Evaluation and Recommendations
Executive summary
The main aim of this report is to identify and evaluate the most effective HRH strategies for Google’s expansion into the Kenyan market through a joint venture. The report begins with a historical background of HRM from the 1800s to date. It also distinguishes between hard HRM and soft HRM before exploring different staffing approaches including geocentric, polycentric and ethnocentric approaches. Considering all the unique cultural and market dynamics of Kenya, HRM dissertation help, It then recommends the polycentric approach as the most appropriate approach for Google’s expansion into the Kenyan market. Just before conducting a PESTEL analysis of the Kenyan IT industry. The report then delves deeper into various HR strategies including recruitment, selection, training and development. Here, the report identifies the Five-Fold grading system as the most appropriate means for Google to identify and select the right candidates. The report then explores both on the job and off the job training techniques as the existing employee training techniques. Ultimately, the report makes recommendations to the Google team on how to effectively manage its human resources.
1.0 Introduction
The practice of human resource management (HRM) among multinational corporations (MNCs) has attracted interest among both academics and practitioners. While some scholars argue that multinationals are unconstrained by the local contexts of the host country when recruiting employees, others have argued that institutional contexts play a significant role in influencing HRM (Meyer and Xin, 2018). however, more recent research has established various global influences on MNC’s HRM, arguing that the HRM frameworks used in parent countries may not be appropriate for international ventures (Horwitz and Mellahi, 2018). Multinationals should use unique HR strategies because the domestic HR strategies may not yield effective results when applied in domestic subsidiaries.

That said, there are there main challenges faced by multinationals when it comes to HR management: inherent HR disconnect, cultural divide, legal and regulation mismatch. In HR disconnect, according to Harzing and Ruysseveldt (2017), multinationals often face the dilemma of implementing the same HR procedures and policies in recruiting, selecting, reward and compensating in all their business units and branches across the globe. On the other hand, regarding the cultural divide, multinational companies often desire to develop a global employee community that maintains the company’s unique values and culture. But, as observed by Meyer and Xin (2018), this can be challenging because of diverse cultures, customs and languages that hinder the alignment of HR strategies in different subsidiaries across the globe. Lastly, every host country has unique employee legal and regulatory laws that multinationals must abide by when setting up teams in different countries. This essay seeks to evaluate how Google while entering into a joint venture partnership with another company in a different host country, can deal with these challenges to establish an effectively operating subsidiary.
Looking for further insights on Recommendations? Click here.
2.0 Organizational profile
Google Incorporation
Google is an American-based multinational company that provides internet-related products and services including search engines, online advertising, hardware, and software. The company was founded by Larry Page and Sergey Brin on 4th September 1998 and is currently headed by Sundari Pichai, who has been at the helm of the company since 2015. The company’s mission is to: “organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful”. On the other hand, the company’s vision statement is to “provide access to the world’s information in one click”. As a multinational company, Google has numerous values that dictate and govern its internal and external and external operations. Some of the company’s values include: “Great isn’t good enough.” “Focus on the user, all else will follow.” “It’s best to do one thing well.” “Fast is better than slow.” “Democracy on the web works.” “You can make money without doing evil.” “There’s always more information.” “You can be serious without a suit.” “You don’t need to be at your desk”. Currently, Google is headquartered at its Mountain View California premises, in the United States.
3.0 Country Profile
3.1 Host Country Profile
Located in East Africa, Kenya is considered one of the fastest-growing regions in sub-Saharan Africa (Edo et al, 2019). According to Hansen and Xydis (2020), the country has is ranked as a developing country, with the economic and political reforms launched by successive leaders since 2002 spurring economic growth into one of Africa’s most technologically advanced countries. The table below illustrates the country’s key data
Kenya Factsheet
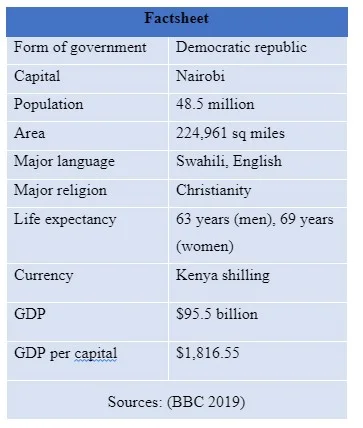
In the recent years Kenya’s technology sector has achieved a significant growth and development, with a market capitalisation of at least 717 million dollars by the end of 2019, representing nearly 60% of the total information technology investments (International Trade Administration, ITA 2021). Kenya is at the forefront of technological advancement and innovations and is considered the continent’s ‘silicon savannah’ – thanks to the government’s heavy investment in the broadband sector. As a host country, Kenya presents great business opportunities in the information and technology sector that businesses can explore, despite the many challenges that they might also need to deal with.
