Computer Networks Security
Networking design
Organization gadgets, for example, switches, firewalls, doors, switches, center points, etc.—make the foundation of the neighborhood (on the corporate scale) and the Web (on the worldwide scale). Making sure about such gadgets is paramount to ensuring the climate and active/approaching interchanges. You likewise must know about security dangers and controls accessible in public exchanged phone organizations (PSTN) framework on the grounds that PSTNs are regularly utilized for PC interchanges. At the point when you construct an organization framework, you take a gander at the lower three layers of the OSI model, albeit numerous different components should be thought of. There are multiple innovations accessible that you can use to assemble an organization, and the test that an organization administrator faces is to pick the right one and the apparatus that accompanies it. It is essential to know the ramifications of choosing a specific innovation, on the grounds that the organization supervisor, at last, chooses what gear is required. While choosing a bit of systems administration hardware, it is critical to know at which layer of the OSI model the gadget capacities (Kusiak, 2020). The usefulness of the gear is significant on the grounds that it needs to adjust to specific principles, it needs to satisfy the hope of the application, and it needs to perform undertakings that are needed by the blueprint - the organization engineering. For students looking for guidance in their engineering dissertation help, understanding these fundamental aspects of network infrastructure is crucial.
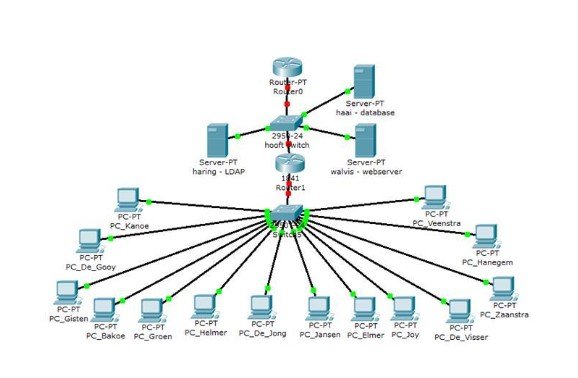
The Open System Interconnected Model (OSI)

IT experts use OSI to show or follow how information is sent or gotten over an organization (Zhu et al., 2017, April). This model separates information transmission over a progression of seven layers, every one of which is answerable for performing explicit errands concerning sending and getting information. The primary idea of OSI is that the cycle of correspondence between two endpoints in an organization can be isolated into seven particular gatherings of related capacities or layers. Each imparting client or program is on a gadget that can give those seven layers of capacity (Zhao et al., 2018, December).
In this engineering, each layer serves the layer above it and, thus, is served by the layer beneath it. Along these lines, in a given message between clients, there will be a progression of information down through the layers in the source PC, across the organization, and afterward up through the layers in the getting PC. Just the application layer, at the highest point of the stack, doesn't offer types of assistance to a more significant level layer (Teixeira & Borsato, 2019). The seven layers of capacity are given by a mix of utilizations, working frameworks, network card gadget drivers, and systems administration equipment that empowers a framework to communicate a sign over an organization Ethernet or fiber optic link or through Wi-Fi or other remote conventions.
