Understanding Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Introduction:
Inflammatory bowel disease comprises two chronic, idiopathic, inflammatory disease. Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Although there are many risk factors for these diseases like genetic and immunological factors which influence the gastrointestinal tract, the main reason for these diseases is still unknown. In some cases, it is difficult to distinguish between the ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s diseases, because they have some clinical features which present in both disorders.
However, each disease has some features or symptoms could help the physicians to diagnose the case whether it is Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis disease. Crohn’s disease more likely to has abdominal pain and perianal disease, while Ulcerative colitis is more tending to have gastrointestinal bleeding. Crohn’s disease shows Cobblestoning mucosa and linear ulcers, fistulae, and ileal involvement while in ulcerative colitis disease shows continuous disease in the absence of fistulizing or ileal disease. Moreover, transmural involvement, and granulomas present in Crohn’s disease, whereas ulcerative colitis does not. Also, Crohn’s disease has a Crypt abscesses and granulomas which not present in Ulcerative colitis.
History:
Crohn’s disease had been discovered and analysed by Dr. Burrill Bernard Crohn along with Dr. Gordon Oppenheimer, and Dr. Leon Ginzburg who had been his two colleagues in the year 1932. Thus the disease was accorded the name of Dr. Burrill B Crohn. Giovanni Battista Morgagni had brought forward the initial clarification of the Crohn’s disease. Being an Italian physician, Giovanni Battista Morgagni, had performed the diagnosis of a patient who had been affected by disease which had been exhausting the capability of the patient to withstand the effect of such a disease in the form of diarrhea and this had been occurring for a long time.
What is the Crohn’s disease?
Crohn’s disease could be comprehended in the form of a chronic and idiopathic inflammatory disease which primarily could be found in the terminal ileum. However, this disease could be also comprehended to have the ability to affect any of the sections of the gastrointestinal tract commencing from the mouth and terminating at the anus of the patient.
Symptoms and signs of the disease:
Crohn’s disease has a variety of symptoms which depends on the severity of the disease. These symptoms vary from mild to severe and from person to another, depending on the part of the digestive tract which is inflamed. Moreover, they usually evolve steadily, but sometimes will come abruptly. Also, the patient may have some of the time without these symptoms (Remission). When the disease is active, there are common symptoms and signs could be seen on the Crohn’s patient which may include fever, diarrhea, low appetite, and weight loss, stomach pain, nausea, fatigue, rectal bleeding, Stomatitis (mouth inflammation) pain around the anus and constipation. Also, the symptoms could extend to joint pain and inflammation, eye inflammation, liver and bile duct inflammation, and skin ulcer and sores. Moreover, Crohn’s disease not just affect adults, but also has an effect on children and that can cause delayed growth in prepubertal patients. The patient may not have all these symptoms because Crohn’s disease affects people in different ways and sometimes the condition will be inert, and the patient has remission time form the disease.
Looking for further insights on Video On Demand Service? Click here.

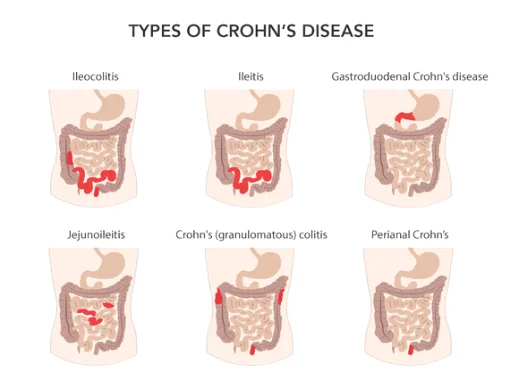
Types of the Crohn’s disease:
Crohn’s disease has a different five categories depending on which part of the digestive tract are affected, and the symptoms are different based on the parts that changed.
Ileocolitis: This type consider is a more popular type of Crohn's disease. It is characterized by inflammation in the last part of the small intestine (the ileum) and the colon and small intestine (Affect about 40% of patients). The patient might have weight loss and diarrhea which consider more common in this type. Also, the patient may suffer from pain in the lower or middle part of the abdomen. Furthermore, this type leads to painful consequences as abscess, intestinal obstruction, and inflammation.
1-Ileitis: This category affects the ileum. And has the same symptoms of Ileocolitis beside other symptoms like Fistulas (connection of two parts they are not usually connected and that could result from inflammation or infection) and has inflammatory abscesses, which could be in the lower right portion of your abdomen. The negative consequences are similar to Ileocolitis.
2-Gastroduodenal Crohn's disease: this type involves the first part of the small intestine (duodenum) and stomach. Low percentages of the patient have been affected by this type, but also, they may also have inflammation on other parts like colon and ileum. The symptoms appear after taking a meal, so patients try to avoid eating because they feel some pain after eating and this cause weight loss. Besides that, they feel full quickly, so they lose their appetite. This type has similar diseases have the same symptoms as, stomach irritation (gastritis), or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)and stomach ulcers. For this reason, recognize this type is difficult sometimes. The complications make Gastroduodenal Crohn's disease worse because it has severe consequences like bleeding in the stomach and intestine which lead to ANEMIA and blood vomiting and vomiting when a narrow part of the bowel is blocked.