Opportunities
Data by Oxford Business Group (2017) indicate that Kenya’s middle class is increasingly growing
The upgrade of broadband services
Stable annual headline inflation (Central Bank of Kenya, 2017)
Foreign investment encouraged by the government through various tax and operational incentives
Growth in GDP
Challenges
Alarming rates of corruption (Boamah, 2019)
High unemployment rates (Gachari and Korir, 2020
3.2 PESTEL analysis
The technology industry in Kenya is influenced by various external and internal business environment factors. These factors can significantly affect Google’s sustainable development as well as its human resource management policies. Table 2 below presents an analysis of those factors using the PESTEL analysis, highlighting how each factor influences and how Google can adapt to those influences.
PESTEL Analysis
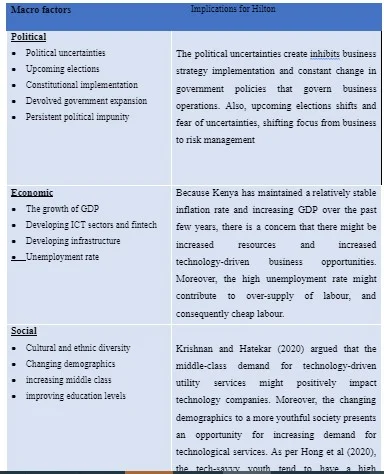
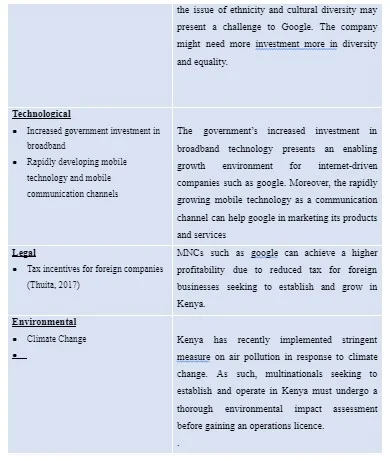
Based on the above PESTEL analysis, the social factors present as the area that need more focus for Google to achieve successful growth.
Why go to Kenya
As earlier mentioned, Kenya’s ICT sector is on a rapid growth, and is currently the regional leader in terms of general information technology infrastructural development, internet connectivity, mobile money, mobile banking and value-added services (ITA, 2020). Data by ITA (2020) also indicate that the country’s ICT sector accounts for 8% of its GDP through information technology-related services – creating at least 250,000 jobs by the end of 2020. The increased internet access within the country as contributed to an increased economic growth, triggering the government to develop a Digital Economic Blueprint, a policy framework that seeks to encourage the country’s economic growth through digital technology (ITA, 2020).
A recent report by World Bank also showed that Kenya’s information technology sector has outperformed the other economic sectors, achieving a landmark growth of 35% in the past decade (ITA, 2020). Compared to its state at the beginning of the decade, the sector has grown 6 times, a remarkable growth that is attributable to global-standard innovations such as mobile money transfer services. Whereas the sector is still poised for long-term growth, reports by KPMG (2020) indicate that the country’s capital expenditure will decrease by at least 13.8%, a phenomenon attributable to the COVID-19 and its impact on the global economy.
Cultural Aspects
An evaluation of the cultural aspects between the home country (United States) and the host country (Kenya) reveals a few cultural differences that Google should take note off. For instance, data from Hofstede Insights (2021) reveals that as opposed to the United States with 91 points on individualism, Kenya has 25 points on individualism. This implies that in a workplace environment, Kenyan employees are more likely to collaborate and work in teams that favour their in-group, and everybody takes responsibility of their group members. This is different from the United States work environment where, in a highly individualised society, the employees maintain a loosely knit relationship and everybody tend to look after themselves. The two societies are therefore different, and this must be considered by Google when recruiting.
Against this backdrop, the polycentric approach to employee recruitment is proves to be beneficial to Google because it allows the company to fill available vacancies by hiring locals. For instance, the local Kenyan partner could get in contact with a local recruitment agency to identify and help recruit locals with adequate skills that could help Google and its partner conduct its business. Because Google would want to expand its Kenyan clientele, it is useful to hire local professionals who understand the local IT market to coordinate its sales marketing strategies. However, the company can apply any of the other approaches if the polycentric approach fails to work (Kurkoski, 2017).
