Krebs Cycle in Aerobic Respiration
The Krebs’s cycle
The Krebs cycle also known as the citric acid cycle is a sequence of reactions through which energy is generated in living cells during aerobic respiration. These reactions occur in the matrix of the mitochondrion of the cell. It involves the conversion of energy rich pyruvate molecules formed during glycolysis to ATP which is a form of energy available for cell metabolism. Before entering the Krebs cycle the pyruvate molecules are converted into acetyl coenzymes. The conversion process involves the removal of a carbon dioxide molecule from pyruvate followed by the loss of an electron from NAD+ to form NADH This understanding of metabolic pathways is crucial for students, particularly those seeking healthcare dissertation help. The remaining acetyl then combines with coenzyme A to form acetyl coenzyme A. The acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle and the following occurs

1. Acetyl CoA combines with oxaloacetate forming a molecule with six carbons known as citrate
2. Citrate then rearranges producing isocitrate
3. Oxidation of the isocitrate produces a- ketoglutarate which is a five carbon molecule and the remaining carbon is released ascarbon dioxide. In this step a molecule of NADH is also produced by the reduction of NAD+
4. A further oxidation of a ketoglutate produces succinyl CoA with the release of another molecule of CO2 and another molecule of NADH
5. The succinyl CoA releases coenzyme A to form succinate and at the same time phosphorylates ADP forming ATP.
6. The succinate is oxidized to form fumarate and in the process FAD is converted to FADH2. The fumarate formed in the previous step is the hydrolysed to form malate. The malate formed is then oxidized to form oxaloacetate thus the cycle is complete.
The glycolysis of one glucose molecule results in the production of two pyruvate molecules. This means that one glucose molecule passes through the Krebs cycle twice and results in the production of two molecules of ATP, six molecules of NADH and two molecules of FADH.
The electron transport chain
This is the last part of aerobic respiration and it uses atmospheric oxygen. This process involves the movement of electrons through a series of electron transporters which undergo of redox reactions. The chain itself is made up of four complexes which are made up of a group of proteins. Parts of these proteins are coded for in the mitochondria DNA. The fifth complex of this chain is found in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. The transfer of electron between the complexes is responsible for the generation of energy. The first complex receives two electrons brought to it by NADH. These are the electrons produced from the digestion of the ingested food. This complex has NADH dehydrogenase. This complex pumps four hydrogen ions from the matrix and across the membrane. Complex two receives FADH2 directly without it passing through complex one. The 1st and second complexes are connected to the third by ubiquinone and this channel allows the transfer of electrons from both component one and two to component three. Component iii pumps protons through the membrane and passes its electrons to cytochrome for transport to component four. In component four, oxygen is reduced after which it picks two hydrogen ions to form water. This removal of hydrogen ions creates an ion gradient used in chemiosmosis. Complex five uses this concentration gradient to produce ATP through the proton rotation of this complex. Every cycle of electron transport generates thirty glucose molecules.
Glycolysis
This is a multistep metabolic pathway by which one six carbon glucose molecule is broken down producing two molecules of the three carbon atom keto-acid known as pyruvic acid. It occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and involves many enzyme catalyzed reactions. This process takes place in 10 steps five of which are preparatory phase and the rest five steps referred to as pay-off step. In the preparatory phase two molecules of ATP are used to break down the six membered glucose ring, to form trios phosphates. Glucose is phosphorylated and converted into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. In the pay-off phase the glyceride-3-phosphate formed during the preparatory step is converted into pyruvic acid and ATP is formed. For each molecule of glucose two pay-off steps occur and two pyruvic acid molecules are formed. A detail of the 10 steps are discussed below.
1. The first step is the conversion of D-glucose into glucose - phosphate a process catalyzed by enzyme hexokinase
2. The glucose-6-phosphate produced in step 1 rearranges to fructose-6-phosphate catalyzed by glucose phosphate isomerase.
3. Fructose-6-phosphate is converted into fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aided by enzyme phosphofructokinase and magnesium as a cofactor
4. Fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate is then split into two isomeric sugars, dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.aided by enzyme aldose.
