Mental Health and Nursing Students
Introduction
Students’ mental state and coping mechanism can significantly affect the students’ outcomes and level of knowledge. Universities have an important role to play in providing support for students with mental health problems that may affect the students’ progress and ability to learn says by (Caleb 2013). According to the (Health Foundation 2019) a quarter of the total nursing students number are leaving the course for many different reasons in the UK. Most of the reasons are related to the financial state of the students and other reasons such as workload and the absence of support while enrolling in the program. Changing demographics in higher education may partially account for the higher prevalence of mental health issues (Johnson 2018). The students’ satisfaction is also one of the main reasons that a large number of nursing students are quitting the program. Nursing students satisfaction can play a major role on the nurses students progress in the nursing program .This satisfaction does not only mean how the students feel about the program its self but it's also measure the educational achievement and determine within the students are ready to start the training year. The clinical learning environment is important for nursing students satisfaction and important for them to demonstrate what they have learned in the classes to help the students to achieve their academic goal. According to (Jokelainen, 2011) the clinical learning environment is an interactive network of forces within clinical setting that influences learning outcomes. Satisfaction levels can be measured considering a lot of factors according to (Hirsch , 2015) in a cross sectional study showed that teaching dimension and the curriculum presented the highest mean followed by the environment dimension. The atmosphere of the clinical learning environment includes the clinical setting, the staff interacting with the students and the patients (EL Mokadem, and EL-Sayed Ibraheem 2017).
Dig deeper into Support Worker to Nursing Care with our selection of articles.
The evaluation of satisfaction that concerns the field of study in colleges is regarded as amongst the basic college subjects and significant portion of its activities belongs to the institutional procedure and behavior. Since the satisfaction and the interest in the field of study has been a key factor in the success and the education of the student, this issue must be a foremost priority in educational planning. In this context, there is need in the field of nursing of special abilities in interested individuals. There are a number of studies showing the students’ probation rate being greater than the satisfaction. A correlation exists between the students’ academic achievements and their satisfaction level related to their field of study. The studies have revealed that 90 percent students have satisfaction with the field of study and having a positive perception about it. One of the key factors enhancing students’ motivation and interest about the academic field of study is the satisfaction level with their field of study, income, and social position. Several studies have revealed that students’ previous information about the study field, description of duties, social image, the relationship of the students with professors, trainers, and hospital personnel, educational facilities, type of university, and related method of management are the key factors leading to the satisfaction about the study field among the students.

Aim of the review
The number of students leaving the program is increasing while the world is in a high demand for stuff nurses. It is a critical problem that can lead to an obvious lack of a good health care quality in hospitals and health facilities. Also it can play a major factor in nurses’ burnout and work overload overload. The purpose of this review is to evaluate the level of satisfaction among nursing students and the factors affecting that.
Method
This narrative review serves to provide comprehensive overview of wide recent and current papers that discuss the level of satisfaction among nursing students worldwide and the factors affecting on that. The literature has been searched in various electronic databases, such as Research Gate, Open Science, PMC, and American Journal of Health Sciences. Key words are used while searching for the literature. Key words are Nursing students satisfaction, Factors affecting nursing students, Nursing students, student nurses, Personal satisfaction; Education, nursing; Motivation; Educational measurement . The limitation has been put on the search to available materials in English. There have been 8 peer reviewed research papers identified for the review purpose. All of these studies have been published after 2010. The subjects of these studies are full time and graduate nursing students. These students are on campus students and doing a degree course rather than diploma course. The inclusive criteria and exclusive criteria are given below.
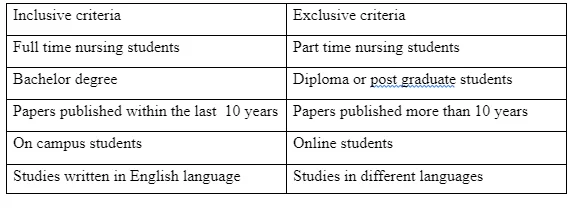
The literature studies in this paper have had the main focus on the student satisfaction related to clinical environment. The researches in consideration are analyzed and compared and contrasted among them. The transparency is maintained throughout the study with the detailed summary of all papers studied provided in the Table 1. A logical process is followed in selecting the published evidence in terms of the keywords, inclusion/exclusion criteria, and chronology.
