Exploring Organizational Culture and Leadership in Sweden
Executive Summary
The paper focuses on discussing the organisation culture and business management in Sweden. The leadership qualities are of two types and are beneficial for developing suitable leadership styles that are being useful to understand the leadership technique in the organisations. Human capital management theory is also evaluated here in this part also where leadership plays a crucial role in managing human capital of the organisations. The countries Germany and Switzerland are being seen for human capital management to be applied in this project to understand the leadership style and business culture in the countries. Future team leader impacts are also seen in this paper, making it a comprehensive study for business dissertation help. Finally, the leadership challenges that persist due to the 4th industrial revolution will be discussed for identifying effective leadership practice. The impact of those challenges that can be seen over in this part is also discussed.
1. Introduction
Leadership is important practice of the organisations in the recent era of globalisation where the leaders try to develop suitable organisational vision and create good strategic planning for leading the team members towards achieving future success (Luff, 2017). The study is effective to analyse the leadership style of the country Sweden through two different leadership theoretical approaches which are contingent and participatory theory. The leadership theories and practice are evaluated to understand the Swedish culture to lead the team members towards achieving future success as well as identify the leadership practice for developing multi culture and multi generational team in the organisational workplace. In addition to this, the human capital theory and management will also be evaluated in the countries Germany and Switzerland in order to review the leadership style and approaches in both the countries. The comparison will be helpful to understand the strategic planning of human capital management in both the countries, Germany and Switzerland. Moreover, the study also provides a scope to analyse the existing challenges related to leadership and management after the fourth industrial revolution to acknowledge the problems of the organisations in managing their operations and human capital. The study also focuses on analysing the impacts of the emerging digital, empathy and gig economies on the increase of the virtual and remote workforce.

2. Leadership styles in Sweden
These organisational cultures have an adverse impact on the leadership styles that is to be followed in Sweden. The leaders are highly required in the company. A leadership style is highly required in the organisation so that leaders can work in an ethical and proper manner in the organisation (Levi and Mezrar, 2019).
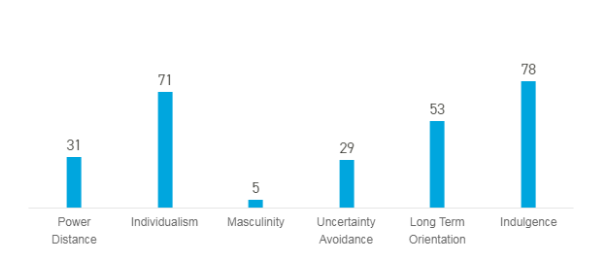
Hofstede culture is the model through which it is possible to analyse the culture at Sweden and then review the leadership style and approaches to maintain human capital in the organisations in the country. As per the figure above, power distance is 31 which means it has low score on power distance and it further indicates that equal rights, superior accessibility, coaching leaders, convenience hierarchy at the organisational workplace and being independent where the leadership is direct and participative at the workplace (Guo, 2017). The individualism score is 71, Sweden is individualist society where the people prefer to take care and think about themselves and close family members. The scope of masculinity is low which indicates that there is equal opportunities provides to both male and female members at the organisation and it is feminine society which further helps to balance work-life activities. Uncertainty avoidance has high score with 29 which further indicates that, that there is low preferences towards avoiding uncertainty and the individual prefer to work hard and innovatively to create flexible workplace for achieving higher in a creative way. Long term orientation is low, which shows the people on Sweden believe in short term success. Indulgence also scores high where people enjoy life and believe in spending leisure time including positive attitude and optimism in the society (Hofstede insights, 2020).
