Prevalent Eye Diseases in Telangana
Findings and Trends
This section highlights key findings of the study, as well as trends in relation to the subject matter as per the demographic and climatic variables tested. The section will also discuss methodology testing and how variables were tested alongside each other on Microsoft Power BI to achieve results that can be used to build on knowledge and create wisdom, as defined in the research earlier. Initially, before embarking on studying Cataract as a specific disease, it was important to gain a glimpse of the composition of the state of Telangana in relation to patients, eye diseases, and other social and demographic factors that are crucial to the study, and this phase is defined as phase I of testing. This has helped in distinguishing different patterns in Cataract patients while exploring the correlation of demographic factors to Cataract patients in phase II of the study. The EMR record was tested extensively in phase I of the methodology testing to create a research design that can lead to a simplistic and structured data analysis, again, transforming the EMR from an unstructured to a structured zone for analysis as per the Cynefin Framework discussed in the earlier chapter.
Phase 1- Highlights of Overall Indication to Eye Diseases in Telangana
From the analysis of the overall data, the following trends were identified:
The analysis shows that Emmetropia, Astigmatism, and Conjunctivitis are the most prevalent eye diseases among the youth population (ages 21-40) in Telangana.
For older adults, (ages 41-70), the analysis shows that Cataract and Pseudophakos are the most prevalent eye diseases.
Paloncha, Kothagudam, Kothagudam Bazar, Bhadrachalam, Mauguru, Madhapur, Kondapur, Adilabad, Yellandu, Kondapur and Tekulapalli are the top ten locations with the highest hospital visits, with Paloncha being identified as a high-risk location because of the presence of the state run thermal power plant.
The analysis shows a consistent pattern for high prevalence of Cataract within the minimum ranges of temperature (20oC - ~30oC).
The analysis also shows that Cataract is the most prevalent eye disease in the rainfall season.
Some of the visual patterns have been captured and identified below for a more in-depth explanation:
a. Gender and Eye Disorders


Figure 1 indicates that between the year 2011-2019, 53% of the patients were male patients who were seen for eye disorders, and 47% were female patients. This finding is in line with the gender study that was conducted on 2.3 million patients of all those who presented to LV Prasad Institute from the years 2011-2019 (Das et al, 2020). Globally, one of the social determinants of health that has been universally identified is gender. In India, health inequalities between men and women have played a pivotal role in disease development, including eye disorders. With respect to eye care, women have been generally cited to have higher rates of blindness in India and are less likely to access appropriate eye services (Clark et al 2016, Messmer 2015). However, as we can see from the study which was focused on Telangana, this is not the case, as male patients exceeded female patients, and this could be for the reason that Telangana has been ranked as one of the top ten innovative and developed states in India according to the India Innovation Index 2019 (Gorka, 2019) where access to healthcare is available and appreciated by both male and female. India has been one of the countries where efforts to strengthen the evidence-base for blindness control has received significant attention from policy planners and program managers. Over the past four decades, a series of population-based blindness and visual impairment surveys have been undertaken in India, using different survey methods. This included detailed eye examination surveys as well as rapid assessments (Mathews, 2015). In addition, when studying the correlation between profession and clinical visits, it appeared that home makers, employees in the government and private sectors, and students make the top three categories of those are who most affected. Figure 2 depicts this analysis and portrays the top six professions taken from the analysis. We can also see that workers in Agriculture and manual laborers tend to present themselves with eye disorders as well, and that could be to the nature of the job, in which they are exposed to certain chemicals, dust, and usually work in heated environments. Recent estimates from the World Health Organization indicate that 90 per cent of all those affected by visual impairment live in the poorest countries of the world (Diaz, 2011). India is home to one‐fifth of the world's visually impaired people and therefore, any strategies to combat avoidable blindness must take into account the socio‐economic conditions within which people live (Diaz, 2011). Home-makers could also translate to housewives, who are at higher-risk of visual disorders, and this is in line with a study that was conducted in 2009 on women in Indian culture, where it showed that housewives are more likely to suffer from heart diseases than working women, and that is due to lack of education, lifestyle that is based on obesity and cultural myths that do not focus on women’s health. Having a similar study related to eye disorders and visual impairment, as per the study based on the sample of the population from Telangana, the same pattern can be seen and it can potentially be from these similar reasons (Murthy, 2005).
Dig deeper into Coagulation Cascade Testing And Factor with our selection of articles.
b. Occupation and Clinical Visits

c. Location and Eye Disorders in Older Age (41-70)