Review method
A systematic narrative review method has been adopted in this study. The literatures used provide essential insights to the topic of this paper. The topics’ published research is compiled and examined critically of these resources (Gopalakrishnan and Ganeshkumar, 2013). The literature used in this study can be theoretical, systematic, methodological, historical, integrative, or argumentative. According to Wright et al, systematic review is the review of evidence on the formulated topic using the explicit and systematic methods for the identification, selection, and critical appraisal of primary researches and extracting and analyzing data from the inclusive studies of the review. A systematic review has been carried out in this paper with an unbiased assessment of the studies. The studies for review are selected in such a way that they can be the best evidences for the review to draw a meaningful and unbiased conclusion.
Analysis of Retrieved Evidence
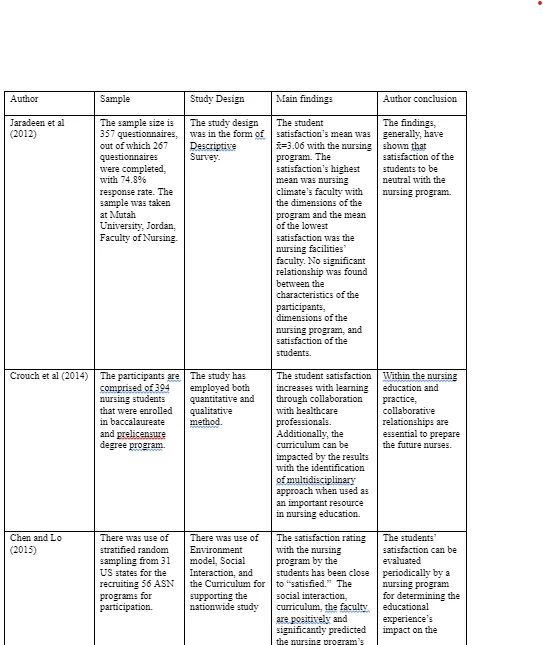
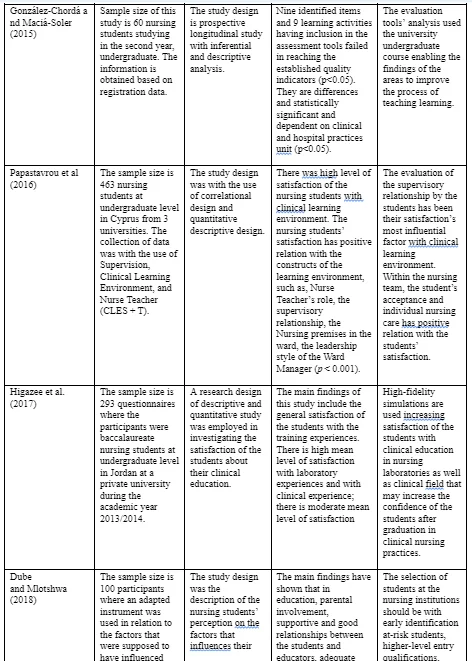
In the study conducted by Jaradeen et al (2012), the researchers developed questionnaire on the basis of student satisfaction literature review. The questionnaire is comprised of two parts: (a) introductory section about the study’s purpose and the background information of the students; and (b) there are 6 subscales: follow up academic performance, personal and academic development, nursing climate faculty, nursing facilities faculty, clinical practice, and instruction and curriculum. These 6 subscales have 46 items grouped within it. In the study conducted by Crouch et al (2014), an integrative method is used with experimental correlational and descriptive design forming the foundation of the study’s quantitative aspect. For the data analysis SPSS is used. The data storage is done in a computerized database and experimental correlational and descriptive analyses done on the collected data. The Chi square and t-test are carried out in assessing the correlation between the evaluation of the students before and after the inter-professional collaboration’s implementation. In the study conducted by Chen and Lo (2015), following a series of literature review and discussions with regards to comprehensive appraisal of student satisfaction, a conceptual model, CFSE (Curriculum, Faculty, Social Interaction, and Environment) is developed. This model is used for supporting the factors that measures the satisfaction of the nursing students. There is synthesis of the CFSE model in accordance with several literature review and concepts. The CFSE model’s fundamental is the belief that satisfaction of the student evolves from a dynamic process that an interaction influences and which is between learning and teaching environment on one hand and the student on the other hand. In the study conducted by González-Chordá and Maciá-Soler (2015), there is use of teaching method using clinical practice, simulated practice, and integrates theory through shared competencies and learning outcomes in the mentioned four disciplines that guides the content and avoid disruptions of the learning’s ongoing process.