3. Discussing the leadership approaches
Participative theory:
The participative leadership style is characterised by communicating with others, facilitating the conversations, sharing the information and knowledge openly as well as encouraging the people to share their ideas, synthesising the available information and taking the best possible decision (Combes et al., 2017). Here, the leaders participates in the organisation and cooperate with others for developing better decision making behaviour and thus it is also beneficial of the leaders at Sweden to develop strong organisational workplace and enhance creativity and innovation to develop strong decision for achieving future success. The partnership working practice at the workplace further helps in reducing the task burden and increasing the quality of the task initiated. Deciding together in a group through communication and internal collaboration also helps to complete the task efficiently (Cuadros, 2020). Additionally, the partnership working practice at the workplace further helps in reducing the task burden and increasing the quality of the task initiated through team working activities and participative leadership style, where the leaders are efficient to direct and support all the followers in the organisational workplace. These further enhance creativity and innovation of the firms to achieve future success by strong communication and cooperation wi9th the leaders (Toppinen et al., 2019).
Contingency theory of leadership:
The leaders under the contingency leadership style aims at motivating the employees and improving the other factors such as nature of the tasks, clear roles and responsibilities as well as leader’s personality so that it would be possible to lead the team members towards achieving future success. It is related to relationship development where the leaders try to develop strong bonding and corporate relationship with the followers for better performance and accomplishing the organisational tasks (Lee et al., 2019). The leadership style and situational behaviour at the workplace are effective or the leaders to create bonding and improve trust and loyalty among the staff members. The Swedish culture is also effective where it is possible for the leader to develop strong bonding and achieve the future sustainable goals. The leaders try to create proper decision in the organisational workplace with proper cooperation and communication with the employees and it further helps to achieve future organisational success (Toppinen et al., 2019). The leadership style formed by this contingency theory is ethical and helpful one for the business in Sweden in future.
These two theories can easily help in influencing the leader in Sweden which is available in the organisation. Both the contingency theory and participative theory are highly necessary for the organisation to follow a particular leadership style. The future team leader will get a time for the specific task to perform within specified time (Ricard, 2020). Thus key decisions and strategy is generally made so that a proper leadership quality can be shown through those cases (Tuna, 2018).
4. Human capital management in Germany and Switzerland
Human capital management is essential for the organisational leaders to achieve future success and lead the team members efficiently. The human capital management is developed through recruitment and selection, compensation and structured salary, collaboration and communication, health and safety and providing suitable organisational culture. The organisations in the recent era of globalisation try to manage human capital to manage diverse workforce and retain them, for long run. As per the comparison, Germany is one of the renowned workplace where the employees try to move or migrate from other international countries. Germany has provided several job opportunities to the staff members and the training and development programs of Germany are also effective to attract the staff members towards achieving their career objectives and fulfilling the organisational goals (Trading Economics, 2020a). On the other hand, Switzerland is also famous lace in terms of recruitment and selection where the employment rate is good. As per the figure below, the employment arte of German is increasing in the last years. However, in the recent pandemic era of COVID 19, the employment rate decreases due to job loss and closure of the organisations. This is the major reason of low employment rate in Germany in the recent era.

The employment arte of Switzerland is also good where the leaders at the country are able to manage human capital and create values for them. However, over the years, the employment rate of the country is decreasing due to economic slowdown and lack of growth and developmental opportunities in the country (Trading Economics, 2020b).
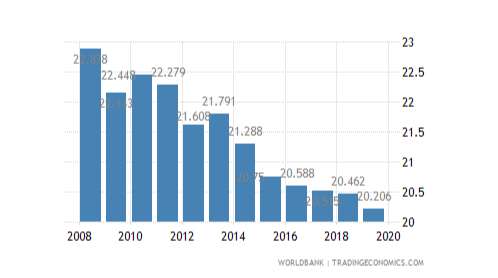
The figure below reveals that in Germany, the increment structure of the employees is good which indicates suitable management of human capital in the country, where there is 12% increments rate in 18 months. The leader and management team of the business firms are efficient to handle the employees and create values for them. The organisational leaders are also able to manage health and safety, fulfil the needs and preferences of the staff and develop collaborative working practice through which they try to manage their human capital to achieve future success (Trading Economics, 2020a).