Cataract seemed to be the most disease that has affected older age in Telangana. Cataract is a condition known to affect older age, and this study revalidates the information.
d. Location and Eye Disorders in Younger Age (11-20)


Astigmatism, which is an irregularity of the shape of the cornea was present in younger age population as per Figures 4 and 5. Astigmatism has been linked to being a hereditary condition in ophthalmology. In both contexts, it appeared to be that eye disorders are mostly concentrated in residents from the district of Paloncha, and even though this district has a higher literacy rate than state average is 77%, 10% higher than that of the state average which is at 67%, it has been reported that it has been hit with pollution and contaminated water in 2015. The state-run thermal power plant installed in 2015 caused pollution and health disorders including eye disorders (Kaur, 2019). Residents complained of gray water, and doctors in Paloncha confirmed that the prolonged exposure to air and water pollution has led to higher incidences of respiratory diseases, tuberculosis, skin diseases, blurring of vision and irritation in the eyes, such as Cataract, Cornea, Anterior Segment, Retina, and Glaucoma (Kaur, 2019).
e. Consistent Prevalence of Cataract in Rainfall

The close relationship between climate, environment and the development of Cataract is crucial to understand for future preventative measures. In Telangana, it shows that Cataract is the disease most prevalent in rainfall.
Phase 2 - Analysis of Cataract in Telangana
After completing phase 1 of the research, it has been revealed from the data that there is a high cataract rate among patients, and therefore this has led to examining cataract as the main disease in this paper. In addition, cataract is a major cause of vision impairment in many low-income settings (Vashit et al, 2011). The analysis identified demographic correlations to cataract development as well as a potential relationship with weather variables which have been tested in several ways throughout the data analysis process.
Breakdown of Cataract by Gender

Identifying Cataract patients came to 102,509 patients from the years (2011-2019). Therefore, the sample study of patients is based on 102, 509 patients who presented themselves to LVPEI during that timeframe. The figure above shows the gender composition of Cataract patients. There is a total of 48,219 (47.04%) who are male, while 54,290 (52.96%) are female.
Breakdown of Cataract Patients by District

The above figure shows the breakdown of the number of cataract patients across the districts – urban, rural, and metropolitan. It is clear that cataract is most prevalent in the rural areas with 58,123 cases of cataract recorded. This is followed by metropolitan with 27,150 cases of cataract recorded while the urban district has 17,236 cases of cataract recorded. Eye diseases worsen the quality of life and satisfaction of an individual (Thevi, et al, 2012). It has been observed that the spatial location, the cultural and financial condition of the individuals and most importantly the access rate to healthcare organization are considered to be the perceived barriers. It is scientifically evident that cataract is considered to be one of the potential causes behind the visual impairment or blindness mostly among the middle and poor resourced families (Thevi, et al, 2012). The varied reasons behind these variations might be attributed to the spatial location which creates troubles to access the distant health care centers especially for the female patients (Kaur, 2018). Moreover, the awareness about the eye diseases and the financial crisis plays the most significant roles for the worsening condition of cataract among the rural populace. The studies conducted by both Joshi (2015) and Murthy et al. (2014) have supported this opinion. Moreover, again as per the affirmations of Kuldeep Dole (2013) who conducted a cross sectional survey highlighted about the expanded charges of the modernized strategies involved for cataract such as intraocular lens implantation and microincision phaco. Another important reason behind the rising number of cases in the rural areas are due to their mindset to utilize the traditional eye medicines which demonstrated contradictory outcomes due to the toxicity and infections caused by the agents.
References used here:
Thevi, T., Basri, M. and Reddy, S.C., 2012. Prevalence of eye diseases and visual impairment among the rural population–a case study of Temerloh hospital. Malaysian family physician: the official journal of the Academy of Family Physicians of Malaysia, 7(1), p.6.
Kaur, K., 2018. Cataract Blindness: Socioeconomic Factors Associated with Treatment Barriers and High Blindness Rates for Women in Rural Regions of Andhra Pradesh.
Joshi, M.V., 2015. Epidemiological study of patients availing free cataract services of national programme of control of blindness. Journal of Clinical Ophthalmology and Research, 3(1), p.9.
Cataract Patients by Age

