Multimodal Approach to Nursing Care
The write up will focus on using Bio-Psycho-Pharma-social (BPPS) model including environment to assess a patient needs and create a person-centred care plan. BPPS model is a multimodal tool used by clinicians to enable them to recognise the patient present situation, the significance in the interaction with history. The model also helps in structuring and guiding person-centred care through nursing assessment, formulation, and care planning (Barrera-Herrera et al., 2019). BPPS model is tailored to prevent challenging behaviours, communication difficulties, and diagnostic overshadowing which in turn reduces costly observation and improves patient experience while protecting liberty (Hext et al., 2018). The Nursing and Midwifery council code of conduct stated that it is imperative that patient confidentialities are kept throughout the write up, therefore in this essay, the pseudonyms are used for names and location (NMC, 2018). The focused patient on this essay is known as James. James a 22years old man was transferred from Emergency Department (ED) to the acute ward as a formal patient. Following James BPPS assessments, the four domain including environment are discussed in

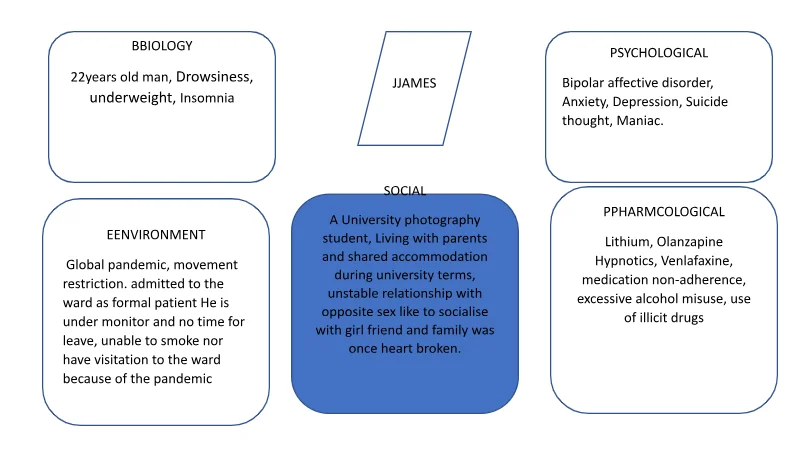
James, 22 years old Black British man a photographic student, lives with parents and also lives in a shared accommodation during university session. James, episode of relapse was due to non-adherence to his medication and changes in lifestyle during his stay at the university and unable to visit his parents and girlfriend whom he loves staying with every weekend he visits his parents. The decision for James referral to the psychiatric ward was made by the psychiatric doctor, who considered James presentation of maniac symptoms and mental health history of bipolar disorder. It was reported that, James appeared catatonic because of his presentation at the ED which continues on his arrival on the ward. James was not communicating with anyone (mute), he was not eating/ drinking and he did not dress appropriately. On arrival to the ward, James physical health examination was observed, as it is recommended by Royal College of psychiatrist that, the clinicians must assess the psychiatric patient physical health screening enabling them to identify undiagnosed physical health, red flags or threshold. Patients admitted to psychiatric hospital must receive comprehensive physical health screening within twenty-four hours on admission to the ward (Pettipher & Ovens, 2015). Although, James was aware of his mental health disorder, he complies with his medication with the support of his parents. However, due to the global pandemic restriction in journey making has led to inconsistence in his family support towards his medication and lifestyle and his meeting up with his girlfriend. The pandemic lockdown has affected James negatively that his delusional believe is that his girlfriend will discontinue their relationship because of his inability of his visitation. James has experienced relationship breakdown due to his unstable mood. The delusional believe has led to changes in James attitude and he resulted in excessive use of alcohol and illicit drugs. James uncontrollable use of the non-prescribed drugs led to his relapse symptoms in maniac, depressive mood, and suicide thought. Aldinger & Schulze (2016) provide evidence that, there is a significant link between mental health illness and seasonality. It is reported that mania episode has its peaks in spring and summer and a third peak in mid‐winter, while depression shows high occurrence in winter and spring. Additionally, there are links that climate factors, such as mean daylight hours, mean daily temperature, and the daily number of sunshine hours, are associated with relapse in bipolar disorder. Furthermore, Aldinger & Schulze (2016) mentioned that, influenza A and B, including coronaviruses infections has connection with the three respiratory viruses that are associated with depressive disorder. However, influenza B was linked to history of suicide attempts and psychotic symptoms (Aldinger & Schulze, 2016).