Recruitment and selection
For the past few years, the IT industry has faced recruitment challenges occasioned by a shortage of high skilled workers. According to industry reports by KPMG (2020), the shortage of technological skills at a global level is now higher than it has been since 2008. The report further revealed that the lack of specific IT skills in areas that are critical to the future global economic growth such as artificial intelligence experts, cybersecurity experts and data analysis experts is alarming. Similar reports by Muncaster (2021) also indicate that the shortage of cybersecurity specialists, for example, is above 4 million compared to 2.93 million in the last one year. This constantly increasing tech skill gap and shortage requires a structured approach to recruitment and selection of tech workers.
5.1.1 Workforce Planning
Willis et al (2018) defined workforce planning as the activity of estimating an organization’s demand for employees while evaluating the sources that might fulfil the demand. Having realised that the global IT industry is facing a shortage in workforce, it is essential for Google and its venture partner to develop a workforce plan that would not only help understand the organization’s projected HR changes but also identify the workforce demand and supply gaps and how this can impact the organization’s performance. For instance, developing a workforce plan would help determine the number of vacancies required in the new location. Similarly, as proposed by Akyurt et al (2021), it wold help identify and address issues of staff turnover. Consequently, through a workforce plan, Google and its venture partner will benefit from a productive workforce that is not only diverse but also aligns to the organizational structure.
Vacancy Identification
To effectively set up a base in Kenya, Google will need to fill several organizational positions including head of HR/administration, chief engineer, chief operation’s officer, and chief marketing/business development officer. These employees will be selected based on a predetermined selection criterion that considers the respective positions, their qualifications, job experiences and job descriptions.
Recruitment Process
The managers will recruit the employees based on their job positions. This can be executed through two major approaches namely broad-based approach and targeted approach. As per Rodney et al (2019), the broad-based approach entails attracting recruits with no specific qualifications or characteristics. It is most effective when recruiting employees for a one-time task, or when the task does not require any specific skills. On the other hand, targeted recruitment is effective when the job has clearly defined qualifications of characteristics. It involves identifying the target audience and directing vacancy advertising to that audience. In this case, Google would find targeted recruitment as the most appropriate strategy because they will require employees with specific skills.
Advertising and Application Methods
The company can select the methods of advertising and application based on the job vacancies. For Google, positions such as receptionist can be available at the desk while key positions such as HR manager, marketing manager and finance manager can be advertised through local press, IT jobs press, social medial and through the company website (Gumus, 2018).
5.1.5 Sources of Recruitment
Based on existing rule of thumb, there are two main sources through which Google can attract applicants namely: external sources and internal sources. As per Al-Khasawneh et al (2018), external sources entail recruiting employees from outside the organization. This can be achieved by advertising the vacancies on magazines, newspapers, job advertisement websites, trade fairs and recruitment agencies. Whereas advertising on these platforms may be expensive, they have a wide reach potentiality and may help identify suitable candidates relatively much faster.
5.1.6 Selection Method
The main aim of selection is to identify suitable candidates. According to Ashraf (2017), selection in the recruitment process entails evaluating candidates based on their qualities in terms of how those qualities match the job specification. This implies that an organization that employs an effective selection process end up with not only highly qualified employees but also higher employee retention and low turnover.
Different organizations adopt different selection techniques based on staffing needs and resources. Nonetheless, some of the methods involved in selecting employees include phone interviews, preliminary screening, and face-to-face meetings (Gumus, 2018). Other organizations have also used cultural fit selection. That said, most organizations combine these techniques within one interviewing process, whereby they conduct preliminary screening before they conduct telephone interviews, in-person interviews and cultural fit selection (CIPD, 2015).
Google would benefit from cultural fit selection because the company maintains specific organizational cultures that are critical for its operation success. In cultural fit selection, the hiring personnel asks the candidate a few questions that help to determine whether the candidate can fit to the organization’s culture. It is an important recruitment which ensures that the candidate’s values align to the organization’s values. However, the cultural fit technique is a subjective analysis and therefore the recruiting personnel can only rely on their gut feelings rather than an objective criterion.
