Effective Management of Employee Absence
Some organisations have extremely high levels of absence. Why is it important to proactively manage this?
In the recent era of globalisation, the multinational corporate firms are suffering from the employee management issues, where there is high absence among the employees. This is critical issue, for which the performance of the organisations be hampered and the companies fail to maximise the organisational goals and objectives. In this regard, the organisations need to focus on managing the major issue of employee absence in the organisation in different ways such as giving them freedom to perform, maintaining harmony, safety and security of the employees, restructured salary and introducing performance related pay as well as encouraging their creativity in the workplace. Through these strategic planning, it is the responsibility of the corporate firms to manage the workforce and mitigate the absence of the employees in the organisations (Brewster, 2017). Hereby, it is important to proactively manage the issue of absence among the employees as there are several benefits of managing the issue. In the next sections, it is effective to identify the reasons behind managing the issue of employee absence in the workplace.

Enhancing cooperation:
Through managing the employee absence at the workplace, it is possible to enhance collaboration in the workplace, where the employees can cooperate with each for performing better and share their views and understanding with each other.
Improving communication:
Internal communication can be maximised through managing the absence among the working force, where the employees try to participate with their full potential and enhance internal communication. Positive attitude, open discussion, helping each other and sharing each other‘s skill and knowledge are effective in the workplace which provide a scope to enhance communication among the employees in long run (Sparrow, Brewster and Chung, 2016).
Maximising organisational goals and objectives:
The organisational goals and objectives can also be maximised through managing the issue of absence among the workforce, where the employees are encouraged at the workplace to perform better and fulfil the objectives of the organisation successfully. In addition to this, the organisations can also maximise their profitability and sales volume by leading the employees through improving their efficiency and performance (Noe et al., 2017).
Job satisfaction:
Job satisfaction is another advantage of managing the organisational absence among the workforce, where the workers are getting involved with each other as well as with the senior team members. In this situation, continuous communication and collaboration as well as respect for each other and internal trust further maximise the job satisfaction of the employees in the workplace, where the employees are encouraged to perform better and maximise their job responsibilities. It further reduces stress and provides a happy workplace where the employees can perform efficiently.
Improving innovation and creativity:
Innovation and creativity can be managed well in the workplace where the management of the issue of absence among the workforce further provides a scope to improve participation of the staff and encourage their creativity and innovation to perform better and maximise the organisational performance.
Maximising performance of the organisation:
The performance of the organisation as a whole can be maximised through managing the issue of absence in the workplace where the employees try to participation and the managers encourage them to work efficiently and contribute with their full capabilities in order to enhance the performance of the organisation (Bratton and Gold, 2017).
Building stronger community:
Through managing the absence in the organisational workplace, the organisations can enhance the participation of the employees and it in turn helps to develop stronger community in the workplace. It is beneficial for the employees to feel valued at the workplace and enjoy the benefits of working in the organisation. The quality of work can be maximised where the human resource managers are able to boost the employee’s satisfaction and develop string community in the organisation.
Boosting productivity:
Through managing the issue of absence among the employees in the organisation, it is also possible for the managers of the human resource to boost the productivity of the organisations, where the employee participation is helpful to enhance the company’s activities and manage the decision making practice efficiently. All the employees try to participate well with their potential; and skill to develop effective organisational tactics to fulfil the organisational aims and objectives and thus the management of the issue of absence in the workplace in effective for the organisations to boost the productivity in long run (Mondy and Martocchio, 2016).
Increasing product quality and service excellence:
Increasing the organisational product quality and service excellence can be possible through managing the absence among the employees. Through continuous participation, the employees become experienced and skilled to perform better and develop quality products successfully of the benefits of the customers. Apart from that, the workers are concerned about serving the customers in a better way and in this regard they become skilled to understand the customer’s mind set and perception and according to that the employees aim to improve their service excellence to maximising satisfaction level of the customers.
Developing partnership working:
Development of the partnership working practice in the organisation can be ensured through managing the absence among the employees, as there can be possible to maximise the participation of the employees, where continuous participation and employee’s cooperation are effective to develop the practice of partnership working. Here, the organisations and encourage the employees to cooperate with each other and work as partnership basis which also provides an opportunity to the employees to share their knowledge and skill with other colleagues and team members for better performance.
