Leadership Competence in Public Health
Executive summary:
Asthma is the health condition, in which patients have poor lung functions. This health condition is characterised by heavy cough, wheezing, chest tightness and breathing issues. Through carrying out the systematic process of health assessment it is possible to determine the current health needs of asthma patients which assists the health professionals to develop a relevant care plan in terms of promoting their health and wellbeing. This study is going to present the health assessment of a patient, Mr B who suffers from asthma. The study will present the baseline health report of this patient by discussing his current physical health condition, emotional and psychological wellbeing, medical history, pre-medical history and his living standard that are contributed to developing asthma in this patient. For those requiring additional guidance, healthcare dissertation help can offer valuable insights into the comprehensive analysis needed. Finally, the report will make a short recommendation, in which it will recommend the suitable advice or strategies that need to be implemented by Mr B to become free from the issues of asthma, such as lifestyle changes and dietary changes.
Critically Examine the Significance of Leadership Competence in Professional Public Health Practice, Using the Related Frameworks to Support Your Discussion

Introduction
The challenges facing the public health workforce has seen a dramatic upsurge over the past few years. For public health to serve society effectively, more efficient and scientifically sound practitioners and leadership development systems need to be established (Wright et al., 2000). Besides, adequate academic preparation for fieldwork is crucial. Basically, leadership competencies have been termed as the leadership skills and behaviors that significantly contribute to superior performance. Leadership competency has enabled public health organizations to better identify and develop and nurture leaders as the focus on the same promotes better leadership (Wright et al., 2000). Following the importance of leadership competencies to professional public health, this paper aims to critically examine and discuss the said significance using the frameworks besides creating a personal and professional development in alignment with professional leadership competencies.
Discussion
Organizational viability is dependent on the effectiveness of the leadership of the organization. Notably, effective leaders engage in not only personal direction but also professional leadership behaviors. Individual leadership behaviors involve building trust, caring for people as well as acting morally. On the other hand, as highlighted by the frameworks, professional leadership behaviors are inclusive of setting missions, creating a process for achieving the organizational goals, aligning the processes and the procedures amongst other roles (Wright et al., 2000). Personal leadership is a mediator of the association between professional leadership and the presence of willing cooperation. To be successful, leaders need to be concerned with task-related issues and people-related issues. Professional leadership provides direction, process, and coordination to the organization's members to attain the organization's goals. In doing this, the leaders set visions and missions for the organization, create a process for achieving the organization's goals, aligning operations and the procedures, the people within the organization, and the infrastructure to achieve the organizational goals (Wright et al., 2000). For personal leadership, it is defined as leaders' individual act in conducting the roles of professional leadership inclusive of a demonstration of expertise, building trust, caring, and sharing for people, and acting morally. From the Covey framework, personal leadership terms success as growing oneself while professional leadership involves growing others. According to the PHSKF framework of leadership, leaders need to work collaboratively and in a commissioning based culture. Professional leadership consists of the provision of administration to drive improvement (Wright et al., 2000). Also, experienced leaders need to communicate effectively with others within an organization. They need to design and manage programs and projects within an organization.
Leadership at the personal level has been noted to have a link with professional supervision. For instance, personal leadership has been found to carry a professional message to the organization.
Leaders cooperate and willingly contribute their efforts to the realization of organizational goals. Developing willing cooperation is a necessity for professional leadership. An experienced leader provides direction. For public health organizations with a passion for excellence, vision is their critical element, which is promoted by a professional leader (Popescu et al., 2016). Besides giving direction, experienced leaders implement and manage a systematic process. The process being driven by the professional leader should aim to achieve the common purpose of the organization. The leaders also offer coordination as a critical element of professional leadership. Coordination is inclusive of acquiring the essentials that are crucial to the operation of an organization. Each leader provides leadership to individuals that s/he supervises. To remove barriers to cooperation, leaders resolve strategic alignment (Popescu et al., 2016). Notably, professional leadership includes the formal part of leadership, setting the organization's vision and mission, and creating processes and procedures as discussed. Having a common goal and strategy to achieve a goal is a very important aspect of professional leadership.
As discussed earlier, personal leadership acts as the individual behavior of leaders in conducting the responsibilities of professional leadership (Popescu et al., 2016). As already mentioned, these are inclusive of expertise, trust, caring, sharing, and morals. Expertise is the ability and competence of leaders. Notably, leaders are positively perceived relative to their competence. Expertise provides power to leaders (Popescu et al., 2016). If employees have confidence in their leaders' expertise, they are more likely to cooperate to willingly attain the organization's goals. Trust is termed as the perceived honesty, sincerity, and dependability of leaders (Popescu et al., 2016). In the context of leadership, building trust is an essential component. Trust is a powerful force in leadership. Also, members of an organization will be more willing to cooperate if they trust theidirection Learners should thus strive to build trust in the quest to achieve organizational goals. Caring is the empathy and politeness that leaders have to employees (Popescu et al., 2016). They should be able to listen to the members to enhance cooperation, thus improving an organization. Professional leadership calls for the sharing of authority and information. Besides, moral behavior needs leaders to provide a moral code that dictates leaders' and members' conduct in performing their responsibilities in an organization (Popescu et al., 2016). Personal leadership is an essential contributor to willing cooperation among members of an organization. Professional leadership leads to a favorable view of the unique aspects of leadership.
