Pressure Ulcers: Prevention and Control
Introduction
Decubitus ulcers, or otherwise referred to as Pressure ulcers are clinically defined as skin lesions or injuries on the skin. They are usually caused by a variety of factors. Statistics reveal that over 1 million users live with the condition in the United States (Pancorbo- Hidalgo et al, 2006). There rises the need to research on possible ways and methods of prevention and control of this condition.
Reasons for undertaking the research
Pressure ulcers have a rampant effect among the elderly people. Its effect has increasingly been based on its natural causes. Basic information regarding the causes and effects of this condition is unknown to a better part of the public. Research on this particular topic would enlighten and provide more information on the effects and possible significant preventions of this condition. This condition is primarily caused by pressure, prolonged on the skin surface by various means; which include friction, medication, shearing forces, temperature and humidity. The ignorance of information regarding this condition is proven to be consequential and dire. The fact that bed sores increasingly are one of the biggest modern societal clinical conditions necessitates its research.
Take a deeper dive into Healing of Diabetic Foot Ulcers with our additional resources.
Research Question and Hypothesis
Research Question
Does the lack of information regarding pressure ulcers contribute to the increasing number of diagnoses of the condition in modern clinical settings?
Research Hypothesis
Through lack of or inadequate information and awareness on Pressure ulcers among the elderly, there are increased chances of contraction and diagnoses of the condition.
Research Objective
The purpose or objective of this research is to analyze the causes, effects and impact of pressure ulcers as a condition that rampantly affects the general public and establish the possible means and ways in which its spread can be controlled and prevented. The basis of performance towards this objective is the control and prevention of this condition in relation to modern clinical and medical practice.
Comparative discipline
In a comparative analysis, this research looks at Cerebral Palsy. Cerebral Palsy refers to a non- degenerative disorder that generally affects the nervous system. There are a number of symptoms and factors associated with Cerebral Palsy as a condition that affects the elderly. Some of these symptoms include the increase in the level of pains, more frequent falls and tremors by the patients. The victims with this condition also have great and increased difficulty in walking and swallowing (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, 2013). Similar to Pressure Ulcers, Cerebral Palsy not only affects the elderly people, the condition has also been clinically seen to be a major societal problem that necessitates control and prevention from a clinical angled approach.
Sources of Information
Based on a number of areas to be covered by the issue of Pressure ulcers, the following two articles were greatly relied upon.
Guest J., Fuller G., Vowden P., Kathryn R. (2018) Cohort Study evaluating pressure ulcer management in clinical practice in the UK following initial presentation in the community: costs and outcomes. BMJ Open
Bluestein D., Javaheri A., (2008) Pressure Ulcers: Prevention, Evaluation and Management. American Family Physician. Volume 78, Number 10
Methodology
The best method of collection of information relating to this research is literature review. Literature review, in this context, can be classified to include both qualitative and quantitative research methods. In a systematic manner, information relevant to this research has been identified, collected, evaluated and analyzed to come up with a vivid and understandable finding. Literature review provides an intensive form of research methodology, therein proving valuable and reliable as a method of research in this kind of issue. Compared to the issuance of questionnaires as a method of research, literature review is not as time consuming in as much as it requires the verified study of different articles and books. This method of research is also cost effective as it only requires a visit to the library; the source of literature. This research has also adopted the use of surveys. The type of survey to be used in this kind of research articles is the digital surveys. These surveys are to be conducted specifically to the affected individuals; both directly and indirectly. Directly affected individuals include persons diagnosed with the actual condition. Indirectly affected individuals include people with relations to the victims or patients, for instance their friends, families and medical practitioners or concerned persons. In contrast to physical surveys, digital surveys are both cost effective and time accommodating. The results from general surveys are usually efficient and comprehensive, and therefore prove very useful to this research (Constantin E. et al, 2014).
Continue your exploration of Comprehensive Care Pathway for Venous Leg Ulcer with our related content.