Organisational culture:
Proper organisational culture can be developed through managing the issue of employee absence and maximising the participation of the employees in the organisational through maximising the participation of the employees, it is possible to develop suitable culture, where the mangers influence the employees to share each other’s views and knowledge and maintain transparency and accountability at the workplace. Positive attitude, open conversation and respect for each other can also be enhanced which in turn contributes positively to manage the organisational culture, where the employees can work with freedom and harmony.
Many organisations fail to evaluate training and therefore cannot prove that it is a worthwhile business investment. Using Kirkpatrick’s (1959) Evaluation Model, outline how an organisation may go about conducting an evaluation process?
There are many organisations which are not efficient to evaluate the existing training and development program in the workplace and thus it is difficult for them to understand whether the training program is worthwhile or not. The organisations need to develop effective evaluation model for analysing the benefit of the training program in the organisation and evaluate whether the staff members are getting benefits from such training or not. In this regard, the Kirkpatrick’s (1959) Evaluation Model is effective to evaluate the training and development programming the organisational context, where it is possible for the organisational management team to evaluate the training and analyse the effectiveness of the existing training and development program in the organisational workplace.

As per the Kirkpatrick’s (1959) Evaluation Model, there are four layers which are reactions, learning, behaviour and results, which are important to evaluate the existing training program which in turn helps the companies to analyse the effectiveness of the training and development program. In this Kirkpatrick’s (1959) Evaluation Model, the first level is reaction, where the manager in human resource department of the firm needs to analyse the perception of the staff and employees, and how do they react about the training program. Hereby, for successful evaluation, it is necessary for the human resource managers to empower the employees and identify their views an understanding about the training program. From the staff members, it is possible to get reliable answer whether the training and development program in the organisation is effective or not for them to maximise their skill and abilities. The performance of the employees depends on the skill, experience, knowledge, abilities and personality and through the reaction of the employees, it is necessary to acknowledge the perception of the employees, whether they are happy with the training program or not, whether they could maximise their skill and knowledge through such training or not at the workplace.
In the second phase of the Kirkpatrick’s (1959) Evaluation Model, there is learning, where it is possible for the human resource manager to analyse whether the staff get proper knowledge from the training or not. In this regard, the evaluation of the skill and knowledge of the staff members and the abilities of the employees need to be analysed so that it is possible to understand the effectiveness of the training program for maximising the skill and knowledge of the staff. It is also necessary in this second step to analyse whether the training is informative or not so that it is possible to evaluate the effectiveness of the training in informing the staff about the organisational working practice and culture and organisational goals and objectives so that the employees can acknowledge the organisational practice and gain proper understanding to perform better in near future (Abdelhakim et al., 2018).
In the third stage of the Kirkpatrick’s (1959) Evaluation Model, the behaviour of the participations will be analysed well in the organisational context, where it is possible for the human resource managers need to evaluate the phenomenon that in what extent the participants can change their behaviour in the organisational context. It is necessary for the organisations to analyse the training program where the managers must focus on the behavioural change of the employees, where through the effective training and development program it is possible to teach the employees about the organisational culture, personal behaviour and attitude at the workplace while working with others. result needs to be evaluated in the four stage as per the model of Kirkpatrick’s (1959) Evaluation, where it is easy to demonstrate whether the training program is ultimately effective to enhance the organisational performance for maximising the productivity of the firm or not. In this context, the human resource managers of the companies must focus on the performance level, efficiency of the staff in managing the customers of the organisations, service excellence of the companies and the overall performance of the firm. The managers also identify and acknowledge the sales volume and profitability in each year to evaluate the effectiveness of the training program in the workplace (Reio et al., 2017). On the other hand, the managers are also concerned about evaluating the performance and efficiency of the employee to assess the contribution of the employees, who are the major stakeholders of the company to contribute positively and maximise the organisational aims and objectives.
