Navigating Cross Cultural Leadership
Introduction:
Cross cultural leadership is one of the most important leadership approaches that is associated with understanding how leaders operate in today’s globalised and multicultural businesses context. Cross cultural leadership discusses, how the organisational leaders can adapt themselves to any cultural environment and can work effectively with partners and clients in terms of meeting common organisational goals. This report is going to highlight the culture in Spain and how it impacts on activities, performances and behaviour of future leaders. The business report has chosen USA and Germany in terms of discussing Human Capital Management (HCM) process in these counties with discussing how future leaders operate in the competitive market in these two countries, In addition to this t report will also focus on highlighting challenges that the future business leaders are going to face due to the digital as well as gig economy and the 4IR report with increasing number of remote and virtual workforces in these countries. Finally, the report will make a suitable conclusion in which it will depict the main aspects of the overall discussion that will assist learner to understand the inferences of entire discussion. If you need further assistance with your business dissertation help, feel free to reach out. .
Discussing culture of Spain and two relevant leadership approaches and their impact on the behaviour of the future team leader: Culture of Spain and its impact on leadership approaches: Culture in Spain:
According to Bird and Mendenhall (2016), culture plays important roles on business, economy and leadership approaches of a country. Spanish culture is characterised by its liberal and robust social system, strong education, strong economy, high cost of living, liberal social values, strong infrastructure for businesses operating here, flexibility of citizen to welcome any innovation as well as positive changes in market and adaptability of Spanish people to any culture and trend. While it comes to discuss the business culture and cross-cultural leadership in any country, it is important to discuss the overall economic condition, trade and business environment in this country which impact on leadership and management system operating in this country. Spain is highly agrarian country. Although during the middle of 20th century the nation was primarily rural, with robust business approaches and highly adaptability in any business culture, the country has successfully developed many industries over here which lead to severe urbanisation. As mentioned by Bonsu and Twum-Danso (2018), industrial activities and business adaptability of any nation are associated with its economic, social and cultural development. Spain performs wide ranges of commercial activities such as export of asparagus, olive oil, conserved fish, wine, oranges, almond, saffron and canned artichokes. Highly adaptive and robust social perception and modern viewpoint of its citizens, assist business leaders In Spain to switch to highly modern technologies in using effective leadership approaches that not only assist this country to get high success in domestic as well as international business market but also inspire the new generation to choose their future aim as to be a strong as well as successful business leader. As stated by Branco (2018), positive and highly robust culture in any country is associated with developing strong business context which not only improves the economic condition of country but also improves the overall social, demographic and political infrastructure. The government of Spain focusses on providing more opportunities to international investors and marketers in terms of making industrial development in this country which not only improves the overall employment facilities and economic growth in this country, but also assists organisations to hold the cross-cultural integration in the leadership approaches, In this context, the business leaders of Spanish organisations can efficiently manage teams that consist of staffs of different culture and educational background. According to Carrier (2016.), culture impacts on overall perception, intelligence, assumption and decision of people. In Spain the positive and adaptive culture assist the organisational leaders to adapt in any team and group which allows them to bring about new thoughts, ideas and innovation in the management and leadership approaches in organisation that can enhance the competitive advantages of the organisation in international business landscape (Smith and Peterson, 2017). On the other hand, high economic growth, strong education system and increasing industrial growth in Spain improves the overall economic condition of citizen with high per-capita income and high cost of living; Therefore, in Spain people invest more in buying best goods and services without considering the prices which compel businesses operating here to use proper leadership approaches and strategies in terms of coming up with new and innovative products and services that can meet customer’s demand. .

Two different leadership approaches:
Due to ever-increasing number of potential customers and increasing rivalries in domestic market in Spain, organisations operating in this country focus on making consistent research on leadership approaches in terms of taking the best leadership styles that can assist organisations operating there to cope up with increasing competition in home market as well as in international market (Schedlitzki et al. 2017). In this context, two important leadership approaches are usually used by the organisational leaders in Spain based on its multi-cultural business context are, Democratic Leadership and Transformational leadership approach. As Spain has successfully maintained strong trade relation with different developing countries across the world such as USA, UK, Germany, Japan, France and many other countries, businesses operating in this nation focus on maintaining democratic and transformation leadership approaches to maintain sustainability of this trade relation and healthy economy in this country. As mentioned by Stephan and Pathak (2016.), while selecting leadership, approaches, organisational leaders need to focus on culture, economy and overall social perception and cultural trend in this country. In this context, due to highly adaptive national culture, modern business operation and highly competitive position of Spain as a business entity in international business market, businesses operating here need to focus on such leadership approaches that can assist them to cope up with changing market trend and ever-increasing customer demand in international market. Democratic and transformational leadership is relevant to the current business culture and economic trend in Spain that assist organisational leaders to develop such leadership styles that assist teams to involve actively in any official and business-related matter.
