Titrating Sodium Hydroxide With Sulphuric Acid
LAB REPORT: TITRATING SODIUM HYDROXIDE WITH SULPHURIC ACID
Introduction
Titration is a technique that is used to carry out quantitative studies entailing neutralization reactions of acid-base to help in the determination of the concentration of a solute in a solution. As such, a solution with an accurate concentration, known as a standard solution is gradually added to a solution whose concentration is unknown, till the chemical reaction between the two is complete (Flaschka, 2013). To determine the concentration of a solute in a particular solution, a sample of the solution is combined with the reagent of the standard solution. Consequently, the volumes of the standard and unknown solution and the concentration of the reagent solution are then used calculate the concentration of the unknown in a process known as acid-base precipitation (ZHANG et al., 2018). If you are seeking education dissertation help, understanding techniques like titration can be crucial for your research.
In this particular experiment, sodium hydroxide is titrated with sulfuric acid, and then an indicator, Phenolphthalein is used to determine the end point of the titration, when the chemical reaction between the two solutions is complete. The indicator usually changes colors at different pH values. Phenolphthalein is an indicator that is colorless in acidic solutions while turns pink in basic solutions. In titration, when the color changes, it means that the acid has finally been all neutralized and therefore the acid that initially made the solution colorless has no more base to react with (ARYANGAT, 2018).

For this experiment, to determine the concentration of sodium hydroxide by titrating with sulfuric acid, the neutralization reaction is as follows;
H2SO4 + 2 NaOH → Na2SO4 + 2 H2O
The neutralization happens when the acid and the base are in comparable stoichiometry, in which the amount in moles of the sulfuric acid is equivalent to the amount in moles of the sodium hydroxide base.
Further, the changes in pH that occur during the acid-base neutralization reaction are measured through a pH meter and then the pH results noted down. Subsequently, the changes in the pH of the solution are plotted against the amount of the acid added to produce a titration curve which is illustrated in a graph. This shape is significant in explaining what happens during the reaction.
Aim and objectives
The main aim of this laboratory experiment is to determine the concentration of sodium hydroxide solution by titrating with sulfuric acid. The objective is to perform the titration of the sodium hydroxide solution which is base, and an acid, sulfuric acid in order to be able to calculate the molarity of the sodium hydroxide solution.
Materials and methods
Apparatus:
Conical flask 1 x 250 cm 3 Filter funnel Beaker 1 x 250 cm 3 Burette 1 x 50 cm 3 Pipette 1 x 20 cm 3 White tile, Stirring rod, burette clamp and stand
Chemicals:
a) 100 cm 3 0.2 M Sulfuric acid, H2SO4 solution
b) 10 cm 3 solution containing Sodium hydroxide NaOH (with pipette)
c) Phenolphthalein solution
Procedure:
Health and safety: Eye protection and avoiding direct skin contact with the chemicals.
- Use the funnel to pour a few cm 3 of the NaOH solution into the burette.
- Transfer 20 cm 3 of the 0.2 M sulfuric acid to the conical flask by using a pipette
- Titrate the sulfuric acid with the sodium hydroxide in small volumes while swirling gently till the color changes from clear to pink and then record the burette reading
- Refill the burette back to the zero mark, add drops of the indicator and titrate again taking note to stop 2 cm 3 before the previous recorded end point, then add continue titrating dropwise until there is a color change. Record the accurate measurement of the end point.
- Repeat process again to have another accurate measurement for averaging
- Determine the concentration of sodium hydroxide through calculation
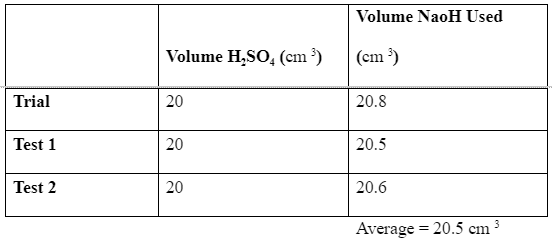
Results
The first titration is a test reaction to determine the closest range within which the solution gets fully neutralized (PAULING, 2015). Based on this initial trial test, two further tests are the carried out to obtain the closest average to the most accurate answer. In this experiment, the trial reading was 20.8 cm 3, while the first and second tests were 20.5 cm 3 and 20.6 cm3, an average of 20.5 cm 3. Which is the amount of sodium hydroxide that when added to the solution of the indicator and the acid, the color begins to change. This information is summarized in the table below. We can now use these results to calculate the accurate concentration of the sodium hydroxide based on the equation of reaction as below;
Data:
Titrating NaOH with H2SO4
The equation is: H2SO4 + 2NaOH 🡪 2H2O + Na2SO4
Calculation of concentration
Mole H2SO4 reacts with NaOH:

Molarity of NaOH, [NaOH]