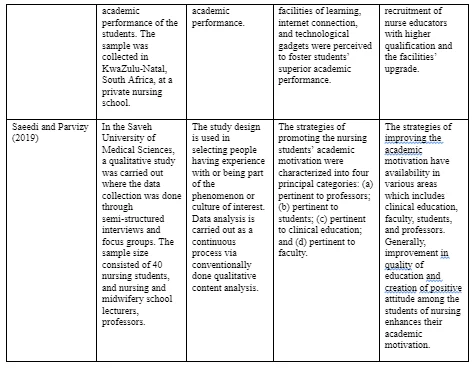
In the study conducted by Papastavrou et al (2016), descriptive statistics are used in calculating standard deviation, mean, and frequencies from the demographic data. The data’s reliability with Cronbach’s alpha is estimated. The deviation of data from normality is taken into account to select the non-parametric inferential statistics. Analysis is done by the correlation between CLE’s five constructs and correlation coefficient of the Spearman’s rho. In the study conducted by Higazee et al. (2017), the data analyses are done by SPSS. There is use of descriptive statistics (standard deviation, mean, and frequencies) in describing the sample and for the calculation of the mean score for student satisfaction in the clinical and laboratory setting. The groups were compared with use of t-test. Each instrument’s reliability is analyzed with the use of test-retest reliability and Cronbach alpha. The study conducted by Dube and Mlotshwa (2018) have captured data on excel sheet after gathering and examining their completeness. The questionnaires were subject to coding, computing, and analyses with the use of SPSS and with the support of statistical consultation service of the University KwaZulu-Natal. There is use of descriptive statistics in summarizing and analyzing data with the use of charts, graphs, and frequency tables as these provide clear and accurate picture of the findings. The study by Saeedi and Parvizy (2019) exercised the data gathering continuing till data saturation, Along with the data gathering, a simultaneous data analyses is conducted (after one week at the maximum). After a week, and following the interview, the content transcription of the verbatim is done to encode and analysis. The data analysis is carried out on the basis of the conventionally done qualitative content analysis. With this respect, the transcribed texts and the audio files are read and listened to for a number of times for achieving the participant comments’ general perspectives. Later on, there is review of the interviews to encode. Throughout the review, there is extraction of the primary codes and its categorization on the basis of differences and similarities so that extraction can be done of the categories and subcategories.
Discussion
The satisfaction of the students have its contribution to affective, social, and intellectual growth as with college and classroom retention, college persistence, motivation, and academic performance. The students who are satisfied are more dedicated and successful in accomplishing their goals compared to their unsatisfied counterparts. Jaradeen et al (2012) have shown the choice of the nursing studies by the students is because of the opportunity of finding jobs easily or for entering nursing the students’ score was just enough. A study carried out on the fourth and second year nursing students have shown innovation, autonomy, decision making, and independence accomplished with the help of self concept (Ahmed et al., 2010). Another study revealed that clinical skills are lacking in students before their graduation. Jaradeen et al (2012) study has shown that the satisfaction of the students, although, is neutral, the students of high percentage had satisfaction with the instructions and curriculum, which can be an aspect of nursing program. The satisfaction of the students is derived from the provision of safety and the instructors’ accessibility and with the members of the nursing faculty being responsible for the protection of students from the hazards of the hospital. Further, the findings have shown the friendliness of the students and this finding has consistency with other studies. This study has shown that to the faculty, the sense of belonging is lacking with the students; which may be, at least partly, because of the opportunity provided by the nursing field for finding a job or due to the fact that the choice the students had with the nursing on the basis of the university score. For the students whose mother tongue is not English, dissatisfaction to speak English is another factor. The study by Jaradeen et al (2012) has shown that students have dissatisfaction with problem solving skills, critical thinking, and writing. These findings have consistency with the arguments of Jinks and Pateman19. The students have strong dissatisfaction with decision making skills and to take responsibility. There has also been dissatisfaction of the students with nursing facilities, especially cafeteria services and restroom cleanliness. The reason that can be attributed to this is the awareness of the students of the importance of preventing infection and the universal precaution with regards to them. Moreover, this study has shown the low score of the students in the follow up of academic performance, facilities, and clinical practice. Thus, the nursing faculty is advised to be focusing on clinical training and acquisition of the students of required skills that the nursing career needs.