Cerullo and Strakowski (2007) provided insight to the relationship that occurs through epidemiological research between bipolar disorder alcohol and substance misuse. In their discussion, Cerullo and Strakowski (2007) revealed that, lifetime prevalence of alcohol and substance misuse in bipolar patient is at least 40%, which have a mutual relationship with negative effect on the illness outcome including frequent and prolonged affective episodes, lower quality of life, decrease in treatment adherence and suicidal behaviour. Additionally, Post and Kalivas (2013) agreed that, medication non-adherence, alcohol and substance misuse as a stressor is crucial to episode of reoccurrence, thus appear to be potential vicious cycle to recurrence and magnitude of responsively to others. García et al (2016) explained that, there is a significant connection between medication adherence and the patient behaviour agreeing with medical advices provided. Patient not adhering to medications, attending to medical appointments, discontinuation with provided interventions and incompletion of doctor’s implementation could lead to lapses in illness symptoms, increase in hospitalisation and incur excessive hospital cost. Bipolar disorder and healthy life change could possible increase rebound depression, mania and suicide thought/ attempt (Jawad et al., 2018). Pagès-Puigdemont et al. (2016) added that, non adherence to clinical and medication advice including poor therapeutic alliance could result to decrease in achieving remissions and recovery of the patient. Bipolar disorder is rated as one of the top leading disability affect the global (WHO, 2001). Talbot et al (2012), emphasis that insomnia or sleeplessness is a significant symptom that is associated with bipolar disorder which during mania episode there is reduction in sleeping or stays in sleep. Furthermore, Kaplan and Harvey (2013) agreed that, insomnia or hypersomnia are common among people suffering depressive phases of bipolar disorder. Sleeplessness persistence could result to illness relapse, such as mania, depression, anxiety and irritability. However, induced sleep deprivation is also associated with hypomania and sleep loss is highly connected with daily manic symptoms (Kaplan and Harvey, 2013). James’ episode of depression has led to suicide thought. Hyman (2019) confirmed that, there is a notable connection between suicidal behaviour such as attempt and suicidal ideation are related to phases, associated with depressive aspect of the illness. Suicide as a consequence of depressive episodes is one of the primary causes of increased mortality in patients with bipolar disorder (Hyman, 2019). Furthermore, Saunders and Hawton (2014) emphasised that, depression is a major risk factors of attempting and committing suicide within general world population as well as psychiatric population. Depression is diagnostic described as chronic depressive symptoms.
Saunders and Hawton (2014) mentioned that, depression consumes BD patient lives than manic or hypomanic episode as it takes more than one-half of their time. It is also agreed that, maniac symptoms are often present during depressive episode; the presence of the mixed state of depression and manic symptoms is a significant risk to suicidal behaviour. According to the academy journal by Aldinger and Schulze (2016), emphasis on environmental factors and seasonal effects could influence mood regulations in bipolar patients. The review mentioned that, bipolar patient with seasonal patterns form minority but they suffer more clinical symptoms. Furthermore, it was elaborated that, mania has its symptoms peak in spring and summer and mid-winter, while depression shows high occurrence in winter and spring. In further investigation, there are indications that climate factors, such as mean daylight hours, mean daily temperature, and the daily number of sunshine hours, are associated with relapse in bipolar disorder (Aldinger and Schulze, 2016). James relapses is due to medication non adherence, alcohol and substance misuse is caused by environmental circumstances due to long term pandemic lock down. Therefore, James’ illness became worsen due to less social support, events and usual contact. James mental health state examination is seen in Appendix 2.
Care plan
To achieve quality and productive care, BPPS is the tool to enable clinician to achieve person centred care. The care tool provides extensively insight on the patient on going illness and history of a patient to enable create adequate care plan on the on-going problems and relatively the patient illness. Likewise, BPPS tool also provide in-depth access and understanding to patient’s present health and environmental situation, which will help to identify risk factors and prognosis (Clark & Clarke, 2014). Combination of BPPS and nursing process stage support the clinician to rigorously assess patient’s physical and mental health problems, which will support the nurses to prioritise diagnosis, set reasonable and practicable goals for quick recovery. Care plans are made up with collaboration of the members of multidisciplinary team (MDT), the patient and the allowed family members. Members of the MDT must be able to communicate in an easy and understanding method rather than using medical jargons to form which the non- medical professionals will breakdown during the care plan meeting to avoid confusion and misunderstanding. Avoiding medical jargons and communication breakdown will enable the patient and their family to have full contribution to their care planning and achievement (Pitt & Hendrickson, 2019). 72 hours care plan is implemented and evaluated frequently following James admission. The care plan, which includes all physical and mental assessment, is to identify the current and future needs of the patients through the 5 steps of nursing process for gaining access to the formation diagnosis that helps in prioritising intervention and care during his stay in the hospital and possible after discharged (J et al., 2020). James’ care plan will focus on two area which includes the pharmacology non adherence and environment which has been the source of his health deterioration. It was identified that James health relapses is due to his unable to physically meet his support as a result of the movement restriction from one area to the other because of the world pandemic experience. Emergency care plan is made to support James with person centred care and quick recovery. Emergency care plans provide rapidly accessible information about the patient’s condition, his preference, and the agreed recommendations for care (Pitcher et al., 2017). The care plan will focus on two parts of the BPPS. The pharmacology and social, psychological and the evidence-based care plan will be discussed in Appendix 4.
