Type-2 Diabetes Among the Elderly
Introduction
The type-2 diabetes is the condition in which the body cells are unable to use sugar in the blood to efficiently convert them into energy. The key cause of type-2 diabetes are overweight, intake of artificial sweeteners, lack of physical exercise, stress and genetic condition. The symptoms of the disease include increased amount of thirst, frequent urination, fatigue and others (Zheng et al., 2018). In the UK, type-2 diabetes is one of the leading health issues among the population as well as elderly. This is evident as 6% of the UK population that is 1 in every 16 individuals in the UK are considered to suffer from diabetes and among them 90% of them are suffering from type-2 diabetes (Diabeties, 2020). Moreover, half of the people suffering from diabetes in the UK are found to aged 65 years and over with 10% being over 75 years of age and 14% being over 85 years of age (BGS, 2018). Thus, in this study, the demographic prevalence of type-2 diabetes among the elderly in the UK is to be determined in borough of Lambeth. Further, the health inequalities and social determinants of health-related with type-2 diabetes in the UK is to be explained. In addition, local policies and public services along with interventions available for management of type-2 diabetes in the UK is to be discussed. For those undertaking research in this area, seeking healthcare dissertation help can provide valuable insights and support.

Background
An individual is likely to develop type 2 diabetes at age of 45 years or older. This is because with saging the insulin resistance in the body increases along with impaired functioning of the pancreatic islet is seen among individual leading them to develop increased blood sugar (Bakris et al., 2020). The lack of physical activity leads the body muscles to remain sedentary which create lack of need for them to work in changing glucose from the blood to energy. It leads to build-up of glucose in the blood in turn making the individual suffer from diabetes (Sami et al., 2017). The obesity leads to increased fat deposition in the body which leads the cells unable to use glucose from the blood and become insulin resistant leading the individual to develop type-2 diabetes (Chatterjee et al., 2017).
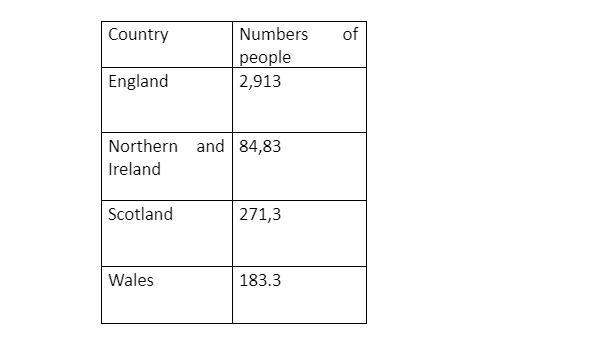
According to Diabetes UK, (2003-2020) statistic suggested that a slightly higher proportion of adult men have diabetes. Men account for 56 per cent of UK diabetes and women accounts for 44 per cent. According to the prevalence diabetes (2018) there are 3.9 million people diagnose with diabetes England 3,319,266 Northern Ireland 99,833 Scotland 301,523 Wales 198,883 UK 3, 919,505 and more than 500 people die prematurely every week due to the disease (diabetes UK 2019). As note there is estimated 327,587 , resident in Lambeth , 31% of population live in area of high deprivation, 44th most deprived local authority in England the 9th most deprived local authority in London . Lambeth population is ethnically diverse , 60% of Lambeth population (3 in 5) described their as other than white British. 24% are black almost half of these 11% black Africa Demography facts sheet (2017). 16000 people are living with the condition an increase of 3000 in a year according to Lambeth and Southward Diabetes UK group (2018) As you can Lambeth has prevalence rates and most deprived . In UK, the health of BME people is generally worse off in comparison to the general population due additional socio-economic and nutritional factors ( Patel et.al ,2005).
