Leadership theories and styles
- 10 Pages
- Published On: 6-12-2023
First section
Styles of North American (Western) leadership
Western leadership style is more subordinate centred approach where there is high internal communication and cooperation to perform better. The leaders communicate with the subordinates and empower them in the organisational decision making behaviour. There are also incentives and rewards for creating values for the subordinates and the leaders try to encourage them to perform better in long run (Larsson et al., 2017). Continuous motivation and guidance also help the subordinates to increase their creativity for better performance and productivity. For those studying HRM dissertation help, understanding these dynamics is crucial for effective organisational management.

LMX theory
LMX or Leader-Member Exchange Theory is effective for managing leadership style and develop suitable corporate culture ion the organisation. The goal of the theory is that, there is two-way relationship between leaders and followers. The leaders try to influence the behaviour of the followers in the organisation with incentives and working culture (Chow, Salleh and Ismail, 2017). The leaders also try to fulfil the commitment towards their followers as well as satisfy them by fulfilling their needs and personal requirements. LMX theory is hereby effective to develop leadership style with harmony and freedom to work in the workplace as well as maximise the performance of the followers (Lee et al., 2019).
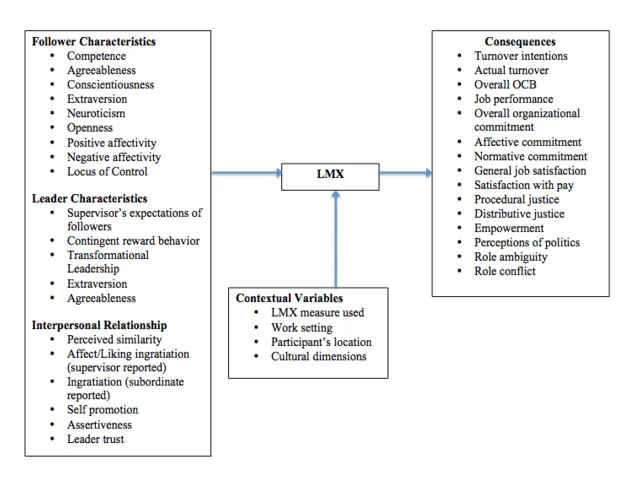
Ohio state and Michigan studies on leadership
Ohio state and Michigan studies on leadership are effective to develop suitable leadership and management strategy where the leaders try to lead the followers towards achieving success. Ohio State of university reveals that there are two characteristics of leaders and each is independent to another (Deshwal and Ashraf Ali, 2020). Two leaders behaviour are initiating structure and considerations. Under initiating structure, the leader toes to create good corporate structure for leading the employees and on the other hand, consideration refers to showing concern for the feelings and needs of the followers, where the leaders focus on fulfilling the requirements of the followers for motivating them in long run (Deshwal and Ashraf Ali, 2020).
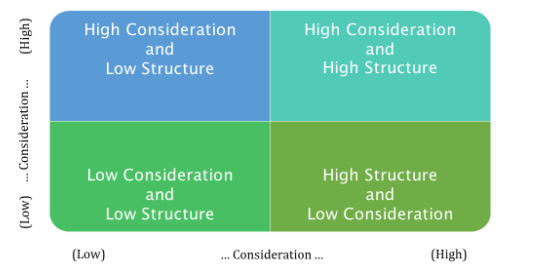

