Shetland Arts Development Agency Case Study
Executive summary
Business strategic planning is an important processes that ensures that the business plans sets and executes various activities that enables it to achieve its goals. Business strategy therefore becomes an important part of every business. Shetland Arts Development Agency (SADA) is a charitable arts development agency in United Kingdom, has strong presence in the island of Shetland. It manages various art centers, theatres, and galleries. It has a mission of promoting, developing, and celebrating the distinctive art, culture, and creativity of the islands, resulting in a Shetland that is creative, confident, and connected, making it an ideal resource for art dissertation help.
The organization has competency in quality, authenticity, and originality in developing its brand. Its competitors also enjoys large market share. It builds its strength in strategizing culturally and in ensuring that it overcomes the challenge of underfunding, this paper recommends that it should diversity to other sources of income and improve on the existing ones.
Introduction

Shetland Arts Development Agency (SADA) is a charitable organization that was established in 2006 as a foundation organization of the Scottish Arts Council to replace Shetland Arts Trust that was founded in 1985. Its main aim is to encourage and assist in promoting as well as advancing the processes of creating, practicing, and presenting all forms of art that include visual arts, performing arts, and creative arts. This paper will provide a descriptive and analytical case study of Shetland Arts Development Agency. In particular, it will describe and analyze its organizational strategy and aims, its organizational structure, marketing strategy, cultural strategy and thereafter, give recommendations based on identified risks and opportunities.
Organizational Strategy and Aims
An organizational strategy is the sum of all action an organization intends to undertake to achieve long-term goals (Gerry et al, 2009). When these actions are combined together, they form an organization strategic plan. Organizational strategy must originate from organization’s mission, vision, and core values (Sinofsky & Iansiti, 2010).
Organization mission explains why the organization exists and it sets out what the organization should do to fulfill its purpose. Vision describes what will be achieved by the organization by fulfilling its mission (Bilyk, 2009). Core values are what the organization believes in (John & Richard, 2011). Shetland Arts Development Agency’s mission is to “promote, develop, and celebrate the distinctive art, culture, and creativity of the islands, resulting in a Shetland that is creative, confident, and connected.” By pursuing this mission, Shetland has a vision of achieving inspiration and innovation that bears value, giving people freedom of enjoying life while working and learning, availing individual creative opportunities to everyone, and ensuring that everyone achieves his or her full creative potential. Additionally, improving life circumstances, styles, and choices of people through personal development and achieving full social and economic potential of the island (Creative Scotland, 2017). Whether the organization will fulfill its mission and visions depends on many factors, which includes external and competitive environment, internal resource, competences, and capabilities.
Organizational Structure
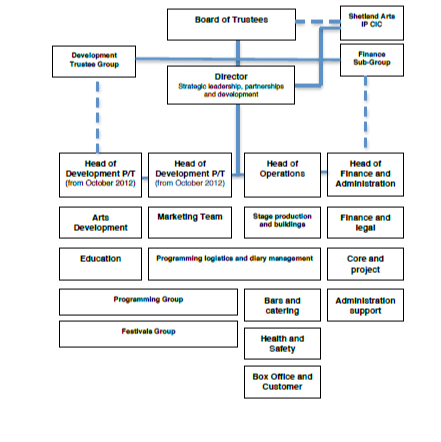
SADA is strategically organized into three distinct areas of governance. These areas consist of development, operations, and administrative governance. The trustee group heads these three areas of governance. The board of trustees appoints a director who is tasked with reporting to the board and is tasked with the strategic leadership, creating partnership, and development functions (see Appendix 1). Therefore, the Director plays an important role in the organizational structure of SADA. S/he deals with both the board of trustees through providing long term planning, developing strategies that the organization may require to remain on top of their competitors and deals with governance issues as required by the board of trustees. The Director also is tasked with guiding the staff through providing short and medium term operation management strategies to various departmental heads. Strong board of trustees as well as management team assists the Director (Zhao, 2011).