The concentration of BME groups in the most deprived neighbourhood in London in comparison with the rest of the British population (centre on Dynamic of Ethnicity 2011) is a cause of concern because there is a close relation between deprivation and Diabetes. On this not , it has been argued that such inequalities BME can contribution to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment of diabetes. (Patel , 2009) Similarly, language barriers, lack of support and long working hours among of groups can hamper attempts to seek medical support, leading to untimely death due to diabetes. As already noted Diabetes is one of the major cause of death in Borough and is more prevalent among BME group, costing NHS billons of pounds. NHS spend at least £19 billion ( £27 million a day)on diabetes equivalent to 10% of its entire budge , 80 % of it spent treating complication (diabetes UK 2019). This is a huge burden on the tax payer and puts the NHS under enormous strain. Due to the recognition of the this financial huge burden, the NHS introduced the NHS check intervention in 2013 to tackle this .
Prevalence 2018-19 Diabetes U K
England 3,319,266
Northern Ireland 99, 833
Scotland 301,523
Wales 198,883
U K 3,919505
Minority ethnic group key statics on diabetes 2018
Bangladesh Men 8.2% women 5,2%
Black Africa 5% 2.1%
Black Caribbean 10% 8.4%
Chinese 3.8% 3.3%
Indian 10.1% 5.9%
Pakistanis 7.3% 8.6%
Evidence suggests that BME groups are more likely to develop Diabetes than other population of in the UK and also men are affected than women (diabetes UK 2019) Deprivation is strongly associated with higher levels of this problem in BME groups. The key polices tackling this problem, are as follows Government has put in place the health check for day -to-day management of diabetes, people with diabetes need to look after and manage their diabetes on a day to day basis, which involves taking medication (including injections).
My work place is made of elderly patient 65 years and over , and most of than are admitted with type 2 diabetes and other complication. Patient with type 2 diabetes undergo regularly check-ups to help mange the condition. It is also important to recognise the symptoms of a hypo , and in my place of work the is an emergency hypo box containing hypo treatments, which help tackle the hypo. Diabetes UK (2019) diabetes is a lifelong condition that needs to be monitored and manage well, having the right care and support is essential for the wellbeing of all people with diabetes. For the most part people with diabetes are able to do it themselves. It is also important to know that people with diabetes in the place are undergo once a year annual review, by healthcare professionals and there is 15 vital checks and services that every one with diabetes whatever the type should get for free from health team every year, it’s a way of detecting any early signs of complications so that they can be treated successfully, enabling people with diabetes to lead a health life. During this physical check, individual are able to talk about the needs agree personal targets and get support such as to stop smoking, emotional and psychological support and dietary advice.
The diabetes patient also get a free flu vaccination every year to stay healthy, as there is a greater risk of severe illness such as pneumonia, if they get flu. There is NHS diabetes prevention program (education) between 40-74 years , this programme helps people to understand and manage their condition better and gain the confidence and skills to take control of their own health. There are also signpost to e-learning course , type 2 diabetes and Me is a free step- by- step Online guide for people who have recently received a type 2 diagnosis. The diabetes UK advocacy services in (2017) provided serve related to access to strips , pump adult National Institute for health and care Excellence, NICE diabetes UK (2019 ) recommended care process for people living with diabetes , these are check for haemoglobin (HB) blood sugar levels, blood pressure, cholesterol , serum, creatinine, urine albumin , fact, body mass index (BMI) smoking and eyes retinal screening.
According to diabetes UK, National diabetes Audit shows that , at least 4 in 10 people with diabetes express emotional and psychological, depression , anxiety and emotional distress as a of diabetes. Tackling the crisis reduces variation inequality and access to care process and treatment target.( Diabetes UK). It is also interesting to know that in my work place the diabetes transformation fund has led to 96 additional inpatient specialist nurse to help tackle and improve the condition (diabetes UK 2017 ). Able to identified the public health issue (diabetes) within my practice area of practice , has enabled me to assess the impact of the government intervention NHS Health Check in tackling diabetes among the BME communities in the borough of Lambeth. The research as explore the prevalence of Diabetes among BMA in the communities , also discussed health implications of diabetes . The objective also assesses the impact of the government intervention, NHS check in tackling diabetes among BME communities in London boroughs.