In terms of maintaining economic growth and healthy trade relation with international business leaders, the organisational leaders in Spain are highly adaptive and robust to any culture and trend, which develop cross-cultural leadership styles in organisation. Different theories in this context can be used by organisational leaders to make better implementation of two above-mentioned leadership approaches (Tsai et al. 2019). By using the concept of Implicit Leadership Theory (ILT), it can be stated that team members in an organisation have the underlying assumptions, stereotypes, schemas and beliefs that impact on how an organisational leader visualised in front of them. Based on this concept, it can be stated that, while using democratic and transformational leadership approaches into practices, Organisational leaders would analyse the expectation, stereotype and schemas of team members which will assist organisational leaders to understand exactly what personal and professional characteristics are expected from them by their team members. In Spain, organisational leaders operate in multicultural leadership context, in which they focus on involving team members, managers as well as higher officials, into any discussion regarding business related matter in terms of taking effective as well as highly relevant business strategies. In cross cultural leadership context of Spain, it is difficult for organisational leaders to hold definite personality and professional characters as well as skills in them while implementing the transformation leadership styles into practice, as in this leadership styles, the organisational leaders need to make consistent changes in strategies and decision-making process. In this context Tzu and Adams (2016), mentioned in their article that, the Implicit Leadership Theory (ILT):, although can be used in the democratic leadership approaches, it is not possible to be used in the transformational leadership approaches, as in this type of leadership process, the characteristics and behaviour of leaders changes while adapting into different business culture which makes contradiction with the stereotype and assumptions of team member about their ideas leader. In this context, the future leaders can use another important Cross-Cultural theory such as Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions. By using this theory, organisational leaders can adapt to the different business culture in Spain which not only assist the business to grab high level of competitive advantages but also assist organisational leaders to shape their professional leadership skills to achieve organisational goal to get a strong position in the international business landscape. While dealing with the multicultural leadership context, the organisational leaders can use the theory in democratic and transformational leadership approaches in assisting their organisation to grab high level of competitive advantages in the international market. As argued by Arnulf and Larsen (2019), although the Hofstede’s Cultural Diosmetin theory can be successfully used in the current democratic and transformational leadership context, it can also create some conflict, mis-communicational and disagreement in teams that have members from different cultural background background. Another important theory that can be used in his context GLOBE - The Global Leadership and Organizational Behaviour theory. Based on this theory, the organisational leaders in Spain, need to consider the common beliefs and values of definite culture in the team which is needed to maintain the uniqueness of that culture. Therefore, it can be stated that although this theory leads to develop the understanding of organisational leaders regarding speciality and uniqueness of any particular culture to respects values as well as decision of different staffs in work-team belonging to different culture, while working in multi-cultural business landscape, organizational leaders need to focus on mix-culture context, rather than focusing on only individual culture in the team.
In terms of maintaining economic growth and healthy trade relation with international business leaders, the organisational leaders in Spain are highly adaptive and robust to any culture and trend, which develop cross-cultural leadership styles in organisation. Different theories in this context can be used by organisational leaders to make better implementation of two above-mentioned leadership approaches (Tsai et al. 2019). By using the concept of Implicit Leadership Theory (ILT), it can be stated that team members in an organisation have the underlying assumptions, stereotypes, schemas and beliefs that impact on how an organisational leader visualised in front of them. Based on this concept, it can be stated that, while using democratic and transformational leadership approaches into practices, Organisational leaders would analyse the expectation, stereotype and schemas of team members which will assist organisational leaders to understand exactly what personal and professional characteristics are expected from them by their team members. In Spain, organisational leaders operate in multicultural leadership context, in which they focus on involving team members, managers as well as higher officials, into any discussion regarding business related matter in terms of taking effective as well as highly relevant business strategies. In cross cultural leadership context of Spain, it is difficult for organisational leaders to hold definite personality and professional characters as well as skills in them while implementing the transformation leadership styles into practice, as in this leadership styles, the organisational leaders need to make consistent changes in strategies and decision-making process. In this context Tzu and Adams (2016), mentioned in their article that, the Implicit Leadership Theory (ILT):, although can be used in the democratic leadership approaches, it is not possible to be used in the transformational leadership approaches, as in this type of leadership process, the characteristics and behaviour of leaders changes while adapting into different business culture which makes contradiction with the stereotype and assumptions of team member about their ideas leader. In this context, the future leaders can use another important Cross-Cultural theory such as Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions. By using this theory, organisational leaders can adapt to the different business culture in Spain which not only assist the business to grab high level of competitive advantages but also assist organisational leaders to shape their professional leadership skills to achieve organisational goal to get a strong position in the international business landscape. While dealing with the multicultural leadership context, the organisational leaders can use the theory in democratic and transformational leadership approaches in assisting their organisation to grab high level of competitive advantages in the international market. As argued by Arnulf and Larsen (2019), although the Hofstede’s Cultural Diosmetin theory can be successfully used in the current democratic and transformational leadership context, it can also create some conflict, mis-communicational and disagreement in teams that have members from different cultural background background. Another important theory that can be used in his context GLOBE - The Global Leadership and Organizational Behaviour theory. Based on this theory, the organisational leaders in Spain, need to consider the common beliefs and values of definite culture in the team which is needed to maintain the uniqueness of that culture. Therefore, it can be stated that although this theory leads to develop the understanding of organisational leaders regarding speciality and uniqueness of any particular culture to respects values as well as decision of different staffs in work-team belonging to different culture, while working in multi-cultural business landscape, organizational leaders need to focus on mix-culture context, rather than focusing on only individual culture in the team.