With collaborative relationships in educational courses rapidly gaining popularity, Crouch et al (2014) conducted a study to determine the extent of the nursing students’ satisfaction with nursing programs. Because of more demand for nurse educators than the supply, the on-campus programs are turning away many students as they have not been able to fill faculty positions in meeting the demands. There shortage of the nursing faculties bore a risk to prepare the nurses of the next generation. The answer is that within the nursing education and practice, collaborative relationships are essential to prepare the future nurses. The study conducted by Crouch et al (2014) explored the usage of multidisciplinary approach to the nursing education. The study has found that the student satisfaction increases with learning through collaboration with healthcare professionals. Additionally, the curriculum can be impacted by the results with the identification of multidisciplinary approach when used as an important resource in nursing education. The evaluation of the students is a direct communication means and serves the purpose of staying with the students. The increasing trend in education is students’ participation in the education experience. For this reason, voices should be given to the students in terms of the requests, concerns, and values. One way of achieving this is the collaborative teaching in ensuring the voices of the students being heard and acted upon. This has been an innovative solution to meet the healthcare needs and enrolment demands. Apart from the curriculum, quality of faculty, provision of safety and the instructors’ accessibility, language of instructions, and students’ participation in the educational experience through multidisciplinary approach; there is another important area where students can be satisfied or dissatisfied, which is social interaction and environment. Chen and Lo (2015) have found that social interaction between the students and the faculty is vital to develop the positive learning environment, and thereby leading to student satisfaction. These findings are endorsed by Zafrir and Nissim (2011), Rowbotham (2010), and Ojeda et al. (2011).
Chen and Lo (2015) study have found that students have lesser degree of satisfaction with the ADN or ASN programs in the environment area. The students have also shown lower level of satisfaction with the nursing skill labs and it must be noted that equipments cease to be up-to-date always, sometimes insufficient for their use and not in good repair. This aspect has been discussed with the study conducted by Jaradeen et al (2012) that found similar results and discussed above. The information technology, today, is the health care’s integral part. Thus, nursing program’s improvement can take place with instructions that are computer assisted in facilitating learning about the technological equipments that are rapidly changing and usable in clinical practice (Floyd et al., 2010). Chen and Lo (2015) have also highlighted on the students’ satisfaction based on the curriculum of the nursing studies and clearly stated syllabus and knowledgeable faculty who encourages learning. These aspects have been discussed with the study conducted by Jaradeen et al (2012) that found similar results and discussed above. The quality and training problems of the nursing education have resulted in demand for educational changes. The study conducted by González-Chordá and Maciá-Soler (2015) provided ways of approaching continual improvement in the teaching and learning process’ quality via the results and assessment tools’ analysis in order to establishing indicators in allowing the identification of the ways to improve the process and application of the actions on the basis of the pedagogical research and its best results. González-Chordá and Maciá-Soler (2015) argues that the traditional lectures were usable in explaining the nursing process. However, the problem based learning or the cooperative learning has emerged as the potential alternative, since the student is placed by these learning at the center of the teaching learning process, enabling considerable learning and provision of good results in spite of its difficult implementation.

