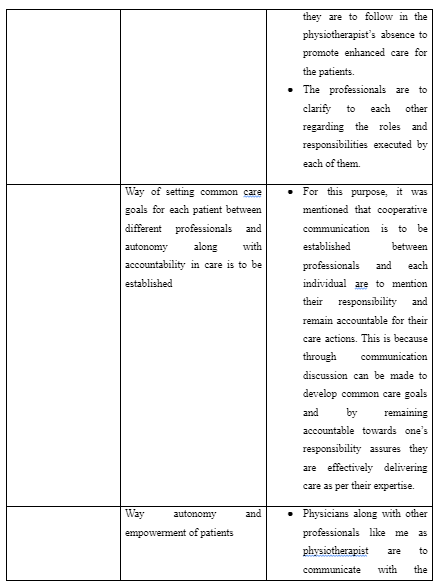
In the neurological ward, the other inter-professional learning activity includes the way I as a physiotherapist is responsible to educate both the nurses and patients to execute supportive and continuous physical activity for effective recovery from their health. This is because often stroke patients in neurological ward are found to avoid complying with the nurses in using supportive physical equipment such as wheelchair, walking sticks and others or execute physical activity of walking to promote their mobility out of lack of trust in the intervention (Lupo et al. 2018). Moreover, it is mentioned that nurses due to lack of knowledge of providing physical support to stroke patients often led to delivery hindered care to them leading towards their fall and deteriorated physical health (Polat et al. 2019). Thus, I learned that in inter-professional care at the neurological ward for stroke patients, shared responsibility between professionals are to be developed to deliver high-quality care at all times. For this purpose, through effective interaction, detailed sharing of information regarding physical care and techniques are to made for the nurses by the physiotherapist which they are to follow in the physiotherapist’s absence to promote enhanced care for the patients. Moreover, the professionals are to clarify to each other regarding the roles and responsibilities executed by each of them.
In the oncology ward, the inter-professional learning activity included the way common care goals are to be set for each patient between different professionals and autonomy along with accountability in care is to be established by each professional in delivering care. This is because avoiding to be responsible for own care techniques and working beyond the expertise in healthcare for the care professionals leads them to harm the patients as well as develop unnecessary conflict with colleagues leading to create hindered collaboration and coordinated care delivery (Bosworth et al. 2017). Moreover, without common care goals in inter-professional care, the health professionals would be unable to work in a unified direction to deliver effective support in enhancing the health of the patients out of differences (Burhansstipanov and Shockney, 2018). For this purpose, it was mentioned that cooperative communication is to be established between professionals and each individual are to mention their responsibility and remain accountable for their care actions. This is because through communication discussion can be made to develop common care goals and by remaining accountable towards one’s responsibility assures they are effectively delivering care as per their expertise (NMC, 2018).
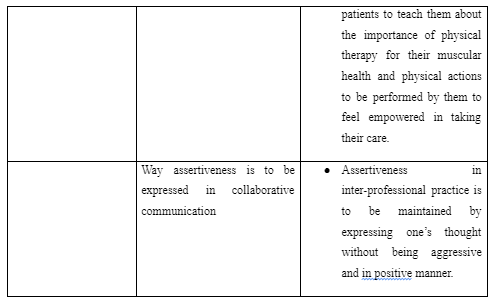
In the musculoskeletal medicine ward for outpatients, the inter-professional learning activity included developing information about the way autonomy and empowerment of patients are to be promoted by me as physiotherapist through coordination with the physicians. For this purpose, it was mentioned that physicians along with other professionals like me as physiotherapist are to communicate with the patients to teach them about the importance of physical therapy for their muscular health and physical actions to be performed by them to feel empowered in taking their care. This is because often patient with musculoskeletal difficulty fear of further worsening of their condition by involving in physical activity, in turn, try to develop a sedentary life and contributes to raise chances for their disability (Rodrigues et al. 2018). Thus, education about the positive effects of physiotherapy and way to achieve them is to be provided to the patients by the physicians so that they try to avail care and be empowered to support their own health. In the process, it is also mentioned that physiotherapist is to work in cooperation with the physicians to understand the complication and history of health for each patient. This is because physicians are well-informed about the musculoskeletal difficulties faced by patents over the years (Gray et al. 2017). Thus, on the basis of the information, the physiotherapist can identify the physical therapy to be avoided and provided for each patient for appropriately enhancing their health without error in care with person-centred approach.