Systematic approach
Statement of objective
As perfectly phrased, the research seeks to analyze the general impacts of Pressure Ulcers as a condition that mostly affects the elderly, and then establish possible means, methods and ways in which this condition can be prevented, or controlled.
Data Collection
Information on Pressure Ulcers from various sources and the aforementioned methods was collected and disseminated in form of this research. There is the ultimate risk of developing pressure sores to all persons. However, it has been scientifically depicted that the condition is highly likely to be acquired by persons who are very ill, with poor postures, deformities, impaired mobility, compromised and malnourished skin or people with other neurological conditions. From a foundational basis, pressure sores develop from the application of sufficient pressure or distortion on the surface of the skin, which impairs the blood supply to certain areas of the skin (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, 2015). A report conducted shows that this condition; Pressure Ulcers; present a major burden to individuals from both direct and indirect angles. The most vulnerable group of persons to whom this condition can be debilitating to is that composed of people aged over 70 (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, 2015). Importantly, this kind of condition has been clinically proved to be potentially serious and could, in certain instances, eventually lead to life- threatening complications. Such life- threatening complications include gangrene and blood poisoning. According to the reports on death and severe harm incidents reviews to the National Reporting and Learning System, pressure sores comprised the largest proportion of victim safety occurrences, totaling to 19% of these reports. The prevalence of this condition has hereof been determined to be 1 of 4 common harms by the NHS Safety Thermometer, which is a local tool used to measure, monitor and analyze harms to patients and victims across a variety of settings such as care homes, nursing communities and hospitals on monthly bases.
Data Evaluation
Further research on the matter displayed decubitus ulcers to range in severity. The intensity of its symptoms range from the mere reddening of the skin to severe and deep craters/ holes formed on the skin which consequently exposes the muscles or bones. The skin overlying the sacrum, heels, hips and coccyx are the most common seeable sites affected by bedsores. Other sites are however normally affected; such include the skin underlying the elbows, ankles, shoulder back, knees and cranium. As a matter of concern, this condition significantly threatens the healthy- being of patients with limited mobility.
Analysis
Even though 70% of patients suffering from this condition are usually persons older than 65 years, young persons with neurological impairments and other severe illness are also susceptible. In the same context, this condition would generally affect any person as long as the factors that lead to it are met. Predisposing elements in the issue of pressure ulcers have been classified, in different contexts, to be either extrinsic or intrinsic. Extrinsic elements include external factors such as friction, humidity, shear forces or pressure. Intrinsic elements, on the other hand, constitute internal factors such as comorbidities, poor nutrition, skin aging and limited morbidity (Bluestein D, 2008). Comparing the various articles and researches conducted, statistics arrived at prove to fall within the same range rates. An average conclusion can therefrom be drawn from the statistical data, which would fall within the ambiance of efficient information. The same reports and articles provide the impact of this condition and how it affects people of different age groups. The indifferences in reports and information collected are greatly dependent upon the setting. Higher rates are usually recorded in intensive care units, compared to hospitals. This is because it in intensive care units where the patients are less mobile and may have severe illnesses. The Fourth National Pressure Ulcer Prevalence Survey found the annual prevalence rate in hospitals to be 10.1%. In long term care settings, the prevalence and incidence rates were found to range from 3% to 30%. There is little knowledge on the precise incidence and prevalence rates in home care, however, studies report incidence and prevalence rates of 4- 15% and 5- 15% respectively.

Presentation of Findings
Directly affected persons may be individuals from any age group. As a matter of fact, in Europe, the prevalence rates in relation to the susceptibility to this condition range from 4.7% to 32.1% in hospital settings and 8.5% to 22% in nursing homes (Bluestein, 2008). From various reports and research conducted, the prevalence of this condition varies and but still falls within certain percentages. Comparative study also reveals the prevalence rates to be 26% in Canadian health care settings (Mclnnes et al., 2015). In addition to these statistical data, in 2013, documentation reveals 29,000 of global deaths arose from pressure ulcers, which is up from 14,000 deaths in 1990 (GBD, 2013).
