Enhancing Education through Data Architecture
Providing a Brief Overview of your Chosen Organisation
The chosen organisation for the present study is a secondary state school based in the UK (school x). School x is an academy converter, community school that enrols 1900, gender mixed pupils, from which 350 are in the 6th from. There are a high proportion of students from minority ethnic backgrounds, who speak English as an additional language.
¼ of the students are of White British background;
¼ from Indian background;
½ is made of students from Africa, Caribbean, Pakistani and others ethnic minorities.
39.9% pupils whose first language is not English
18.8% pupils eligible for free school meals;
1.9% pupils with an SEN Education, Health and Care Plan;
The school employs 250 teaching and support staff.
Describing the Organisational Problem Identified for this TMA
The schools are educational institutions, which aim at the education of the public by promoting the development and wellbeing of the society (reference). School x business goal is expressed by their vision that aims at the development of highly literate, articulate, numerate, resilient and confident students, equipped with the qualifications and skills required to succeed in the 21st century (reference). This way, the organisational problem comes up from the school x need to:
Manage students’ academic progress;
Manage their finances;
Manage their operations.
Hence, the question that defines the problem: How can data management enhance teaching and learning processes?
Explaining the Relevance to the Organisation and Problem
Data Architecture arises from the data needs of an organisation to achieve their business goals. Therefore, Data Architecture is the data map (master blueprints) that facilitates the integration of a data system to manage data as an asset, by identifying data storage and processing needs (International, 2017). School x has as business vision the development of well qualified students. For such, there is the need to design a business strategy in order to manage their enterprise needs. Data Architecture adds the technological extension to their business strategy, by enabling the understanding of how data needs to flow around the organisation. Hence, by understanding the decisions that have to be made:
Academical;
financial;
operational;
Hence, as to achieve their business goal, the school x needs to have in place a method, an organisation that will ensure that, the required information is available at the right time and at the right place. Hence, it falls under the data architecture, to secure that data will be managed as an asset by adding value to the organisation – school x (International, 2017). Data modelling and design (DM&D) focuses on the need of the organisation to represent and communicate the data in a precise way, which serves the purpose that aims for. DM&D is the process of creating a data model, which will ensure that the data is processed and outputted as an asset (International, 2017). School x, requires that the right data is available at the right time, at the right place and also with the right format. Thus, school x data model will provide:
a vocabulary glossary around data;
the understanding about school x’ s data and systems;
an essential communication tool during the projects;
a starting point for customization, integration and/or replacement of an application,
School x, utilises a School Information Management System (SIMS) modular application that enables the storing of the school data such as recording students’ legal registration, achievement and sanctions and to manage public examinations. School x also utilises SIMS to manage their financial and operational activities. Consequently, DM&D is of primordial importance for school x, by enabling that the data stored, processed and outputted by SIMS has the right format to be used as an asset.

Describe the Activities Undertaken or Planned with Outcomes
Data Architecture
In terms of Data Architecture, following DAMA-DMBOK2 and the online article by (Parkinson, 2017), there is the need:
To define the data vision in line with the business vision.
In the case of school x, the data requirement focuses on the students’ data. For the present assignment the financial and operational data requirements are not addressed. However, it is understood that, both the financial and operational data management requirements exist to support the students’ data needs.
To define how the business information requirements will be met.
In terms of information requirement, school x needs to:
. To keep a record and have access to students’ personal details: Previous schools; family background; medical conditions; etc.
. To track and record students’ learning progress for the several subjects;
. To record and have access to the students register following a weekly timetable with different times and classrooms for each subject/class;
To translate the business information required into a roadmap.
For the present assignment, given that school x, already has in place a School Information Management System (SIMS) as their main data tool. It was decided only to illustrate and comment a simplified map of the SIMS in place at school x. Based on (reference) SIMS uses client-server architecture. This is a distributed application structure that partitions tasks or workloads between the servers and the clients. For school x, this translates into inputting all the information regarding the students:
. Personal details;
. Attendance;
. Behavior;
. Learning progress;
This information is then, stored into SIMS file-server through a local area network (LAN) (reference), possible of being accessed from outside the school through a wide area network (WAN) (fig. 1). SIMS back-end service is based around Microsoft SQL Server – a relational database management system that uses a structure and language consistent with first-order predicate logic.
