Identifying Lung Cancer with H and E Staining
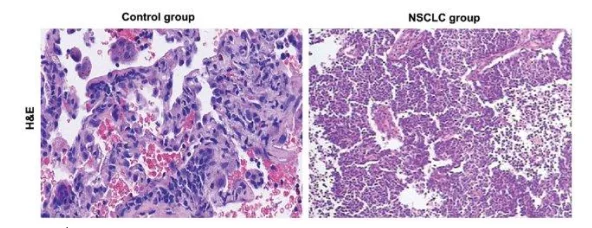
Bronchogenic carcinoma is subtype of the lung cancer, which is basically a neoplastic growth that starts from the epithelial tissue of the bronchiole. This is of two types one is small cell lung-cancer and another is non-small-cell and both of them have same kind of symptoms (Behera, 2010). The most common cause of this carcinoma is smoking and other causes are like exposure to some radioactive gas, excessive pollution and/or genetic predisposition. The histopathology detection of bronchogenic carcinoma cell and normal lung can be done by using H and E staining (Haematoxylin and Eosin) among the four mentioned histology staining like H&E, Masson’s Trichrome, Van Gieson and PAS staining. This stain is used to detect the cellular and the tissue structure in details by the pathologist and the range of this staining is very wide from cytoplasm and nucleus to the features of extracellular matrix (Feldman, et al, 2014). The haematoxylin stains the nucleus in blue and the cytoplasm and extracellular matrix stained with eosin and turn pink. This staining is best to detect the lung tissue from the bronchogenic carcinoma patient as this will differentiate at the cellular level and this carcinoma type is either small cell or non-small-cell carcinoma. (Petersen, et al, 2010) Understanding these distinctions is vital for healthcare professionals, and seeking healthcare dissertation help can provide further insights into effective research methodologies in this area

Explain in detail the key identification points for the normal and the diseased tissue, which parts of the tissue will be targeted by the stain?
This stain will be uptake by the cell nuclei, cytoplasm and the extracellular matrix and it gives the knowledge regarding the pattern, cell shape and size, which is helpful to distinguish from the normal cell to carcinoma cell. As during the carcinoma the uncontrolled growth pattern will change the shape and structure of the cell, so the carcinoma cell can be mainly distinguished from the normal cell by its shape and structure through the staining. The cell nuclei fragmentation in carcinoma cell can be the key point to detect, as the colour will be deconvoluted in the cell carcinoma type after uptake of the stain. Cell nuclear segmentation also observed in the cell having larger density which occurs due to the uncontrolled growth of the tissue in the cancer cell type. (Vahadane, et al, 2013) The key features for the staining for carcinoma cell are deep nuclei staining due to large amount of nuclei in carcinoma cell, the deep staining and the intercellular bridges are observed sometimes but they are rare. The nuclei-cytoplasmic ratio for bronchogenic carcinoma are higher than that of the normal cell type of the lung (Bernardi, et al, 2018). In some subtype keratinization also observed in the tissue which cannot be seen in case of the normal cell type. Lepidic growth pattern also observed in case of the adenocarcinoma subtype. The neoplastic cell also does not show any tissue boundary after staining where as the normal lung cell shows. The normal lung cell has a specific architecture which can be observed after the staining but the carcinoma cells do not have any specific architecture, so they seem to be arranged in a haphazard manner. There is a huge variation of cell size in case of the carcinoma cell, and the nuclei are sometimes very prominent even many times larger than the normal nuclei. (He, et al, 2012) The hyperchromatic nuclei means the dark coloured nuclei is the most prominent feature of the carcinoma type and also sometimes giant cells are appeared which is nothing but the combination of the genetic materials of the different cell types, this differs largely from the normal cell of lung. Thus the main targeted part of the tissue by this staining is the cell cytoplasm, nucleus and the extracellular matrices.
What is the resulting outcome?
As the tumour propagating, here the carcinoma tissue are differentially stained by the H&E stain than that of the normal cell type, so the resulting outcome will be a clear distinguishable characteristic of the carcinoma type. Also different cell carcinoma for bronchogenic carcinoma like, small-cell, non-small cell can also be distinguished by this staining procedure. This can be used as the primary detection tool for the carcinoma detection in case of lung cancer, but to confirm it, along with H and E staining other immunohistochemical staining is needed, by which the cell marker can be differentiated for the normal and carcinoma cell type. (KaKodKar, et al, 2016)
Compare the advantages and disadvantages of the stains used.
The main advantage of this staining technique is it’s less complexities and easier preparatory method. It can also differentiate largely the carcinoma cell from the normal cell types clearly.
The disadvantages are like the process is time consuming if paraffin technique is used to prepare slide and if frozen slides are used then the image resolution will decrease rapidly, so there will be a chance of mixing of normal cell with carcinoma cell types. The specificity of this staining is lesser than that of immunohistochemical staining procedures. The procedure is also human error prone and sometimes it is difficult to identify specific type of carcinoma cell from a group of subpopulation. (Inamura, 2018)
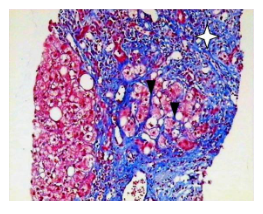
Liver hepatitis is an inflammatory condition of the human liver, which mainly caused due to the viral infection and it’s secondary causes are like the use of drugs, toxin or alcohol and also sometimes this is due to autoimmunity. The impacts of this disease is many fold mainly on the metabolism. Liver hepatitis are many types like, A, B, C, D and E. Among these A is short term and acute, whereas B, C and D are chronic and long term and E happen to be specific for pregnant women. (Mahtab, 2012) The liver hepatitis cell can be distinguished from the normal hepatic cell by using Mason’s Trichrome staining among the four mentioned staining procedure like, H&E, Masson’s Trichrome, Van Gieson and PAS staining. This staining procedure is used to detect the hepatic pathologies like the hepatitis as well as cardiac, muscular and nephrological pathologies (Krishna, 2013). This stain shows the blue colour to the collagen and the background hepatocyte shows red colour along with the other structures. The stain is uptake by the type I collagen, which is present in the vessels wall and also in the portal tract and this appears in the injured liver tissues. This stain is used to differentiate the liver cell from the injured liver cells by the liver hepatitis or other chronic liver diseases (Singh, et al, 2018).