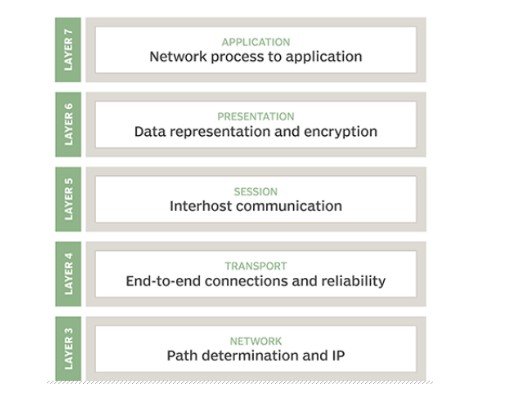
Seven layers of the OSI model
The application layer: The application layer is the OSI layer nearest to the end client, which implies both the OSI application layer, and the client cooperate straightforwardly with the product application. This layer connects with programming applications that actualize a conveying part (Zhao et al., 2018, December). Such application programs fall outside the extent of the OSI model. Application-layer works regularly incorporate distinguishing correspondence accomplices, deciding asset accessibility, and synchronizing correspondence. While recognizing correspondence accomplices, the application layer decides the personality and accessibility of correspondence accomplices for an application with information to communicate (Kusiak, A. (2020). While deciding asset accessibility, the application layer should choose whether adequate organization assets for the mentioned correspondence exist. In synchronizing correspondence, all correspondence between applications requires collaboration that is overseen by the application layer. This layer underpins application and end-client measures (Zhao et al., 2018, December). Correspondence accomplices are recognized, the nature of administration is distinguished, client verification and protection are thought of, and any imperatives on information language structure are recognized. Everything at this layer is application-explicit. The presentation layer: Interprets or organizations information for the application layer dependent on the semantics or language structure that the application acknowledges. This layer is likewise ready to deal with the encryption and decoding that the application layer requires. The session layer: Create, coordinate, and end app-to-app conversations. The authentication and reconnection after an absence involving their services. This layer defines how long a device is waiting for the response of another program. For example, X.225, AppleTalk, and Zone Information Protocol are session layers protocols (ZIP). The transport layer: The transport layer expands on the organization layer to give information transport from a cycle on a source machine to a cycle on an objective machine. It is facilitated by utilizing single or numerous organizations, and furthermore keeps up the nature of administration capacities (Zhao et al., 2018, December). It decides how much information should be sent where and at what rate. This layer expands on the message, which is gotten from the application layer. It guarantees that information units are conveyed mistake-free and in succession. The transport layer causes you to control the dependability of a connection through stream control, mistake control, and division or desegmentation (Kusiak, 2020). The transport layer likewise offers an affirmation of the effective information transmission and sends the following information in the event that no blunders happened. TCP is the most popular illustration of the vehicle layer. The network layer: This layer gives the useful and procedural methods for moving variable length information arrangements (called datagrams) starting with one hub then onto the next associated with a similar network (Zhao et al., 2018, December). It makes an interpretation of sensible organization address into actual machine address. A network is a medium to which numerous hubs can be associated, on which each hub has a location and which licenses hubs associated with it to move messages to different hubs associated with it by only giving the substance of a message and the location of the objective hub and letting the network discover the best approach to convey the message to the objective hub, potentially directing it through moderate hubs (Kusiak, 2020). On the off chance that the message is too huge to possibly be sent starting with one hub then onto the next on the information connect layer between those hubs, the organization may execute message conveyance by parting the message into a few pieces at one hub, sending the sections freely, and reassembling the sections at another hub (Kusiak, 2020). It might, however, need not report conveyance mistakes (Zhao et al., 2018, December). Message transmission on the network layer is not inherently ensured to be reliable, but a protocol for the network layer may provide reliable communication, but it does not have to. The layer for data links: the layer for a protocol in a program that transfers data into and out of a physical network connection. This layer deals with problems created by bit transmission errors. It means the transmitting and receiving devices are not overshadowed by the data flow rate. This layer further allows data to be transferred to Layer 3, where handled and routed, on the network layer. Physical layer: transports data by means of interfaces between electric, mechanical, or procedural. This layer sends computing bits across the network from one device to the other. It defines how physical links to the network are formed and how bits are expressed in predictable signals, either by electric, optical, or radio waves.
Continue your exploration of Laptop World Plc Case with our related content.
Cross-layer functions
Cross-layer capacities, benefits that may influence more than one layer, include: Security administration (media transmission) as characterized by ITU-T X.800 suggestion. Management capacities - capacities that empower the setup, launch, observing, and ending of the interchanges of at least two substances. Multiprotocol Mark Exchanging (MPLS) - works at an OSI-model layer that lies between layer 2 (information connect layer) and layer 3 (network layer). MPLS can be utilized to convey an assortment of traffic, including Ethernet edges and IP bundles. ARP - interprets IPv4 addresses (OSI layer 3) into Ethernet Macintosh addresses (OSI layer 2). Domain name administration – an application layer administration used to look into the IP address of an area name.Section 2
hierarchical design model (Lan)This section describes the access, distribution, and core layers in more detail. Following the introduction of the three-layer model, we explore the hierarchical model in medium-sized businesses. Finally, we delve into the benefits of a hierarchical network design.