5. The next step involves a rapid interconversion between glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate by the aid of triophosphate isomerase . Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is then removed to be used in the next step.
6. An inorganic phosphate from the dehydrogenation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is added to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate resulting into the production of 1, 3-bisphophoglycerate
7.Enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase then transfers a phosphate group from 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerateto ADP forming ATP and 3-phosphoglycerate.
8. A phosphorous atom in 3-phosphoglycerate is translocated to position two forming 2-phosphoglycerate aided by enzyme phosphoglycero mutase.
9. A water molecule is then removed from 2-phosphoglycerate by enzyme enolase forming phosphoenolpyruvic acid.
10. The enzyme pyruvate kinase then transfers a phosphorous atom from phosphoenolpyruvic acid and adds it to ADP to form ATP and pyruvic acid thus the completion of the process of glycolysis.
Method and results
1. 40ml o water and 10ml of lime water was put into a 100ml beaker
2. A straw was then put into the solution
3. The time was set and each student asked to breath out into the solution through the straw
4. This was continued until the solution turned cloudy
5. The experiment was then repeated after asking the students to run down the stairs and back to the laboratory
6. Changes in the recorded time taken for the solution to become cloudy were studies and the two conditions
Results
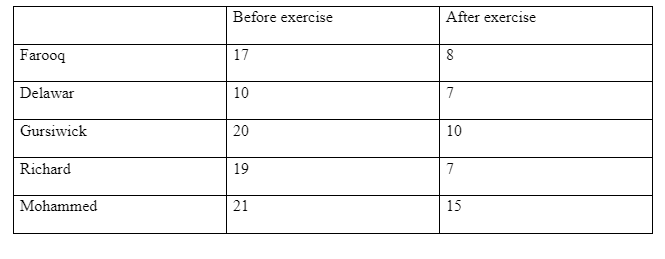
From the results obtained there was a difference in the time taken for the limewater to turn cloudy between when the students had not exercised and when they had exercise. Before the exercise the limewater took longer to turn cloudy compared to after the exercise. This is explained that during exercise the body’s oxygen demand goes high because of increased muscle contractions and a corresponding response by the cardiovascular and respiratory system to supply the oxygen demand. Increased breathing implies both inhalation and exhalation. Hence more carbon dioxide is produced leading to the limewater turning cloudy faster. It is the presence of carbon dioxide that makes limewater cloudy. The abnormality in Mohammed’s results can be as a result of other respiratory conditions such as asthma.

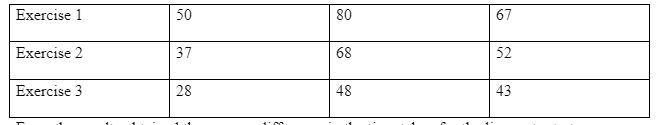
From the results obtained there was a difference in the time taken for the limewater to turn cloudy between when the participants had not exercised and when they had exercise. Before the exercise the limewater took longer to turn cloudy compared to after the exercise. This is explained that during exercise the body’s oxygen demand goes high because of increased muscle contractions and a corresponding response by the cardiovascular and respiratory system to supply the oxygen demand. Increased breathing implies both inhalation and exhalation. Hence more carbon dioxide is produced leading to the limewater turning cloudy faster. It is the presence of carbon dioxide that makes limewater cloudy. The abnormality in the results of A can be as a result of other respiratory conditions such as asthma.
Asthma
Asthma is a long term medical condition in which a person’s airways become inflamed, sensitive, and narrow and swell and produce extra mucus. This makes breathing difficult and can trigger wheezing, shortness of breath and coughing when exposed to asthmatic triggers. The two types of asthma are allergic asthma which is caused by allergens and non-allergic asthma which is caused by factors such a dad weather conditions, atmospheric pollution, exercise, stress and some medications. Asthma is incurable all that is done is to control its symptoms. In the diagnosis of asthma a physical exam is carried out to rule out other possible respiratory diseases with almost the same sign sand symptoms. Tests can also be carried out to determine the functionality of the lungs. These tests include lung pulmonary tests to evaluate air circulation and spirometry. Asthma can affect both the young and the old and can be detected at any point of one’s life. A person who has lived many years without any sign of asthma can suddenly become asthmatic while some people only display the condition after exposure to allergens
Pollution
Air is made up of several components such as oxygen carbon dioxide, nitrogen and rare gases of which argon accounts the largest fraction and water vapor. In addition to these there are other particles which can be introduced in the atmosphere which should not be there these including dust from farming or mining activities and acidic gases such as carbon (IV) oxide. These pollutants are harmful to health. When we breathe polluted air the heath of respiratory system and especially the lungs is compromised. This is because the respiratory system has an internal covering of a max membrane and the lungs are supposed to absorb air which is then transported to bloodstream for the supply of oxygen to the body tissues and organs.