Leadership competence plays a significant role in the change management process in healthcare. Leaders have to acquire and maintain the professional tasks' expertise within their competence (Al-Abri, 2007). Basically, managing change encompasses the handling of the complexity of the process. The change management process involves evaluating, planning, and implementing operations, tactics, and strategies by professional leadership in the public health context (Al-Abri, 2007). Change management is crucial to service improvement as applied to the delivery of public health (Hardison, 1998). The process is not only dynamic but complex and challenging. Leaders thus combine technological interventions and people-oriented solutions in managing change (Al-Abri, 2007). Growth in healthcare occurs rapidly, therefore unpredictable. Leaders are, however, ever ready with competence to work the same. The leadership explains to the organization's employees and members the rationale for change and the importance of endorsing the same (Al-Abri, 2007). To leaders, the change management process is sometimes demanding and fatiguing. Leaders take time and are committed to promoting change within their public health organizations (Hardison, 1998). Leaders are required to understand the process of change management (Al-Abri, 2007). They should help employees and other organization members not only stricture but also formulate an effective team by forming new organizational structures and creating a shared vision that focuses on the authentic employee's outcome.
Leaders establish a clear vision of the change process's direction as a crucial element for assuring successful change management. Besides, they measure and monitor the change process's outcomes as an essential measure for noting whether the change process has fulfilled the preset goal or not (Hardison, 1998). The leaders also record and focus on the emerging problems that result as a result of the change. This enables future management in a proper and best manner (Al-Abri, 2007).
Changes have created problems for public health organizations in a global context. Consequently, these have driven individual public health organizations to change accordingly to continue performing and improving healthcare quality (Al-Abri, 2007). Leaders have offered training on the changes in technology to the stakeholders. Besides, they have recorded all emerging problems and formulated the most relevant and appropriate solutions for each (Al-Abri, 2007)
Effective communication and team collaboration are crucial in healthcare in improving the quality of life (O'Daniel et al., 2008). Patient safety is put at stake with ineffective communication among health professionals. For instance, lack of critical information, fundamental misinterpretation of information, and lack of clarity in orders from leaders all contribute significantly to ineffectiveness in communication among healthcare professionals and other significant stakeholders (O'Daniel et al., 2008). Incidences of medication errors can occur due to a lack of communication. Besides, the errors significantly contribute to causing severe injury and fatalities, such as patient deaths. Leaders are thus at the frontline in ensuring effective communication with a public health organization.
Team collaboration in healthcare relates to the assumption of professional roles and cooperation by healthcare professionals (O'Daniel et al., 2008). Besides, team collaboration involves sharing responsibility for problem-solving and decision making in formulating and implementing plans for patient care in improving the quality o care in public health. Through team collaboration, awareness of the team members of the various knowledge and skills is integrated, thus improving the team's competency (O'Daniel et al., 2008). This impacts positively on patient care and outcomes. Trust, respect, and collaboration form the basis of effective teamwork. In teamwork, all employees work for the common goal of the organization. In a public health organization or setting, communication is easier with a cohesive team that easily works together (O'Daniel et al., 2008). There are several barriers faced by leaderships in the events s/he is making efforts to ensure effective communication. The challenges range from gender differences, cultural differences, and ethnic differences.
Leadership competence has been at the forefront of promoting effective communication and team collaboration in public healthcare organizations (O'Daniel et al., 2008). Several leadership skills are effectively applied to enabling effective personal performance and professional practice. First, a leader needs to commit to excellence and measure the important things noted in the change management process (McMahon, 2017). Also, leaders need to possess supportive skills. In so doing, leaders need to be compassionate with the employees, considerate of their concerns. Coaching and mentorship skills are also crucial to enabling effective public health organizations (McMahon, 2017). As already discussed, communication skills are an essential and very important leadership skill that is ultimately inevitable should a leader need to enable effective performance and professional practice. Following the PHSKF model's aspects, leaders need to work collaboratively, communicate with others, and provide leadership to drive improvement.