Employee Training and Development
Concept of Employee Training and Development
Employee training and development is often carried out by organizations to enhance personal knowledge, skills and attitudes that are necessary to adequately complete a task (Armstrong and Landers, 2018). Rodriguez and Walters (2017) remarked that employee training normally benefits the organization by increasing employee skills and knowledge. Alternatively, as Abba (2018) argued, employee training and development are meant to enhance employee’s willingness to perform their tasks within the organization by acquiring the necessary skills. Without training, as per Fletcher et al (2018), it takes longer for employees to familiarise with their job and become productive enough to enhance the organization’s performance.
Training Methods
Chaudry et al (2017) wrote that an effective employee training program helps to develop existing talent while improving employee engagement. Therefore, it is imperative for organizations to select the suitable and most effective training method that can help employees deal with internal and external changes in the business environment. This means that Google must understand the distinction between two major training techniques namely: on the job training and off the job training.
On the job training (OJT)
Rodriguez and Walters (2017) identified OJT as one of the most popular employee training techniques in the technology industry. Ideally, the technique provides an opportunity for employees to acquire skills and knowledge of a job while working. Therefore, On the job training can be applied by Google in different ways including job rotation, mentoring and job instruction technique. In mentoring, as per Abba (2018), a senior employee provides psychosocial support and skills guidance to a junior employee, while in job rotation, an employee changes from one job or project to the other. Job rotation increases adaptability, flexibility and adaptability and motivation as an employee tries different jobs (Armstrong and Landers, 2018).
Off-The Job-Training (Off-JT)

As opposed to OTJ, Off-TJ’s focus on increasing a groups’ learning needs rather than an employee’s learning needs. According to Rodriguez and Walters (2017), it creates an opportunity for employees to acquire different knowledge and skills across different roles. On this note, Fletcher et al (2018) observed that a typically common type of Off-the job training technique is off is simulation, where the employee gets trained using an equipment or machine that resembles what they would use while on the job. This would be suitable for Google employees who use delicate and expensive computer equipment because it would prepare them for handling the machines in real life while minimizing risk of damage. However, simulation might be costly because the company must buy the training equipment.
5.2.4 Evaluating Employee training
Whereas it might seem straightforward to evaluate employee training, it can get challenging depending on which evaluation approach is taken. HR managers are often challenged with the question of whether they should evaluate training based on how much an employee should remember or on how much they can practice the learned knowledge. Nonetheless, this should not be a challenge because Donald Kirkpatrick’s developed four models of training evaluations that can be used by HR managers across different industry fields. In applying the Kirkpatrick’s evaluation model, Google HR managers should identify four main things: the employees ‘reaction i.e. what the employees feel and think about the training; learning i.e. how the employees have retained the skills and knowledge delivered through the training; behaviour i.e. how well the employees can put into practice what they have learned; and results i.e. the overall impact of the training on the organization’s bottom line.
5.2.5 Development
Going by the writings of Abba (2018), employee training only focuses on the lower ranking employees such as supervisors and trainees. On the other hand, development mainly targets administrators. This proposition is supported by Rodriguez and Walters (2017), who noted that employee development programs take longer-term perspectives and may extend into career reviews and planning for individual employees. It is a program that seeks to cause individual progression and growth (Armstrong and Landers, 2018). Consequently, it helps employees to understand their strengths and weaknesses and develop them to enhance customer satisfaction.
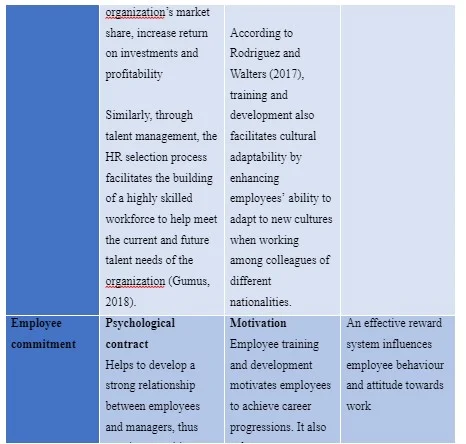
Reward Management
Employee reward systems are among the best and most effective ways managers can send a message to employees that they recognize their efforts (Mendis, 2017). It influences employee behaviour and attitude towards work. That said, organizations can either reward employees based on individual performance and behaviour or take a team approach, whereby a team is rewarded by the reward is divided among the team members based on their efforts and contribution to the task – also known as team-based reward system (Boldureanu et al, 2020).