Explain in detail the key identification points for the normal and the diseased tissue, which parts of the tissue will be targeted by the stain?
The normal liver tissue is predominated with the presence of type I collagen, which is present in the capsule and in the portal tract and can be stained with the Masson’s trichrome staining, in case of diseased cell type this type I collagen shows the reactive fibrosis which can be observed by the staining. Which shows the presence of excess connective tissues and also periportal fibrosis, where the extracellular matrix gets remodelled as well as excessive collagen deposition occurs. The bright blue coloration of the portal tract appears due to the excess type I collagen in damaged hepatic tissue. In some cases thin and broad septa for fibrosis are observed in the damaged/diseased tissues. Other key features that are observed in the liver with hepatitis are the pattern of the scarring that appeared around the central vein and also the fibrosis associated with the perisinusoidal part that separates the hepatocyte cords. Also the formation of the fibrous septa is one of the major feature which leads to the advance stages to secondary stage of fibrosis. (Suvik, et al, 2012) In the normal tissue there will be no feature of nodule formation but in case of liver with hepatitis there will be a series of nodule surrounded by the fibrous gland.
What is the resulting outcome?
The normal liver tissue shows the pattern and structural feature while staining with the Masson’s Trichrome which is vastly different from the hepatitis tissues, as the excessive collagen type I will be present in damaged tissues, this can be clearly distinguishable with the help of this staining procedure. The resulting outcome is therefore, to detect the liver fibrosis and other liver diseases, specially the chronic hepatitis at its earlier phase with the help of this histopathology staining.
Compare the advantages and disadvantages of the stains used
The major advantage of using this Masson’s Trichrome is its clear nature of identification of the fibrosis and the septa in the liver tissue with hepatitis. The contrast of the blue colour with the light pink in the background makes it easier to identify the collagen structure in the disease tissue. (Alisi, et al, 2011) Whereas the normal H and E staining could not differentiate the collagen structure very clearly. This method is far more advantageous than the traditional histopathological staining procedures.

Disadvantage of this staining are like the lack of specificities, as this staining also not very specific like the immunohistochemical staining.
References
Alisi, A., De Vito, R., Monti, L. and Nobili, V., 2011. Liver fibrosis in paediatric liver diseases. Best Practice & Research Clinical Gastroenterology, 25(2), pp.259-268.
Behera, D., 2010. Text book of Pulmonary Medicine.
Bernardi, F.D.C., Bernardi, M.D.C., Takagaki, T., Siqueira, S.A.C. and Dolhnikoff, M., 2018. Lung cancer biopsy: Can diagnosis be changed after immunohistochemistry when the H&E-Based morphology corresponds to a specific tumor subtype?. Clinics, 73.
Feldman, A.T. and Wolfe, D., 2014. Tissue processing and hematoxylin and eosin staining. In Histopathology (pp. 31-43). Humana Press, New York, NY.
He, L., Long, L.R., Antani, S. and Thoma, G.R., 2012. Histology image analysis for carcinoma detection and grading. Computer methods and programs in biomedicine, 107(3), pp.538-556.
Inamura, K., 2018. Update on immunohistochemistry for the diagnosis of lung cancer. Cancers, 10(3), p.72.
KaKodKar, U.C., Vadala, R. and Mandrekar, S., 2016. Utility of Cell-Block of Bronchial Washings in Diagnosis of Lung Cancer-A Comparative Analysis with Conventional Smear Cytology. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research: JCDR, 10(4), p.OC25.
Krishna, M., 2013. Role of special stains in diagnostic liver pathology. Clinical Liver Disease, 2(Suppl 1), p.S8.
Mahtab, M.A., 2012. Liver: A Complete Book on Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Diseases-E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Petersen, T.H., Calle, E.A., Zhao, L., Lee, E.J., Gui, L., Raredon, M.B., Gavrilov, K., Yi, T., Zhuang, Z.W., Breuer, C. and Herzog, E., 2010. Tissue-engineered lungs for in vivo implantation. Science, 329(5991), pp.538-541.
Singh, A., Seth, R., Gupta, A., Nayak, B., Acharya, S.K. and Das, P., 2018. Chronic hepatitis E–an emerging disease in an immunocompromised host. Gastroenterology report, 6(2), pp.152-155.
Sun, X., Cui, F., Yin, H., Wu, D., Wang, N., Yuan, M., Fei, Y. and Wang, Q., 2018. Association between EGFR mutation and expression of BRCA1 and RAP80 innon-small cell lung cancer. Oncology letters, 16(2), pp.2201-2206.
Suvik, A. and Effendy, A.W.M., 2012. The use of modified Masson’s trichrome staining in collagen evaluation in wound healing study. Mal J Vet Res, 3(1), pp.39-47.
Vahadane, A. and Sethi, A., 2013, November. Towards generalized nuclear segmentation in histological images. In 13th IEEE International Conference on BioInformatics and BioEngineering (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
Viksna, L., Strumfa, I., Strumfs, B., Zalcmane, V., Ivanovs, A. and Sondore, V., 2012. Future Aspects of Liver Biopsy: From Reality to Mathematical Basis of Virtual Microscopy. Liver Biopsy: Indications, Procedures, Results, p.257.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



