Orthopedic Patient Care: Case Study on Left Arm Pain in Edward Lewis
Introduction
Orthopedic conditions are injuries and diseases that affect the musculoskeletal system. This body system includes the muscles, bones, nerves, joints, ligaments, tendons, and other connective tissues. Damage to any of these tissues or structures can come from chronic orthopedic diseases or an injury. This assignment will focus on the care of the orthopedic patient. Here we discuss the role of orthopaedactrics and long-term condition care. Nurses have the duty to all patients receiving care. Therefore the writer will examine the patient using a pseudonym to maintain confidentiality.
A 38-year-old right hand dominant European man, Edward Lewis, was referred for evaluating left arm pain, numbness, tingling, and slight subjective weakness. For the case study, the assignment will focus on left arm pain. In this case study, we also discuss the psychosocial aspects and the ongoing management that is required. A critical analysis of the management and current government health and social care policies will be addressed in this assignment. Additionally, those seeking healthcare dissertation help will find that examining such aspects is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of patient care and policy impact.
ABOUT ORTHOPAEDIC CONDITION

Orthopedic conditions are injuries and diseases that affect the musculoskeletal system. This body system includes the muscles, bones, nerves, joints, ligaments, tendons, and other connective tissues. Damage to any of these tissues or structures can come from chronic orthopedic diseases or an injury.
General orthopedic problems include:
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to Structure and Function of Skull.
- Acute injuries, such as traumatic bone fractures and dislocated joints
- Arthritis is a joint inflammation causing pain, joint damage, and loss of joint function. There are more than 100 different types of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and gout.
- Bursitis is inflammation and irritation of a bursa. Bursae are fluid-filled sacs inside joints that cushion ligaments, tendons, and muscles as they move over bones.
- Muscle atrophy, which is the loss of muscle tissue causing weakness and difficulty moving. It can occur with lack of use, such as bedridden or damage to the nerves controlling the muscle movement.
- Musculoskeletal cancer is the spite of any of the tissues or structures of the musculoskeletal system. Examples include osteosarcoma (bone cancer) and chondrosarcoma (cartilage cancer).
- Orthopedic, autoimmune diseases occur when the body's immune system mistakenly starts attacking its healthy cells and tissues.
- Osteomalacia causes an adult's bones to soften. Vitamin D deficiency is the most common cause of this condition.
- Osteomyelitis, which is an infection in the bone
- Osteoporosis, which is the loss of bone density making the bones weak and brittle. It increases the risk of fractures.
- Pinched nerve, which is when a spinal nerve root becomes compressed or irritated. A nerve root is where a spinal nerve branches off the spinal cord and exits the spine between two vertebrae. Spinal disc problems are the leading cause of a pinched nerve.
- Tendinitis is inflammation and irritation of a tendon. It is a form of overuse injury from repetitive motions or forces.
- Tenosynovitis is inflammation of a tendon sheath. Tendons are strong cords of connective tissue that attach muscles to bones. Tendons that pass through bony tunnels, such as the wrist, have a sheath surrounding them. These sheaths allow the tendon to move through the tunnel smoothly.
It’s best to see a doctor at the first sign of trouble with your bones, joints, or muscles. In many cases, the problem is due to overuse or strain, but it's better to rule out more severe injury as soon as possible than to wait and risk the chance of the problem getting worse. Seek immediate medical care (call 911) for a severe injury involving any part of the musculoskeletal system, such as bone fractures and joint dislocations.
The symptoms of orthopedic issues will vary depending on the specific condition and body part.
Symptoms include:
- Deformities or unusual appearance of a joint
- Fatigue combined with joint pain or swelling.
- Joint stiffness and limited range of motion
- Muscle spasms
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness
- Pain may be mild, moderate, or severe and sharp, dull, achy, cramp, stabbing, or burning.
- Swelling of the injured or diseased area
- Warmth and redness in case of infection or inflammation
Such symptoms as pain, muscle spasms, numbness, swelling, and stiffness may come and go depending on the specific condition and your activity level. Pain and other symptoms from orthopedic conditions can limit activity if it worsens with movement.