Access Layer
The access layer interface allows access to the rest of the network by end devices such as PCs, printers, and IP devices. Routers, switches, bridges, hubs, and cable links should be used in the access layer. The principal aim of the access layer is to provide a way to connect devices to the network and to monitor which devices can interact on the network.
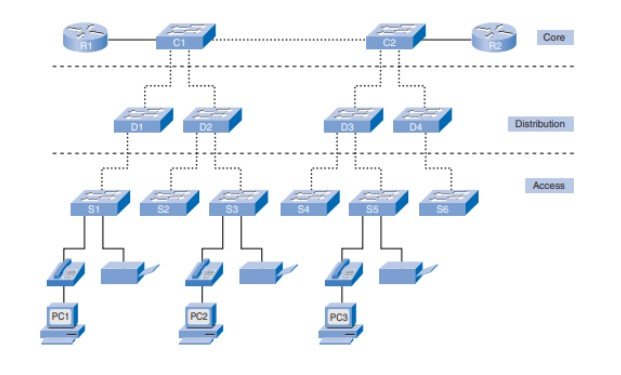
Distribution Layer
Until being passed to the core layer, the distribution stage aggregates the data received from the access layer switch to its end destination. The distribution layer tracks network traffic flow through policies and delineates transmitted domains through routing functions between the virtual LANs (VLANs), which are calculated on the access layer.
Core Layer
The high-speed backbone of the Web is the central layer of hierarchy design. For interconnection between distribution layer modules, the core layer is essential such that the Core is highly accessible and redundant. The central region still has Internet access. The Core adds traffic to all computers in the delivery layer, meaning that vast volumes of data can be forwarded easily.
Vlan configuration
Virtual local networks or VLANs are becoming relevant because the size of the networks exceeds traditional local networks (LANs). Originally, a LAN connected to a server through cables at a physically shared venue, a community of computers and associated devices (hereinafter "local"). A significant number of LANs are now wireless rather than Ethernet networking machines, but most LANs use a mix of both forms of communication (Rao et al., 2019). Over time, organizations, which need solutions to allow networks to expand in scale, functionality, and complexity, have expanded their network demands (Zou et al., 2018).VLANs, by their virtual existence, bypass the physical constraints of the LAN, allow businesses to extend their networks, segment them to improve security measures, and reduce network latency. Essentially, VLAN is a set of machines or network nodes that connect with each other as a single LAN when they currently reside in one or more segments of the LAN (Liu et al., 2017). A sector is theoretically divorced and is usually used by a single department from the rest of the LAN via a bridge, router, or switch. This means that a workstation sends packets, but not one above it enters all workstations on the VLAN.
VLAN Trunking
VTP, available with the products from Cisco Catalyst, offers effective ways to transmit a VLAN through each switch. The possibility of VLAN pruning is also available, which prevents the transmission of traffic through some switches. Users can render certain systems unaffordable or unaffordable for pruning (Ahmad, 2020). One principle in VTP is that larger networks can need the limited operation of switches as VLAN servers. VTP provides different recovery solutions after a crash or for reliable transmission of redundant network traffic (Rahmanzi et al., 2020).
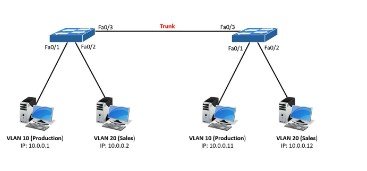 The principle of VLAN trunking usually parallels other forms of IT trunking. Data needs to work less to get into particular areas of network infrastructure by putting services in specific agreements, or supervisors can do less to facilitate these data transfers. The connections between switches form part of this process of efficiency, which makes network traffic more rapid and effective Sakti, M. G. (2020).
