Operation Management at Toyota
Activity 1 [Case 1]
1.0 Effectiveness of Operation Management Principles
About Operation
Operations are regarded as business functions that an organization involves transforming materials into finished products and services and to market them to final users for earning a profit. These functions are utilized to develop products and services for the customers and to provide the final products (Kachwala & Mukherjee, 2009).
About Operation Management
Operation management comprises planning, systematizing and administering procedures, and making essential developments for ensuring higher productivity. It is essentially the administration of resources, for instance, raw materials, human resources, and machinery, among others, to either produce or to deliver a product or service. The regular operations required to support the organization’s strategic objectives.
Main Business Functions of Toyota
There are three basic business functions of Toyota, which are:

Production function: Production is the main function of any automobile company, including Toyota. Toyota produces a variety of vehicles at different ranges. It demonstrates the connection between the quantities of productivity and diverse quantities of inputs utilized in the production procedure. In short, it signifies the total output manufactured from a selected quantity of several inputs. Typically, the production function of an organization is the transformation of raw materials into finished products. These raw materials are categorized as land, ingredients, human resources, capital, and natural resources among others.
Financial function: Financial is the second most important function of Toyota. It is a part of the financial management of the company. Financial function is focused on the control and planning of financial resources. In Toyota, the financial function comprises the acquisition and utilization of money essential for effective functions. It is the lifeblood of the business of Toyota. It involves investment decisions, dividend decisions and liquidity decisions of the business. Marketing function: Marketing is also an essential function of Toyota’s business. It helps the company to recognize and source potentially successful products for the market it operates and then promotes itself by differentiating. The marketing function for Toyota comprises undertaking marketing research, developing a marketing plan and developing a product plan among others. It also comprises developing strategies for advertisement, product distribution, pricing, after-sales services, and public relations.
Current Operation Management Principles of Toyota
Lean Production
One key principle of operation management in Toyota is a lean concept. It is a production procedure that concentrates on the use of raw materials and procedures in such a way that generates value for the final customer. Based on lean operation principle, any expenses on resources, which do not generate value for the ultimate customer is wasteful and require to be eliminated. In this circumstance, value is described as any activity, product, service or procedure, which the customers will be enthusiastic about paying (Coetzee & et al., 2016).
Waste Reduction
The principle of operation management in Toyota is to reduce and eliminate wasteful practices and activities, which does not generate value for the customers. It is one of the most vital prerequisites for making Toyota a successful company. This thought is an inner portion of Toyota’s operational effectiveness, and it assists in enhancing the productivity of the company (Sengupta & Sengupta, 2013). There are seven kinds of waste according to this principle, which is demonstrated in the following figure.
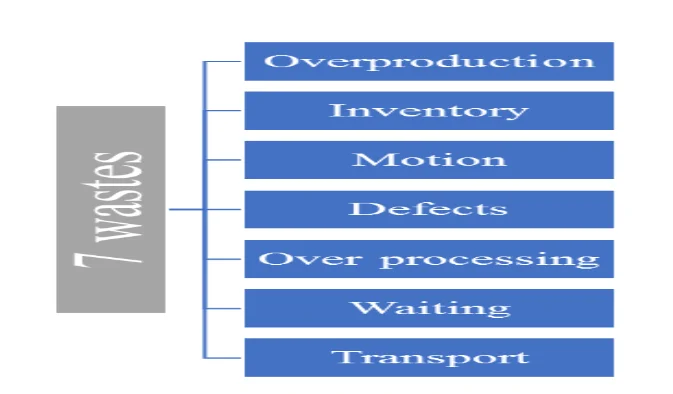
Six Sigma
Six sigma is another important principle of Toyota. It is a methodical strategy used to eradicate errors in operations. This strategy utilizes statistical approaches for enhancing the quality of products and services through reducing the inconsistency in business and operational procedures, from production to engineering and distribution. The six sigma of Toyota comprise 14 key principles, which help to determine the organizational culture, which are:
Implementation of long-run philosophy
Creation of constant movement
Utilisation of pull and avoidance of excess production
Heijunka
Utilisation of visual measurement
Utilisation of verified technology
Monitor and reflect
Choose gradually and apply quickly
Reflection of practices (Hallam & et al., 2010)
Activity 2 [Case 1]
2.1 Introduction to the Concept of Continuous Improvement
Constant improvement is regarded as the practice of continuously evaluating and improving operational procedures. It is a method of recognizing opportunities for rationalization of the operations and for minimizing waste. The concept is intellectual. In short, it is regarded as a never-ending procedure for the accomplishment of flawlessness in business.