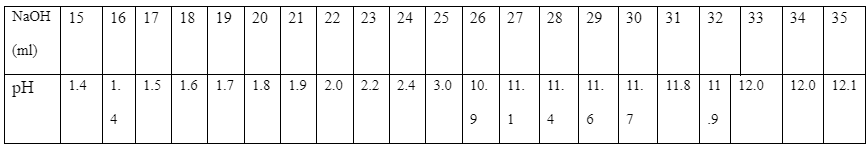
pH Meter results and Graph
A pH meter is used to measure the changes in the pH and then noting them down. The changes in the volume of NaOH in the burette are also recorded with the pH changes. These are plotted to give the curve.
In the experiment, during the first test, the color changes to light rose pink at a volume of 25.5ml while in the second test, the color changes at 25.6ml. The exact pH meter results are as tabled below:
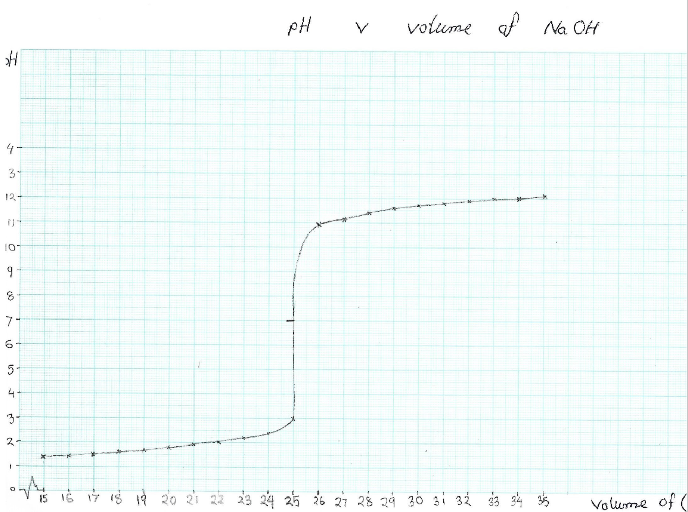
The figure below is a plot of the pH changes as 0.3 M NaoH.is added gradually to 20 cm3 of 0.2 M H2SO4
Discussion
The applications of the acid-base titration technique are a very helpful in the quantitative analysis and determination of the unknown acid or base solution concentration. For this particular experiment which entails the neutralization of the sulphuric acid with the sodium hydroxide, the reaction equation is;
H2SO4 + 2NaOH 🡪 2H2O + Na2SO4
In the titration, by using H2SO4 as the acid solution with the known concentration of 0.2 M and NaOH as the base solution, we have managed to successfully calculate and determine the unknown concentration as 0.3 M.
As the concentration of the sulphuric acid is already known, we can therefore obtain the concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution by titrating it against the sulphuric acid solution as laid out above in the procedure section. In this experiment, the controlled variables include the volume of the sulfuric acid in the conical flask which has been kept at a constant of 20 cm 3 all through. Further, the molarity of the sulphuric acid solution has also been kept constant at the value, 0.2 mol dm-3, also the number of drops of the phenolphthalein indicator are kept constant. All these efforts are to ensure that we obtain the most accurate results possible to be able to calculate the unknown molarity of the sodium hydroxide solution (McPherson, 2015).
The pH meter results and the graph are also helpful in explaining what occurs as the neutralization reaction takes place. As illustrated by the graph, the curve of the pH changes against the volume of NaOH added, In this titration of a strong base and a strong acid, as the 0.3 M NaoH.is added to 20 cm3 of 0.2 M H2SO4, the pH levels begin increasing slowly and then as the equivalent point is approached, the pH begins to increase rapidly. After the equivalent point, the pH levels increase slowly once more.
This is because the addition of NaOH, decreases the concentration of the H+ ions due to the neutralization reaction; OH−+H+⇌H2O. Therefore, the pH of the solution gradually increases. The equivalence point is the point at which the number of moles of the base equal that of the acid. The pH increases rapidly at this point due to the fact that most H+ ions have been consumed. The equivalence point denotes the completion of the neutralization reaction. The pH of the solution is 7 at this point (as shown in the graph). Gradually adding more NaOH leads to rapid increase in the pH, which eventually levels off at the value of about 11, which is the pH of the 0.3 M NaOH.
Some of the notable precautions that have to be taken during this experiment to minimize errors and ensure accuracy include; rinsing the apparatus after every subsequent use, keenly observing and measuring the volume of the solution during titration, continuously shaking and whirling the solution in the conical flask and finally, making sure the solution in the burette flows slowly, reducing it to drops when nearing the previous reading to make sure there are no mistakes in the accurate measurements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 0.2 M of sulphuric acid were neutralized by 0.3 M of the sodium hydroxide base as presented in the experiment results. In other words, after conducting this experiment systematically and carefully, we can conclude that the concentration of sodium hydroxide that was used is 0.3 M and from the chemical equation, the molar ratio of the reaction between the acid and the base is 1:2.

References
- ARYANGAT, A. (2018). The MCAT chemistry book: a comprehensive review of both general and organic chemistry. West Hollywood, Calif, Nova Press.
- Flaschka, H. A. (2013). EDTA Titrations: An Introduction to Theory and Practice. Kent: Elsevier Science.
- McPherson, P. A. C. (2015). Practical volumetric analysis.
- PAULING, L. (2015). General chemistry. New York, Dover Publications, Inc. https://www.freading.com/ebooks/details/r:download/MDAwMDE4LTgyNTIyMTg=.
- ZHANG, X., HUANG, M., ZHAO, J., LIU, J., YANG, W., & QU, K. (2018). Monitoring acid-base, precipitation, complexation and redox titrations by a capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detector. Measurement. https://nls.ldls.org.uk/welcome.html?ark:/81055/vdc_100059465867.0x00004c.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