In the musculoskeletal medicine ward for outpatients, the inter-professional learning activity included the way dieticians and physiotherapists are to work collaboratively in sharing knowledge to ensure better health of individuals within less time. This is because dieticians mention enhanced quality diet for patients that provide them required nutrients to support body function whereas the physiotherapist provides the physical therapy which is able to enhance physical performance by patients with better nutrition intake, in turn, led to ensure better health (Phang et al. 2018). For example, taking in calcium-rich diet by osteoarthritis patients with the assistance of dieticians improves their calcium intake. This, in turn, helps them to have stronger bones and execute effective physical exercise without hindrance suggested by the physiotherapist that eventually leads to better progressive health scenario for the patients within limited time (Gowan, 2019).
The community rehabilitation centres have the key aim to assist people with any form of disability through community-based medical integration, physical therapy programs and equalisation of opportunities (Parker et al. 2019). In the centre, the inter-professional learning activity included the way assertiveness is to be expressed in collaborative communication along with mutual respect are to be upheld among professionals in the collaborative practice. It was mentioned through the activity that assertiveness in inter-professional practice is to be maintained by expressing one’s thought without being aggressive and in positive manner. This is because aggressiveness in communication develops dispute and lack of respect for one another in inter-professional care delivery which led to hindered coordination in care (Roper et al. 2017). Thus, in the rehabilitation, the physiotherapists while working with other professionals are to present their opinion with effective evidence in mutual way where both being aggressive and too much passiveness is avoided.
The inter-professional activity in the setting included understanding each other’s responsibility in providing person-centred care. This is required to raising any confusion or duplication care for the patients that leads to wastage of resource and time. In the activity within the community rehabilitation centres, it is mentioned that professionals are to work within their limits and involved in continuous development along with training to provide care as per changing preferences and needs in the healthcare field. The role of the carers in the activity within the placement activities mentions that respect to the patient’s choice of care is to be maintained to provide them support in their best interest. (Refer to Appendix 1)
3. Personal Statement
The inter-professional activity in the placement at the neurological ward led me to understand that effective team working in delivering person-centred care can be established through inter-professional approach by presence of enhanced communication. This is because through communication key health needs and demands identified through diagnosis of their health can be shared among different health professionals. It leads each of the professional develop understanding of the roles and responsibilities to be executed by each of them in delivering person-centred care to the service users for improving their well-being through speedy recovery. As argued by Arakelian et al. (2017), lack of understanding of the needs of the patients leads to error and unsatisfied care towards them. This is because health professionals are unable to determine the intervention effective for better and speedy recovery of the patients based on their current health complication. Thus, effective communication is one of the key roles to be following in delivering person-centred inter-professional care.
The placement in the neurological ward also led me to understand that it is role of each professional in the team to inform other professionals about the techniques to be maintained for the patients care in each of the professional’s absence so that continuous and effective person-centred care is established. For instance, in absence of the physiotherapist, they are to educate the nurses through sharing of information and techniques regarding the way stroke patients are to be supported for walking to appropriately balance their body and avoid falls. In each of the placement, the team responsibility in person-centred care is identified to be coordination and collaboration. This is evident as in each activity; focus on the way collaborative practice can be established through coordination of different health professional in the care field is highlighted. For example, in neurological care, it is mentioned that nursing professionals are to form coordination with the physiotherapist in delivering care to the patients so that continuous improvement of their health is promoted. Moreover, in musculoskeletal medicine ward, coordination between physicians and physiotherapists are mentioned to be established so that enhanced care is provided to the patient.
The activity in the placement led to understand that professional perspective of inter-professional care mentions that each of the professionals is to avoid being rude in asserting any information. This is because rude behaviour with aggressive nature leads the professionals to show lack of respect and tolerance towards other professionals in the team. It leads to develop conflict and dispute among professionals in care delivery. This is because aggressive way of communicating and putting forward points for opposing or supporting any care intervention in inter-professional context leads to show lack of value towards other professionals and makes them feel being dominated (Ogden et al. 2017). The inter-professional activity in the placement led me to understand that common care goals are essential for team members for a single patient to established effective person-centred care. This is because without common care gaols the professionals would act in haphazard manner to fulfil different care support as per their own perspective for the patients in which in turn leads to deliver unstructured and chaotic care support to the patients (Levesque et al. 2018).
The inter-professional activity in the placement led me to understand that diverse health professionals with different expertise are to be involved in person-centred care of the patients. This is because the diverse professionals help to delivery care from different healthcare domain to ensure speedy recovery for the patient (Cederwall et al. 2018). This is evident as in musculoskeletal medicine outpatient unit, the involvement of dieticians along with physiotherapist professionals are mentioned so that they both can implement their diverse expertise in enhancing muscular efficiency of patients suffering from muscular health issues. The activity in the placement also led me to understand that professional perspective of the approach towards person-centred care includes use of complementary and unique abilities of each professional in the team to develop care for the patient. This is because it would lead to include best suggestion from potential professional to develop holistic and improved care for the patients (Arakelian et al. 2017). For instance, in each of the placement activity, it was highlighted that each professional such as me being a physiotherapist or others such as dieticians, neurologist, nurses and like as are provided ability to perform the care actions according to their expertise and share information with one another to enhance patient care.