Relevant information
Information relevant to this research is any information with the general topic of Pressure ulcers. Several books and articles contain information regarding pressure sores. Almost all of them provide information on the causes, factors and pathophysiology behind this condition. Several others provide information on the consequential effects and impacts of the condition on various classes of individuals. As aligned to the objectives of the research, information regarding the causes, effects, impact and possible means of prevention and control of this condition is relevant in this context.
Information found
In regards to the pathophysiology of the condition, inadequate supply of the blood in certain areas results to the reperfusion upon reentering certain tissues. A typical example is an instance of a mild pressure sore which may be experienced by healthy persons who sit in the same position for long and extended periods of time. The aches experienced in the process indicate the impeded flow of the blood to the affected areas. Within a certain period of time, the shortage of blood supply, otherwise known as ischemia, may lead to certain effects, such as tissue damage or even the death of a cell. Consequently, the muscle cells die and the overlying skin which is usually fed through blood vessels also die. Pressure ulcers; however, remain to be one of the eight preventable iatrogenic conditions.
Priority of Information
The main articles for the purposes of this research are:
Guest J., Fuller G., Vowden P., Kathryn R. (2018) Cohort Study evaluating pressure ulcer management in clinical practice in the UK following initial presentation in the community: costs and outcomes. BMJ Open
Bluestein D., Javaheri A., (2008) Pressure Ulcers: Prevention, Evaluation and Management. American Family Physician. Volume 78, Number 10
Pressure ulcers can be prevented through various means; for instance, risk assessment. Through adequate knowledge and awareness, risk assessment may prove to be the best means under which pressure ulcers may be prevented. Risk assessment requires one to first of all identify risk factors and conduct skin inspection; these factors are either extrinsic or intrinsic (Bluestein D, 2008). From the research conducted, there are more than 100 risk factors when it comes to pressure ulcers; such factors include immobility, peripheral vascular disease, malnutrition, cerebral vascular accidents, among others. Another method of control involves interventions. Preventive measures are encouraged when it comes to at risk patients. As a mainstay of preventive steps, pressure reduction to preserve microcirculation has to be done.
12.0 Comparison Table


Conclusions
Based on the findings of the research, this condition generally affects any class of person. The condition greatly affects persons or people of ages 70 and above and with the aforementioned characteristics. The data findings indicate continuously increasing number of diagnoses of pressure ulcers, and not only in the United Kingdom. The need to effectively look for ways in which the condition may be managed, or controlled has been established in the long run.
Impact on clinical practice
This research has amplified the statistics relating to diagnoses on Pressure Ulcers, the causes and dangers of the condition and the consequential possible ways, methods in which the condition could be prevented or controlled. Clinical practice necessitates the implementation of better communication in relation to the creation of awareness of this condition. In a clinical setting, the staff should duly communicate and inform the vulnerable of the possible contraction of the condition and possible ways of avoiding or preventing the condition so as to help manage or control it.
How to use research information
Possible methods in which this condition can be prevented or controlled could be derived from this research. The said methods could prove useful in professional clinical settings and any other care setting. Information regarding the dangers and effects of the condition is also highlighted in this research and therefrom data regarding the condition could prove beneficial in the contribution towards awareness.
Change area
Communication, in accordance with this research, is one of the major areas that could be improved in current clinical practice. Improvement of communication in clinical settings would increase the element of control regarding this condition.
Issues that may require further research and evaluation
This research has foundationally looked at the causes, effects and the consequential impacts of pressure sores to affected individuals, and then the possible ways in which the same could be controlled and prevented. However, in regards to the epidemiology of the condition in relation to settings, there is need for collection and distinction of the data from different settings. For instance findings on controlled tests conducted in work stations, hospital settings, home settings, among many others.
