Operations Management in Retail: Tesco Case
Introduction
This project report aims to understand the way operations management principles plays a significant role in transforming the operational business framework and aids in enhancing the efficacy of the operations (Farkas, 2018). Additionally, the concept of uninterrupted upgrading plays a key feature in case of an operational Project Life Cycle context. Proper evaluation as well as application of the Project Life Cycle is very essential to understand the basic role of the operations management principles in the context of an undergoing project. UK-based large retail company, Tesco has been performing its strategic operations efficiently. In this report, critical evaluation and discussion about the importance of management principles in the domain of operative measures have been performed in the organizational context of Tesco. Next the application of stable improvement and project life cycle in an ongoing operational context has been mentioned. In the final part, critical evaluation and impact of application of the Project Life Cycle has been stated in detail. In conclusion it can be understood proper evaluation as well as application of the Project Life Cycle is very essential in the context of an undergoing project.
Discussion
LO1 Review and critique principles of operations management
Operations management principles are of immense importance in terms of proper regulation of business. In other words, Operations management is considered as an essential functional area of a company that has multidisciplinary facets (Cha, Newman and Winch, 2017). From several historical documents and reports, it has been found that Randall Schaeffer, who was primarily an industry philosopher as well as member of US association of operations and supply chain management, suggested top ten principles of Operations management. Change, Managed passion Reality Fundamentals Organization, Accountability, Variance, Causality, Success, and Humility-these are those major pillars of modern Operations management.

P1
Businesses are indigenously dependent on the proper regulation of operations. Clearly, various inputs must be properly handled to generate optimal output (like products, services) of a business. Being an industry philosopher as well as member of US association of operations and supply chain management, Ma et al. (2018) had understandable knowledge over the operations management. Ma et al. (2018) mentioned 10 key pillars as part of this principle. By understanding this principle in the organizational context of Tesco Plc. practical implementation can be done. Unlike other companies, Tesco has distinguished a job role, namely Project manager, who is responsible for overseeing and managing operational practices (Ng et al. 2020)
Take a deeper dive into Six-Phase Life Cycle Model with our additional resources.
Operations management principles
Fundamentals. In this part, 80/20 rule is practiced, which is named as ‘The Pareto rule’. As per this command, major portion, or 80% of the operational success comes from 20% of the total work (Haass and Azizi, 2018).
Strict maintenance regulation and smart work includes in the 80% part and proper regulation of exercises and responsibilities acquire 20% part.
Change. As change is inevitable, any industry must not be afraid of embracing the changes. Tesco has been successfully making several changes in their working conditions and practices.
Reality. Tesco has employed proficient and skilled project managers and executive managers who are responsible for looking after smooth running operations. Such that minor to major management issues are handled by the Operations department properly (Jafarnia, Soltanzadeh and Ghiyasi, 2018).
Accountability. All the leaders and managers of Tesco have to reciprocate with the mid-level managers and other workers to check if the timely goals are acquired or not. This practice defines Accountability to their roles.
Organization. Organize working practices are essential for optimal and consistent work habits in case of Tesco Plc. Especially in case of manufacturing and retail industry outcome as well as profits is very much dependent on organization (Crawford, BA and Stretton, 2018).
Success. Success not only defines revenue growth but sustainable workflow and collaborative organizational environment in the workplace. Tesco has become a large retail chain while satisfying customer demands as well as satisfying the employee demands (Jafarnia, Soltanzadeh and Ghiyasi, 2018).
Variance. Different work processes or variance of procedures has been part of organizational development practices of Tesco.
Causality. Causes or problematic issues must not be ignored as these problems are essential for implementing changes in the operations.
Humility. Humiliation is not encouraged by Tesco rather managers give them chances to make suitable changes.
Managed passion. Tesco must motivate its managers and their subordinates to work for sustainable growth while satisfying their needs.