The figure above shows the distribution of cataract patients among the different age categories. People in the age category of 61-70 have the higest recorded cases of cataract with 41,736 cases of cataract recorded in this age group. This is followed by people within the age bracket of 51-60, with 30,284 cataract cases recorded and 13,530 cataract cases recorded within the age bracket of 71-80. The younger population below the age of 30 do not seem to present themselves with cataract symptoms. Previously in the research, it was explained that Emmetropia, Astigmatism, and Conjunctivitis are the most prevalent eye diseases among the youth population (ages 21-40) in Telangana.
Cataract Patients as influenced by Occupation

The figure above shows how the different occupation categories are influenced with cataract as a disease amongst patients in that occupation. Homemakers recorded the highest cases of cataract with 14,437 cases recorded. This is followed by people in Government/Private Service with 13,097 cataract cases recorded, and then students at 9,622. This is in line with the correlation between profession and clinical visits on the overall EMR studied in Telangana. It can be concluded that certain professions are a general reason of why eye diseases in general are present in patients. Homemakers, employees in the government and private sectors, and students make the top three categories of those are who most affected. It is also seen that workers in agriculture and who are defined as manual laborers tend to present themselves with eye disorders as well, and that could be to the nature of the job, in which they are exposed to certain chemicals, dust, and usually work in heated environments. Home-makers could also translate to housewives, who are at higher-risk of visual disorders, and this is in line with a study that was conducted in 2009 on women in Indian culture, where it showed that housewives are more likely to suffer from heart diseases than working women, and that is due to lack of education, lifestyle that is based on obesity and cultural myths that do not focus on women’s health. Having a similar study related to eye disorders and visual impairment, as per the study based on the sample of the population from Telangana, the same pattern can be seen and it can potentially be from these similar reasons (Murthy, 2005).
Cataract Patients tested for Smoking and Diabetes
According to a scientific meta analysis conducted by Ye, et al., 2012 a overall of 13 prospective cohort along with 8 case control investigations were included within the analysis. The findings of the investigation highlighted that ever smoking status has a positive correlation with age related cataract (ARC) condition. The study showed the statistical validation of (OR 1.41, 95% CI 1.23–1.62) for the cohort group of investigation and (OR 1.57, 95% CI 1.20–2.07) for the case control gathering of the investigation. Moreover, the subgroup analysis of the investigation also focused about the positive association in between smoking and the development of nuclear cataract having the statistical validation of (NC; OR 1.66, 95% CI 1.46–1.89). Same trends of outcomes were observed also for the category of the case controlled studies NC OR 1.86, 95% CI 1.47–2.36 and also for the cases of posterior subcapsular cataract having the statistical validation with the Odds Ratio of 1.60 and 95% CI 0.97–2.65. With regard to the pathogenesis of the condition, the researchers within the study highlighted that the smoke of tobacco possesses varied range of harmful poisonous chemicals for instance nicotine, and obnoxious gas carbon monoxide, free radicals that cumulatively enhances the oxidative induced stress and therefore eventually plays a significant role for the development of cataract (Beebe, et al, 2010; Truscott, 2005). Another potential factor is the presence of diabetes for the development of cataract among both the populace of developing and developed countries. Though the exact pathogenesis is still not vivid with regard to diabetes however, past scientific confirmations have revealed that the polyol pathway calls for the initiation of the pathological condition (Kiziltoprak, et al, 2019). Therefore, diabetes is considered as potential risk factor for cataract development and also enhances the hazard factor for the intricacies arising after phacoemulsification surgical process among the diabetic populace in comparison to the non diabetic group (Kiziltoprak, et al, 2019). Throughout the world the comprehension of the pathological mechanism for the hindrance or delaying of the development of cataract is still under research and is a matter of challenge among the diabetic populace (Pollreisz, et al, 2010).
Add a few lines here that says to study patients from a holistic point of view and explore all angles of a systematic approach to data analysis, we looked into studying correlation with other underlying habits or diseases of patients to better understand if they are related to the development of cataract. The two symptoms that were tested were smoking and diabetes. Add a few sources that state what past studies have said about correlating smoking, diabetes with cataract.
References used here:
Ye, J., He, J., Wang, C., Wu, H., Shi, X., Zhang, H., Xie, J. and Lee, S.Y., 2012. Smoking and risk of age-related cataract: a meta-analysis. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science, 53(7), pp.3885-3895.
Beebe, D.C., Holekamp, N.M. and Shui, Y.B., 2010. Oxidative damage and the prevention of age-related cataracts. Ophthalmic research, 44(3), pp.155-165.
Truscott, R.J., 2005. Age-related nuclear cataract—oxidation is the key. Experimental eye research, 80(5), pp.709-725.
Pollreisz, A. and Schmidt-Erfurth, U., 2010. Diabetic cataract—pathogenesis, epidemiology and treatment. Journal of ophthalmology, 2010.