However, because organizations need to take a holistic approach to its teams and that its goals should be supported by a team culture, key competencies and team roles, the reward system should be modified to fit to the organization’s goals and strategies (Boldureanu et al, 2020). As such, Google would benefit form a reward system that considers what the employee really wants. For instance, Boldureanu et al (2020) wrote that the technology industry suffers from highly talented employees who have a higher bargaining power as a result of their skills and knowledge. This implies that Google need to establish a reward system that recognises and promotes employee motivation, productivity and satisfaction while improving organizational performance. This makes Google’s compensation program, pay-for-performance, the most appropriate reward system for the new venture because it focuses on rewarding good performance while training employees to improve on their weak points (Ngwa et al, 2019). The pay-for-performance program would help Google to promote workforce productivity and boost employee morale.
The impact of HRM practices

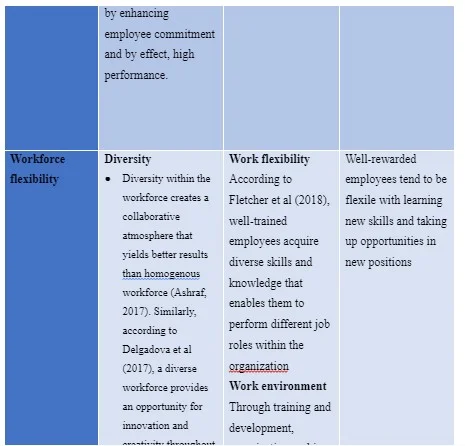
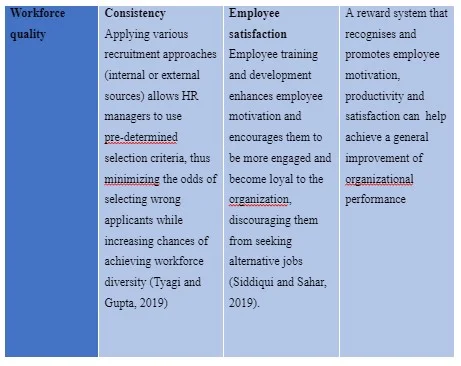
Conclusion and Recommendations
The HRM development indicates the significant role that it plays in organizational performance. Google is one of the leading technological companies globally and is still expanding its operations into sub-Saharan Africa. To successfully expand into Kenya, the company must employ effective HRM strategies. Against this backdrop, this this report has highlighted the important role of recruitment, selection, training and development in dealing with cross-cultural barriers. Meanwhile, the following recommendations are useful in helping Google to effectively achieve its global expansion into Kenya:
The polycentric approach presents as the most appropriate way of employee selecti
The company should choose a recruitment method that suits the jobs specification for each vacant position
The company can effectively evaluate recruits through various techniques including aptitude tests and ability tests
The company needs to apply cross-cultural training as a means of helping new employees to familiarise with the local Kenyan culture so that they can easily deal with local customers
Looking for further insights on Enhancing Workplace Productivity? Click here.
References
Abba, M.T., 2018. Effects of training and development on employee retention in Bauchi State Metropolis Banks. Operational Research, 4(1), pp.24-39.
Aburumman, O., Salleh, A., Omar, K. and Abadi, M., 2020. The impact of human resource management practices and career satisfaction on employee’s turnover intention. Management Science Letters, 10(3), pp.641-652.
Ahmad, I., Danish, R.Q., Ali, S.A., Ali, H.F. and Humayon, A.A., 2019. A comparative study of banking industry based on appraisal system, rewards and employee performance. SEISENSE Journal of Management, 2(1), pp.1-11.
Aktar, A. and Pangil, F., 2018. Mediating role of organizational commitment in the relationship between human resource management practices and employee engagement: does black box stage exist?. International Journal of Sociology and Social Policy.
Akyurt, İ.Z., Kuvvetli, Y., Deveci, M., Garg, H. and Yuzsever, M., 2021. A new mathematical model for determining optimal workforce planning of pilots in an airline company. Complex & Intelligent Systems, pp.1-13.
Al Adresi, A. and Darun, M.R., 2017. Determining relationship between strategic human resource management practices and organizational commitment. International Journal of Engineering Business Management, 9, p.1847979017731669.
Al-Khasawneh, A.L., Malkawi, N.M. and AlGarni, A.A., 2018. Sources of recruitment at foreign commercial banks in Jordan and their impact on the job performance proficiency. Banks & bank systems, (13, Iss. 2), pp.12-26.