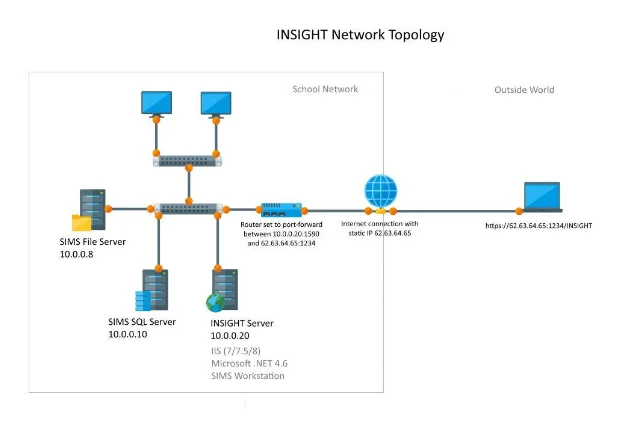
This allows the third-party developers to build products that integrate with SIMS – through Capita's "Partner Program". The client user interface is also built with .NET and manages the data manipulations and reporting workload. The timetabling module included with SIMS is a Windows API application that stores data in flat binary files.
Data Modelling and Design
Following the DAMA-DMBOK2, Data Modelling and Design (DM&D) is the process of fetching and analysing data and representing and communicating it in precise form called data model (International, 2017). Therefore, a data model sets an organisation’s data as understood and required by the organisation (International, 2017).
In line with DAMA-DMBOK2 and (Teka, 2008)) there is the need in a first instance to describe the functional and non-functional requirements of the system.
The functional requirements for school x, are:
Register a student;
Record attendance of students;
Generate various reports;
Generate timetable.
The non-functional are security requirements as classified data is stored in the database. User validation happens during login to ensure that the user has access to the data requested.
For the present assignment, the module analysis adopted, in line with DAMA-DMBOK2 and (Teka, 2008), we have focused on:
Function model, by use case diagrams;
Dynamic model, describing the sequence diagram;
In terms of use cases, these are identified as:
Register student;
Record attendance;
Generate transcript;
View report;
Produce timetable;

The definitions for the different actors and use case descriptors. It can be found on appendix 1.
In order to capture the interaction between the different objects in a set use case, the sequence diagrams figure 3 shows the sequence diagram for the “recording attendance” use cases. The same diagram sequence can be applied to each one of the user cases (Teka, 2008).

Following the different uses cases that the system has, there is the need to simplify the process by decomposing the system into different subsystems. As shown in figure 4, the major subsystems identified are:
Student registration;
Login;
Attendance;
Report card;
Transcript;
Timetable;
Report;
It is an extended description of the subsystem decomposition. It can be found on appendix 2.

Report on Changes/Improvement
In terms of data architecture, the present assignment focused in describing the SIMS in place at school x. Given the present circumstances, it was not possible to carry extensive personal interviews with the senior leading team (SLT), responsible for managing the school data. This way, the present assignment focused mainly on researching articles about MIS in the schools nowadays, which limited the access to information about school x first-hand experience on the development, use and maintenance of their management information system (MIS).
SIMS, is the main MIS, used by school x. SIMS is an all in one, off the shelf software (reference), developed by Capita, that covers the financial, operations and academic data management needs. School x, in the same way as most schools nowadays, rely on third-party service providers, as Capita, to develop and manage the MIS required to run the school. Following (reference), SIMS being an all-in-one MIS, has as pros:
A central data storage – in the case of SIMS, a single cloud database that host all the school x data.
Unified user interface – A single look and feel of the SIMS.
Control over configuration – SIMS is customisable to a certain degree, in line with school x data management needs.
Different departments use the same system – this further allows a more homogeneous interaction with SIMS by the different departments. On the other hand, it also means that, the failure of one system can affect the other systems.
On the other hand, SIMS has as cons:
Price – The British Educational Communications and Technology Agency (Becta), reports that the costs charged to schools from Capita, have increased between 2.5 and 3 times from 1999 levels (reference).
Not user friendly – A good control over configurations, means many times difficult system navigation for a non-technical user.
Incapacity to change the system – Off the shelf, large scale products, means that, tailored changes for the individual users are very hard to make.
Storage – All data is stored in one single place, which can be a single point of failure in terms of data breach. However, holding data in multiple systems can result in mismatching data, duplication of operations, and inability to report or analyse data in the collective.