References
- Bluestein D., Javaheri A., (2008) Pressure Ulcers: Prevention, Evaluation and Management. American Family Physician. Volume 78, Number 10
- Constantin, E., Seitz, B., Eter, B., Promesberger, J., Holger, B., (2014) Efficiencies of Internet Based Digital and Paper- Based Scientific Surveys and the Estimated Costs and Time for Different- Sized Cohorts. Peter Van den Besselaar
- GBD Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators (2013) Global, regional, and national age- sex specific all- cause and cause- specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1999- 2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 (Accessed on the 15th July 2019)
- Guest J., Fuller G., Vowden P., Kathryn R. (2018) Cohort Study evaluating pressure ulcer management in clinical practice in the UK following initial presentation in the community: costs and outcomes. BMJ Open
- Mclnnes, E., Jammali- Blasi, A., Bell- Syer, S., Middleton, V., Cullum, N., (2015) Support surfaces for pressure ulcer prevention. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE)., (2015) Pressure Ulcers. Quality Standard
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (2013) Cerebral Palsy: Hope Through Research (Accessed on the 15th September 2019)
- Pancorbo-Hidalgo PL, Garcia-Fernandez FP, Lopez-Medina IM, Alvarez-Nieto C. (2006). Risk assessment scales for pressure ulcer prevention: a systematic review. J Adv Nurs.
- Topic 2: Minimising language barrier when communicating with breast cancer patients.
Plan the research activity.
19. Demographic of cancer in UK is culturally diverse due to the fact that there are a lot of immigrants from different cultural origins that continue to stream into the country. Some patients, specially those that come from nonmainstream backgrounds can be subjected to delays in seeking health care. In considering cancer patients with limited English proficiency, communication can prove to be a major challenge, especially when communicating with health professional nurse (Cohen et al., 2005). This is due to the fact that health care accessibility is often determined by the ability of the clients to freely interact with the system of healthcare. Research denote that limited English proficiency is related to screening of breast cancer and distress of cancer symptom. Healthcare professional admit that they are not able to communicate well with clients due to the language barrier and this results into provision of less effective patient- centred care. It is also important to note that health literacy and education plays a significant role in the communication between health nurses and clients when discussing a diagnosis with limited English. Proficiency patient (Taylor et al., 2013). The use of an interpreter is found to be useful in bridging the barrier due to limited English proficiency. However, use of interpreter has been reported to be a major challenge due to limited use or access to interpreter resources. Ironically, some research has found that the use of interpreter assist in enhancing the process of health education, however, it reduces patient’s perception of interpersonal care and satisfaction. The purpose of this research was to explore ways in which the language barrier can be minimized between the health nurses and breast cancer patients. This study focused on investigating:
1. ways in which language barrier impact healthcare experience and how this language barrier can be minimized.
2. The perception of negative consequences of related to limited English proficiency clients by the health nurses.
3. The perception of health nurses regarding initiative that that would be employed to minimize the language barrier.
Reason for study
This research is specifically important due to the fact will it explore on various initiative and mechanism that can be employed by the healthcare industry to reduce the effect of language barrier particularly when communicating with breast cancer patients. It will ensure that breast cancer patients receive good treatment from the health professional without being sidelined due to lack of required information.
Research Question
Hypothesis
Minimising language barrier when communicating with breast cancer patients.
In order to meet the objectives of this study, answerable research questions were framed. Notably since these questions were answered appropriately, they were able to meet the objectives of this research, and ultimately, the aim of the study.
They are presented below:
The primary research question is as follow:
How can language barrier between breast cancer patients and health care nurses be minimised?
Other secondary research question include:
How essential is the client’s native language in the health care centre and when can client’s native language be used?