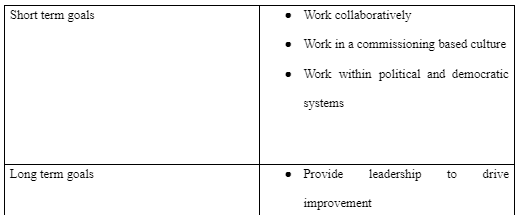
2. Create a personal and professional development plan aligned with professional leadership competencies
A professional development plan is basically a written document used to focus, evaluate, and prioritize professional development activities (Brand, 2014). The PDP is a tangible tool that can be used for future reference with a visual outline. It assists in identifying current and future needs and the resources needed with a structured plan and timeline that demonstrates personal interests and responsibility (Brand, 2014).

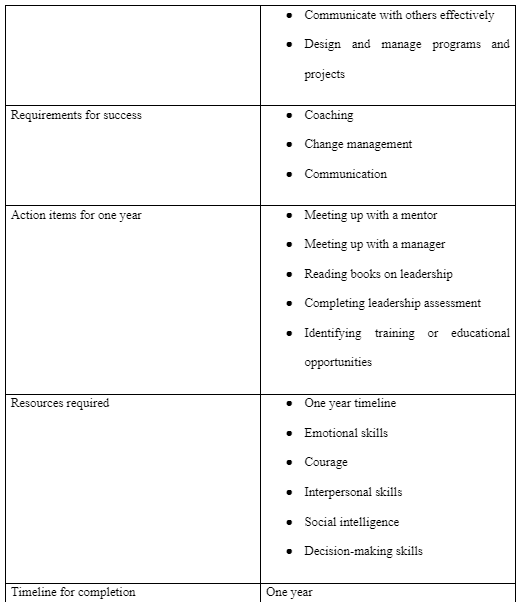
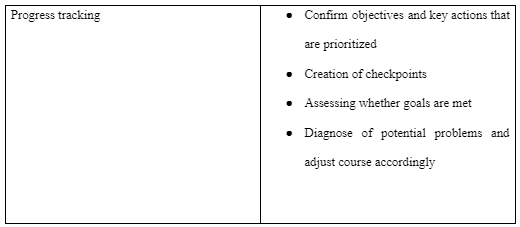
The professional development plan aims to improve leadership competence. The plan's requirements include coaching from a manager or a mentor, change management, and communication practice. To achieve the PDP goals, a meet up with a manager or a mentor will be crucial. Besides, books on leadership can provide information necessary for improving leadership competence. I will also complete a leadership assessment and ide notifies training opportunities to attend and gain the required knowledge. The resources needed for this professional development plan are emotional skills, courage, interpersonal skills, social intelligence, decision-making skills, and a one-year timeline to complete the program. The PDP will take place in a one-year timeline, and the progress will be tracked through the activities highlighted in the model below.
Professional Development Plan Model
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to Leadership Approaches in Enhancing Quality Improvement.
References
Al-Abri, R. (2007). Managing change in healthcare. Oman medical journal, 22(3), 9–10.
Clark, J., & Armit, K. (2010). Leadership competency for doctors: a framework. Leadership in Health Services.
Czabanowska, K., Smith, T., Könings, K. D., Sumskas, L., Otok, R., Bjegovic-Mikanovic, V., & Brand, H. (2014). In search for a public health leadership competency framework to support leadership curriculum–a consensus study. The European Journal of Public Health, 24(5), 850-856.
Hardison, C. D. (1998). Readiness, action, and resolve for change: do health care leaders have what it takes?. Quality Management in Healthcare, 6(2), 44-51.
Hayes, J. (2018). The theory and practice of change management. Palgrave.
Macphee, M., & Suryaprakash, N. (2012). First‐line nurse leaders' healthcare change management initiatives. Journal of Nursing Management, 20(2), 249-259.
McMahon, G. T. (2017). The leadership case for investing in continuing professional development. Academic Medicine, 92(8), 1075-1077.
O'Daniel M, Rosenstein AH. (2008) Professional Communication and Team Collaboration. In: Hughes RG, editor. Patient Safety and Quality: An Evidence-Based Handbook for Nurses. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US);. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2637/
Popescu, G. H., & Predescu, V. (2016). The role of leadership in public health. American Journal of Medical Research, 3(1), 273.
Van Tuong, P., & Thanh, N. D. (2017). A Leadership and Managerial Competency Framework for Public Hospital Managers in Vietnam. AIMS public health, 4(4), 418.
Wright, K., Rowitz, L., Merkle, A., Reid, W. M., Robinson, G., Herzog, B., ... & Baker, E. (2000). Competency development in public health leadership. American Journal of Public Health, 90(8), 1202.
Wright, K., Rowitz, L., Merkle, A., Reid, W. M., Robinson, G., Herzog, B., ... & Baker, E. (2000). Competency development in public health leadership. American Journal of Public Health, 90(8), 1202.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



