Understanding Asset and Liability Management
Asset And Liability Management
Asset and Liability Management generally referred as (ALM), is defined as a process to address the risk faced by a bank due to variance between assets and liabilities either due to change in liquidity or due to change in interest rates. Institutional ability to meet the liability is changing with the changes in liquidity means of the institution where it can meet the liability through converting asset and by borrowing. In order to mitigate the firm’s ability to pay the liability, changes in liquidity is a useful process to manage the asset and cash flows. Business profits depend on the organisational asset and liabilities and it can be managed through cash flows operations. In this context, Asset Liability management (ALM) is generally implemented to manage the bank loan portfolio as well as the pension plans. Bank profitability and long term availably can be managed through ALM where it targets net economic values and the interest margin.

The bank managers are responsible to review the payment and the liabilities to forecast the cash flows and in this regard, it is necessity to ensure the liquid asset of the bank to pay the due debts. The asset earnings need to be converted into cash to increase the cash flows as well as the banks can buy and sell the excess liquidity. In the recent years, the banks are paying attention to manage the both sides of balance sheet, not just only forecast the asset. The financial institutions mainly focus on diversity their assets through investing in many projects to avoid over investing in a single sector and reduce the risk of investment. Asset management system is also efficient for the institutions to manage the cash flows and improve financial operations in long run where liquid asset and the reserves are maintained efficiently.
In order to manage the liability risk and interest risk, ALM is also suitable process, where the banks can manage their risk associated with currency exchange risk, defaults, asset and liabilities and interest etc. for managing balance between the current assess and long term potential earnings, the bank’s board of directors and the senior management team aim to develop the strategy to acquire funds at low cost when operating in the money market.
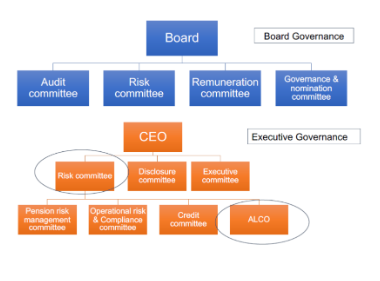
Due to banking industry’s business model and its association with various business risks, there was a need to develop a committee to look after the process of ALM and therefore, the need to develop an asset and liability committee was found.
However nowadays a basic banks governance structure can be seen as follows:
BASIC BANK GOVERNANCE STRUCTURE
To under the functions of ALM, we can look into its main objectives as follows:
1. Net interest income
The banking institutions may earn more interest from its asset but it does not mean that the banks will be profitable as it pays its the liabilities and also there are some other expenses which are such as employee wages, utilise, administrative cost, rent, and management salaries. After subtracting all these expenses, from the net interest income, it becomes negative, which indicates that, the banks are not profitable even after earning interest income. As per the asset and liabilities of the banking institutions, the major assets are personal and commercial loans, securities and mortgage and there are the liabilities like interest bearing customer deposit.
2. Net interest margin
Net interest margin can be determined as the investment of the banking institutions on depositor’s money which is the difference between the rates paid to the bank’s clients and the amount of the borrowers of the funds. Efficiency of the banking institution depends on the investment criteria, if the institutions are able to make positive margin, the investment is efficient. Negative margin means lack of optimal decision making behaviour, where the institution’s expenses exceed the amount of return. The banks utilise some credit products to improve net interest margin which are mortgage and loans, certificate deposits and savings accounts.
3. Market value of a bank’s equity
The economic value of equity (EVE) is calculated by cash flows after subtracting the present value of liabilities. Apart from earnings at risk and value at risk (VAR), the banking institution utilises the economic value of equity for managing the asset and liability. Net present value (NPV) is also another tool to manage asset and liabilities for measuring the economic gain of the bank.
4. Asset and liability management
ALM is the major process which is advantageous for proper planning, controlling as well as maturities, and values of the asset and liabilities so that the banking institutions can mitigate the risk factors and maximise their profitability in long run.
Risk of asset values indicates the interest rate risk where volatility of interest rate affects the increase and decrease of the asset value. It is utilised for calculating the primary dive in the market to assess foreign exchange rates, fixed income bearing securities like equity and bonds. There is inverse relationship between the interest rate and the prices of fixed income bearing securities. There are different types of risks which are discussed further,
Price risk:
According to the increase and decrease of the interest rate, there is fluctuation of the prices of the fixed income securities like bonds which may results to unpredictable gain or loss when the security is being sold.
Reinvestment risk:
With the fluctuation of the interest rate, there raises non-availability of the opportunity to reinvest in the current investment rate and it is subdivided into two types which are duration risk and the basic risk.
Duration risk:
As per the duration risk, the risk is associated with the probability of unwilling pre-payments or the extension of the investment period.
Basis risk:
The risk of not experiencing the exact inverse features to interest rate and the changes in the securities.
The financial institutions aim at transferring the funds between those who are willing to lend and those who is to borrow and this process of known as financial intermediation. The institutions are managed with the financial intermediation by standing between the ultimate lender of the finds and the ultimate borrowers of the funds. Through this financial activities, the institutions are willing to manage their liabilities and increase financial asset to lend more funds to the, to the person who are willing to borrow from the intermediaries. They charge the margin for profit maximisation and it further is known as interest income.
The diagram below is the explanation of the process,

Under the process of financial intermediation, there are many strategies for lending and borrowing through which the funds are being transferred among the individuals and the banking institutions which are explained below,
Investment:
The financial intermediaries such as the mutual funds and the investment banks try to obtain funds from the lenders in order to maximise the investment pool, and it further provides a scope to the financial institutions to invest in different projects through investment diversity portfolio management to earn more as per the different profit margins. The stock market and the money market activities are increasing through this strategy where the intermediaries pay the lenders as per the pre-agreed rate of interest. The investment portfolio is characterised by low risk low gain and high risk high reward formats.

Lending funds to the borrowers:
The financial intermediaries lend fund to the borrowers in short and long period of time. The institutions try to lend money to the people who are willing to borrow as per the pre-agreed terms and condition as well as pre-agreed interest rate. The margin is calculated by the interest expense and the interest income. The funds of the borrowers are ranging from the finance cars and home loans to the corporate looking expansion and running finances where it is helpful to improve the cash flows of the business.
Storage of liquidity assets:
The financial intermediaries are also ale top provide liquid cashes such as cash and bonds in the format of the current accounts. There are silver and gold bonds according to the time period of lending and borrowing. The deposit cards, slips, cheque books and credit cards are deposited by the depositor where the banks are liable to provide their deposits and withdrawals when required as per the needs of the depositors.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