It is notable that electronic records’ assessment tool records the items of larger amount that fails reaching the threshold quality. Prior training received by the students is in relation to the methodology and usage of record system with case methods. However, the nursing students’ innovative presence with the use of mobile devices with electronic registration system can be the reason for the cause of deployment process resistance and hindering their electronic record access (Thistlethwaite et al., 2012). This leads to probable impact on the evaluation results. In spite of these results, the usage of the software and other likewise tools can do improvement to nursing students’ clinical skills and encouragement of them in implementing and learning the nursing process in the time of clinical practice. Thus, promotion of the usage of this tool amongst the clinical nurses is necessary who guides the students. The continual improvement of quality has essentiality for the involvement of all stakeholders. The analysis of the study done by González-Chordá and Maciá-Soler (2015) included the students making the portfolio that helps identifying the possible improvement areas in the process of teaching and learning. In spite of these limitations, the obtained results have usefulness in commencing the development of the strategies for the improvement of the teaching learning process. Papastavrou et al (2016) revealed the positive learning experiences corresponding to the supervisory relationship in conjunction with the individual meetings’ frequency, the support and the presence of the NT and the notion of team spirit in the nursing care environment. The environment suggested by Papastavrou et al (2016) and the team spirit reflects the components of social interaction that has been argued and by and large supported by Chen and Lo (2015) and have been discussed above. The study by Papastavrou et al (2016) have shown the satisfaction by the nursing students with the practice environment and have been related significantly to all CLES + T dimensions: nurse teacher’s role and supervisory role, nursing premises on the ward, leadership style of the ward manager, and pedagogical atmosphere (p < 0.001). Although this study is in agreement with the studies conducted by Jaradeen et al (2012) and Chen and Lo (2015), these two studies have shown neutrality or dissatisfaction of the nursing students with the environment in contrast with the study by Papastavrou et al (2016), showing satisfaction of the nursing students. However, with the faculty or pedagogical atmosphere, all three studies have shown students’ satisfaction.
Higazee et al. (2017), too, support most of the findings by Jaradeen et al (2012), Chen and Lo (2015), and Papastavrou et al (2016) with respect to high level of satisfaction with respect to lab training. The satisfaction of the nursing students is moderate with regards to clinical training. The findings are same with Jaradeen et al (2012), Chen and Lo (2015), and Papastavrou et al (2016) that have found general satisfaction with their laboratory setting learning. The researchers, Higazee et al. (2017), are also suggestive that there is greater confidence and control among the students in the lab setting in relation to structured scenario compared to the actual patients in the clinical settings. Dube and Mlotshwa (2018) have shown that in education, parental involvement, supportive and good relationships between the students and educators, adequate facilities of learning, internet connection, and technological gadgets were perceived to foster students’ superior academic performance. Although many aspects of this study has distinct similarity with the study conducted by González-Chordá and Maciá-Soler (2015) and Crouch et al (2014) with respect to internet connection, and technological gadgets; there are some new fronts in the study such as poor family background of the students which contribute towards poor academic performance. Dube and Mlotshwa (2018) have also espoused the peer group influence, which is similar to social interaction having influence on students’ satisfaction as argued by Chen and Lo (2015). Dube and Mlotshwa (2018) are also proponents of use of English language as a negative influencer to the nursing students who do not know English very well. Jaradeen et al (2012) echoed similar findings in their research.
Nonetheless, some new angles of students’ satisfaction have been added by Dube and Mlotshwa (2018). In the study by Dube and Mlotshwa (2018), some factors are identified by the respondents that can bring about improvements to the students’ academic performance. The most important among them are the involvement of the parents in the education, and academic support services. Dube and Mlotshwa (2018) have also mentioned nurse educator-student relationship as a factor to improve student satisfaction, which is also echoed by González-Chordá and Maciá-Soler (2015), Chen and Lo (2015), and Papastavrou et al (2016). One final factor for the nursing students’ satisfaction which is not discussed in details by other authors is the strategies of improving academic motivation. The motivation is required by different areas that include students, faculty, clinical education, and professors, as argued by Saeedi and Parvizy (2019). These strategies, at least a part of it, have been the extraction from the direct comments of the participants, while another part was subject to determination on the basis of the problems that the participants’ highlighted. The participants of this study espoused that to create interest and positive attitude in nursing has been effective for the students’ academic motivation. There is a positive relationship between the academic motivation and interest in the study in nursing students. The root of the negative thoughts about the study field is due to lack of information and effect of friends and peers, not having awareness about the nursing profession, are some of the de-motivating factors for the nursing students.