External and Competitive Environment
The key organization that offers massive competition to Shetland in terms of creative arts is Creative Scotland. It is involved in arts, screen, as well as other creative industries. It invests in young people with exciting talents. It is also involved in creative industry and focuses on all creative ideas in Scotland. Through its Board of directors, it champions for creative Scotland in all aspects. Second, key competitor is Scottish Natural Heritage is an organization funded by the Scottish government and has a mandate of promoting and improving natural heritage, helping people enjoy their heritage and ensures that natural heritage is sustainable used by all Scottish population. Thirdly, Historical Scotland is another government agency that is concerned with safeguarding the country’s historic environment and allows people to enjoy the heritage on behalf of the Scottish Ministers (SADA 2016).
Internal Resources, Competencies, and Capabilities
Every organization faces limited resources. According to Song et al (2008), organization will only achieve its objectives if it manages its resources well. Resources are always limited therefore, in order for an organization to develop its core competence; it should allocate its resources to key areas (Wojciechowska, 2016). Resources include organizational workforce, facilities, equipment, and finances (Jiang, 2014). Shetland operates Mareel Center that deals with music, cinema, and creative industries. It also operates Bonhoga gallery located in Weisdale Mill, Garrison theatre in Lerwick, which promotes programmes in music, craft, theatre, visual arts, dance, and literature as well as film activities throughout the year.
Competencies include those activities that are perceived to be the strengths of the organisation. This gives them a competitive advantage in the market place (Kantola, 2016). Key competencies can also come from experience, talent and through research and development (Gupta, 2006). The culture and the authenticity of their products give Shetland Arts Development Agency a competitive advantage (Historic Scotland 2008).
Key Stakeholders, Suppliers, and Buyers
The key stakeholders in this organization includes non-governmental organizations, educational institutions, Trust funds such as Heritage Lottery Fund, Scottish government, Visit Scotland, Creative Scotland, Historic Scotland, Scottish Natural Heritage, Royal Society for the Protection of Birds, Museums galleries Scotland and community of Shetland. The buyers mainly include people of the island as well as other visitors from Britain and abroad (Pooke, 2012).
Consumer Needs and Target Market
Organizations derive their motivation from meeting the needs of its customers. To meet successfully the needs of the customers, it is important that the organization have a clear understanding of its customers as well as their specific needs. With this knowledge, organization will put in short term and long-term strategies that will help it effectively meeting the specific needs of its customers and in essence, achieve its entire organizational goals.
Corporate edge of Shetland Arts Development Agency described its target market as customers who are “At the top end of international societies: older, affluent but putting a value on values and liking ‘rarity.” They prefer to visit a place which is not only different but also highly distinctive and to buy products that are produced from a culture whose value they admire” (SADA 2016).
This means that the customers of Shetland Arts Development Agency are affluent and are willing to pay premium prices in return for authentic and high quality products. They are customers who go after genuine experiences and seek to know how the products they purchase are produced and by whom. Therefore, consumer needs of Shetland Arts Development Agency include genuine experiences and fine quality product, which the organization has to supply. Their key preference is in genuine local arts, crafts, tradition, environmental issues, and heritage. Hence by attaining these preferences, the organization should strategically plan how their products will meet these requirements (SADA 2016).
Marketing Strategy
Marketing strategy is an important process that should be included in strategic planning. Marketing strategy as set of actions that are planned to be undertaken with the intent of increasing revenue and market share. Consequently, these actions help the organization to achieve its business goals (Ferrell & Hartline, 2014). In coming up with marketing strategy, three elements must be involved; target customer description, means of reaching those customers and how to retain this customers (Song et al, 2008).
Marketing strategy is important to organizations because of the following; to begin with, it helps the organization to set clear vision for the future. It clarifies organizational goals, aims, and activities giving the management the idea of what to prioritize according to the market demand and supply (Shankar & Carpenter, 2012). Therefore, a well-planned marketing strategy will ensure that every task undertaken by the organization falls under a given time and budget schedule. Secondly, it enables the organization to maximize resources by outlining the best strategy to use without wastage of resources. For instance, it will determine whether the organization uses online or digital marketing strategy to reduce cost or settle for trade shows and workshops that are quite costly. The marketing strategy will point out to the required methods that will be effective in increasing revenue and market share (Fifield, 2012). Lastly, with a good marketing strategy, an organization will be able to create an effective content message-marketing plan that will enable it to compete in today’s crowded marketing landscape. This is because it will prioritize its plan according to the market requirement and therefore improve its product quality (Doole & Lowe, 2008).