Air pollutants such as ozone and free radicals have the following effects on the lung tissues. Ozone causes damage to the air racks the site of exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs organic pollutants get transformed into reactive metabolites in the air ways through enzyme activity causing injury to the lungs and posing dangers of cancer, one of the most dangerous pollutants is asbestos. Asbestos is a chemical made from a naturally occurring fiber substance and was widely used in roofing of houses; insulation in industries and as fireproof materials until it was banned on inhalation, the fine asbestos fibers enter the respiratory system. The body reacts by roughing them up in a layer of mucus surrounding the lungs. As the exposure increases accumulation occurs and although most of it is gotten rid of some of it enters and settles in the respiratory system. Long term exposure in the lungs causes a fibrotic disease of the lungs called asbestoses in this condition make causes breathing difficulties and it is serious and life threatening.
Chemical components of cigarettes
Cigarettes contain approximately 600 chemical components. Its smoke has around 7000 chemicals among which over 60 are carcinogenic. Some chemical constitutes of concern are nicotine which is a poisonous alkaloid which makes cigarette smoke cools. This substance collects in the lungs and is possible cause of cancer, carbon dioxide which reduces the oxygen carrying capacity of the lungs,
Health effects of cigarette smoking
Cigarette smoking harms nearly all organs in the body especially the lungs. In the lungs it damages the airways and the alveolus. The damage occurs in the form of inflammation. This may result in breathing problems such as short breath when alveoli are destroyed oxygen and carbon (iv) oxide exchange becomes compromised. The worrying thing is that the destruction of the alveoli is permanent. Emphysema and chronic bronchitis and lung cancer are some of the chronic diseases caused by tobacco cigarette smoking also triggers asthmatic attacks. Smoking also destroys Cilicia leading to more respiratory infectors such as pneumonia and tuberculosis.

Other types of cancer that can result from cigarette smoking include cancer of the esophagus, mouth, large mouth, throat, liver and myeloid leukemia. Cigarette smoking is worse because often the passive smokes get health effects for instance children whose parent
Evaluation
Air pollution poses serious health effects with different pollutants posing different effects. Nitrogen dioxide which is emitted from motor vehicles and industries increases lung infections for people with asthma and causes airway inflammation. Another pollutant is asbestos. It is dangerous because when it is crushed it divides into millions of fibers. It is these fibers that pose serious effects to the respiratory system on inhalation. It can also cause a special type of cancer known as mesotholiama a cancer which affects the linings of the chest and abdomen. To avoid pollution as a result of asbestos undamaged asbestos should be left alone and no more production should occur. Disease resulting from exposure to asbestos requires consistent exposure over a long period of time.
Several reports have been done on the health effects of smoking. These reports have discussed both the long term and the immediate impacts of smoking. The long term effects of smoking include the coating of the lungs with tar causing like cancer, increased work by the heart to try and ensure the limited oxygen gets to all body tissues. This results in narrowing of airways causing a risk of blood pressure and stroke, eye cataracts, emphysema, cancer, stomach ulcers and even impotence. The immediate effects of smoking include increased breathing rates, increased and rate of metabolism. It deteriorates elastin in the lungs causing its contraction and relaxation during breathing, makes the walls of the respiratory track to become thick and inflamed, narrows airways and destroys cilia by deposition of tar thus cigarette smoking affects almost all parts of the body by affecting the respiratory system.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