Andeyo Okutu, J., 2021. Effect of organizational compensation and reward system on employee performance at Kenya Revenue Authority (Doctoral dissertation, Moi University).
Armstrong, M.B. and Landers, R.N., 2018. Gamification of employee training and development. International Journal of Training and Development, 22(2), pp.162-169.
Ashraf, J., 2017. Examining the public sector recruitment and selection, in relation to job analysis in Pakistan. Cogent Social Sciences, 3(1), p.1309134.
Boamah, F., 2019. New perspectives on corruption reform in the electricity sectors of Kenya and Ghana.
Boldureanu, G., Ciulu, R., Arustei, C.C. and Boldureanu, D., 2020. The Importance Of Organizational Rewards On Attracting And Retaining Students At Work. Transformations in Business & Economics, 19(2B), p.50B.
Central Bank of Kenya 2017. Inflation Rates. https://www.centralbank.go.ke/inflation-rates/ (Accessed on 14/8/2012)
Chaudhry, N.I., Jariko, M.A., Mushtaque, T., Mahesar, H.A. and Ghani, Z., 2017. Impact of working environment and training & development on organization performance through mediating role of employee engagement and job satisfaction. European Journal of Training and Development Studies, 4(2), pp.33-48.
Cherif, F., 2020. The role of human resource management practices and employee job satisfaction in predicting organizational commitment in Saudi Arabian banking sector. International Journal of Sociology and Social Policy.
CIPD (2015) Resourcing and Talent Planning: Annual survey report. London: CIPD
De Freitas, B.C., 2017. Human Resource Reforms in Public Administration: The Importance of the Reward System. HOLISTICA–Journal of Business and Public Administration, 8(2), pp.49-58.
Delgadová, E., Gullerová, M. and Ivanová, E., 2017. Recruitment and selection processes in Slovak enterprises and multinational corporations. International Journal of Organizational Leadership, 6(2), pp.211-220.
Delgadová, E., Gullerová, M. and Ivanová, E., 2017. Recruitment and selection processes in Slovak enterprises and multinational corporations. International Journal of Organizational Leadership, 6(2), pp.211-220.
Edo, S., Okodua, H. and Odebiyi, J., 2019. Internet adoption and financial development in Sub‐Saharan Africa: Evidence from Nigeria and Kenya. African Development Review, 31(1), pp.144-160.
Esaku, S., 2020. Job creation, job destruction and reallocation in Sub-Saharan Africa: Firm-level evidence from Kenyan manufacturing sector. Cogent Economics & Finance, 8(1), p.1782113.
Fletcher, L., Alfes, K. and Robinson, D., 2018. The relationship between perceived training and development and employee retention: the mediating role of work attitudes. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 29(18), pp.2701-2728.
Gachari, J.M. and Korir, J.K., 2020. Effect of Fiscal Policy on Unemployment in Kenya. Journal of Economics and Finance (IOSR-JEF), 11(1), pp.19-31.
Gümüş, A.P.D.Ç., 2018. RESEARCH METHODS USED IN MEASUREMENT OF ADVERTISING EFFECTIVENESS AND COMPARATIVE STRENGTHS. The Online Journal of Communication and Media–April, 4(2).
Hamadamin, H.H. and Atan, T., 2019. The impact of strategic human resource management practices on competitive advantage sustainability: The mediation of human capital development and employee commitment. Sustainability, 11(20), p.5782.
Hansen, J.M. and Xydis, G.A., 2020. Rural electrification in Kenya: a useful case for remote areas in sub-Saharan Africa. Energy Efficiency, 13(2), pp.257-272.
Harzing, A.W. and van Ruysseveldt, J. eds., 2017. International human resource management: A critical text. Sage Publications.
Hong, C.Y., Lu, X. and Pan, J., 2020. Fintech adoption and household risk-taking (No. w28063). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Horwitz, F.M. and Mellahi, K., 2018. Human resource management in emerging markets. In Human Resource Management (pp. 337-357). Routledge.
Kenya
Kianto, A., Sáenz, J. and Aramburu, N., 2017. Knowledge-based human resource management practices, intellectual capital and innovation. Journal of Business Research, 81, pp.11-20.