In terms of Data Modelling and Design (DM&D), the present assignment, supported by (Fung, Visscher, Smith, & Wild, 2001; Visscher & Bloemen, 1999), cited by (…………, 2007). Revealed that the use of MIS in schools, tends to be mainly used for clerical functions in order to solve structured problems*, such as e.g., the construction of timetables. Although, this improves the daily, operational, data management efficiency of schools, MIS in schools are not yet currently applied as a teaching and learning enhance tool. This is due to several reasons. This translates into a challenge bringing together administrative and classroom-level data. In the case of school x, SIMS is an off the shelf product and not a customised system, which means that, there was no predefinition of school x individual requirements. A customised system, and it would require the classification of the Content Information Architecture for school x, as described in the DMBOK (DAMA International, 2017). It would be a first step for the development of a MIS to support the decision making for ill-structure problems. As referred by (reference), ill-structured problems required problem diagnosis and the search for solutions. As described by (Visscher, 1996), cited by (Reference). There are four ways to achieve such outcome:
Analysing the correlation between variables, for example, between maths and computer science achievement.
Analysing patterns during a period of time, for example, staff rotation and students’ achievement.
Answering what-if questions, for example, will the student (y) behaviour improve if moved into a different class with less behaviour issues?
Information system-based policy evaluation, for example, what are the effects in repeatedly removing the same students from the classroom, on students’ achievement and behaviour?
School x MIS, SIMS, is a client-server (stand-alone) application, this means based on the study by (reference), that there will always the need to deal with database server management, clients upgrade, software interoperability and lack of support of different client platforms. Accordingly with (reference), the best way to manage the vast amount of data schools that produce to support decision making for ill-structure problems. It would be a cloud solution, as a platform with web access on the client side. This way, there would be no need for school x to deploy its own data centre, providing an easier access to the resources for all the stakeholders via web browser.
A description of the key distinguishing characteristics of cloud computing along with an explanation of why this topic is of relevance to the data management community and (if applicable) to your organisation.
Cloud computing (CC) is the access of computing services, such as applications, storage and processing power, via internet from a cloud service provider, with the option to pay as you go (reference). Hence, the organisations can avoid the investment of an IT infrastructure and maintenance it by only paying for the service that required. However, cloud computing providers get benefit from the returns of their investment by offering the same service to a wide range of customers.
CC accounts for more than a third of all IT spending worldwide (reference), translating into a sharp decrease in IT housing spending.
CC can be divided into three main models:
Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS);
The fundamental computing services such as physical or virtual servers, storage and networking are useful for companies that develop applications and require control of almost all the components.
Platform-as-a-service (PaaS);
It includes on top of storage, networking and virtual servers, tools and software, namely middleware, database management and operating systems to develop applications.
Software-as-a-service (SaaS);
It allows the access per-use by the customer of an IaaS via internet or app. Decreasing this way the dependence on the hardware and operating system specs. CC is a disruptive technology (reference), by changing drastically the way enterprise software is developed, distributed and implemented. CC is of higher importance to the data management community, by affecting all the actors in the IT industry (reference).
A summary of each article.
Development of Students Information Management System based on Cloud Computing Platform by Ibrahim A. Alameri and Gleb Radchenko. Addresses the need is also essential that institutes of higher education have in creating and managing information regarding the educational process.
The study then introduces different CC models:
Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS);
Platform-as-a-service (PaaS);
Software-as-a-service (SaaS);
The authors explain that it is possible to consider three types of CC infrastructure:
Public – provided for open use (e.g., government organisation);
Private – provided for single use of an organisation (e.g., business unit);
Community – provided for a specific community (e.g., policy);
The authors refer that a combination of two or more CC infrastructures (public; private; community) results in a hybrid infrastructure. The study also underlines that the share of resources and operation outsourcing produces security a concern in CC.
The study SIMS proposal, highlighting five main actors:
Admin*;
Teacher*;
Head of the department*;
Head of School*;
Student*;
The SIMS applications architecture:
Web browser client*;
Microsoft Azure cloud*;
ASP.NET Server*;
SIMS user interface*;
SIMS controller*;
SIMS model*, provided by ADO.NET* and windows Azure SQL Database*;
The study concludes by presenting the outline and Architecture of the SIMS development and implementation based on windows Azure platform.
The shift to Cloud Computing: The impact of disruptive technology on the enterprise software business ecosystem, by Lambert J. M. Nieuwenhuis, Michel L. Ehrenhard and Lars Prause. Discusses how the value network of enterprise software solutions has disruptively changed as a consequence of moving from on-premise to Cloud-based technology. Traditionally enterprise software vendor’s distribution was made by partners such as Value-Added Resellers (VARs), which included sales, installation, technical consulting, training and customization at the clients’ organisation. CC on its turn doesn’t have nothing to resell, technically install and no need to logistics. Previous studies have mainly focused on CC adoption, economic benefits, business model evolution and the changing value creation logic by value network from a wider perspective. The authors differentiate between:
“The Cloud” - data software and hardware centre and the service provided;
Enterprise software - software application, tools for modelling organisational processes;
IT development tools;
VARs.