Human Capital Management (HCM) statistics in USA and Germany:
Human capital management (HCM), is the systematic process of managing, recruiting, optimising and developing the strength of human resources in organisation (Lin et al. 2017). While it comes to discuss the HCM in national context, it needs to discuss that what are the impacts of HCM on economy and culture of a nation. Here the report has selected two countries such as Germany and USA to discuss their HCM statistics in terms of discussing how HCM influences the future leaders to develop relevant mixed capabilities as well as skills while managing teams in cross-cultural business environment.
In USA the Human Capital Management (HCM) market size has been valued at USD 5,218.9 million during late 2018. The HCM statistics shows that, USA has made great revolution in HCM process in terms of grabbing high-skilled and eligible human resources in multinational organisations operating here. Based on The Global Economic Forums Report, 2018, while measuring the Global Human Capital Index, it is seen that, in case of having talent potentials, USA grabbed second position after Singapore as competitive country in the world. As mentioned by Starr et al. (2018), HCM is the measurement of human talent population in a country that determines how much the country can successfully use their human talent in terms of gaining not only the high economic growth but also social, political and industrial growth. The Global Economic Forums Report, 2018 suggests that, USA has successfully used the human resources in developing economic growth and grabbing strong competitive position in international cross-cultural business landscape. As argued by Akhmetshin et al. (2018), sometimes Global Capital Index and HCM cannot be used as the parameter of measuring overall economic condition in a country. For example, although in USA the HCM statistics show high level of growth (nearly 10.3%) during the year 2018 from last years, the overall economic growth cannot define the actual economic condition of many of rural and semi-urban population whose per-capita income is very low. On the other hand, while discussing the HCM process in USA, that is considered to be second competitive country in the world, there are many small and medium sized businesses and industries in rural and interior areas of America which are going to be insolvent due to tough competition in local market by international marketers. In this context, USA focusses on providing development and training on business administration and marketing operation to future organisational leaders, in terms of inspiring them to get good jobs in multinational companies operating here. In addition to this, USA has used artificial intelligence (AI) in effecting manner which has assisted the talent pool in this country by enhancing future leadership and management skills.
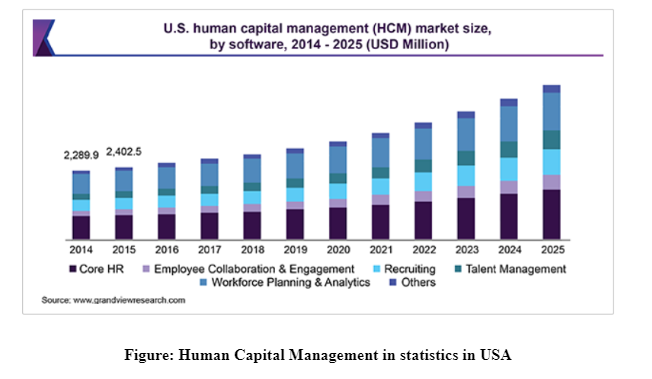
On the other hand, Germany although has strong economic situation, it has grabbed lower competitive position in the international market as compared to the USA. Although in Germany, there are many high-skilled staffs and organisational leaders who inspire future business leaders to develop their professional and professional skills in such a manner that will assist the business leaders to gain strong competitive advantages in international business landscape. As mentioned by Kariv et al. (2016), proper HCM framework inn a country inspires its future leaders and managers in terms of gathering innovative and relevant skills in competitive market which will make this country to grab strong economic growth. Germany, although has gabbed lower grade as compared to USA in maintaining its competitiveness in international market, in this country, has successfully managed, developed and controlled the overall human resources. Unlike , USA, in which human talent are provided with development training and educational opportunities only in case of who residing in urban and metropolitan area, in Germany, the country focuses on developing professional and personal leadership skills in every corner of the nation to make the country highly strong in managing as well as using the human resources in effective manner to grab strong economic as well as competitive position in international business landscape.