Orthopedic injuries, such as bone fractures and joint dislocations, can lead to complications and require immediate medical attention. Seek primary medical care (call 911 for help) if you, or someone you are with, have any of the following symptoms:
- Deformity of a joint or bone
- Difficulty moving a joint or extremity
- Hearing a snapping, grinding, or popping sound during the injury
- An open wound or bone sticking through the skin
- Severe pain or swelling
Acute or chronic trauma is a common cause for many of them. Acute trauma is a sudden injury. Regular trauma results from repetitive motions or forces on a joint or joint structure, such as a tendon. These injuries happen gradually over time, such as weeks, months, or years even.
Degenerative changes are another common cause of orthopedic conditions. Joints and joint structures can sustain wear and tear over time. It's causes changes that can result in such situations as osteoarthritis and spine problems.
What are the risk factors for orthopedic conditions?
Each specific orthopedic issue has its own set of risk factors. In general, risk factors may include:
- Aging
- Being overweight or obese, which puts extra pressure on bones, joints, and joint structures
- Having a chronic disease, such as diabetes
- Playing sports or participating in recreational activities.
- Smoking
- Using improper lifting techniques and body mechanics
- Working in a profession involving the same tasks every day, which increases strain on your body
Reducing your risk of orthopedic conditions
You may be able to lower your risk of orthopedic conditions by changing risk factors you can control, such as:
- Balancing strength training with stretching exercises
- following your treatment plan for medical conditions.
- Cross-training with a variety of activities
- Learning correct posture, body mechanics, and ways to lift heavy objects
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Quitting smoking
- Strengthening your bones with weight-bearing activities and plenty of calcium and vitamin D
- Wearing protective equipment during sports and recreational activities
It's essential to see your doctor regularly if you develop an orthopedic condition. Early treatment can often result in a better outcome and can help you avoid future problems.
Treatments for orthopedic conditions will differ depending on the problem. However, orthopedic treatments have some common goals and approaches. In general, this includes correcting physical problems, relieving symptoms, improving quality of life, and preventing future problems. There are various ways to accomplish these goals, including RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation), over-the-counter and prescription medicines, joint injections, and physical therapy. In some cases, orthopedic surgery may be necessary to resolve the problem.
Without proper treatment and adequate recovery, many orthopedic conditions can lead to disability and chronic problems. Talk with your doctor about your specific situation. Ask about the potential complications and how you can work with your doctor to prevent or treat them
The physiological aspects and management
A 38-year-old right hand dominant European man was referred for evaluating left arm pain, numbness, tingling, and slight subjective weakness. Upon evaluation, he noted a five-month history of pain, extending from his shoulder down the lateral aspect of his left arm to his thumb and index finger. He also complained of numbness and tingling in his left thumb and index finger. Upon questioning, he did note the mild loss of adequate motor function in both hands, but no balance, bowel, or bladder abnormalities. His past medical history was significant for congenital cardiac disease with a history of the great vessels' surgical transposition and current moderate cardiac myopathy.
Physical exam:
He was found to have 5/5 strength with manual motor testing in all muscle groups except for his left bicep, which graded 4/5. He was hyperreflexia in his bilateral brachioradialis and throughout his bilateral lower extremities. He had slight ataxia and optimistic Hoffman's sign bilaterally.
Imaging studies:

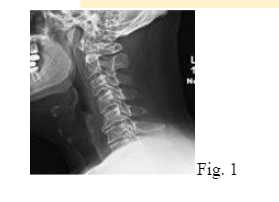
- Plain radiographs of the cervical spine showed straightening of cervical lordosis and moderate degenerative disc disease (DDD) from C5-C7 (Fig. 1).
- MRI scan without contrast showed severe spinal stenosis, primarily from C5-7, with associated spinal cord compression and cord signal change. The posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL) appeared thickened from C5-C7. (Figs. 2a and 2b)
- CT scan without contrast showed the DDD mentioned above and ossification of the PLL (OPLL) from C5-C7 with central bony stenosis (Figs. 3a and 3b).

DIAGNOSIS:
Surgical options:
Given the patient's loss of lordosis and multilevel stenosis with OPLL, a posterior laminectomy from C4-T1 with instrumented fusion from C4-T2 was chosen. It might help avoid the complications of Dural tear and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak associated with anterior decompression in patients with OPLL. Additionally, given his lordosis loss. The patient agreed with the procedure. The patient optimized medically for surgery.