Objectives
In order to meet the aforementioned aim of this study, it was of great significance to break it down into achievable objectives. Notably, the most suitable objectives was arrived at through the use of S.M.A.R.T philosophy. This acronym was applied due to the fact that it provides a clear guideline for the development of realistic and achievable goals. S.M.A.R.T objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time bound. Through application of S.M.A.RT acronym the following objectives were arrived at:
To reduce language barrier between breast cancer patients and health nurses.
To reduce language barrier between breast cancer patients and nurses in the UK by 50 percent.
Identify one (1) other discipline that could be connected to this research activity
Medical translation- The field of medical translation is an integral part of medical care and as such is always growing. Qualification requirements of this field are high and learning never stops because the field of medicine is encrusted on innovation and research. Medical translators need to pass a series of language proficiency tests and this coupled with fluency in a couple of native languages is a major boost. Medical translation demands precision when handling medical information and should not be confused with interpretation. These language experts ensure that best healthcare is provided by nurses to breast cancer patients.
The two sources are:
SOURCE 1: Von Ah, D., Habermann, B., Carpenter, J. S., & Schneider, B. L. (2013). Impact of perceived cognitive impairment in breast cancer survivors. European Journal of Oncology Nursing, 17(2), 236-241.
SOURCE 2: Koller, M., Aaronson, N. K., Blazeby, J., Bottomley, A., Dewolf, L., F ayers, P., …& EORTC Quality of Life Group. (2007). Translation procedures for standardised quality of life questionnaires: The European Organisation for Research and Treatment of cancer (EORTC) approach. European Journal of Cancer, 43(12), 1810-1820. – not enough information was found in relation to my topic from recommended data bases from Torrens Library.
Gather information research
Online survey.
Internet survey has become one of the most important research tools applied in various research projects. It has been estimated that online survey encounter about 20 per cent expenditure on global data collection in 2006. It provides capabilities that go beyond other types of self-supervised questionnaire. In this study, decided to choose online survey this is because the method is cheaper, simpler and faster. Additionally, the period of data collection is shortened due to the fact that the collection and proceeding of data can be achieved within a short period of time. The online survey offers a dynamic way of interaction between the questionnaire and the respondent as compared to other methods of data collection.
Interview
Interview are major qualitative method of data collection used for social research projects. They are mainly applied in areas where there is need to achieve personalized data. Additionally, they are used in areas where they are high need to probe the underlying factors. In this study, I opted to apply interviews as a method of data collection. This is because interviews provide a comprehensive description and analysis of the much – needed information regarding the subject under study. They can offer information that the respondents may be reluctant to provide. There are therefore essential for finding a solution to a given problem.
briefly explain why one (1) of your information sources is particularly relevant according to objectives and your workplace requirements.
One of the information sources used in this research proves to be important in this research due the fact that it is in line with the objectives of this study, as such, it provide a detailed explanation of the underlying issues particularly on impacts of language barrier among the breast cancer patients. It provides a framework on how this problem can reduced to a level that can be tolerated. It brings fort on how nurses can handle breast cancer patients with limited English proficiency to access appropriate healthcare service.
In order to minimise the effect of language barrier between breast cancer patients and nurses the study analysed the following information.
1. Use of interpreters
2. Cultural training
3. Internal grammar and translation books
4. Basic language course
5. Written translation signs
Prioritise information based on the research objective.
Source 1: Von Ah, D., Habermann, B., Carpenter, J. S., & Schneider, B. L. (2013). Impact of perceived cognitive impairment in breast cancer survivors. European Journal of Oncology Nursing, 17(2), 236-241.
Source 2: Koller, M., Aaronso, N. k., Blazeby, J., Bottomley, A., Dewolf, L., Fayers, P.,… & EORTC Quality of Life Group. (2007). Translation procedures for standardised quality of life questionnaires: The European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) approach. European Journal of Cancer, 43(12), 1810-1820.