2.2 a. Critique of Operation Management Principles within Toyota
From the analysis of operation management, it can be stated that the hierarchical organizational structure of the company inhibits the flexibility of business operations. Furthermore, the organization maintains the culture of confidentiality, which is another key weakness of the company. It minimizes the reaction times in locating the emerging issues of the business. The lean production system of the company also faces criticisms. It is alleged that the lean principle is based on the group piecework system, where managers involve in whole-time observation and disciplining of underperforming employees, which return to the concept of Taylor’s scientific management principle. Another important criticism of the lean principle used in Toyota is continuous concentration on the development and eradication of waste, which generates pressure in the workforce. Lean philosophy makes the workplace much scientific and impersonal, where employees work under persistent pressure that can have a determinable influence on productivity and effectiveness. Another similar principle used by Toyota is six sigma, which also intends to accomplish a similar objective. It is regarded as a corrective activity rather than a precautionary and practical method to problem-solving. Besides, it is more of an appraisal system, which is a great instrument for recognizing and observing developments, but critical for conducting any project.
Continuous Improvement Plan
Specific and Measurable Objective 1: Enhancement of employee productivity by developing a stress-free learning environment and culture
Resources required: Experienced human resource managers and supervisors
Results of review/follow up: Result in reviewed through the performance appraisal process and also through personal interaction with the underperforming employees. Accordingly, a proper strategy will be developed to solve the productivity and learning issues in the company. Specific and Measurable Objective 2: Ensure better reaction time within the organization for quick operational activities
Resources required: Top management support to change the organizational structure from highly hierarchical to decentralize.
The timescale of review: Everyone year
Result of review/follows up: The result can be reviewed by analysing the performance of the company in the market and its rapidity to deal with any market changes.
Specific and Measurable Objective 3: Enhancement customer satisfaction through providing better services
Resources required: Experienced team and market researcher
The timescale of review: Annual basis
Result of review/follow up: The level of customer satisfaction will be measured by surveying to analyse the satisfaction rate, complaint rate and issues they are facing, and proper measures will be taken accordingly.
2.2 b. Effectiveness of Continuous Improvement Plan
The continuous improvement plan is a continuing effort to enhance productivity, operational procedures and customer services through minimization of waste or by enhancement of quality. This constant effort helps to develop competitive benefit for the company. For Toyota, the continuous improvement plan has bought the following advantages. More involved employees: The plan has hit to employee involvement in the company. At its core, the plan is developed to empower employees to learn and progressively enhance the effectiveness of the work procedures. The plan permits employees to know that their thoughts are also important for the company. A stress-free learning environment has allowed employees to test any new concept carefully and, if they become effective, is to be applied companywide. This changes the roles and duties of employees from being a passive performer to be an active player in the business procedure. Competitive products: Continuous improvement plan determines the development of procedures and products. The plan looks for ways to develop the business and hence, to enhance the value of the products and services. This results in more refined and overall more economically competitive product and service offerings by the company. Improved customer service: Customer satisfaction begins with comprehending what customers find value and performing to provide them the value. The continuous improvement plan gives an outline for recognizing customer values and issues in the service delivery procedure. Through using the plan, the company has been able to align the products and services to latent customers’ value. This results in products and services that forestall the requirements of customers (McBride, n.d.). Development of proactive learning culture: The continuous improvement plan helps to develop a practical learning culture where they voluntarily concentrate on developing new abilities or improving the business. It challenges the employees to enhance their skills and knowledge. This eventually permits the organization to stay ahead from the other rivals.
Mass Customisation
Mass customization is regarded as the procedure of incorporating mass standardization principles. This strategy syndicates the flexibility and personalization of custom-made products with low unit expenses. This is also termed as ‘made to order.’ Mass customization permits customers to develop the product while maintaining the expenses nearer to bulk created products. In certain situations, the elements of the products are sectional. Mass production and customization have usually been at the two contrary extremes of the product range. Nevertheless, incorporating these together appears to be practice in current times with the strong possibility that it would be a constant trend of the future. Toyota has faced challenges with the application of mass customization in its production and operation system. This has also resulted in a low level of profitability and weakening competitive power in the industry (Selladurai, 2004). Toyota has found that mass customization philosophy is different than the continuous improvement philosophy and was an unfamiliar way of conducting business for the company. Both philosophies necessitate diverse organizational structures, values, administrative roles, systems, learning and training methods, and customer relations. Hence, mass customization was proving to be much expensive and hard for the company, which led it in a weak competitive position in the market. To implement this, the company requires to consider the implementation of certain different strategies, which are adaptable to changing the atmosphere.