Presently, several modern trends, like Reconfigurable manufacturing system (RMS), Behavioral management Business Process Reengineering (BPR), Lean Manufacturing process, Six Sigma model, etc. have been followed by many large companies for better outcome and sustainable future. Some may have been non fruitful, but the corporate must not take the adversities as the final point. Companies have to move on by taking lessons from faults (Bassi, 2017).
Six Sigma model
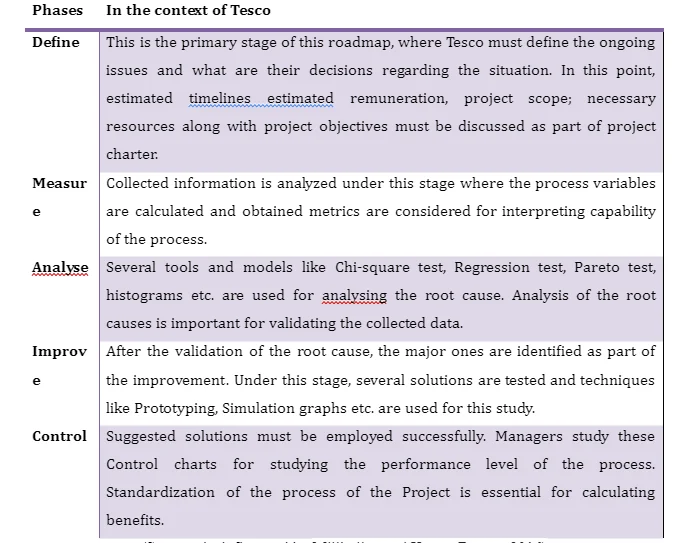
Six Sigma model is considered as one the most practical yet convenient tool for solving analytic data-driven problems of operations management. This methodology is comprised of five metrics as Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control. These metrics are essential for understanding developing areas of operations management. In other words, Six Sigma model can be considered as an important tool of Continuous process improvement plan. Tesco Plc. has focused over making process variations such that satisfaction rate of customers is enhanced over time. Tesco has taken step towards identifying potential developing areas such that customers can be facilitated with better service quality and buying experience.
M1 Six Sigma methodology and Lean principles
Six Sigma method
Six Sigma methodology aims towards providing 99.96 % defect free services and products to the end-users (Akhavan Tabassi et al. 2019). Mainly this method is data-driven tool that focuses over continuous improvement of services to satisfy customer needs and demands. Define, Measure, Analyse, Improve, and Control, or shortly DMAIC Roadmap has made it the most convenient as well as effective Continuous process improvement tool.
Lean Principles
Literally, Lean is a useful way to eliminate activities that are considered as process waste in an orderly manner. Overproduction, Defects, Non – Utilized Talent, Waiting, Motion, Inventory, Transportation, and Extra-Processing are such process wastes that must be removed for making the operations lean yet competent (Abyad, 2018). Moreover five value added approaches are part of lean principles which enables an organization to enhance customer satisfaction rate and lower process cycle time. TPS – Toyota Production system is main source from where the concept of lean process has been expanded. Taiichi Ohno of Toyota termed this as “Muda” or wastes. Goods manufacturing and service industries follow this TPS and eliminate process wastes. Those principles are-
Define value
Value stream mapping
Pull establishment
Attain perfection
Value stream mapping, Kaizen, SMED are examples of tools and models for understanding Lean Principles.
LO2
Continuous improvement plan is part of this lean methodology. Tesco must implement this TPS generated model for better operational management, reducing process wastes, increasing processing speed, and enhancing quality standards of goods and services. Proper application of TPS generated lean principles is essential for continuous improvement (Zwikael et al. 2018). In fact, process waste are segregated into three parts, Muda (7 wastes), Mura (unevenness waste), and Muri (burden waste), which mean there exist more number of process waste than actually calculated before. These wastes cannot be removed totally from the process flow; rather these wastes can be reduced up to an extent that would not hamper the flow. Plan-Do-Act-Check (PDCA) framework can be practices by the former policymakers and managers of Tesco for understanding the present situation and lowering the operational risk, such that the necessary tasks could also be performed under time (Zwikael et al. 2018).