KPMG 2020. Everything Changed or did it? https://www.hnkpmgciosurvey.com/ (Accessed on 14/8/2012)
Krishnan, S. and Hatekar, N., 2020. Understanding the burgeoning Indian middle class through its expenditure and asset-ownership patterns. In The Middle Class in World Society (pp. 219-241). Routledge India.
Kurkoski, J., 2017. Applied R&D in HR: Google’s People Innovation Lab. In Academic–Practitioner Relationships (pp. 312-323). Routledge.
Martono, S., Khoiruddin, M. and Wulansari, N.A., 2018. Remuneration reward management system as a driven factor of employee performance. International Journal of Business & Society, 19.
Mendis, M.V.S., 2017. The impact of reward system on employee turnover intention: a study on logistics industry of sri lanka. International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, 6(9), pp.67-72.
Meyer, K.E. and Xin, K.R., 2018. Managing talent in emerging economy multinationals: Integrating strategic management and human resource management. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 29(11), pp.1827-1855.
Muncaster P. 2020. Cybersecurity Skills Shortage tops four million. https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/cybersecurity-skills-shortage-tops/ (Accessed on 14/8/2012)
Munshi, A., 2019. Impact of HR Policies on Gender Inclusion in Indian Army: An Empirical Study. South Asian Journal of Human Resources Management, 6(1), pp.9-28.
Ngwa, W.T., Adeleke, B.S., Agbaeze, E.K., Ghasi, N.C. and Imhanrenialena, B.O., 2019. Effect of reward system on employee performance among selected manufacturing firms in the Litoral region of Cameroon. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 18(3), pp.1-16.
Oxford Business Group 2017.The Report. Kenya, 2017. https://oxfordbusinessgroup.com/analysis/top-shelf-growing-middle-class-encouraging-consumer-goods-producers (Accessed on 14/8/2012)
Pham, N.T., Tučková, Z. and Jabbour, C.J.C., 2019. Greening the hospitality industry: How do green human resource management practices influence organizational citizenship behavior in hotels? A mixed-methods study. Tourism Management, 72, pp.386-399.
Rodney, H., Valaskova, K. and Durana, P., 2019. The artificial intelligence recruitment process: How technological advancements have reshaped job application and selection practices. Psychosociological Issues in Human Resource Management, 7(1), pp.42-47.
Rodriguez, J. and Walters, K., 2017. The importance of training and development in employee performance and evaluation. World Wide Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Development, 3(10), pp.206-212.
Saeed, B.B., Afsar, B., Hafeez, S., Khan, I., Tahir, M. and Afridi, M.A., 2019. Promoting employee's proenvironmental behavior through green human resource management practices. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 26(2), pp.424-438.
Shrivastava, S., Nagdev, K. and Rajesh, A., 2018. Redefining HR using people analytics: the case of Google. Human Resource Management International Digest.
Siddiqui, D.A. and Sahar, N., 2019. The impact of training & development and communication on employee engagement–A study of banking sector. Sahar, N. and Siddiqui, DA (2019). The Impact of Training & Development and Communication on Employee Engagement–A Study of Banking Sector. Business Management and Strategy, 10(1), pp.23-40.
Tang, G., Chen, Y., Jiang, Y., Paille, P. and Jia, J., 2018. Green human resource management practices: scale development and validity. Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources, 56(1), pp.31-55.
Thuita, G. W. (2017). An investigation of the effect of tax incentives on the FDIs: a case of EPZs in Athi River Kenya.
Tyagi, P.K. and Gupta, S.K., 2019. Recruitment And Selection Process In Travel Trade Organisations Of Chandigarh: An Evaluation.
Vincent, M.M., Alala, O.B. and Kiongera, M.F., 2017. Effect of Employee Reward System on Job Satisfaction among Non-Core Staff in Catholic Sponsored Secondary Schools in Bungoma Diocese, Kenya. Int. J. of Multidisciplinary and Current research, 5.
Willis, G., Cave, S. and Kunc, M., 2018. Strategic workforce planning in healthcare: A multi-methodology approach. European Journal of Operational Research, 267(1), pp.250-263.
Yusoff, Y.M., Nejati, M., Kee, D.M.H. and Amran, A., 2020. Linking green human resource management practices to environmental performance in hotel industry. Global Business Review, 21(3), pp.663-680.
Zaid, A.A., Jaaron, A.A. and Bon, A.T., 2018. The impact of green human resource management and green supply chain management practices on sustainable performance: An empirical study. Journal of cleaner production, 204, pp.965-979.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