Government Policies and Strategies for type-2 diabeties
In the UK, NHS Diabetes Prevention Programme (NHS DPP) is present as the healthcare joint committee from the Public Health England (PHE) working with the NHS England in delivering effective care and control regarding type-2 diabetes among individuals (gov.uk, 2018). In short-term, the program focuses on recognising people who are at increased risk of facing type-2 diabetes or are likely suffering from type-2 diabetes but remains undiagnosed (gov.uk, 2018). It is important aspect of the program as many elderlies are seen to be living in the UK undiagnosed from the type-2 diabetes. The late detection of type-2 diabetes leads individuals to have worsen health condition which require intricate intervention in managing it and ensuring well-being of the patients (gov.uk, 2018). Thus, timely and early detection of type-2 diabetes among the elderly is important to avoid them from facing worsened health condition.
The NHS DPP involves educating individuals regarding the way to maintain healthy body weight (gov.uk, 2018). This is essential as obesity is considered to be risk factor for type-2 diabetes. The NHS DPP also leads to support individuals in achieving effective dietary recommendations needed for type-2 diabetes management and allows achievement of Chief Medical Officer’ (CMO) to provide physical activity recommendations to people to help them manage and avoid type-2 diabetes (gov.uk, 2018). It is important part of the program in supporting elderly with type-2 diabetes for managing their proper health condition because diet and exercise is seen to create position health condition for diabetic patients.
In the UK, National Service Framework for Diabetes is been developed with the aim to enhance the service quality and standards regarding various nature of care related to diabetes. The framework aims to allow the person suffering from any type of diabetes regarding the way to manage their lifestyle. For this purpose, the framework arranged structured educational intervention to be provided to the patients so that they learn regarding risk towards their health and the lifestyle activities to be adopted in effectively controlling the health condition (assets.publishing.service.gov.uk, 2018). Thus, this programme is effective to support elderly with type-2 diabetes because it acts to deliver them education and improve their knowledge regarding the actions avoided to be performed as well as lifestyle activities needed to be changed to improve their health and attain well-being. The National Service Framework for Diabetes along with National Service Framework for Older People together acts to deliver support services for the elderly to help them led better life. This is because elderly people are often found to have poorly managed diabetes which increases their risk of facing hospital admission and longer hospital stay (assets.publishing.service.gov.uk, 2018). Thus, the framework is effective for the elderly suffering from type-2 diabetes as they would able to get effectively arranged care services specialised for their health condition.
The NHS Right Care Diabetes Pathway is developed by the NHS England which informs about the core components regarding optimal services related to diabetes management, evidence for the opportunity to lower care variation and ensure improved health outcome of the patients (NHS, 2018). This program is effective for the local authorities trying to support healthcare and lifestyle changes in the elderly with type-2 diabetes in the UK. This is because it guides them regarding the way clinical commissioning groups are to be used to work with general practitioners to involve them in the National Diabetes Audit to improve diagnosis of the disease among the elderly. Moreover, it supports the local authorities to determine the way they are to structure education so that better actions are promoted to improve treatment targets regarding type-2 diabetes for the elderly (NHS, 2018).
Intervention for type-2 diabeties
The type of intervention I will plan to tackle the (public health) diabetes are as follows working with patient behaviour and education practically participating on showing people how to use the diabetes devices, testing to reduce hypo, focusing more in obesity, and educating people on unhealthier food . campaigning on government taking action on food industry as commitment as part of public health England, for sugar, salt, calories and labelling reduction programme (diabetes UK 2017), which is grassroot of the disease. Diabetes is impacting multiple aspect of individual lives and a significant proportion of people with diabetes are also managing complications, government intervention, on greater access to education and technology is helping to create awareness of the disease.