Pharmacology plan
The nice guidance to all mental health medication is that there is interference between the prescribed medication and non-prescribed medication, tobacco alcohol and other illicit drugs. The interference could lead to therapeutic and psychological effect of prescribed medication interventions including economic and re-hospitalization of the patient (NICE Pathways, 2017). Jawad et al. (2018) agreed that, relapsing and remitting conditions are common among the many psychiatric patients and mostly among the people with bipolar disorder due to poor reasoning and lack of insight to their treatment which could lead to severity of their illness, reduce the treatment effectiveness, wastage of healthcare resources and higher increase in suicide. The above evidence shown that all prescribed medication available to James has higher risk of interference with alcohol and illicit drugs in conjunction of medication non-compliance has result to the severity of his illness. Hayden B. Bosworth et al. (2011), agreed with WHO (2019), that the magnitude of medication non-adherence and the scope of its consequence continue to be concerning. Therefore, there must be interventions to improve the current pharmacological treatments, rather than developing new medical treatment. El-Mallakh & Findlay (2015) stated that, there should be a person-centred support service to enhance medication compliance with psychiatric patients, considering the patient attitude towards treatment, perception of need to take the medications, specific environment, and cognitive behaviour. El-Mallakh & Findlay (2015) suggested that, health care professionals should improve patient medication adherence as part of their routine care for patient with long term chronic illness within the community. Additionally, Semahegn et al. (2020) suggested that, healthcare system should design programs to take the edge off the medication non-compliance in major psychiatric disorder patients. In his semahegn et al said “comprehensive approaches targeting the factors that affect medication non-adherence can bring great positive outcomes. These can be helpful to the policy makers, engaged clinicians and other care givers to integrate methods to boost therapeutic alliance and improve medication adherence”. The planned intervention to support James to ensure person centred care on medication non-compliance during the University session are referrals to the community mental health service and the community pharmacist to support him during the university terms these will be a tailored approach as the specific barrier of James medication non-adherence was identified. Furthermore, van der Laan et al. (2017), also mentioned that, the clinician and pharmacist should continue to remind the patient about the risk factors of his illness as a problem and advise the patient to perform health related behaviour to resolve the problem by taking their medication and following the therapeutic treatment (van der Laan et al., 2017).

Psychological plans
Jacobs et al. (2010) agreed that, medication and cognitive behaviour therapy could be a significant support and treatment for suicidal thoughts. Furthermore, evidence has shown that interpersonal psychotherapy and cognitive behaviour through clinical trials are better treatment for depression and suicidal thought and behaviour. Additionally, Saunders & Hawton (2014) mentioned that, there is significant connection between bipolar disorder and depression which could eventually result to suicide thought and act. It was reported that antidepressant medication cannot solve depression related with suicide, however Lithium remain perfectly in consistent with reduction of suicide thought and acts. In conclusion, this essay has been able to discuss James and his illness, using a BPPS perspective, with a shared decision-making model in mind. The use of effective care plans for person-centred treatment and care has also been used throughout the essay.
References
Aldinger, F. and Schulze, T. (2016).Environmental factors, life events, and trauma in the course of bipolar disorder. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 71(1), pp. 6-17. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12433.
Barrera-Herrera, A., Attard, C., & Chaplin, R. (2019). Oxford textbook of inpatient psychiatry (1st ed., p. 85). Oxford University Press.
Cerullo, M. and Strakowski, S. (2007). The prevalence and significance of substance use disorders in bipolar type I and II disorder. Substance Abuse Treatment, Prevention, and Policy, 2(1). doi: 10.1186/1747-597x-2-29.
García, S. et al. (2016). Adherence to Antipsychotic Medication in Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenic Patients. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology, 36(4), pp. 355-371. doi: 10.1097/jcp.0000000000000523.
Kaplan, K. and Harvey, A. (2013). Behavioral Treatment of Insomnia in Bipolar Disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry, 170(7), pp. 716-720. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.12050708.
Jacobs, D., Baldessarini, R., Conwell, Y., Fawcett, J., Horton, L., & Meltzer, H. et al. (2010). practice guideline for the assessment and treatment of patients with suicidal behaviors (p. 15). American Psychiatric Association.
Nursing & Midwifery Council. (2018). The code: Professional standards of practice and behaviour for nurses, midwives and nursing associates. London: Nursing & Midwifery Council.
Post, R. and Kalivas, P. (2013). Bipolar disorder and substance misuse: pathological and therapeutic implications of their comorbidity and cross-sensitisation. British Journal of Psychiatry, 202(3), pp. 172-176. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.112.116855.
Saunders, K. and Hawton, K. (2014). Suicidal behaviour in bipolar disorder: understanding the role of affective states. Bipolar Disorders, 17(1), pp. 24-26. doi: 10.1111/bdi.12267.
Talbot, L. et al. (2012). A test of the bidirectional association between sleep and mood in bipolar disorder and insomnia. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 121(1), pp. 39-50. doi: 10.1037/a0024946.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