NB: Count of uid, stands for the count of patients’ id, a unique identifier of each patient.
The table able above shows the number of cataract patients who are either diabetic, have history/symptom of smoking or both.
A total of 102,509 cataract patients were recorded.
102,479 cataract patients are neither diabetic nor have symptom of smoking. This means these patients had only symptom of cataract.
28 of the cataract patients are diabetic, while only 2 of the cataract patients had symptom of smoking.
However in our study we got a very low association in between diabetes and cataract. Similarly hardly any association was available in between smoking and cataract within the study population. These may be attributed to the error occurred during the time of assortment of data as every details might not be accurately reported for every patients within EMR. According to the scientific evidence cataract is considered to be a multifactorial disease and varied factors apart from smoking and diabetes for instance hereditary material, age, noursihmnet status, exposure to ultraviolet radiation and trace metals can also be the causal factors for the development of catarct (Balasubramanian, et al, 1993) . Add a few lines that say the correlation between them were very low and that is perhaps due to data collection of patients and perhaps not everything was recorded in the EMR, or that perhaps in the state of Telangana eye disorders seem to be a separate issue and other factors do not correlate.
Reference
Balasubramanian, D., Bansal, A.K., Basti, S., Bhatt, K.S., Murthy, J.S. and Rao, C.M., 1993. The biology of cataract. The Hyderabad cataract research group. Indian journal of ophthalmology, 41(4), p.153.
Cataract Patients Tested Against Weather Variables
Please add a paragraph here that says this part, which was identified in the research as data merging was highly complex to test because of the number of cells and because we had to work with both discrete and continuous variables.
Plotting only the cataract column against weather variables:

This particular plotting has shown a correlation with continuous variable cumulative rainfall and cataract and this is in accordance with the investigation of Balasubramanian, et al, 1993 as he reported that cataract was found to be more frequent in cloudy weather conditions as pupils of the eye expands more to allow more light to enter and the lens gets enhanced exposure to UV radiations. Moreover, water vapours can filter IR not UV radiation.
Reference
Balasubramanian, D., Bansal, A.K., Basti, S., Bhatt, K.S., Murthy, J.S. and Rao, C.M., 1993. The biology of cataract. The Hyderabad cataract research group. Indian journal of ophthalmology, 41(4), p.153.
The above chart shows the result of plotting Cataract disease with one of the weather variables (Here, cumulative rainfall was used). Since the column for cataract diseases alone is a non-continuous variable (Has only Cataract as value), the resulting chart is empty with a single data point showing only one of the values from the cumulative rainfall (which is a continuous variable). This is applicable to all weather variables. (FIX THE PARAGRAPH PLEASE, EXPAND ON IT AND ENHANCE IT BECAUSE I DON”T THINK I UNDERSTAND IT. THIS WAS FROM THE DATA ANALYST) The data has been generated with the aid of data analytics tool to explore the association in between specific cataract condition and variables of weather. The groups were categorized as cataract patients and non cataract ones so that the impact of weather condition can be correlated with ocular diseases (Refer Appendix for the reports). (Then here say we had to generate extensive reports from the data analytics tool used here to see which specific cataract condition is most present at the different rainfall measures, and we did that across all weather variables, and tested for both cataract and non cataract patients, as non cataract patients were used as the control group to be able to find insights that correlate the impact of weather variables on the development of ocular diseases). Please state that all these reports have been included in the appendix as they are complex to present in this section, but that the summary of the findings are explained here.
What was the most relevant finding was that the disease Pytergium was found to be most affected by global radiation and windspeed, and cataract most prevalent in rainfall).
The close relationship between climate, environment and the development of Cataract is crucial to understand for future preventative measures. In Telangana, it shows that Cataract is the disease most prevalent in rainfall.
Consistent Prevalence of Pterygium in Relation to Global Radiation

We analyzed patients who presented with Degeneration symptoms, and correlated the diagnosis to climatic factors, such as humidity, rainfall, temperature and global radiation. The above analysis shows the top 5 most prevalent degeneration right-eye diseases as impacted by global radiation. Pterygium shows to be most prevalent at over 46% of the total global radiation value. The analysis was done on a patient basis and not a disease basis, as the data showed that one patient can develop more than one disease.
Consistent Prevalence of Pterygium in Relation to Windspeed