The principle of VLAN trunking usually parallels other forms of IT trunking. Data needs to work less to get into particular areas of network infrastructure by putting services in specific agreements, or supervisors can do less to facilitate these data transfers. The connections between switches form part of this process of efficiency, which makes network traffic more rapid and effective Sakti, M. G. (2020).
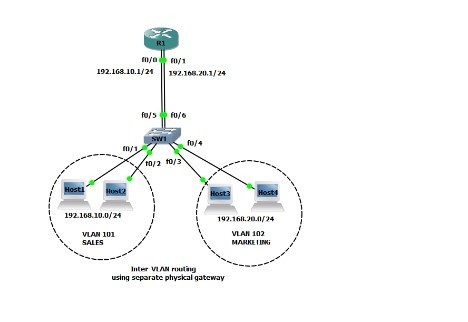
Inter VLAN routing
If there is a firewall or a Layer 3 switch that offers routing facilities, hosts in one VLAN cannot connect with hosts within another VLAN. The method of transmission of network transportation from one VLAN to another VLAN is inter-VLAN routing. There are three options: legacy, stick-on-one, and SVI Layer 3. Legacy used a multi-Ethernet network router (Fata & Kusuma, 2018). In various VLANs, each router interface was linked to a switch socket. The physical interface functionality of a router is quickly drained by needing a VLAN interface. The inter-VLAN routing procedure for the router on a stick only requires one physical Ethernet interface to route traffic between different VLANs on a network (Sutanto, 2018). An 802.1Q trunk setup and a link to a trunk port on a Layer 2 switch are provided for the Cisco IOS router Ethernet adapter. The router interface is set up with sub-interfaces for routable VLANs. Software-based virtual interfaces with a single physical Ethernet port are configured as sub-interfaces. The modern way of using SVIs is to route between the VLAN networks via Layer 3. The SVI is built on the switch for a VLAN. The SVI has the same router interface functions as the VLAN (Mathew & Prabhu, 2017). It offers Layer 3 processing for packets to or from the switch ports of the VLAN.
DHCP Server
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol that enables the use of network services such as DNS, NTPs, and any networking protocol based on UDP or TCP, to simplify the operation of devices in IP networks. The DHCP server offers each computer in a network a dynamically customizable IP address and other network configuration parameters for interacting with other IP networks. DHCP is an upgrade to the older BOOTP protocol. DHCP is a core feature of the DDI solution (DNS-DHCP-IPAM) (Bhagwat et al ., 2017).
DNS server
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol that enables the use of network services such as DNS, NTPs, and any networking protocol based on UDP or TCP, to simplify the operation of devices in IP networks. The DHCP server offers each computer in a network a dynamically customizable IP address and other network configuration parameters for interacting with other IP networks. DHCP is an upgrade to the older BOOTP protocol (Hentunen, 2018). DHCP is a core feature of the DDI solution (DNS-DHCP-IPAM).
Access control
Access control is a fundamental component of data protection that defines who’s permitted to access and use business knowledge and services (Ouaddah et al., 2017). Via authentication and authorization, access management policies ensure sure people are who they think they are and that they have sufficient access to company records. Access management can also be used to block physical access to campuses, constructions, rooms, and data centers (Zhang et al., 2018). Access management distinguishes users by checking different authentication accounts that could be usernames and passwords, PINs, biometric scans, and tokens. Multifactor authentication is often used in several Access Control Scheme, which requires many authentication mechanisms to validate the identity of a user. If a user has been authenticated, access management authorizes the required access level and approves behavior relating to the passwords and IP addresses of that user (Ouaddah et al., 2017). Access control protects sensitive information from getting into the wrong hands, including consumer records, identifying data, and intellectual property. Over and beyond, businesses fear leaking data from both internal and external channels without a robust access management strategy (Cruz et al .,2018). For hybrid multi-cloud cloud organizations, services, software, and data are also stored in premises and the cloud. This is of special significance. Access management can offer more stringent access protection for these settings beyond single sign-on (SSO) (Zhou et al ., 2019).