The inter-professional learning activities in the placement led me to understand that for successful person-centred care the professionals are to communicate the actions to be executed by the patients and other professionals. This is because it helps to empower patients as well as professionals to have knowledge in taking action to ensure improved health condition of the patient (O’Sullivan et al. 2018). It is evident from the neurological ward and musculoskeletal medicine outpatient centre, where direct communication with the patients and other professionals are mentioned to be established so that patients can feel empowered in taking care and professionals can be ensured of delivering the right care. In the placement, I learned that role of inter-professionals to maintain effective team working is to communicate with one another in clarifying role to be played by each individual for promoting health of the patient. As commented by Williams et al. (2020), clarification of the roles to be played by each professional in inter-professional care for patients leads to avoid raising conflicts among service providers due to interference. This is because each of the individuals remains aware of the activity to be performed, in turn, avoiding to interfere in others’ work activities to deliver duplicated care to the service users. As argued by Sanko et al. (2020), without clarification of care responsibility in inter-professional working the health professionals lack direction and develop confusion in delivering care. Thus, clarification of each other’s roles is essential in inter-professional working to deliver person-centred as specific care responsibility for the patients is fulfilled with support from different professionals without confusion. (Refer to Appendix 1)
In the placement, I identified that inter-professional and collaborative working is executed on the policy context of NMC. This is evident as according to NMC Code effective communication is the key to deliver appropriate care because it assists in discussing and identifying the needs of patients. Moreover, the NMC Code mentions to avoid deliver care beyond any expertise of the professionals and shared responsibilities are to be appropriately known by professionals in delivering smooth care. The NMC Code also mentions that autonomy and empowerment to the patients are to be provided so that appropriate care can be delivered. The Code further mentions that care responsibilities are to be shared among individuals and effective delegation is to be maintained so that appropriate care without confusion is provided to the patients (NMC, 2018). The Health and Social Care Act 2012 mentioned that collaborative working among professionals is to be established for delivering enhanced care to the service users in their best interest and improve their well-being (assets.publishing.service.gov.uk, 2012). In discussion of the existing placement activity, it is seen that coordination in care is one of the key context identified in inter-professional working of person-centred care. Thus, it indicates the legislation is to be followed in determining the principles to be considered in inter-professional care. (Refer to Appendix 2)

The role of the carers in development of care services for the patients as per review of the placement activity is that evaluate the case history of the patient by consultation with the physicians. This is because the physicians or doctors are individuals who diagnose the patient over the years and have effective knowledge regarding the strength and limitation of body functioning of patient. Thus, the consultation is important so that the carer does not provide any support that would not be suitable for the individuals in resolving their complex health condition. The role of the carer in developing services for patients as per placement activity is to avoid any confusion in care for the patients. This is because it would lead to inappropriate care instances for the patients that would eventually deteriorate their health instead of enhancing it creating increased suffering from the patients.
The placement activity informed that role of the carers includes to work within the limitation of their abilities, knowledge and skills. This is because working beyond expertise and competence leads professionals to cause harm to the patients out of error in care. Moreover, it is also learned that role of carers in inter-professional approach is to engage in continuous professional and inter-professional training to enhance team performance in delivering support to the patients. This is because the healthcare field is continuously changing and accordingly alteration in team working is to be made so that appropriate care by following innovation can be provided.
Dig deeper into Children's Learning and Development through Partnership Working with our selection of articles.
References
- Arakelian, E., Swenne, C.L., Lindberg, S., Rudolfsson, G. and von Vogelsang, A.C., 2017. The meaning of person‐centred care in the perioperative nursing context from the patient's perspective–an integrative review. Journal of clinical nursing, 26(17-18), pp.2527-2544.
- assets.publishing.service.gov.uk 2012, Health and Social Care 2012, Available at: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/138268/C3.-Factsheet-Promoting-better-integration-of-health-and-care-services-270412.pdf [Accessed on: 29 July 2020]
- Bosworth, H.B., Pini, T.M., Walters, C.B. and Sih-Meynier, R., 2017. The future of patient engagement in the oncology setting: how practical patient engagement recommendations and innovative inter-professional education can drive change. J Participat Med, 9, p.e7.
- Burhansstipanov, L. and Shockney, L.D., 2018. Team-Based Oncology Care. In Team-Based Oncology Care: The Pivotal Role of Oncology Navigation (pp. 1-11). Springer, Cham.