On the other hand, the salary increment of the country is also effective for the employees where the employees can structure salary and increments within 10 months. Additionally, the practice of diversity management, new interviewing tools, and experience and feedback management are mandatory for handling the human capital and improve the participation of the employees in the country (Trading Economics, 2020b).

Both the countries are effective to handle the human capital and boost the performance of the employees in long run. In the recent era of globalisation, Germany and Switzerland try to improve their performance in the global economy and there are efficient to handle the industrial revolution, adopt latest technological infrastructure and enhance their creativity and innovation for maximising future objectives. The organisations in both the countries are also growing at a rapid rate and the countries are successful to manage the human capital in the organisations through effective human resource management strategies, enhancing cooperation and communication, engaging the staff, effective empowerment and fulfilling the needs and preferences of the employees (Fortune Business Insights, 2019). As per the comparison, Germany is more efficient were the leaders are successful to manage human capital and the employment rate in Germany is growing at a rapid rate for efficient strategy to fulfil the employee’s values by providing them monetary incentives, rewards and bonus, managing health and safety, enhancing strong bonding, recognition and achievement in the workplace as well as flexible to work.
5. Challenges of future leader in fourth industrial revolution
In the recent era of fourth industrial revolution, there are major challenges which may have crucial impacts on the leadership style and managerial practice. The leaders may suffer from managing the multi culture and multi generation team in the workplace. After the fourth industrial revolution, there is agile technology as well as collaborative force of new technologies is generally seen such as Artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT). Hence, the leader will face the challenges of managing the experienced and skilled workforce in the organisational workplace. It becomes difficult for the leaders to manage multi cultural team with diverse workforce irrespective of their cultural differences, language gap as well as differences in skill set and experience. Hence, it is major challenge for the future leaders to maintain good team with skilled workforce in such an era of digitalisation with agile technology. The leaders also face the challenges related to anticipating and creating change, staying agile, maintaining inter generational collaboration as well as promoting diversity and inclusion (Cuadros et al., 2018). These are the major challenges which may deteriorate the working efficiency and performance of the workforce. The leaders also will face issues related to enhancing organisational creativity and technological innovation, managing training and technical programs or the employees as well as staying focused and motivated with technical practice due to industrial revolution. The changes such as agile method, robotics and Artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) is increasing at a rapid rate and this further raise the issue for the leaders to manage their workforce. The whole infrastructure of working in the recent years is changing over the period of time due to fourth industrial revolution and thus the leaders also will face challenges in future related to the lack of infrastructure, developing firms capabilities, incorporating latest technology in the workplace as well as managing environmental sustainability, which is also another major factor in the recent years to manage the organisational activities (Ricard et al., 2017). There are also several risk factors which raise issues for the future leaders which are lack of capital management, poor investment as well as poor organisational infrastructure and the skilled employees who can handle the latest working practice and innovative IT technology to deal with the customers. These are the major issues, for which the leaders will face difficulties to maximise the organisational performance and lead the employees creatively.

6. Impacts of the emerging digital, empathy and gig economies
Digitalisation of the organisational activities is one of the major changes in the recent of globalisation where the enhancement of IT infrastructure as well as the leadership style and innovation in managing the organisational operations will lead the team members towards achieving future success more innovatively. There are several impacts of digital transformation of the industry where the firms are able to improve their operational excellence and conduct their operation in a fast pace (Yusuf, Walters and Sailin, 2020). This is also effective for the organisations to fulfil their strategic aim within effective time and in a creative way. The digital economic transformation also encourages the organisational leader to be creative and enhance technological innovation for better management practice and achieve future success with high technological innovation including AI and IoT (www.unwe, 2020). The organisations can encourage the employees for better managerial practice and improving creativity to work in a different way as well as helps the entrepreneurs to achieve future success. The gig economies are mainly characterised by province of short term and freelancing types jobs in the economy as opposed to permanent jobs. In the recent era of globalisation and digitalisation of the organisation, there is huge numbers of firms across the globe which contacts freelancers for working with them to achieve the organisational aims (Dubey et al., 2017). The numbers of freelancing in the market across the globe is also increasing at a rapid rate which enhances flexible working culture, freedom to work and improving efficiency of the employees. Thus, there are crucial impacts of digital transformation of the business and gig economies on the employment, leadership style and organisational growth positively (Gunasekaran et al., 2017).