Privileged Access Management
Privileged Access Management (PAM) refers to programs that handle users' accounts safely and allow them to access essential organizational resources. These may include supervisors, computers, apps and other user categories (Pintér & Zana, 2020). Privileged user accounts are cyber criminals' high priority targets. That's because they have higher permissions in programs that allow them to access sensitive data and/or modify mission-critical software and systems at the administrative level. 44% of abuses of privacy included privileged names in the preceding year. Privileged Access Management is often referred to as privileged account management (PSM). The privileged supervision of sessions is, in reality, part of a healthy scheme of PAM. Everywhere there are privileged accounts (Purba & Soetomo, 2018). There are also different kinds of privileged accounts available online and in the cloud. They vary from other accounts because they have high permission thresholds for large numbers of people, including modifying the settings. In comparison, specific individuals also have keys, at least briefly, to a single privileged account. For starters, a privileged account is the root account on a Linux device. Another confidential form of understanding is the account owner of Amazon Web Services (AWS). Another type is a business username for the Twitter official company profile (Barboi et al., 2019). Privileged accounts face a significant risk. Cyber hackers are keener than any other form of performance to snatch passwords from secret accounts. Therefore, IT agencies face a challenge.
IPsec
Usually, two forms of VPNs can be selected in the world from one organization (Purba & Soetomo, 2018). OpenSSL or IPSEC. While several people switched to OpenSSL mode due to its recent relatively easy implementation, IPSEC based VPNs are still used by businesses since they are not usable in OpenSSL-based VPNs, with additional layers of protection (Bhattacharjya et al., 2020). While SSL-based VPNs have their own protection mode capabilities, IPSEC VPNs take it to the next stage to have rigorous methods to ensure data security that is not possible in SSL-based VPNs. IPSEC is the IP Protection standard. It is a standard IETF set of protocols that provide data authentication, integrity, and secrecy between 2 communications points in the IP network. It specifies the packages which are encrypted, decrypted, and authenticated. It specifies the IPSEC protocols necessary for protected key exchanges and key management (Purba & Soetomo, 2018).
Vpn their security features and firewalls
Firewalls secure the IT networks of an organization by having the opportunity to reduce network traffic by an inspection of each network packet and the required approach. Firewall configurations typically include limiting the ports on one side of the firewall, e.g., Telephone. The traffic form that can travel through a particular port such as HTTP can also be restrained (Jingyao et al., 2019). If the client tries to connect to a limited port or to use a protocol that is inappropriate (a port that is not protected by a security "rule"), the client is automatically removed from the firewall. Firewalls can also be used to limit user access to such servers inside the Intranet business. Assets and vulnerabilities to web-based assets are growing dramatically, and we need to protect our networks from known and unknown risks (Purba & Soetomo, 2018). Firewalls are a standard method to carry out this mission. In recent years, these networking devices have improved a lot. It is not enough for today's firewalls only to block undesirable traffic and enable approved traffic among networks (Zain ul Abideen et al., 2019). More than packet filters are required. We are searching for essential functions of security, such as Denial of Service (DoS) and intrusion detection systems. One of the two types was Current firewalls. Hardware-based firewalls (sometimes known as devices) use a specific hardware platform and a proprietary operating system (Purba & Soetomo, 2018). Standard hardware and a Standard OS, as Windows NT Server 4.0 is used in software-based firewalls (i.e., stripped of everything but the bare essentials in an effort to minimize security exposures). On the hardware and OS platform are identical Network security firewalls, both hardware-based and software-based (Panchakarla, 2019). Particular attention should be paid to firewalls with a VPN part or alternative. VPNs are implemented by several organizations to protect contact between the business network and distant customers. It is easier to handle all roles by integrating a VPN and firewall in one solution.