- Cederwall, C.J., Olausson, S., Rose, L., Naredi, S. and Ringdal, M., 2018. Person-centred care during prolonged weaning from mechanical ventilation, nurses’ views: an interview study. Intensive and Critical Care Nursing, 46, pp.32-37.
- Gandolfi, M., Valè, N., Dimitrova, E., Zanolin, M.E., Mattiuz, N., Battistuzzi, E., Beccari, M., Geroin, C., Picelli, A., Waldner, A. and Smania, N., 2019. Robot-assisted stair climbing training on postural control and sensory integration processes in chronic post-stroke patients: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Frontiers in neuroscience, 13, p.1143.
- Gowan, J., 2019. Supporting your practice: Osteoarthritis: Non-surgical approaches. Australian Pharmacist, 38(4), p.40.
- Gray, J.M., Frank, G. and Roll, S.C., 2017. Integrating musculoskeletal sonography into rehabilitation: therapists’ experiences with training and implementation. OTJR: occupation, participation and health, 37(1), pp.40-49.
- Leary, K.S., Marchini, L., Hartshorn, J. and Johnsen, D.C., 2019. An emulation model in critical thinking used to develop learning outcomes in inter professional practice. Clinical and Experimental Dental Research, 5(4), pp.406-412.
- Lee, D.K. and Kim, S.H., 2018. The effect of respiratory exercise on trunk control, pulmonary function, and trunk muscle activity in chronic stroke patients. Journal of physical therapy science, 30(5), pp.700-703.
- Levesque, J.F., Harris, M.F., Scott, C., Crabtree, B., Miller, W., Halma, L.M., Hogg, W.E., Weenink, J.W., Advocat, J.R., Gunn, J. and Russell, G., 2018. Dimensions and intensity of inter-professional teamwork in primary care: evidence from five international jurisdictions. Family practice, 35(3), pp.285-294.
- Lupo, A., Giovanni Morone, M.D., Cinnera, A.M., Pucello, A., Coiro, P., Personeni, S., Francesca Gimigliano, M.D., Iolascon, G. and Paolucci, S., 2018. Effects on balance skills and patient compliance of biofeedback training with inertial measurement units and exergaming in subacute stroke: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Functional neurology, 33(3), pp.131-136.
- NMC 2018, NMC Code of Conduct, Available at: https://www.nmc.org.uk/globalassets/sitedocuments/nmc-publications/nmc-code.pdf [Accessed on: 29 July 2020]
- O’Sullivan, G.A., Hanlon, C., Dentry, T., Morris, T. and Banting, L., 2018. A qualitative exploration of the client experience of inter-professional practice in the delivery of ActivePlus: a combined smoking cessation and physical activity intervention. BMC health services research, 18(1), pp.1-11.
- Ogden, K., Barr, J. and Greenfield, D., 2017. Determining requirements for patient-centred care: a participatory concept mapping study. BMC health services research, 17(1), p.780.
- Parker, S., Hopkins, G., Siskind, D., Harris, M., McKeon, G., Dark, F. and Whiteford, H., 2019. A systematic review of service models and evidence relating to the clinically operated community-based residential mental health rehabilitation for adults with severe and persisting mental illness in Australia. BMC psychiatry, 19(1), p.55.
- Phang, J.K., Kwan, Y.H., Goh, H., Tan, V.I.C., Thumboo, J., Østbye, T. and Fong, W., 2018. Complementary and alternative medicine for rheumatic diseases: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Complementary therapies in medicine, 37, pp.143-157.
- Polat, B.S.A., Yiğit, Z., Köklü, K., Köylü, N. and Sonkaya, A.R., 2019. A neurological approach to fear of falling in patients with stroke. MSD, p.317.
- Rodrigues, E.V., Gallo, L.H., Guimarães, A.T.B., Melo Filho, J., Luna, B.C. and Gomes, A.R.S., 2018. Effects of dance exergaming on depressive symptoms, fear of falling, and musculoskeletal function in fallers and nonfallers community-dwelling older women. Rejuvenation research, 21(6), pp.518-526.
- Roper, R.R., Johnson, A.J. and Bostwick, E.N., 2017. A target’s perspective: Verbal aggressiveness, coping strategies, and relational harm. Communication Research Reports, 34(1), pp.21-28.
- Williams, E., Presti, C.R., Rivera, H. and Agarwal, G., 2020. Preparing students for clinical practice: The impact of a TeamSTEPPS® inter professional education session. Nurse Education Today, 86, p.104321.
Appendices
Appendix 1
Appendix 2:
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