The food eaten by the individuals has a major impact on causing type-2 diabetes among elderly. Thus, development of effective intake of nutritious food in right amount by following an enhanced diet chart is one of the key areas of intervention in preventing and controlling spread of type-2 diabetes. The patients suffering from type-2 diabetes are required to take complex carbohydrates and avoid inclusion of simple carbohydrates in the diet to effectively control blood sugar level. This is because complex carbohydrates lead the body to take time in breaking down and digestion of the food leading to avoid increased level of blood glucose to be formed at slower rate, in turn, keeping control on the blood glucose level (Neuenschwander et al., 2019). The elderly with type-2 diabetes are required to take in increased amount of protein-rich foods as they have little impact on raising blood sugar level in the body as well as provides energy to resolve fatigue and enhanced functioning of the body Guasch-Ferré et al., 2017). The intake of increased fibre and vitamins are to be used as intervention in the form of food for the type-2 diabetic patients as it helps in keeping the blood sugar low by slowing the absorption of glucose in the blood (Guasch-Ferré et al., 2017).
The other intervention for type-2 diabetic patients to be made is making them involve in physical exercise. This is because exercise helps the diabetic patients to make their body cell use increased amount of sugar from the blood and increases sensitivity of the body cell to use glucose, in turn, countering insulin resistance which is responsible for the worsening of the disease (Zhao et al., 2018). According to Jayawardena et al. (2018), the individuals with type-2 diabetes are required to involve in two to three hours of physical exercise. This is because physical exercise not only allows to control blood sugar level but also helps in avoiding other risk factor towards health related to type-2 diabetes such as heart diseases, obesity and others (Zhao et al., 2018). The self-monitoring is an essential intervention required to be followed by type-2 diabetic patients because the approach leads individuals to measure their blood sugar regularly through glycaemic meter to check the impact of the treatment and if any immediate actions are required to manage raised blood sugar level (Young et al., 2017).
The pharmacological intervention to be made for managing type-2 diabetic patients is Metformin. This is because Metformin impacts to lower the amount of sugar released by the liver in the blood. It leads the body also to respond more effectively to the insulin which is the hormone that plays the role of controlling the blood sugar level in the body (Griffin et al., 2017). According to NICE, in case the individual with type-2 diabetes faces gastrointestinal side-effects on using standard-release metformin, then the trial of modified-release form of metformin is to be used (NICE, 2019). The other intervention to be made in controlling type-2 diabetes among the elderly is providing them insulin therapy. In this therapy, insulin is injected within the fat muscle of the body to allow gradual release of extra insulin in the body to be used by the body cell in lowering the blood sugar level (NICE, 2019).

Conclusion
In conclusion , We need more sustained commitment from government and NHS, national and locally to reduce inequalities , to ensure that progress continues and is stepped up where needed, in order to address the diabetes crisis and radically reduce the harm now and in the future.
Looking for further insights on Trends in Health and Social Care Industry? Click here.
References:
Bakris, G.L., Agarwal, R., Anker, S.D., Pitt, B., Ruilope, L.M., Rossing, P., Kolkhof, P., Nowack, C., Schloemer, P., Joseph, A. and Filippatos, G., 2020. Effect of finerenone on chronic kidney disease outcomes in type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine, 383(23), pp.2219-2229.
BGS 2018, Diabetes, Available at: https://www.bgs.org.uk/resources/diabetes [Accessed on” 14 January 2021]
Chatterjee, S., Khunti, K. and Davies, M.J., 2017. Type 2 diabetes. The Lancet, 389(10085), pp.2239-2251.
gov.uk 2018, Health matters: preventing Type 2 Diabetes, Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/health-matters-preventing-type-2-diabetes/health-matters-preventing-type-2-diabetes#:~:text=The%20goals%20of%20the%20NHS,diabetes%2C%20over%20the%20longer%20term [Accessed on” 14 January 2021]
Griffin, S.J., Leaver, J.K. and Irving, G.J., 2017. Impact of metformin on cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis of randomised trials among people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia, 60(9), pp.1620-1629.