P2
Goal-oriented planning is necessary for making a continuous improvement plan. Several philosophies related to operations management have been presented in several journals and corporate reports. Plan-Do-Act-Check (PDCA) framework can be taken as a tool to practice continuous improvement culture.
Plan: The company executives and managers must reciprocate with other retail chain managers and senior managers for getting better knowledge about the present situation of the company. For instance, there have been several nuisances regarding online ordering issues and payment over online medium (Sánchez et al. 2018). In such situation, the customer relationship manager and customer care executives must communicate with the customers empathetically and they must escalate the issue to upper level. Proper planning is essential for dealing with such issues as this may lower the satisfaction rate among the customers if not looked into (Demirkesen and Ozorhon, 2017). Do: Next perform the tasks, which were decided at the previous sessions in the planning stage. The managers must indulge with the lower level employees for better results and motivate them to work (Karuppiah et al. 2018). Check: After straightforward execution of planning, quality control and checking of the metrics are essential step. If the resulted showed improved project after comparing to previous one, the managers must generate work process and workers must act as per that. Act: As stated before, after generation of the work process and workers must act as per the process guideline. This model must be continuously followed by the officials for better results.
M2 Efficacy analysis of Plan-Do-Act-Check (PDCA) framework
Root Cause Analysis Bottom Line, Lean Kanban application, is such examples of tools to interpret continuous improvement culture. Among all these other models, Plan-Do-Act-Check (PDCA) framework has been applied in this context as this tool aids to understand the developing areas as well as focus over improving quality standards of the process (Moreno et al. 2016). In fact, Lean Six Sigma model, Six Sigma model, other also used for analyzing the usefulness of the plan. After making appropriate suggestions if the project fails, as per Plan-Do-Act-Check (PDCA) framework, still the standards of the organization stays consistent at the previous place (Moreno et al. 2016).
D1 Tools and models under continuous improvement plan
Root Cause Analysis Bottom Line, Lean Kanban application, and Plan-Do-Act-Check (PDCA) framework are some concepts and theories with which helpfulness of a continuous improvement plan can be studied. In Tesco this rule must have been practiced for maintaining the optimal input-output equation (Zimmer et al. 2019). These principles have been considered by several companies and businesses because of its predominant critical features that rationalize with the actual situation of the supply chain and operations management.
Root Cause Analysis
As the name suggests, Root cause analysis tool aids the managers to go deeper for understanding the major causes behind any problems. In this case, complex data and information handling is performed as lots of information is considered for attaining the key reason behind the effect (Zimmer et al. 2019).
Lean Kanban application
Lean Kanban is a data-driven systematic approach that had been developed by Toyota group. This application aids the professionals to lower the cycle time, improve the quality standards of the tasks, and attain competent productive results.
LO3 Application
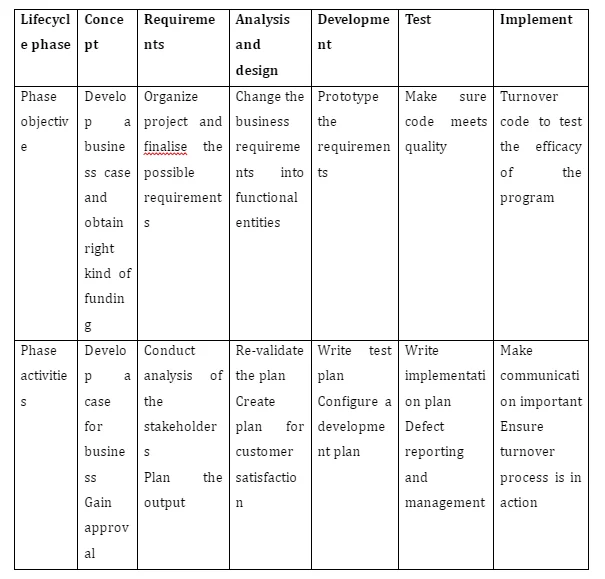
Diversified skills are part of Operations management that includes analytic skills, creativity, people management, organizational abilities, and innovative viewpoint to perform responsibilities (Dimitrova and Mancheva-Ali, 2017). Project management involves overseeing, strategy planning, implementing, managing resources, controlling of inputs and outputs, and regulating of tasks profitably. Moreover, internal as well as external stakeholders play critical role in case of managing such tasks. As per Project Life Cycle in the context of Tesco, initiation phase, planning phase, execution phase, and termination phase are the four major segments that have been stated below along with detailed analysis (Shinoda et al. 2017).