Critically discuss social, ethical, and legal considerations proposed network design from any cyber threats.
As a prospective information security expert, you must consider the nature of an organization's legal and ethical obligations. The information management specialist plays an essential part in an organization's approach to handling responsibility for privacy and security threats. In current litigation societies around the world, rules are often applied in civil cases, in which defendants who file claims against organizations are granted substantial penalties (Allhoff & Henschke, 2018). These damages are often punitive and often assessed as dissuasive. In addition, information technology experts need to be fully knowing the present law climate to mitigate damages and eliminate risks resulting from cyber and physical attacks, and to reduce damage from litigation proceedings (Allhoff & Henschke, 2018). Security practitioners will help to maintain a company focused on its main priorities by training administrators and staff about their legitimate and ethical roles and effective use of information technology and security (Marsden et al., 2020).

Law and Ethics in Information Security
A dynamic concept with multiple implications and interpretations is ethics. In 2006, Paul and Elder called ethics "a set of concepts and principles that guide us to decide what comportement helps or harms sentient creatures." In this report, we speak about ethics regulating data security in particular (Cheruvalath, 2018). In this article, the legal questions of computer security and Entrepreneurs were discussed quite briefly. The goal of cyber safety is to protect networks from malware threats and to protect data from unintended disclosure. Risks and threats to security can occur due to a lack of proper ethical actions. The need to secure legislation elements in integration, identity records, and transaction history is a critical concern in the use of information technology (IT). Customers should be worried that other users around the globe access knowledge contained in the cloud (Lundgren & Möller, 2019). A Survey of respondents revealed that anonymity remains the main obstacle to incorporate cloud computing (CHAPTER, 2020). The privacy challenges of SMEs include lack of clarity, inadequate user access, and confidence. Any ethical literature focused on the organizational duty to protect sensitive data from security abuses. It also discusses the lack of customer accountability about how firms and their third party suppliers use, collect, interpret, and collect their personal information. When Enterprises outsource their cloud app and data, they cannot be closely managed. Enterprises must also meet their country's legal requirements and secure consumer privacy. e.g., data collected on cloud systems outside of A country is unethical in violation of privacy laws. In cases such as data injury, harassment, unauthorized entry, unavailability of infrastructure fault, lack of user control can be troublesome (Cheruvalath, 2018).
Cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities faced by businesses in the ethical context
Today's cybersecurity challenges include the security of IT systems used in businesses and more extensive digital networks, including essential national infrastructures (Cheruvalath, 2018). Unfortunately, there is a growing amount of cybersecurity threats against companies in preliminary safety studies by actors from a company like Symantec (2016) and Verizon.com (Allhoff & Henschke, 2018), but there is a shortage of knowledge on the functionality and future impacts of the attacks. Therefore, recent cybersecurity reports should be evaluated, and the protection of organizations should be fully understood in an ethical sense. The risks to firms should then be fully understood (Allhoff & Henschke, 2018). Since companies do not have ethical behaviors, they are vulnerable. Any organization may become susceptible to attacks of social engineering, for example, because of a lack of experience. If an individual is not adequately qualified to distinguish a genuine business email from a phishing email, he is endangering an organization. In comparison, the lack of care for career growth and upgrading our skills will contribute to the lack of knowledge of emerging cyber challenges such as DDoS, social engineering, hacktivism, and credential malware. So workers are not attentive, and this may lead to specific financial and legal threats (Allhoff & Henschke, 2018). Organizations invested extensively in infrastructure capital and personal time to build countermeasures to protect secrecy, integrity, and access to knowledge (Allhoff & Henschke, 2018). To obtain a satisfactory security solution, which satisfies the needs