In terms of CC business ecosystem, the study reports, that focuses mainly on three characteristics:
Platform – habitually provided by a single firm; includes services, tools, and technologies;
Symbiosis – refers to the relation between stakeholders within an ecosystem;
Co-evolution – means the development of ecosystem overtime by adding products and services to the core platform, thus creating extra value.
Regarding how value is created on-premise enterprise software. The study differentiates between:
VAR – bound contractually to a software vendor;
Consultant – more independent than VARs.
Addressing how value is created in Cloud-based enterprise software, the study highlights in particular the work by Boillat and Legner (2013), that distinguish deployment models (SaaS and PaaS). Referring the business model Enterprise SaaS + PaaS in which the enterprise software is provided within a platform, adding content value.
In terms of methodology, it adopts a qualitative approach supported by desk research with semi-structured interviews focusing on three specifics Cloud-base solutions:
Microsoft Dynamics AX;
SAP S/4HANA;
Sales force Sales Cloud;
In terms of generic value network of Cloud-based enterprise software:
Roles, actors and activities don’t disappear from moving from on-premise to Cloud-based technology;
The role of the consulting partner changes from an IT-intensive to a more business process management role due to the IT infrastructure on the client side becoming less complex;
IT consulting it is still pertinent because of security, data migration, interface definition, customization and mobile application development;
New value-added services occur through partners: financial consulting; license management; environmental consulting and service aggregation;
The vendor becomes a service provider in terms of: Infrastructure; Platform; Application; License;

Project management changes to a more agile approach in line with Cloud-based enterprise software process;
Through the technological platform provided. External developers, customers and partners can develop application, which extend the core functionality of the enterprise software;
The IT infrastructure becomes less relevant, allowing cloud customers to focus more on their core business.
In terms of future research, the study points out its limitations:
The study did not address the hybrid Cloud deployment model;
The study focused on the main actors, roles and activities not being entirely comprehensive;
Due to the short innovation cycles within the IT industry, it is expected for the findings to be quickly out-dated;
A comparison, contrastive analysis and evaluation of each article’s contribution to assessing the impact of cloud computing on the knowledge areas defined by the DAMA-DMBOK Data Management Framework.
The article, Development of Students Information Management System based on Cloud Computing Platform by Ibrahim A. Alameri and Gleb Radchenko, presents a Cloud-based platform as the best option for a SIMS, by not requiring an onsite data centre and enabling the sharing of resources for all users via internet. The study, the shift to Cloud Computing: The impact of disruptive technology on the enterprise software business ecosystem by Lambert J.M. Nieuwenhuis, Michel L. Ehrenhard and Lars Prause. Analysing the impact on the value network of enterprise software solution is considered as a consequence of changing from on-premises to Cloud-based technology. Data-Governance highlights the organisation need to manage data as a valuable asset (International, 2017). The study by (reference1) suggests a Cloud-based SIMS as the best option, in line with Data Governance aim by not requiring the up-front invest in an IT infrastructure, plus the maintenance costs, while facilitating the sharing of resources by all the actors via internet. DAMA-DMBOK describes Data-Architecture as the effective management of data, systems and data storage (International, 2017). Data Modelling and Design is defined by DAMA-DMBOK as scoping and communicating data in a precise form called the data model. The system proposed by (reference1), do not affect directly the data model. However, by changing the system to a Cloud-base one, it frees the client from relying on the device specs, increasing the computing capacity and so, the data model possibilities. DAMA-DMBOK describes Storage and Operations as the design, implementation and support of stored data to maximise its value (International, 2017). The SIMS designed by (reference1), by being hosted in the cloud, also aims at increasing the data storage and operation capacity and so, the data value. Data security is defined by DAMA-DMBOK, as the process that ensures data privacy and confidentiality. The study by (reference1) highlights that, while Cloud computing offer many computing capacities, it raises apprehensions regarding security. Data integration and interoperability is defined by the DAMA-DMBOK, as the process of data consolidation between data bases, applications and organisations (International, 2017). The system proposed by (reference1), underlining that interoperability is one of the issues of a stand-alone client-server application and one of the possible benefits of adopting a Cloud-based solution.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