Flexible Specialisation
In recent times, the mass production paradigm has been substituted. However, there is still no sole strategy to manage operations that have become leading in the automobile industry. Among diverse strategies for managing production and operations, one of the most important is flexible specialization. In this strategy, organizations concentrate on distinct portions of value-adding procedures and cooperate within networks to develop entire products. Such a strategy requires highly developed networks, efficient procedures for cooperation and development of long-run connections between organizations (Rees, 2001). With the advent of flexible specialization, Toyota has undertaken development in its supply chain. Toyota’s production system intends to provide a high degree of flexibility so that the organization can react with the market changes along with accomplishing profit by conducting cost minimization functions, which certifies long-run prosperity.
Agile Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing is another concept of production and operation management. This strategy empowers organizations to react rapidly with the customers’ requirements and alterations in the market, while still regulating the expenditures and quality of products and services. It is observed as the next phase of lean strategy in the development of production and operation methods. In today’s globalized market, the agile manufacturing model is created in reaction to the continuously changing new economy and increasing international competitiveness. This strategy is based on quick thinking and in reality, is an idea of maximum flexibility. There are certain differences in agile manufacturing and lean methods used by Toyota. While lean philosophy was intended to minimize the waste in production and operation activities, agile philosophy is developed to enhance flexibility and reactiveness (Khan & Dalu, 2015). The objective of lean is to eradicate everything that does not generate value, while the objective of an agile process is to thrive in a quick-paced and uncertain business environment. Therefore, agile manufacturing can help to enhance the efficiency of the business in today’s environment.
2.3 Strategies for Achieving Continuous Improvement of Improved Efficiency at Toyota
In recent times, Toyota has developed traditional operational practices in the context of the global car manufacturing industry. Similar to any other operational framework, Toyota’s operational system is intellection. Two important philosophies of this system comprise only products that are in demand and sold are produced and smooth and uninterrupted movement, which arrive JIT to be administered. In this procedure, stocks are observed as waste, which frequently termed as production issues. By minimizing the stock, the issues can be solved. A most important strategy for the company is continuous improvement, where employees are inspired to give recommendations for developments (Benders & Morita, 2004). While the economic performance of the company is extensively considered as superior, the employees also function under high stress. At virtually every assembly line, the physical working situation is tight, and the employees perform within the tight timetable, on which they have no power and conduct monotonous activities at a high pace. To deal with these issues, Toyota has begun to experiment with different approaches. One of the approach intended to enhance efficiency is to minimize the demand of employees by implementing a high technology system in production and operational activities. Toyota has applied a technically sophisticated production line, which enhances the production and operational efficiencies of the company. The new production line is planned to be worker friendly. The strategy has several elements, which are:
Segmented lines: These segmented lines are created around activities, which are separated by buffers.
Ergonomic procedures: These procedures comprise a newly developed ergonomic evaluation method and different instruments to enhance the physical working context.

Mechanization and automation: Toyota have concentrated on mechanization and automation of different products and operational activities to reduce human dependencies and also to minimize their stress level for doing the monotonous works.
Changes in strategies: Toyota has also developed supporting personnel strategies for applying the changes and also changed the positioning towards continuous improvement. The revised strategy put more focus on enhancing individual capability and personal improvement and on developing working conditions in an extensive sense.
The way a company plans its operations and products determines the level to which it will achieve profitability in the long run. The effectiveness of Toyota’s operation management so far is associated with the fact that the organization has been able to connect the theoretical strategies with practical approaches to enhance productivity. However, with the changes occurring in the industry in terms of lifestyle patterns of customers, it has become much challenging to understand their behaviours. Therefore, Toyota needs to continually learn and improve the operational and production strategies to recognize new competencies and procedures that will empower the company to react to these rapid changes in market demand.
References
Benders, J. & Morita, M., 2004. Changes in Toyota Motors’ operations management. International Journal of Production Research, Vol. 42, No. 3, pp. 433-444.
Coetzee, R. & et. al., 2016. Lean Implementation Strategies: How Are The Toyota Way Principles Addressed? South African Journal of Industrial Engineering, Vol. 27, No. 3, pp. 79-91.
Hallam, C. R. A. & et. al., 2010. Analysis of the Toyota Production System and the genesis of Six Sigma programs: An imperative for understanding failures in technology management culture transformation in traditional manufacturing companies. Technology Management for Global Economic Growth, pp. 1-11.
Kachwala, T. T. & Mukherjee, P. N., 2009. Operations management and productivity techniques. PHI Learning.
Khan, J. G. & Dalu, R. S., 2015. Lean and Agile Manufacturing as productivity enhancement techniques - a comparative study. IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering, Vol. 12, No. 1, pp. 52-56.
Selladurai, R. S., 2004. Mass customization in operations management: oxymoron or reality? Omega, Elsevier, Vol. 32, No. 4, pp. 295-300.
Sengupta, M. & Sengupta, N., 2013. Toyota Motor Corporation: Committed to Quality, Rewarded by Smiles. Cases in Management, pp. 161-200.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