Guasch-Ferré, M., Merino, J., Sun, Q., Fitó, M. and Salas-Salvadó, J., 2017. Dietary polyphenols, Mediterranean diet, prediabetes, and type 2 diabetes: a narrative review of the evidence. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2017.
Jayawardena, R., Ranasinghe, P., Chathuranga, T., Atapattu, P.M. and Misra, A., 2018. The benefits of yoga practice compared to physical exercise in the management of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews, 12(5), pp.795-805.
Neuenschwander, M., Ballon, A., Weber, K.S., Norat, T., Aune, D., Schwingshackl, L. and Schlesinger, S., 2019. Role of diet in type 2 diabetes incidence: umbrella review of meta-analyses of prospective observational studies. bmj, 366, p.l2368.
NHS 2018, Diabetes treatment and care programme, Available at: https://www.england.nhs.uk/diabetes/treatment-care/ [Accessed on” 14 January 2021]
NICE 2019, Type 2 diabetes in adults: management, Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng28 [Accessed on” 14 January 2021]
Sami, W., Ansari, T., Butt, N.S. and Ab Hamid, M.R., 2017. Effect of diet on type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review. International journal of health sciences, 11(2), p.65.
Young, L.A., Buse, J.B., Weaver, M.A., Vu, M.B., Mitchell, C.M., Blakeney, T., Grimm, K., Rees, J., Niblock, F. and Donahue, K.E., 2017. Glucose self-monitoring in non–insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes in primary care settings: a randomized trial. JAMA internal medicine, 177(7), pp.920-929.
Zhao, R.R., O’Sullivan, A.J. and Singh, M.A.F., 2018. Exercise or physical activity and cognitive function in adults with type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance or impaired glucose tolerance: a systematic review. European Review of Aging and Physical Activity, 15(1), p.1.
Zheng, Y., Ley, S.H. and Hu, F.B., 2018. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 14(2), p.88.
Appendix
Day to day management of diabetes is very important , it involves taking medication , including injections at the right time. Blood glucose testing level is very important because it help to monitor for symptoms of hypoglycaemia and hyperglycaemia levels.
According to statistics there is also several risk factors that are contributed to this , such as family history of type 2 diabetes, age – being older than 40 or older than 25 for some black and minority ethnic (BME) groups , certain ethnicities.
Public health England provided the Healthier You’ the diabetes prevention programme and it was available across the whole England in 2018 to 2019 , 185,000 referred from primary care, at least 78,000 taking up the programme to date, the programme is reaching groups who are most at risk , statistically 25% of the patients were from BME groups and 45% were under the age of 65. We also understand that 44% of those taking up the programme are men .
National strategy and policy to prevent type 2 diabetes set out by the national institute for health and care excellence (NICE) educational session for patient with diabetes was successful because it increased an awareness of repeatedly participating in educational sessions, reducing the inequalities , delivering of information , education to support healthy eating and increase physical activity,.
The digital pilot of the NHS diabetes prevention programme (NHS DPP) 2018 is to reduce the incidence of complication associated with type 2 diabetes, heart, stroke, kidney, eye and foot problems.
NHS Health check implemented with flexibility to meet the needs of local communities also to create element of broad spectrum of work to combat type 2 diabetes and obesity . It is essential to address the social normal and diabetes UK (2018) and obesogenic environment that are increasing this level of risk in the first place, particularly in children and young people. Tackling obesity in children and adults is one of seven PHE priority areas, and NHS has developed and set out a plan following the five year forward view. Back in 2015 scientific advisory committee on nutrition recommended that the average population intake of sugar should not exceed 5% of total dietary energy ( reduce sugar in take ) “change for life “ such as Eat well guide” levy on sugary drinks, which help people to make healthier choices. Although type 2 diabetes and obesity alone cannot tackle alone by healthier choice , but it can be expected to make an important contribution and it’s success could help pave the way for broader investment in prevention activity in the future ( PHE health matters blogs 2017).
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