Challenges that the future leaders are going to face due to 4IR as well as emerging digital gig and empathy economy:
In current digital era of business, market leaders face severe issues associated with 4IR or Fourth Industrial Revolution that develops virtual and gig economy across world. In this context Karjalainen et al. (2019) mentioned that, 4IR has developed digital revolution in business, that assisted organisational people to use modern technologies in their work process decision making , business operation and market relation. The 4th Industrial revolution has assisted today's business the artificial intelligence, internet of Things (IoT) and robotics technologies in making the entre business operation faster and perfect. In addition to this, 4IR has created the Gig and Virtual economy, in which people work temporarily as freelancers rather than working as full time workers. Therefore, these can make several issues for future market leaders in current business world to perform their function in effective manner.
One of the most common issues associated with Gig Economy and 4IR that future leaders can face is difficulties in getting high-skilled permanent staffs of organisation. As mentioned by Yusuf et al. (2020), organisational leaders always create the best team in an organisation by selecting high-skilled staffs who can meet the common organisational target. 4IR has introduced virtual and gig economy in the current market, that influence future generation to choose part-time and freelancing job that can create scarcity of the high-skilled permanent staffs for organisation. Therefore, 4IR and gig economy can create difficulties for future leaders to meet their goals in developing high-skilled workforces.
The other issue faced by future leaders is inability to maintain balances and systematic work environment, in which staffs can work permanently and systematically by putting all their effort and times to meet common organisational goals (Mpofu and Nicolaides, 2019). In the near future, it is possible due to the 4IR and Gig economy, that the staffs can work in more than one organisation by involving in freelancing jobs, that can spoil work balance and systematic workforce management process in organisation.
Future leaders can also face the poor work relationship with staffs and team members in near future due to influence of 4IR and gig economy, in which most of official communication and interaction would be performed through online media (Mpofu and Nicolaides, 2019). Therefore, there would not be any physical and face-to face communication which is main sources of creating healthy and friendly work relation between future leaders and staffs.
Conclusion:
From above-mentioned discussion, it can be stated that, cross cultural leadership is associated with determining activities and behaviour global leaders in multi-cultural context. Organisation leaders need to be highly adaptive to different business culture in terms of developing such work process as well as workforces that will assist organisations in terms of grabbing strong competitive advantages in international market. There are many leaderships approaches out of which organisational leaders need to choose the right approaches that assist entire organisational to cope up with current market trend and increasing rivalries in international market. The study also conclu7des that, 4IR had developed gig economy, in which majority of talent population are engaged in part times jobs that can make the future leaders to face severe difficulties in near future. In addition to this, the future organisational leaders will also face difficulties in maintaining healthy and friendly work relation with staffs due to implementation of gig economy and 4IR in the future workplace.
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to Leading And Management Care.

Reference list:
- Akhmetshin, E.M., Sharafutdinov, R.I., Gerasimov, V.O., Dmitrieva, I.S., Puryaev, A.S., Ivanov, E.A. and Miheeva, N.M., 2018. Research of human capital and its potential management on the example of regions of the Russian Federation. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education.
- Arnulf, J.K. and Larsen, K.R., 2019, July. Too inclusive? How Likert-scale Surveys may Overlook Cross-cultural Differences in Leadership. In Academy of Management Proceedings (Vol. 2019, No. 1, p. 10340). Briarcliff Manor, NY 10510: Academy of Management.
- Bird, A. and Mendenhall, M.E., 2016. From cross-cultural management to global leadership: Evolution and adaptation. Journal of World Business, 51(1), pp.115-126.
- Bonsu, S. and Twum-Danso, E., 2018. Leadership Style in the Global Economy: A Focus on Cross-Cultural and Transformational Leadership. Journal of Marketing & Management, 9(2).