SURGERY:
The patient was positioned in the prone position using Mayfield head tongs. A posterior midline approach to the cervical spine was performed. Lateral mass screws were placed bilaterally from C4-C6, and pedicle screws were placed bilaterally at T1 and T2. No screws were placed at C7 to facilitate the placement of the rods.
We now proceeded with a posterior cervical laminectomy from C4-T1 with foraminotomies at bilaterally at C4-5 and C5-6 to address the radiculopathy. There was excellent decompression of the spinal canal with posterior migration of the thecal sac. Appropriately sized and shaped rods were placed, and set caps were placed and tightened. Cross-links were placed for both stability and protection of the spinal cord from the posterior musculature. (Figs. 4a, 4b, 4c, 4d).

Local bone graft from the decompression was morselized and combined with allograft demineralized bone putty. This was placed over the decorticated posterior elements following resection of the facet capsules and the facet joints' debridement.
For pain management, liposomal bupivacaine was used to provide long-acting local anesthetic relief. A deep drain and vancomycin powder were placed. The incision was closed in multiple layers.
POSTOPERATIVE COURSE:
The patient was monitored on the telemetry unit due to his extensive cardiac history. He did well overall without cardiac complications and improvement of his preoperative symptoms. His postoperative pain was well controlled with the liposomal bupivacaine and IV and oral narcotics for 72 hours.
Social behavior with an orthopedic patient
Orthopedic surgeons successfully treat millions of patients yearly using operative or no operative techniques. However, self-reported disability and pain intensity vary widely across patients undergoing similar treatments or surgical procedures, with limited correlations between objective data from radiographs or physical exam and patient self-report. Psychological factors, such as symptoms of depression, health anxiety, or catastrophic thinking, are consistently associated with disability and pain intensity in patients with a variety of musculoskeletal illness concerns.
Despite the abundant research on the importance of psychosocial factors in the care of both surgical and nonsurgical orthopedic patients, including emerging evidence on the efficacy of the psychosocial intervention in improving pain and disability in orthopedic patient’s biopsychosocial models –where both the medical and psychosocial factors are assessed and addressed– have not yet been incorporated in most orthopedic surgical practices. Orthopedic surgeons have a pivotal role in this transition process by noticing when these factors are present, discussing them with patients, and providing referrals to psychosocial treatment, when necessary. Such referrals can occur before orthopedic surgery when emotional health challenges predictive of less postoperative recovery identified or post orthopedic surgery when difficulties coping may develop.
To understand potential barriers toward addressing psychosocial factors within orthopedic practices, we designed a study aimed to survey surgeons' attitudes and ways of noticing, screening, discussing psychological illnesses with patients, and making referrals to address psychosocial issues in patients in need. Our primary null-hypothesis is that there are no associations between the degree to which surgeons refer for psychological treatment and surgeon-specific factors. Our secondary null-hypotheses were that there are no associations between the degree to which surgeons notice, screen, and discuss psychological illnesses and surgeon-specific factors. Additionally, we asked surgeons to rank-order potential barriers to and reasons for referrals to psychosocial treatment. Regardless of your industry or position, it can be easy to miss the forest for the trees. In medicine, that usually means viewing the procedure or the medication or the therapy as the totality of medical care. But patients perceive their experience holistically—from the first appointment to the final post-op evaluation.
Orthopedic surgeons who focus on the patient rather than their condition can provide more comprehensive, patient-centered care. They are adept at building personal, empathetic relationships with their patients, resulting in better communication and, in turn, increased patient satisfaction.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, a discussion of Edward's management plan was established, identifying his needs in an acute setting, however focusing on his needs in the long term. There are various ways to accomplish these goals, including RICE (rest, ice, compression, elevation), over-the-counter and prescription medicines, joint injections, and physical therapy. In some cases, orthopedic surgery may be necessary to resolve the problem. Service delivery in the community was discussed and analyzed to ensure Edward had continuous, high-quality care in the community setting to reduce readmission.