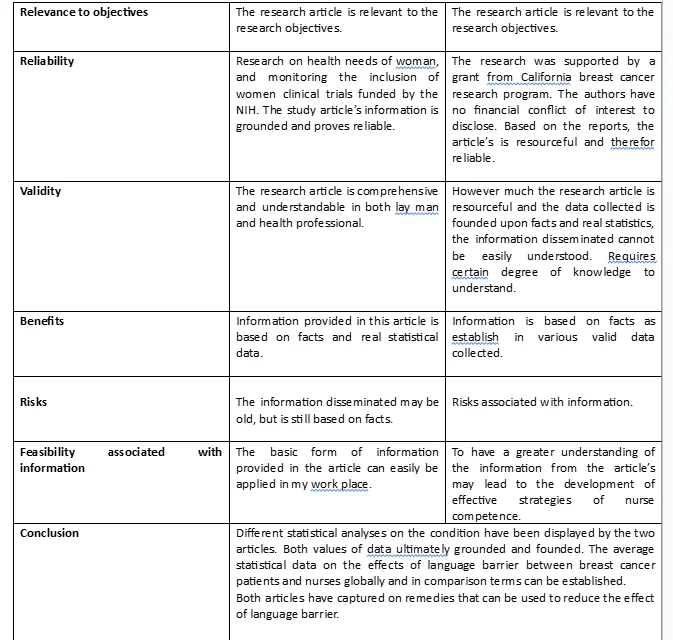
conclusion based on finding.
Activities, health nurses become more aware of the existing recent legislation concerning the language service provided in health care system. They can similarly pursue legislation which will enable them to become active in enhancing language services. In microscopic activities, nurses can know the patient’s culture and language due to the fact that it is integral and part of their activities that cannot be ignored. Health nurses play a major role in promoting and enhancing the health of LEP patients and can assist in minimising by putting initiatives to reduce barriers.
Impact of conclusions may have in term of duty of care requirement.
It is significant to take note of the fact that the participants were treated with top most priority, and this then implies that it is only the researcher who got access to them and no any other third party. In addition, the content of their answers were be treated with top most confidentiality. In this regard, when the participants finished producing their answers and the questionnaires were taken back, for analysis, immediately after the analysis, the answered semi- structured questionnaires were discarded, in order for them not to get to the hands of any third party.

Use information practice.
Information provided by the patients and health workers regarding a particular problem, for instance, information provided by nurses on ways in which the language barrier can be reduced can be utilised by the hospital management team by initiating programmes that will ensure their full implementation.
Identify one area for change in your work place or current practice.
Following the finding it comes out clearly that there is high need of interpreters and therefor every nurse should be assigned at least one interpreters who can assist in minimising the language barrier between the nurse and patients with limited English proficiency.
Identify issues that require further research and evaluation
The challenges and barriers reported by the LEP respondents in this project showed limitation and frustration experienced during patient-nurse interaction and communication as result of the language barrier. In some cases, the interpreter was available however the amount of information regarding the treatment provided was considered insufficient. It was noted that some patients were willing to provide information; however, they were curtailed by the language difference. Nurses in this study demonstrated that error and negative outcome occurred when working with breast cancer LEP speaking clients. While they acknowledge that the provision of services to this population was difficult, the majority thought that already appropriate mechanism and initiatives to minimize the barrier was in place. The feedback provided by the respondents could also imply that available resources were already well utilized to assist in minimizing the effect of the language barrier. Majority of the respondents suggested that English classes as second language classes should be connected to health insurance. However, before the implementation of such classes there is a need to consider the implication for additional research. For instance, if the classes would be easily accessed by the patients who need them, and whether the classes would significantly help in reducing the language barrier. Another suggestion provided by the participants was to provide English classes to all healthcare nurses with limited English proficiency, since it was noted that a significant fraction of nurses that provided healthcare services to the breast cancer patients were foreign professional from different countries. The implication of this suggestion would be the number of classes that will be required to accommodate all the employees, the level of standard that these classes will be required to meet, and the cost that will be incurred in establishing and maintaining these classes it is therefore important for further research to be conducted on suitable ways in which such classes can be established in order to facilitate learning of English as a second language among the foreign professionals.