On the other hand, Michigan studies of leadership refer to the high and low leadership control where the activities are close supervision, job centred, general, employee oriented and laissez-faire continuum (Harrison, 2017). If the leaders tend to close supervision and job centred approach, there is increased leader control and on the other hand, if there is laissez-faire concept in the organisation as well as employee empowerment, there would be increasing employee involvement for encouraging their creativity to perform better.
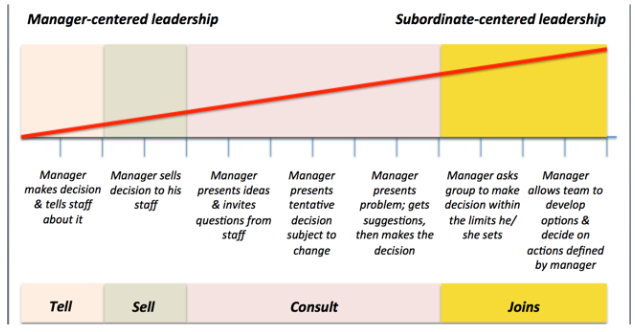
Work of Tannenbaum and Schmidt (1958) on leadership
As per the study of Tannenbaum and Schmidt (1958) on leadership, if the leaders move ways from autocratic leadership style, there would be increase in employee participation and involvement in decision making practice. There are two ways of leadership which are manager centred and subordinates centred (Harrison, 2017). If the leaders try to focus on subordinates and develop subordinates centred approach in the practice, it would be possible to empower the followers and make collaborative decision for the betterment of the activities and performance of the subordinates in long run.
Second section
Factors affecting leadership style
The major factors affecting the leadership trait are such as geographic locations, and external forces in the market such as communication style and perception of the individuals living in the society. Apart from that, the languages and demographic factors including culture and religion also influence the leadership style. Traditional values also recreate leadership style to manage the subordinates and develop suitable practice to lead them efficiently (Talalova, 2017).
Lewis Model of cross-cultural communication
Lewis Model of cross-cultural communication is effective to analyse the cultural impacts on leadership. As per the diagram below, there are many international countries and it is possible to analyse their leadership style and organisational practice to manage performance.

For example, Arab countries are between multi active and reactive. It is close towards multi active which indicates that the leaders are emotional and they mostly talk about time to manage the working activities in the organisations. Additionally, the culture is towards people oriented and the leaders try to manage the subordinates by empowering them and improving involvement of the followers in the decision making behaviour (Pavlović, 2019). Reactive culture also indicates people oriented, managing patient, using connections and there is link between social and professional life where the leaders show emotion and be polite to respect the followers and lead them towards achieving future success. On the other hand, the western culture is different from this, where UK and USA are close to linear active style of leadership. Under this approach, the leaders are job oriented, confronts with logic and sticking to the fact and truth to maximise performance and productivity of the subordinates (Talalova, 2017). There is separate social and professional life among the leaders and subordinates and there is lack of people engagement in the organisational decision making behaviour, where the leaders focus on job related activities to achieve future success.

Reference List
Chow, T.W., Salleh, L.M. and Ismail, I.A., 2017. Lessons from the major leadership theories in comparison to the competency theory for leadership practice. Journal of Business and Social Review in Emerging Economies, 3(2), pp.147-156.
Deshwal, V. and Ashraf Ali, M., 2020. A systematic review of various leadership theories. Shanlax International Journal of Commerce, 8, pp.38-43.
Harrison, C., 2017. Leadership theory and research: A critical approach to new and existing paradigms. Berlin: Springer.
Larsson, G., Sandahl, C., Söderhjelm, T., Sjövold, E. and Zander, A., 2017. Leadership behavior changes following a theory‐based leadership development intervention: A longitudinal study of subordinates’ and leaders’ evaluations. Scandinavian journal of psychology, 58(1), pp.62-68.
Lee, A., Thomas, G., Martin, R. and Guillaume, Y., 2019. Leader-member exchange (LMX) ambivalence and task performance: The cross-domain buffering role of social support. Journal of Management, 45(5), pp.1927-1957.
Pavlović, V., 2019. Massive corpora and models of cross-cultural communication styles in Cognitive Linguitics: The case of the N1 V (for) N2 to-infinitive construction in English. Review of Cognitive Linguistics. Published under the auspices of the Spanish Cognitive Linguistics Association, 17(1), pp.29-52.
Talalova, L.N., 2017. What for Do We Learn the Foreign Languages, or Why Do We Always Have Problems within Cross-Cultural Communication?. In Youth of XXI Century in a Scientific, Cultural and Educational Environment: New Values, Challenges, Perspectives (pp. 451-454).
Looking for further insights on Leadership Theories and Organisational Performance? Click here.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