P3
As discussed before in this report, initiation phase, planning phase, execution phase, and termination phase- are the stages of the Project Life Cycle. Business case, estimated time limit, resources, project plan, work breakdown structure are important parts under the cycle (Shinoda et al. 2017).
Initiation phase
In the initiation phase project risks, objectives and deliverables are identified. Tesco has to describe the timeframe for completing the tasks. Apart from timeframe, project budget, approval signatures evaluated data of previous year, falls under the project proposal (Farkas, 2018). Tesco has to mention their risks, constraints along with strategic sales action plan that would include sales channel, services and goods, budgeted costs, projected sales, distribution strategy, deadline, and KPIs. Sales channel include wholesale, in-store and digital market.
Planning phase
In the planning stage, major deliverables in terms of products and services are mentioned under speculated time periods. After studying the business case, the practical condition would be comprehensible to all (Bassi, 2017). Next short-term goals would be considered after looking at the potential issues. Project roadmap can be generated using Six Sigma model.
Execution phase
Implementation of the planned actions would be performed under this stage. After reviewing the output standards, the execution process must be monitored and managed by the officials.
Termination phase-
At this stage, key findings are documented and results are analyzed. In fact, after the completion of the project certain developing areas are taken for further enhancement. Tesco must take those results for planning its next steps and analyzing the performance of project (Bassi, 2017). Performance indicators must be speculatively analyzed by the project managers for better results.
M3
Analyse the rationale for the project methodologies, tools and leadership within the Project Life Cycle for a given project.
D2 Interpretation of the Project Life Cycle
The evaluation of the chosen project is carried out through a series of systematic interconnected steps that helps in understanding the steps associated with the project. In the current context the lean management system and sig sigma processes helped in managing wastage and enhancing the level of efficiency within the project (Ma et al. 2018). In similar regards, it is important to understand the factor that the steps in the project can possibly help in overcoming the shortcomings and challenges witnessed within the project. The challenges such as shortage of time and resources can be quoted as one of the prime barrier in project development and continuation.
LO4
In this part the Project Life Cycle would be reviewed with proper explanation.

P4
Managing large projects by identifying the possible key characteristics and examining the possible reasons for increasing the project efficiency is carried out by identifying the key characteristics and associated risks. The risks negatively influence the performance and possible methods of exploring the counter influence of successfully delivering the expected project outcomes. The current assignment makes use of traditional approach to project management, leading to the following outcomes. As influenced by Sánchez et al. (2018), the traditional project outcomes provides good results under ideal conditions which includes abundance of resources. The aspect of pre-planning plays an important role in enhancing the expected level of efficacy. In similar terms, it can be conclusively stated planning is conducting by concentrating on the existing resources. Despite the abundance of project management literature, the life cycle of the current project is poorly evaluated. Rather than carrying out a post mortem of the current project, the analysis needs to be continuous to avoid project lag (Zwikael et al. 2018). The goal of the current project is to collect maximum data and work on understanding the possible ways that can be implemented for ensuring better project management success.
M4
Perspective is the prime theory of work related to project management. The perspective should work on considering the possible ways that can be implemented to understand the possible ways of ensuring the contribution towards the goals set. The current project needs to be set as per the basic definitions of project management. The aspect of quality, time and scope needs to be rightly evaluated for ensuring better project outcomes (Zwikael et al. 2018). Hence, it can be conclusively stated it is important to make sure that the project deliverables are rightly mentioned.