Conclusion
There are eight primary studies selected for this review, which is done in systematic narrative design to evaluate and measure the satisfaction of the nursing undergraduate students in eight different institutions across the world. With respect to learning environment and teaching facilities and qualities, large scale satisfaction is found among the students, although there are elements of neutrality as well. However, there are iota of dissatisfaction among nursing students with respect to physical infrastructure of the nursing institutes, especially nursing facilities, such as cafeteria services and restroom cleanliness. There shortage of the nursing faculties has led to student satisfaction increasing with learning through collaboration with healthcare professionals in a multidisciplinary approach. Another area of importance is the social interaction between the students and the faculty which is vital to develop the positive learning environment, and thereby leading to student satisfaction. For greater satisfaction of the nursing students there should be continual improvement in the teaching and learning process’ quality via the results and assessment tools’ analysis in order to establishing indicators in allowing the identification of the ways to improve the process and application of the actions on the basis of the pedagogical research and its best results. To improve the training and teaching quality and thereby enhance student satisfaction, their innovative presence with the use of mobile devices with electronic registration system can be the reason for the cause of deployment process resistance and hindering their electronic record access. However, usage of the software and other likewise tools can do improvement to nursing students’ clinical skills and encourage them in implementing and learning the nursing process in the time of clinical practice. Finally, in education, parental involvement, supportive and good relationships between the students and educators, adequate facilities of learning, internet connection, and technological gadgets are also perceived to foster students’ superior academic performance and consequent increased satisfaction. In this review, a critical factor is that almost studies included in the review supported and complemented each other, although in each paper there are some new aspects highlighted. Overall, large scale satisfaction among the undergraduate nursing students found in all studies, although some negative perceptions and dissatisfaction do exist.
References
Ahmed, I., Nawaz, M. M., Ahmad, Z, et al. (2010) ‘Does Service Quality Affect students' Performance? Evidence from Institutes of Higher Learning’, African Journal of Business Management, 4(12): 2527-33.
Crouch, S. J., Fillmore, L., Phelps, S. L., and Ukot, E. (2014) ‘Enhancing The Learning Environment Of Nursing Students Through Interprofessional Collaboration’, American Journal of Health Sciences, Vol(5), No(1): 1-24.
Dube, M. B. and Mlotshwa, P. R. (2018) ‘Factors influencing enrolled nursing students’ academic performance at a selected private nursing education institution in KwaZulu-Natal’, Curationis, 41(1): 1850.
Floyd, E., Lewis, N. C., and Walker, E. H. (2010) ‘Creating a learner-centered environment in nursing education: An immersion experience’, Journal of Adult Education, 39(1), 11-17.
Gopalakrishnan, S. and Ganeshkumar, P. J. (2013) ‘Systematic reviews and meta-analysis: understanding the best evidence in primary healthcare’, Family Med Prim Care, 2:9–14.
Higazee, M. Z. A., Rayan, A., Ades, M. A., and Alrawashdeh, F. (2017) ‘Nursing Students’ Satisfaction with Their Clinical Experiences’, International Journal of Nursing and Health Science, 4(2): 16-21.
Jaradeen, N., Jaradat, R., Safi, A. A., and Tarawneh, F. A. (2012) ‘Students Satisfaction with Nursing Program’, Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 34, No. 1, March.
Ojeda, L., Flores, L. Y. and Navarro, R. L. (2011) ‘Social cognitive predictors of Mexican American college students’ academic and life satisfaction’, Journal of Counseling Psychology, 58(1), 61-71.
Papastavrou, E., Dimitriadou, M., Tsangari, H. and Andreou, C. (2016) ‘Nursing students’ satisfaction of the clinical learning environment: a research study’, BMC Nurs., 15: 44.
Rowbotham, M. A. (2010) ‘Teacher perspectives and the psychosocial climate of the classroom in a traditional BSN program’, International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship, 7(1), 1-14.
Saeedi, M. and Parvizy, S. (2019) ‘Strategies to promote academic motivation in nursing students: A qualitative study’, J Educ Health Promot., 8: 86.
Thistlethwaite, J. E., Davies, D., Kid, J. M., MacDougall, C., Matthews, P., Purkis, J. and Clay, D. (2012) ‘The effectiveness of case-based learning in health professional education A BEME systematic review: BEME Guide No. 23.’, Med Teach., 34(6):e421–e444.
Zafrir, H. and Nissim, S. (2011) ‘Evaluation in clinical practice using an innovative model for clinical teachers’, Journal of Nursing Education, 50(3), 167-171.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