SADA had employed unique selling point (USP) strategy that has helped it differentiate itself from its competitors. Its brand implementation strategy sought to inspire people of Shetland to deliver proudly its brand promise by developing a unique profile that gives it a competitive advantage in global market as a place of visit, investment and an area in which to buy from and stay (Chuwiruch et al, 2015). This they have achieved through the following;
- Building local understanding of Shetland brand and the place it holds in the future of the island.
- Accepting the recognition that Shetland’s products and services do not always meet or even exceed the customers’ expectation and that their aim is to close this gap between what is promised and what is actually delivered.
- Involving all stakeholders such as businesses, public agencies, voluntary players and other individuals and it has to ensure that it works with all these stakeholders to support the brand.
- It must come up with a method of reviewing progress made, measuring impacts and identifying the number of opportunities available (SADA 2016).
By creating Promote Shetland as a marketing arm of the SADA, the organization has developed marketing and promotional strategy. Promote Shetland will be involved with promotional activities focused on promoting Shetland’s food, filming opportunities, and knitwear through providing visitor information, informing the prospective visitors on the goods and services that SADA offers. Promote Shetland contracted Shetland Amenity Trust to help it with encouraging trade, talent as well as inward investment. Promote Shetland has gone step further in developing creative industries. Using digital media advertisement, it has ensured that the artists and crafts men reach the target market (Scotland Museums Galleries 2015).
In order to have an effective marketing strategy, there should be well-developed elements of differentiation (Khankaew et al, 2015). SADA brand has developed its key elements of differentiation through having a vision of self-reliant and successful Shetland, achieving measurable export, as well as tourism targets, having philosophy of excellence as inspiration that gives it justification of high prices it charges. In addition, Shetland has an element of strategic positioning in a small, clever country, which gives it advantage compared to large, struggling peripheral community. Moreover, its customers are successful idealist whose main concern is fine quality rather than quantity and are ready to pay high prices for the products (Shetlands Arts 2008).
SADA has developed sales and pricing strategy that are unique. It charges premium prices for its goods and services. Pricing strategy is based on quality. The idealist customers take much care in the quality and most of them are affluent therefore, the organization has to price its products fairly to reflect the fine qualities of its products (SADA 2016).
Cultural Strategies
In trying to achieve its objectives, an organization usually has to get involved with highly segmented audiences. They are segmented in terms of socioeconomics, cultural heritage, lifestyle, language, tradition, and education. Therefore it is paramount for an organization to come up with ways of reaching all these segments of its audience in a manner that is effective and rewarding (Song et al 2008). Every organization will therefore strive to break through these segments and connect emotionally with the audiences. Every customer is unique and therefore requires a unique approach while trying to satisfy his/her preference and tastes. The function of cultural strategy is to ensure that they allow the organization to reach out and build relationship with their customers and audiences (McDonald & Dunbar, 2013).
SADA’s brand reflects the people and the place. It focuses on soul, origin, and fineness of the place and its people. Soul is taken to mean of the place such as its people, landscape, and music. Origins represent the tradition of the place. Every product produced by the organization should originate from the island. The knitwear and music should be reflecting the long-standing tradition of the island. Fineness can be based on trust and honesty as well as quality. In doing so SADA seeks to ensure that it conserves the cultural assets of the Shetland.
Through developing and supporting various cultural aspects in music arts and heritage and giving every individual an opportunity to explore his or her own potential, SADA has an effect of strengthening the identity of the community, ensuring that the pride of the community is preserved and raising the community’s confidence in its own culture and tradition. Moreover, SADA has engaged in ensuring that prosperity is made possible for the current as well as future generation through sustainable development. The cultural strategy of Shetland aims to portray the culture of the island to be among the richest as well as most diverse in the region and beyond (SADA 2016). Amongst the rich cultural heritage of the Shetland island that the organization has employed in its cultural strategy includes; impressive archeological remains, Scottish and Scandinavia blended culture, much alive musically-rooted tradition, strong craft base with a very outstanding, fine knitwear known globally, boat building tradition, skilled workers in wood, leather, stones, ceramics and glass works. In addition, Shetland has a vibrant art scene with various activities that goes on every time throughout the year.
