Learning Strengths
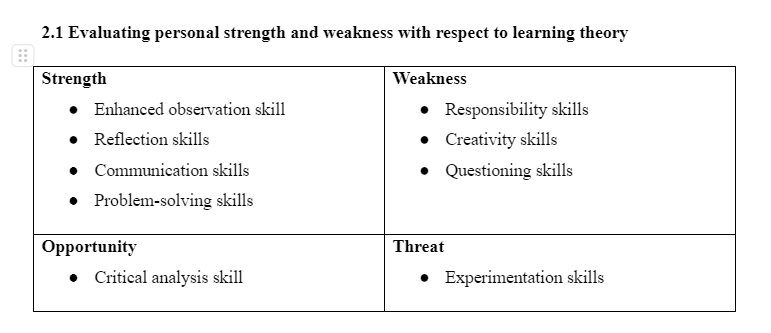
The principles of experimental learning theory inform that being a good experimental learner the individuals require to have improved observation skills, critical analysis and synthesis skill, reflection skill, experimental skills, curiosity, problem-solving skills and others (Kolb and Kolb, 2017). In my learning process, the teachers have often praised me about the intellectual and minute information I provide to them during field trips by observing the environment and experiences gained from it. It led me to understand that I have strength of effective observation skill in respect to experimental learning theory that I follow to get educated in my studies. Moreover, the teachers and peers have praised me regarding the way I minutely provide reflection regarding my experience in studies. It has often led me to determine where I lack concept and skills gaps that are hindering my studies. In respect to experimental learning, the presence of effective reflection skill is essential which I have as mentioned by the teacher that leads me to determine it as one of my strength since I am an experimental learner. My peers inform that I have enhanced problem-solving skill which is evident as I have always been able to overcome complex barriers during observation to gather information for using it in executing studies. The problem-solving skill is mentioned to be one of the key principles of experimental learning and the presence of skill therefore acts as my strength to successfully show that I am experimental learner. This framework is crucial in the context of education dissertation help as it underscores the importance of active learning and skill development.

In contrast, my peers have reported that in some instances they have seen me to act in an irresponsible way and avoid being a potential observer to gather information to be shared in the class. Since presence of responsibility skill is one of the key principles of experimental learning, thus the lack of the skill indicates it to me one of my weakness as an experimental learner. The teachers report that though I have effective observation skills but I often fail to present them in creative way by relating the knowledge with existing theories and concepts taught in the class. Thus, being an experimental learner, I have weakness of creativity skill which is mentioned to be one of the key skills to be present in individuals following experimental learning. However, my teachers inform that I do have effective communication skills to be used in overcoming the creativity issue in the learning. The presence of this skill acts as my strength being an experimental learner because through communication with others I can take assistance from them to improve my creativity skills. The analysis of strength and weakness in respect to experimental learning theory informs that I have hindered questioning skills. This lack of skills acts as weakness for me to be a experimental learner because without asking potential questions I can no further delve deep into experiments to develop greater informative observation to be used in executing studies.
3.1 Evaluating two learning theories
The behaviour learning theory informs that all the learned behaviour and skills are attained through interaction with the surrounding environment and the innate or inherited factors have minimum influence on the learning (Patey et al., 2018). The strength of using the theory for learning is that it provides information about different practical methods or techniques to be implemented in shaping the learning process for effective results. Moreover, the theory focuses on supporting learning process by using scientific disciplinary information availed through experimental and vigorous research (Ginja, 2018). However, the criticism of the theory is that it does not consider the way mental processes can influence learning in the environment (Kwasnicka et al., 2016). Thus, it fails to inform the way mentally-ill individuals show certain learned behaviours which are not influenced by the environment. Moreover, the other criticism of the theory is that it fails to consider the influence of biological factors that support learned behaviour in humans. The theory also takes a one-dimensional approach in explaining the learning process due to which it fails to inform the way free will of individual influences the learned information or behaviour in people (Kwasnicka et al., 2016).

The experimental learning theory informs that people develop knowledge in the learning process by transforming data from experiences (Kolb and Kolb, 2017). The advantage of experimental learning is that it allows individuals to effectively apply their learned knowledge immediately in practical field. This is because in the method the learning occurs through solving real-world issues and challenges instead of reel-world problems which provide the learner to develop understanding of the best principles and processes to be used in overcoming challenges in real life (Botelho et al., 2016). The experimental learning creates coaching of the learner based on what they have observed during the practice. Thus, it includes briefing session where coach provides direct review and feedback to the learners to develop their skills and learn better way of taking actions in life (Botelho et al., 2016). The other benefit of experimental learning is that it provides opportunity to individuals in learning impeccable communication and team working skills. This is because the experimental learning occurs in a team where the individuals are provided opportunity to interact with their teammates to develop learning about facts in studies (Jose et al., 2017). The experimental learning helps to accomplish obvious actions and allows students to reflect on their practice habits to determine their personal strength and weakness (McCarthy, 2016). This is evident as the learning process allows the students to make self-monitoring of personal learning to determine their strong skills and weaknesses faced in the course of learning. However, the weakness of using experimental learning theory is that it is a decentralised approach which is regarded to provide less orderly and comfortable ways in which teacher can teach students about learning certain complex information (Botelho et al., 2016). Moreover, the experimental learning process leads the teacher requires increased amount of time in processing the learning approach to educate students. In addition, active assistance from teacher is always required by the student in following this learning theory which in real-life may not always be available (Dyke, 2017).
References
Botelho, W.T., Marietto, M.D.G.B., Ferreira, J.C.D.M. and Pimentel, E.P., 2016. Kolb's experiential learning theory and Belhot's learning cycle guiding the use of computer simulation in engineering education: A pedagogical proposal to shift toward an experiential pedagogy. Computer Applications in Engineering Education, 24(1), pp.79-88.
Dyke, M., 2017. Paradoxes of a long life learning: An exploration of Peter Jarvis’s contribution to experiential learning theory. International Journal of Lifelong Education, 36(1-2), pp.23-34.
Ginja, S., 2018. Commentary: What more can we learn from early learning theory? The contemporary relevance for behaviour change interventions. Frontiers in psychology, 9, p.23.
Jose, S., Patrick, P.G. and Moseley, C., 2017. Experiential learning theory: the importance of outdoor classrooms in environmental education. International Journal of Science Education, Part B, 7(3), pp.269-284.
Kolb, A.Y. and Kolb, D.A., 2017. Experiential learning theory as a guide for experiential educators in higher education. Experiential Learning & Teaching in Higher Education, 1(1), pp.7-44.
Kwasnicka, D., Dombrowski, S.U., White, M. and Sniehotta, F., 2016. Theoretical explanations for maintenance of behaviour change: a systematic review of behaviour theories. Health psychology review, 10(3), pp.277-296.
McCarthy, M., 2016. Experiential learning theory: From theory to practice. Journal of Business & Economics Research (JBER), 14(3), pp.91-100.
Patey, A.M., Hurt, C.S., Grimshaw, J.M. and Francis, J.J., 2018. Changing behaviour ‘more or less’—do theories of behaviour inform strategies for implementation and de-implementation? A critical interpretive synthesis. Implementation Science, 13(1), p.134.
Take a deeper dive into Learning Resources Management with our additional resources.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