Conclusion
It can be concluded from this project report that critical assessment and argument about the importance of management principles is essential for optimal performance of Tesco Plc. Managers and industry researchers study those results such that process performance can be maximized and progressed. In this report, tools like Root Cause Analysis, Lean Kanban application, Plan-Do-Act-Check (PDCA) framework have been discussed in the context of Tesco under continuous improvement plan. Six Sigma methodology and lean principles have been mentioned in this report to understand how to eliminate extra process junks from the process control.
Reference list
- Cha, J., Newman, M. and Winch, G., 2017. Developing the project management body of knowledge: Towards a better understanding of the transformation context. In EURAM Conference 2017.
- Ma, Y., Ma, J., Zhang, P., Ma, Y. and Che, C., 2018. Research and Application of PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) in the Management of Oil and Gas Pipeline Projects.
- Haass, O. and Azizi, N., 2019. Knowledge sharing practice in project-oriented organisations: a practical framework based on project life cycle and project management body of knowledge. International Journal of Project Organisation and Management, 11(2), pp.171-197.
- Jafarnia, E., Soltanzadeh, A. and Ghiyasi, S., 2018. Combined Health, Safety, and Environment Risk Assessment Model Based on Project Management Body of Knowledge Project Management Guide. Journal of Occupational Hygiene Engineering Volume, 4(4), pp.47-58.
- Crawford, L.H., BA, H. and Stretton, A.M., 2018. Bodies of Knowledge and Competency Standards in Global Project Management. The AMA Handbook of Project Management.
- Akhavan Tabassi, A., Bryde, D.J., Mustafa Kamal, E., Dowson, J. and Michaelides, R., 2019. CHALLENGES FOR PROJECT MANAGEMENT IN THE 21ST CENTURY. The European Proceedings of Multidisciplinary Sciences.
- Abyad, A., 2018. Project management, motivation theories and process management. Middle East Journal of Business, 13(4), pp.18-22.
- Zwikael, O., Pathak, R.D., Ling, F.Y., Titov, S., Husain, Z., Yang, L., Sharma, B. and Tay, C.Y., 2018. An Asia-Pacific Comparison of Project Management Capabilities. In Society of Interdisciplinary Business Research Conference.
- Sánchez, D.C. and del Solar Serrano, P., 2018. Integration of the BIM execution plan with the guide to the project management body of knowledge (PMBOK®) of PMI (Project Management Institute)= Integración del plan de ejecución BIM con la guía para la dirección de proyectos (PMBOK®) de PMI (Project Management Institute). Building & Management, 2(3), pp.24-32.
- Demirkesen, S. and Ozorhon, B., 2017. Impact of integration management on construction project management performance. International Journal of Project Management, 35(8), pp.1639-1654.
- Karuppiah, S.D., Marthandan, G. and Shanmugam, M., 2018. An explanatory investigation on the role of communication antecedents in project management. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 96(23), pp.7904-7916.
- Moreno, J.P., Montejano, G.A. and Vilallonga, G.D., 2016, June. Business Intelligence & Knowledge Discovery en el contexto del estándar Project Management Body Of Knowledge del Project Management Institute. In XVIII Workshop de Investigadores en Ciencias de la Computación (WICC 2016, Entre Ríos, Argentina).
- Zimmer, J.C., Chen, L. and Bellah, J.C., 2019. PROJECT MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE: DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF THE PMIS. Journal of Research in Business Information Systems, p.19.
- Dimitrova, V. and Mancheva-Ali, O., 2017. PROJECT MANAGEMENT STANDARDS. Knowledge International Journal, 19(1), pp.421-426.
- Shinoda, M., Nishioka, K. and Mishima, A., 2017. Systematization of the method of project management for education in university. Journal of International Scientific Publications, 15, pp.38-47.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