Additionally, the literature review shows that recently programs of national certification meant for medical interpreters do not exist anymore, and only specific states have such programs. This disparity from one state to another implies that interpreting quality may be compromised thereby resulting in negative consequences. It has also be noted that many programs meant for educating nurses think that the interpreter is deviating from the real information. Implication regarding additional research includes: the most appropriate method of implementing internationally acceptable standards of regulation, whether national rules and regulations should be allowed for certification and interpreters work, and methods of integration to effectively utilise an interpreter into nursing education.
REFERENCES
- Abbe, M., Simon, C., Angiolilo, A., Ruccione, K., & Kodish, E.D (2006). A survey of language berries from the perspective of pediatric oncologist, inerpreters, and parents. Pediatric Blood & Cancer, 47(6), 819-824.
- Ali, P. A., & Watson, R. (2018). Language barriers and their impact on provision of care to patients with limited English proficiency: Nurse’ perspectives. Journal of Clinical nursing, 27(5-6), e1152-e1160.
- Arora, V., Johnson, J., Lovinger, D., Humphrey, H. j., & Meltzer, D. O. ( 2005). Communication failures in patient sign-out and suggestions for improvement: a critical incident analysis. BMJ Quality & Safety, 14(6), 401-407.
- Bischoff, A., & Hudelson, P. ( 2010). Communicating with foreign language speaking patient: is access to professional interpreter enough?. Journal of travel medicine, 17(1), 15-20.
- Cohen, A. L., Rivara, F., Marcuse, E. K., McPhillips, H., & Davis, R (2005). Are language barrier associated with serious medical events in hospitalized Pediatric patient?. Pediatric 116(3), 575-579.
- Ekdahl, A. W., Andersson, L., & Friedrichesen, M. (2010). They do what they think is the best for me. Frail elderly patients preference for participant in their care during hospitalization. Patient education and counselling, 80(2), 233-240
- Flores, G. (2005). The impact of medical interpreter services on the quality of health care: a systematic review. Medical care research and review, 62(3), 255-299.
- Hewett, D. G., Watson, B. M., Gallois, C., Ward, M., & Leggett, B. A. (2009). Intergroup communication between hospital doctors: implication for quality of patient care. Social science & medicine, 69(12), 1732-1740.
- Jayadevappa, R., & Chhatre, S. (2011). Patient centred care- a conceptual model and review of the state of the art. The open Health Services and Policy Journal, 4(1).
- Johnstone, M. J., & Kanitsaki, O. (2006). Culture, language, and patient safety: making the link. International journal for quality in health care, 18(5), 383- 388.
- Kripalani, S., Jackson, A. T., Schipper, J. L., & Coleman, E. A. (2007). Promoting effective transitions of care at hospital discharge: a review of key issues for hospitalists. Journal of hospital medicine: an official publication of the Society of Hospital Medicine, 2(5), 314-323.
- Ngoh, L. N. (2009). Health literacy: a barrier to pharmacist patient communication and medication adherence. Journal of the American Pharmacists Association, 49(5), e132-e149.
- Park, E. K., & Song, M. (2005). Communication barriers perceived by older patients and nurses. International journal of nursing studies, 42(2), 159-166.
- Taylor, D. M., Wolfe, R. S., & Cameron, P. A. (2004). Analysis of complaints lodged by patients attending Victorian hospital, 1997 2001. Medical Journal of Australia, 181(1), 31-35.
- Taylor, S. P., Nicolle, C., & Maquire, M. (2013). Cross- cultural communication barriers in health care. Nursing standard (Through 2013), 27(31),35.
- O Daniel, M., & Rosentein, A. H. (2008). Professional communication and team collaboration. In patient safety and quality: An evidence- based handbook for nurses. Agency for healthcare research and quality (US).
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