and conditions of an enterprise, technological, physical, and procedural monitoring must be combined. These safeguards should be sponsored in order to respond to, research, and develop events of efficient and robust business processes. Reducing risk exposure and learning from accidents really shines a cyber resilience approach. The organizational resilience was seen by (Panchakarla, 2019) as a strategic initiative to minimize vulnerability and thereby reduce the risk that disturbance will occur. The Computer Ethics Center originally introduced the Ten Commandments for Computer Ethics in 1992. A code of ethics that defines their fundamental beliefs, standards, and planned behavior may be in effect for many entities (Panchakarla, 2019). In general, an ethics code will describe the expectations of a company and its workers' goals as the leading IT sector body; for example, the regulation provides its members in the IT sector with a code of ethics which they expect to follow as part of their professional practice. The six points covered in the regulation of ethics of the ACS are the first concern of public welfare, quality of life advancement, integrity, ability, professional growth, and professionalism. Furthermore, data stored in cloud services that circumvent country privacy laws are ethically unethical (Panchakarla, 2019). Training and knowledge are crucial to the development, through complete dedication to security policy, of ethics and security actions of any person in an organization (Allhoff & Henschke, 2018). Any research focuses on teaching and knowledge and how it works to ensure protection. High-level workers need to train alongside each other to meet their targets in safety to make them easier to achieve (Pinté & Zana, 2020). Attacks are strongly induced by unbearable indifference and stupidity, rendering this a crucial area to be regarded by everyone. As a typical small-scale business, workers must fulfill their ability and increase the safety standards to detect and protect them.
Take a deeper dive into Complexities of Cyberspace Regulation with our additional resources.
Conclusion
Finally, ethics is a crucial aspect of ensuring that Enterprises prevent risks and vulnerabilities to cybersecurity. This research is the first to explore the legal problems of cyber protection in small and medium-sized businesses. There are endless and nuanced legal questions. Therefore, ethical data protection and privacy collection must be established. This paper has addressed the Network designs for an organization that identified ethical issues related to cybersecurity in DUX while it is provided different ethical perspectives in cybersecurity has discussed. There are some surveyed studies exposed that training, awareness, and code of practice are practical cybersecurity and privacy protection. Finally, approaches to make ethical policies effective in DUX are suggested.
Reference
Ahmad, I. (2020). Design and Implementation of Network Security using Inter-VLAN-Routing and DHCP. Asian Journal of Applied Science and Technology, 4(3), 37-44.
Allhoff, F., & Henschke, A. (2018). The internet of things: Foundational ethical issues. Internet of Things, 1, 55-66.
Barboi, D., Spivak, B., & Yair, S. A. D. E. (2019). U.S. Patent No. 10,264,026. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
Bhagwat, A. V., Srinivasan, A., & Sangodkar, A. R. (2017). U.S. Patent No. 9,787,633. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
Bhattacharjya, A., Zhong, X., Wang, J., & Li, X. (2020). CoAP—application layer connection-less lightweight protocol for the Internet of Things (IoT) and CoAP-IPSEC Security with DTLS Supporting CoAP. In Digital Twin Technologies and Smart Cities (pp. 151-175). Springer, Cham.
CHAPTER, I. T. (2020). Health Law and Ethics. Health Systems Science E-Book, 220.
Cheruvalath, R. (2018). Internet neutrality: a battle between law and ethics. International Journal for the Semiotics of Law-Revue internationale de Sémiotique juridique, 31(1), 145-153.
Cruz, J. P., Kaji, Y., & Yanai, N. (2018). RBAC-SC: Role-based access control using smart contract. Ieee Access, 6, 12240-12251.
Fata, H. D., & Kusuma, W. A. (2018). Implementasi Routing Inter-VLAN pada Sistem Jaringan Universitas Muhammadiyah Malang. Techno. Com: Jurnal Teknologi Informasi, 17(4), 377-383.
Hentunen, D. (2018). U.S. Patent No. 9,923,961. Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
Jingyao, S., Chandel, S., Yunnan, Y., Jingji, Z., & Zhipeng, Z. (2019, March). Securing a Network: How Effective Using Firewalls and VPNs Are?. In Future of Information and Communication Conference (pp. 1050-1068). Springer, Cham.
Kusiak, A. (2020). Open manufacturing: a design-for-resilience approach. International Journal of Production Research, 1-12.