In this regard, all the multinational corporate firms need to focus on evaluating the training and development program in the workplace to analyse whether the training program is effective or not to maximise the organisational productivity and enhancing the employee’s performance in the workplace. The Kirkpatrick’s (1959) Evaluation Model is effective to provide four step evaluation processes, where the human resource managers can evaluate the performance of the employees and identify the effectiveness and benefits of the training programs in the organisational workplace. Continuous monitoring process of the organisations, reviewing the employee’s performance at a continuous interval and the proficiency of the staff members to perform and contribute efficiently in the organisation are also required to be evaluated in order to analyse the importance and contribution of the tanning and development program in the organisation. hereby, it is necessary for all the human resource management team in every organisation to evaluate the training program to understand that whether the training and development program is worthwhile or not in the workplace, where the employees are getting proper support to enhance the personal and professionals development activities or not in the workplace. In the recent era of globalisation, the multinational corporate firms need to focus on evaluating the existing training and development process to encourage the staff members and motivate them to improve their skill and knowledge by providing informative training where they can change their behaviour and maximises organisational performance by positive contribution of the team members.
Outline the three motivation process theories and discuss their role in the workplace
Motivation is the experience of the desire or aversion where the human resource managers develop effective tactics to motivate the employees in the workplace and maximise their values in the organisational context, so that the employees can feel valued and contribute positively to achieve the organisational performance. In this regard, there are there motivational theories which are Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, Herzberg motivational theory, and Vroom’s expectancy theory through which it is possible to demonstrate the motivational process among the employees.
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs:
The theory of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is effective to understand the basic needs of the individuals in working in the organisation where the five basic needs are proposed through this theory which is psychological, social, safety, esteem and self actualisation. In the psychological needs, the organisations take care of the basic needs of the employees which are food, water, shelter, and clothing, where the organisations try to provide them proper salary and performance related pay so that the basic psychological needs of the employees can be fulfilled. Under the needs of safety and security, the organisations are concerned about managing the safety and security of the employees, so that the staff members can work safely and contribute with their potential to maximise the organisational performance (Lee and Hanna, 2015). In this regard, the organisations develops safety measures in the workplace by implementing emergency exit, fire extinguisher, water availability in case of fire and use of proper uniform in some cases which are effective for managing the safety and security of the employees. In addition to this, there are some organisations that are efficient to provide insurance coverage in case of any accident at the workplace.
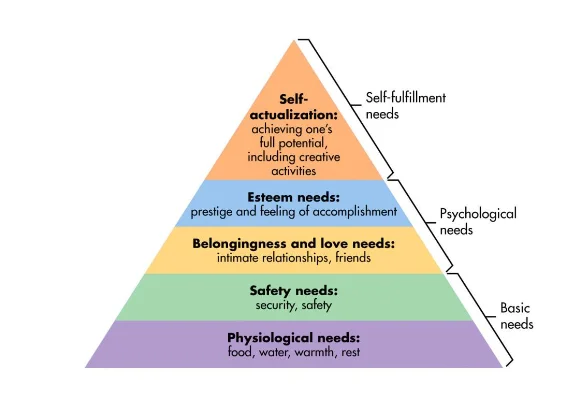
Under the social needs, the needs of belongings and love is crucial, where the internal workforce relationship, trust among the employees, respect and friendship are necessary which in turn helps the employees to feel valued and cooperate with each other to work as a partnership basis with communication and cooperation. Additionally, the self esteem and self actualisation needs are also required to be fulfilled in the organisational workplace, where the manager provide respect and the feeling of accomplishment as well as encourage the creative activities of the employees and give them the chance to achieve success. These activities are effective to fulfil the self esteem and actualisation needs of the staff members. The organisations aim to fulfil these five basic needs to develop suitable working culture where the staff members can feel valued and contribute proficiently.