Risks and Opportunities
The main challenge that Shetland face is drop in core funding. As a charity organization, it depends mostly on funding from Shetland Charitable Trust. The rising cost of energy as well as expansion of the Shetland core activities require huge amount of fund. With these, there is risk of underfunding the projects and therefore necessary measures ought to be put in place to ensure that the organization receives enough funding (Varbanova, 2013). These financial challenges should be faced by reducing cost of operation and increasing income so that it can realize it short term as well as long term goals (SADA 2016).

Recommendations
In order to offset future reduction in grants, there is need for the organization to improve its commercial performance which will ensure that it increase its income. The source of income it receives from footfall and other activities should be increased by marketing and strategic planning. Failure to diversify will mean that the organization will continue to depend on the ever-reducing grant fund and this will hurt the execution of the strategic plan as well as action plan, consequently, the organization will have hardship in balancing its financial books of accounts.
Dig deeper into Shareholder Value in Multinational Corporations with our selection of articles.
References
- Bilyk, B. (2009) Identifying Organisational Strategy: Porter’s Approach. Germany: GRIN Verlag
- Chuwiruch, N., Jhundra-Indra, P., & Boonlua, S. (2015). Marketing Innovation Strategy And Marketing Performance: A Conceptual Framework. Allied Academies International Conference.Academy of Marketing Studies.Proceedings, 20(2), 82-93.
- Creative Scotland (2017). Creative Scotland. [online] retrieved from: http://www.creativescotland.com/#/about/about-‐overview [accessed 25 February 2017]
- Doole, I., & Lowe, R. (2008). International marketing strategy: Analysis, development and implementation. London: Cengage Learning.
- Gerry J., Kevan S., & Richard W. (2009). Exploring Corporate Strategy. (7th Ed) New Jersey, US: Pearson.
- Gupta, R. N. (2006). Business organisation and management. New Delhi: S Chand.
- Ferrell, O. C., & Hartline, M. D. (2014). Marketing strategy: Text and cases. Mason, OH: South-Western/Cengage Learning.
- Fifield, P. (2012) Marketing Strategy. London: Routledge
- Historic Scotland (2008). History of Scotland. [online] retrieved from: www.historic-‐scotland.gov.uk/corporate‐plan-‐2008-‐2011.pdf [accessed 25 February 2017]
- Jiang, W. (2014). Business partnerships and organizational performance: The role of resources and capabilities. Heidelberg : Springer
- John A. P. & Richard B. R. (2011). Strategic Management. Formulation, Implementation, and Control. (12th Ed) McGaw Hill international
- Kantola, J. (2016). Organizational resource management: Theories, methodologies, & applications. Boca Raton : CRC Press
- Khankaew, C., Ussahawanitichakit, P., & Raksong, S. (2015). A Conceptual Framework of Alternative Marketing Strategy and Marketing Outcomes. Allied Academies International Conference. Academy of Marketing Studies. Proceedings, 20( 2), 1-16
- McDonald, M., & Dunbar, I. (2013). Market segmentation: How to do it, how to profit from it. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons.
- Pooke, G. (2012) Contemporary British Art: An Introduction. London; Routledge
- SADA (2016). Business Plan 2012-2015 Shetland Arts. [online] retrieved from http://www.shetlandarts.org/site/assets/files/5835/sada-business-plan-2012-2015-v1_0-final.pdf [accessed on 25 February 2017]
- Scotland Museums Galleries (2015). Museums Galleries. [online] retrieved from www.museumsgalleriesscotland.org.uk/ [accessed on 25 February 2017]
- Shankar, V., & Carpenter, G. S. (2012). Handbook of marketing strategy. Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar Pub.
- Shetland Arts (2008), A Hansel For Art, Lerwick.
- Sinofsky, S., & Iansiti, M. (2010). One strategy: Organization, planning, and decision making. Hoboken, N.J: Wiley.
- Song, M., Podoynitsyna, K., Van Der Bij, H., & Halman, J. I. (2008). Success Factors in New Ventures: A Meta-analysis. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 25(1), 7-27.
- Wojciechowska, M. (2016). Intangible organizational resources: Analysis of resource-based theory and the measurement of library effectiveness. London: Palgrave Macmillan,
- Zhao, Y. (2011). Corporate governance and directors' independence. Austin, Tex.: Kluwer Law International.
Appendix 1: Shetland Organisational Structure
What Makes Us Unique
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