- Branco, M.M., 2018. The influence of responsible leadership on expatriates’ performance: the mediating role of affective well-being at work and the moderating role of cross-cultural adjustment’ (Doctoral dissertation, Master thesis, Polytechnic Institute of Leiria, Portugal).
- Carrier, L., 2016. Case study of cross-cultural leadership of industrial clustering in Brownsville, Texas and Matamoros, Mexico (Doctoral dissertation, University of Phoenix).
- De Ruyter, A., Brown, M. and Burgess, J., 2018. Gig work and the fourth industrial revolution. Journal of International Affairs, 72(1), pp.37-50.
- Fernando, M., 2018. CROSS-CULTURAL LEADERSHIP. Leadership: Regional and Global Perspectives, p.138.
- Hanges, P.J., Aiken, J.R., Park, J. and Su, J., 2016. Cross-cultural leadership: Leading around the world. Current Opinion in Psychology, 8, pp.64-69.
- Kariv, S., Womack, J., Del Rey, B. and Silverman, D.S., Capital Preferences Ltd, 2016. Human Capital Management System and Method. U.S. Patent Application 15/153,776.
- Karjalainen, J., Heinonen, S. and Shaw, M., 2019, March. Peer-to-peer and circular economy principles in the fourth industrial revolution (4IR)–new risks and opportunities. In 2019 International Conference on the Domestic Use of Energy (DUE) (pp. 220-230). IEEE.
- Kerr, C.A., 2016. Cross-Cultural Leadership: Best Practices In Multinational Graduate Education.
- Lee, J., 2017. Toward effective cross-cultural leadership practices for Korean missionaries in international missions. Fuller Theological Seminary, School of Intercultural Studies.
- Lin, C., Yu-Ping Wang, C., Wang, C.Y. and Jaw, B.S., 2017. The role of human capital management in organizational competitiveness. Social Behavior and Personality: an international journal, 45(1), pp.81-92.
- Lin, L., Li, P.P. and Roelfsema, H., 2018. The traditional Chinese philosophies in inter-cultural leadership. Cross Cultural & Strategic Management.
- Mpofu, R. and Nicolaides, A., 2019. Frankenstein and the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR): Ethics and Human Rights Considerations.
- Pacquiao, D., 2018. Attributes of Cross-Cultural Leadership. In Global Applications of Culturally Competent Health Care: Guidelines for Practice (pp. 307-314). Springer, Cham.
- Pathak, S. and Muralidharan, E., 2018. GLOBE Leadership Dimensions: Implications for Cross-Country Entrepreneurship Research. Acad. Int. Bus. Insights, 18, pp.11-15.
- Perry, M., 2018. How can the life, ministry and teaching of the Apostle Paul, address the development of cross-cultural leadership practice that is biblically-based, and informed by relevant secular theory?. Journal of Contemporary Ministry, (4), pp.102-119.
- Peter, G.N., 2018. Leadership: Theory and practice. SAGE publications.
- Poethke, U. and Rowold, J., 2017. The impact of cultural and individual values on transformational and instrumental leadership. In Academy of Management Proceedings (Vol. 2017, No. 1, p. 13870). Briarcliff Manor, NY 10510: Academy of Management.
Reference list:
- Schedlitzki, D., Ahonen, P., Wankhade, P., Edwards, G. and Gaggiotti, H., 2017. Working with language: A refocused research agenda for cultural leadership studies. International Journal of Management Reviews, 19(2), pp.237-257.
- Smith, P.B. and Peterson, M.F., 2017. Cross‐cultural leadership. The Blackwell Handbook of Cross‐Cultural Management, pp.217-235.
- Starr, E., Ganco, M. and Campbell, B.A., 2018. Strategic human capital management in the context of cross‐industry and within‐industry mobility frictions. Strategic Management Journal, 39(8), pp.2226-2254.
- Stephan, U. and Pathak, S., 2016. Beyond cultural values? Cultural leadership ideals and entrepreneurship. Journal of Business Venturing, 31(5), pp.505-523.
- Tsai, C.J., Carr, C., Qiao, K. and Supprakit, S., 2019. Modes of cross-cultural leadership adjustment: adapting leadership to meet local conditions and/or changing followers to match personal requirements?. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 30(9), pp.1477-1504.
- Tzu, L. and Adams, J.Q., 2016. Cross-cultural leadership: leading around the world Paul J Hanges, Juliet R Aiken, Joo Park and Junjie Su. Current Opinion in Psychology, 8, pp.64-69.
- Yusuf, B., Walters, L.M. and Sailin, S.N., 2020. Restructuring Educational Institutions for Growth in the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR): A Systematic Review. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET), 15(03), pp.93-109.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