7. Conclusion
The business structure and culture depends on the countries culture, leadership style and organisational behaviour. Through the above analysis, Sweden is characterised by equal rights, superior accessibility, coaching leaders, convenience, where the leaders try to develop strong team bonding among the employees and develop suitable working atmosphere for working with others to achieve future organisational objectives. The German culture and the culture of Switzerland are also different from each other and both the countries are effective to manage their workforce. The employment rate in both the countries is increasing over the period of time and there are suitable human capital management with higher incentives and strong management. Hence, both the countries are successful to strengthen their employment position and hire the experienced staff members for working efficiently in near future. On the other hand, the industrial revolution further influence the organisations for better performance and in this regard innovation, technological advancement, firm’s creativity as well as the managerial practice are contributing factors to run the organisations efficiently and achieve the future sustainable goals.
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to Exploring Management Styles in Group Presentations Using Gibbs' Model.
Reference List
Combes, B., Nassiry, D., Fitzgerald, L. and Moussa, T., 2017. Emerging and exponential technologies: New opportunities for low-carbon development. [3]
Cuadros, M.D.P.J., Cáceres Reche, M.P. and Lucena, F.J.H., 2018. Analysis of leadership styles developed by teachers and administrators in technical-technological programs: the case of the Cooperative University of Colombia. International Journal of Leadership in Education, 21(1), pp.1-16.
Dubey, R., Gunasekaran, A., Helo, P., Papadopoulos, T., Childe, S.J. and Sahay, B.S., 2017. Explaining the impact of reconfigurable manufacturing systems on environmental performance: The role of top management and organizational culture. Journal of cleaner production, 141, pp.56-66.
Gunasekaran, A., Childe, S.J., Papadopoulos, T., Hazen, B., Giannakis, M. and Roubaud, D., 2017. Examining the effect of external pressures and organizational culture on shaping performance measurement systems (PMS) for sustainability benchmarking: Some empirical findings. International Journal of Production Economics, 193, pp.63-76.
Guo, Y., 2017. Intercultural Business Communication-A Comparison of China and Sweden.
Lee, K., Wong, C.Y., Intarakumnerd, P. and Limapornvanich, C., 2019. Is the Fourth Industrial Revolution a window of opportunity for upgrading or reinforcing the middle-income trap? Asian model of development in Southeast Asia. Journal of Economic Policy Reform, pp.1-18. [3]
Levi, D. and Mezrar, B., 2019. Factors motivating immigrants to establish a business-The case of Sweden.
Luff, P., 2017. The 4th Industrial Revolution and SMEs in Malaysia and Japan: Some Economic, Social and Ethical Considerations. Reitaku International Journal of Economic Studies, 25, pp.25-48. [3]
Ricard, L.M., Klijn, E.H., Lewis, J.M. and Ysa, T., 2017. Assessing public leadership styles for innovation: A comparison of Copenhagen, Rotterdam and Barcelona. Public Management Review, 19(2), pp.134-156.
Toppinen, A., Sauru, M., Pätäri, S., Lähtinen, K. and Tuppura, A., 2019. Internal and external factors of competitiveness shaping the future of wooden multistory construction in Finland and Sweden. Construction Management and Economics, 37(4), pp.201-216.
Tuna, N., 2018. Culture Matters: Analysis of Culture in Sweden and Finland and Its Influence on Innovation and Job Performance.
Yusuf, B., Walters, L.M. and Sailin, S.N., 2020. Restructuring Educational Institutions for Growth in the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR): A Systematic Review. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 15(03), pp.93-109.[3]
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