The analysis above shows the top 5 most prevalent right-eye diseases with Degeneration as a symptom and how the diseases are influenced by maximum windspeed. Pterygium also was also the most present among patients and concentrated at average maximum windspeed of between 10.2 and 10.9.
Can you look at these tables and graphs below? Do you think you understand these? And can come up with one page summary of what it is – what difference are in the tables in cataract patients vs. non cataract patients… I don’t understand them, but I think it means that (at a certain cumulative rainfall number, these diseases are present the most, among them cataract patients etc…. ) Can you add an outside source that summarizes the weather variables in relation to the development of cataract?
When the outcomes for global radiation exposure of non cataract or emmetropia populace is compared with cataract or ocular disease populace a huge difference is observed. The figures demonstrated that predominance of Pterygium is highly associated with global radiation, however with wind speed factor all the conditions demonstrated equivalent effects. Study conducted by Shah, et al, 2016 and Balasubramanian, et al, 1993 highlighted that cataract or ocular disease has a very close association with exposure to radiation. It is evident that in Australia where people were exposed to expanded level of UV radiation showed early initiation of age related cataract (Hollows, et al, 1981). Moreover also in Nepal predominance of cataract was 3.8 times more where people were exposed to more than 12 hours of outdoor exposure (Brilliant, et al, 1983). The possible route of damage is in the DNA material within the epithelium of lens (Kuck et al, 1983). Study conducted by Nordmann, 1962 also highlighted radiation as causal factor for cataract and ocular diseases (Nordmann, 1962).
References Used
Shah, S.I.A., Shah, S.A. and Rai, P., 2016. Factors associated with pterygium based on history and clinical examination of patients in Pakistan. Journal of current ophthalmology, 28(2), pp.91-92.
Hollows, F. and Moran, D., 1981. Cataract-the ultraviolet risk factor. The Lancet, 318(8258), pp.1249-1250.
Brilliant, L.B., Grasset, N.C., Pokhrel, R.P., Kolstad, A., Lepkowski, J.M., Brilliant, G.E., Hawks, W.N. And Pararajasegaram, R., 1983. Associations Among Cataract Prevalence, Sunlight Hours, And Altitude In The Himalayas. American Journal Of Epidemiology, 118(2), Pp.250-264.
Cataract patients
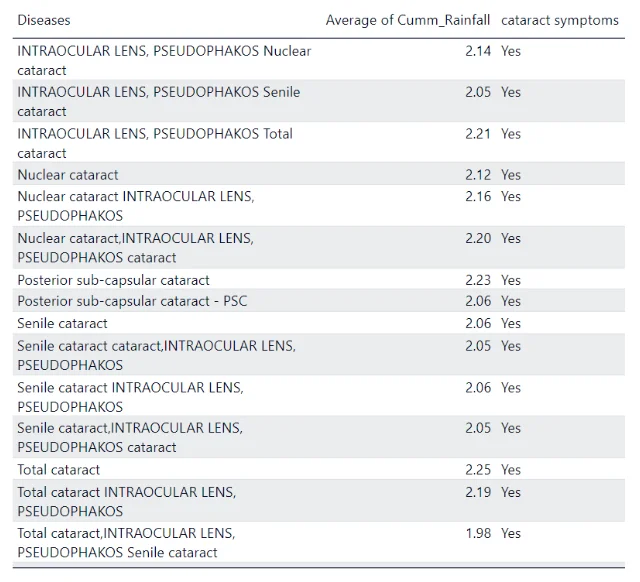
The table above shows the prevalent cataract diseases at different cumulative rainfall conditions.
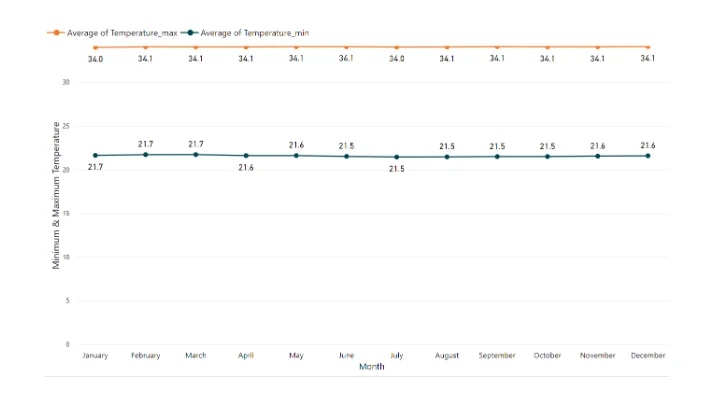
Cataract Patients as influenced by Minimum & Maximum Temperature Conditions:

The table above shows the prevalent diseases at different minimum & maximum temperature conditions.
Cataract Patients as influenced by Minimum & Maximum Temperature across the months:
Cataract Patients as influenced by Minimum & Maximum Humidity Conditions:
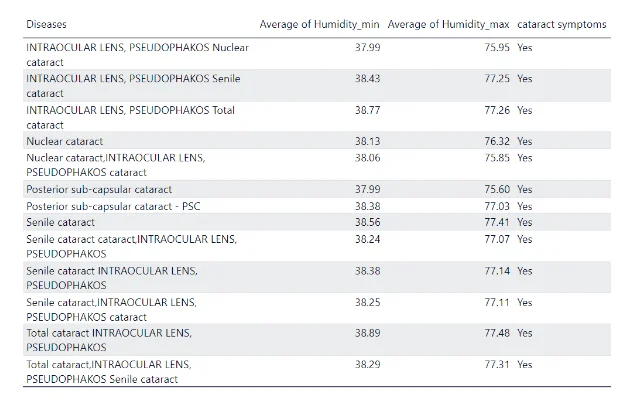
The table above shows the prevalent diseases at different minimum & maximum humidity conditions.
Cataract Patients as influenced by Minimum & Maximum Humidity Conditions across the months of the year:
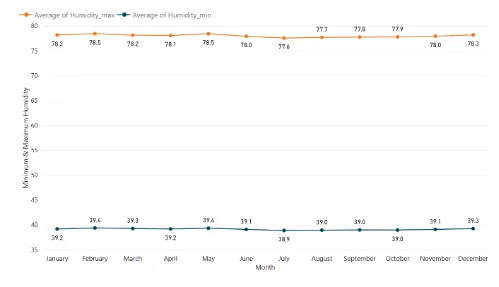
Cataract Patients as influenced by Global radiation:

The table above shows the prevalent diseases at different Global radiation conditions.
Cataract Patients as influenced by Global radiation across the months of the year:

Cataract Patients as influenced by Windspeed:

The table above shows the prevalent diseases at different Global Windspeed conditions
Non-Cataract Patients with Weather Variables
Non-Cataract Patients as influenced by Cumulative Rainfall:

The table above shows the prevalent diseases affecting patients without cataract symptoms (Non-cataract patients) at different cumulative rainfall conditions.
Non-Cataract Patients as influenced by Minimum & Temperature conditions:
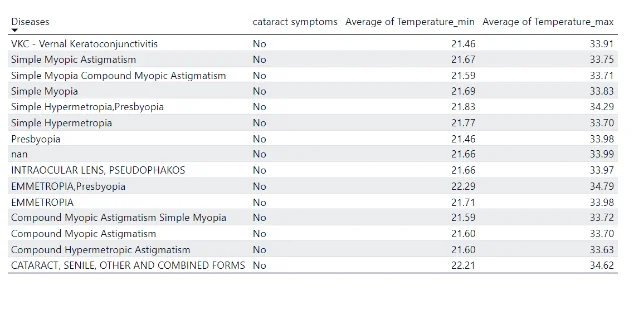

The table above shows the prevalent diseases affecting patients without cataract symptoms (Non-cataract patients) at different minimum & maximum temperature conditions.
Non-Cataract Patients as influenced by Minimum & Humidity conditions:

The table above shows the prevalent diseases affecting patients without cataract symptoms (Non-cataract patients) at different minimum & maximum humidity conditions.
Non-Cataract Patients as influenced by Global Radiation:

The table above shows the prevalent diseases affecting patients without cataract symptoms (Non-cataract patients) at different global radiation conditions.
Non-Cataract Patients as influenced by Windspeed:
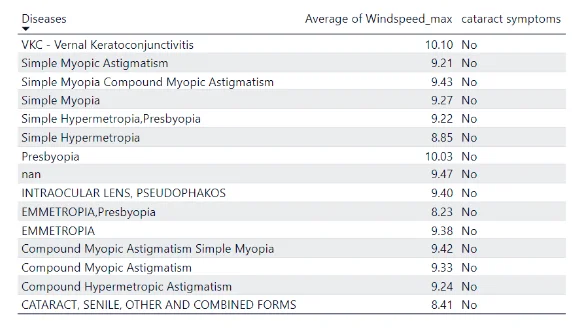
The table above shows the prevalent diseases affecting patients without cataract symptoms (Non-cataract patients) at different windspeed conditions.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