Herzberg motivational theory:
Herzberg two factors motivational theory is effective to maximise job satisfaction and retain the employees for long run. In this regard, the two factors are motivation and hygiene where both the factors are important in the organisational context. The organisations must focus on the hygienic factors to maintain the workplace, where the activities such as working condition, co-workers relationship at the workplace, wage and structured salary, supervisor quality and policies and organisational rules are managed well. In this regard, the organisations focus on managing the organisational policies such as Minimum Wage Act 1948 as well as data protection Act 1998, Health and Safety at Workplace Act 1974, and other workplace legislations which are effective for the organisations to handle the workplace and maintain organisational ethics to create values for all the staff members. Additionally, the safe working condition, managing cleanliness at the workplace and internal relationship among the employees are also necessary to be managed well in order to motivate the employees and encourage their creativity to perform better in long run (Fallatah and Syed, 2018).

On the other hand, the motivational aspects as per the Herzberg motivational theory include personal growth, achievements, recognising, advancement, responsibility and the working pattern which are playing crucial role in motivating the employees in long run. the organisations in this regard provide clear responsibilities as well as promote the employees as per their performance and apart from that, the performance related pay and high recognition at the workplace further increase job satisfaction among the employees. The human resource managers are also concerned about providing the scope of personal and professional development through desisting effective training and development which is also possible to motivate the employees further and lead them towards achieving the organisational success.
Vroom’s expectancy theory:
Vroom’s expectancy theory assumes the behaviour from the conscious choices among the alternatives where the purpose can be maximised well. As per the Vroom’s expectancy theory model, the performance of the employees is based on the factors such as skill, knowledge, abilities, personality an experience. As per the model, there are three sections which are valence, expectancy and instrumentality. In valence, the employees give values to achieve rewards further and in the expectancy, the employees try to relate the efforts to performance and aim at maximising the organisational performance to be instrumental and get performance related rewards (Cascio, 2015).


Under the expectancy, the employees provide efforts for high performance management with proper resource utilisation and maximising their own capabilities and they focus on performance outcome where the organisational aims and objectives can be achieved well. After proper performance and maximising the organisational outcome, the employees are concerned about the rewards that they deserve for such high performance in the organisation. Hereby, for motivation the employees, the managers need to restructure the monetary and on-monetary rewards in the organisational workplace so that the employees can get proper rewards and be encouraged to perform better in near future. All the multinational corporate firms need to focus on motivation factors and designs effective rewards and incentives as well as hygienic factors to encourage the employees and lead them towards achieving the organisational success efficiently.
Reference List
Abdelhakim, A.S., Jones, E., Redmond, E.C., Griffith, C.J. and Hewedi, M., 2018. Evaluating cabin crew food safety training using the Kirkpatrick model: an airlines’ perspective. British Food Journal, 120(7), pp.1574-1589.
Bratton, J. and Gold, J., 2017. Human resource management: theory and practice. London: Palgrave.
Brewster, C., 2017. Policy and practice in european human resource management: The Price Waterhouse Cranfield survey. Boston: Taylor & Francis.
Cascio, W.F., 2015. Managing human resources. London: McGraw-Hill.
DeCenzo, D.A., Robbins, S.P. and Verhulst, S.L., 2016. Fundamentals of Human Resource Management, Binder Ready Version. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Fallatah, R.H.M. and Syed, J., 2018. A Critical Review of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. In Employee Motivation in Saudi Arabia (pp. 19-59). Palgrave Macmillan, Cham.
Lee, J.M. and Hanna, S.D., 2015. Savings goals and saving behavior from a perspective of Maslow's hierarchy of needs. Journal of Financial Counseling and Planning, 26(2).
Mondy, R. and Martocchio, J.J., 2016. Human resource management. London: Pearson.
Moreau, K.A., 2017. Has the new Kirkpatrick generation built a better hammer for our evaluation toolbox?. Medical teacher, 39(9), pp.999-1001.
Noe, R.A., Hollenbeck, J.R., Gerhart, B. and Wright, P.M., 2017. Human resource management: Gaining a competitive advantage. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education.
Reio, T.G., Rocco, T.S., Smith, D.H. and Chang, E., 2017. A critique of Kirkpatrick's evaluation model. New Horizons in Adult Education and Human Resource Development, 29(2), pp.35-53.
Sparrow, P., Brewster, C. and Chung, C., 2016. Globalizing human resource management. London: Routledge.
What Makes Us Unique
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