REFERENCE
- 1.Ayers DC, Franklin PD, Ploutz-Snyder R, Boisvert CB. Total knee replacement outcome and coexisting physical and emotional illness. Clinical Orthopedics and related research. 2005;40:157–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Ayers DC, Franklin PD, Trief PM, Ploutz-Snyder R, Freund D. Psychological attributes of preoperative total joint replacement patients: implications for the optimal physical outcome. The Journal of arthroplasty. 2004;19(7 Suppl 2):125–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Melzack R. Pain--an overview. Acta anaesthesiologist Scandinavica. 1999;43(9):880–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Atlas SJ, Tosteson TD, Blood EA, Skinner JS, Pransky GS, Weinstein JN. The impact of workers’ compensation on outcomes of surgical and nonoperative therapy for patients with a lumbar disc herniation: SPORT. Spine. 2010;35(1):89–97. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Jensen MC, Brant-Zawadzki MN, Obuchowski N, Modic MT, Malkasian D, Ross JS. Magnetic resonance imaging of the lumbar spine in people without back pain. The New England journal of medicine. 1994;331(2):69–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Mechanic D. Sociological dimensions of illness behavior. Social science & medicine. 1995;41(9):1207–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Vranceanu AM, Bachoura A, Weening A, Vrahas M, Smith RM, Ring D. Psychological factors predict disability and pain intensity after skeletal trauma. The Journal of bone and joint surgery American volume. 2014;96(3):e20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Vranceanu AM, Safren S, Zhao M, Cowan J, Ring D. Disability and psychologic distress in patients with nonspecific and specific arm pain. Clinical Orthopedics and related research. 2008;466(11):2820–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Janssen SJ, Ter Meulen DP, Nota SP, Hageman MG, Ring D. Does Verbal and Nonverbal Communication of Pain Correlate With Disability? Psychosomatics. 2015;56(4):338–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Janssen SJ, Teunis T, Guitton TG, Ring D, Herndon JH. Orthopedic Surgeons’ View on Strategies for Improving Patient Safety. The Journal of bone and joint surgery American volume. 2015;97(14):1173–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Vranceanu AM, Hageman M, Strooker J, ter Meulen D, Vrahas M, Ring D. A preliminary RCT of a mind-body skills-based intervention addressing mood coping strategies in patients with acute orthopedic trauma. Injury. 2015;46(4):552–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Riediger W, Doering S, Krismer M. Depression, and somatization influence the outcome of total hip replacement. Int Orthop. 2010;34(1):13–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Rolfson O, Dahlberg LE, Nilsson JA, Malchau H, Garelick G. Variables are determining outcomes in total hip replacement surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91(2):157–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Bruinsma WE, Becker SJ, Guitton TG, Kadzielski J, Ring D. How prevalent are hazardous attitudes among orthopedic surgeons? Clinical Orthopedics and related research. 2015;473(5):1582–9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Tosti R, Ilyas AM, Mellema JJ, Guitton TG, Ring D, Science of Variation G Interobserver variability in the treatment of little finger metacarpal neck fractures. The Journal of hand surgery. 2014;39(9):1722–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Teunis T, Janssen SJ, Guitton TG, Parisien R, Ring D. Do orthopedic surgeons acknowledge uncertainty? CORR. 2015. ahead of print.
- 17. Teunis T, Janssen SJ, Guitton TG, Vranceanu AM, Goos B, Ring D. Surgeon personality is associated with recommendations for operative treatment. Hand. 2015;10(4):35–39. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Vranceanu AM, Safren SA, Cowan J, Ring DC. Health concerns and somatic symptoms explain perceived disability and idiopathic hand and arm pain in an orthopedics surgical practice: a path analysis model. Psychosomatics. 2010;51(4):330–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Vranceanu AM, Jupiter JB, Mudgal CS, Ring D. Predictors of pain intensity and disability after minor hand surgery. The Journal of hand surgery. 2010;35(6):956–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Farzad M, Asgari A, Dashab F, Layeghi F, Karimlou M, Hosseini SA, et al. Does Disability Correlate With Impairment After Hand Injury? Clinical Orthopedics and related research. 2015;473(11):e414–20. 3470-6.29(10) [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Continue your exploration of Oral Hygiene Instructions for Patients with Removable Acrylic Partial Denture with our related content.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