Liu, J., Tan, C. S. Y., Yu, Z., Lan, Y., Abell, C., & Scherman, O. A. (2017). Biomimetic supramolecular polymer networks exhibiting both toughness and self‐recovery. Advanced Materials, 29(10), 1604951.
Lundgren, B., & Möller, N. (2019). Defining information security. Science and engineering ethics, 25(2), 419-441.
Marsden, C., Meyer, T., & Brown, I. (2020). Platform values and democratic elections: How can the law regulate digital disinformation?. Computer Law & Security Review, 36, 105373.
Mathew, A., & Prabhu, B. (2017). A Study on Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) and Inter-VLAN Routing. International Journal of Current Engineering and Scientific Research (IJCESR), 4(10).
Ouaddah, A., Abou Elkalam, A., & Ouahman, A. A. (2017). Towards a novel privacy-preserving access control model based on blockchain technology in IoT. In Europe and MENA cooperation advances in information and communication technologies (pp. 523-533). Springer, Cham.
Ouaddah, A., Mousannif, H., Abou Elkalam, A., & Ouahman, A. A. (2017). Access control in the Internet of Things: Big challenges and new opportunities. Computer Networks, 112, 237-262.
Panchakarla, B. P. (2019). Design and Implementation of Firewall to Inspect Traffic in Encrypted VPN Tunnels (Doctoral dissertation, University of Missouri--Kansas City).
Pintér, A., & Zana, L. (2020). U.S. Patent Application No. 16/568,656.
Purba, A., & Soetomo, M. (2018). Assessing Privileged Access Management (PAM) using ISO 27001: 2013 Control. ACMIT Proceedings, 5(1), 65-76.
Rahmanzi, M. Z., Fitri, I., & Aningsih, A. (2020). Load Balancing Performance in Etherchannel Technology Using the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) Method. Jurnal Mantik, 3(4, Feb), 540-547.
Rao, J., Yang, W., Zhang, Y., Ture, F., & Lin, J. (2019, July). Multi-perspective relevance matching with hierarchical convnets for social media search. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 33, pp. 232-240).
Sakti, M. G. (2020). Analisis Pengaruh Penggunaan VTP Pruning Pada Jaringan VLAN. Journal of Telecommunication, Electronics, and Control Engineering (JTECE), 2(1), 44-53.
Sutanto, P. H. (2018). Perancangan Virtual Local Area Network Berbasis VTP Dan Inter-Vlan Routing. Jurnal Teknik Komputer, 4(2), 125-134.
Teixeira, K. C., & Borsato, M. (2019). Development of a model for the dynamic formation of supplier networks. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 15, 161-173.
Zain ul Abideen, M., Saleem, S., & Ejaz, M. (2019). VPN Traffic Detection in SSL-Protected Channel. Security and Communication Networks, 2019.
Zhang, Y., Kasahara, S., Shen, Y., Jiang, X., & Wan, J. (2018). Smart contract-based access control for the internet of things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(2), 1594-1605.
Zhao, J., Bai, J., Zhang, Q., Yang, F., Li, Z., Zhang, X., ... & Bai, R. (2018, December). The Discussion about Mechanism of Data Transmission in the OSI Model. In 2018 International Conference on Transportation & Logistics, Information & Communication, Smart City (TLICSC 2018). Atlantis Press.
Zhou, Z., Guo, Y., He, Y., Zhao, X., & Bazzi, W. M. (2019). Access control and resource allocation for M2M communications in industrial automation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 15(5), 3093-3103.
Zhu, Y., Wang, J., & Wu, K. (2017, April). Open system interconnection for energy: A reference model of energy internet. In 2017 IEEE International Conference on Energy Internet (ICEI) (pp. 314-319). IEEE.
Zou, J., Lan, J., & Shao, Y. (2018). A hierarchical sparsity unmixing method to address endmember variability in hyperspectral image. Remote Sensing, 10(5), 738.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