3-Jejunoileitis: this type is characterized by inflammation of the middle part of the intestine (jejunum) and the final part of the small intestine(ileum) around 20% of children and 4% of adults have this type. The patient may have cramping after taking meal and abdominal pain. Children who affected by this type may have delayed growth development. People with jejunoileitis susceptible to have more severe complications. Also, patients could suffer from other symptoms such as arthritis or skin lesions.
Crohn's (granulomatous) colitis: This form affects colon only. Patients with colitis have inflammation in the colon. This type is affected around 60% of Crohn’s disease. However, about 20% of this type affected in the colon only. Approximately (30% to 45%) of people with Crohn’s disease have granuloma which is a small area of inflammation in tissue. Crohn’s colitis shows similar symptoms of ulcerative colitis. It is tough to distinguish between the two types of disease (Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s colitis). The main symptom is diarrhea, while inflammation in the colon can cause rectal bleeding than inflammation in the small intestine. Also, the patient could have other symptoms like fistula, skin lesion, joint pain, and abscesses around the anus. Furthermore, the patients tend to have more than one type at the same time which lead to affect more parts of the body.
Most common parts of the pathology:
Most cases of Crohn’s disease affected the small intestine only by around 33%, while about 20% just in the colon, while approximately 47% of cases involved in both the small and the large intestine. According to this percentage, that means the small intestine has around 75% of the cases (the terminal ileum affected by around 90%). As shown in the figure up to one-third of patients are affected outside the intestinal tract which is known as an extraintestinal tract.
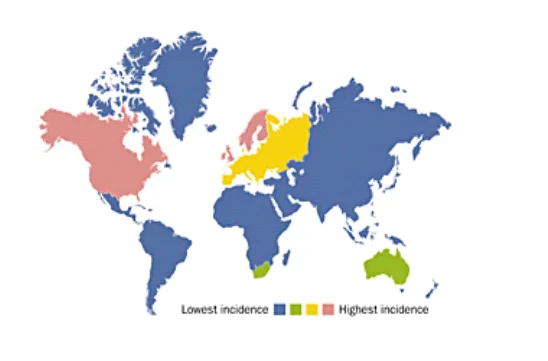
Epidemiology of the disease:
Crohn’s disease is an infirm, and irremediable chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) affecting more than 2.5 million persons in the Western world and the incidence is increasing in the developing world. Several studies show that the prevalence of the Crohn’s disease has a high percentage of occurrence in the western countries like USA, UK, Canada, New Zealand, and Scandinavian countries and western Europe while the rate is low in the developed countries like African countries, Asia and Eastern countries. The percentage of incidence of Crohn disease varies from 26 to 199 cases per 100,000 persons. In the US, approximately around 201 per 100,000 persons have Crohn’s disease. The European (Ashkenazi) Jewish heritage have a high percent of incidence for the Crohn’s disease among other races. They have from 2-4 times higher prevalence than members of the general population. The overall occurrence of the Crohn’s disease in Europe is around5.6 in 100000. In western countries show that the percentage of Crohn’s disease has a slight increasing especially in (Sweden and Denmark). Comparing between the data from the 1980s which reported that the incidence was around 4.1 per 100,000 person-years, while the ratio for 2003-2005 around 8.6 per 100,000 person-years. In North America, the highest percentage for Crohn’s disease was 319 per 100.000 person-year, while in Europe the portion was 322 per 100,000 persons. The highest incidence percentages were 20.2 per 100.000 person-year in North of America, comparing to Europe the rate was around 12.7 per person-year. In Asia and the Middle East, the ratio is 5.0 per 100.000 person-year. Overall, the studies show that there is a significant increase in the percentage of Crohn’s disease by around 75% over the time.
Age, sex, and race-related demographics:
Despite that, the Crohn’s disease can occur at any age, but the disease has two peaks of distribution. The first peak occurs between the late adolescent early adulthood (15-30 years), and another generation could be identified which has the range of 60-70 years of age. However, the majority of the cases which had been diagnosed so far had been observed within the patients who had not reached the threshold of 30 years of age. Within this entire observation, the approximate measure of 20-30% of the cases had been associated with the patients who had been reached 20 years of age and had been diagnosed with Crohn disease. The proportion of older patients who had been diagnosed with the colonic and distal Crohn disease had been considerably high. On the other hand, the patients who have been of comparatively young age, had exhibited greater propensity towards contracting the ileal disease, to the most extent. Apart from this, the Crohn’s disease is also reflective of the fact that affected personnel are comprised by both male as well as female patients. However, the higher rates of prevalence are observable in women only. The rate of prevalence could be understood to be (1.1to 1.8 times) higher in women in comparison to that of men, primarily in the western nations.

Pathophysiology of the Crohn’s disease:
Although the cause of Crohn’s disease is still unknown, there are many hypotheses involves in the disease including (Genetic, environmental factors, and other factors.). Every person has unique pathogenic that composed of these factors. In spite of the fact 40 microbes had been utilised including those of the bacteria, viruses and yeast, along with the utilisation of in excess of 100 genes concerning the pathophysiology of Crohn’s disease, it could be determined that the causality of CD is not associated with any specific or individual factor. In terms of this, the more current as well as greater applicable hypthesis could be understood in the form of this particular disease being engendered by a diversified as well as multiplicity of factors which completely neutralize both the genetic as well as the immunity system of the host of such a disease and compromise the ability of the host to resist to the effects of the disease.
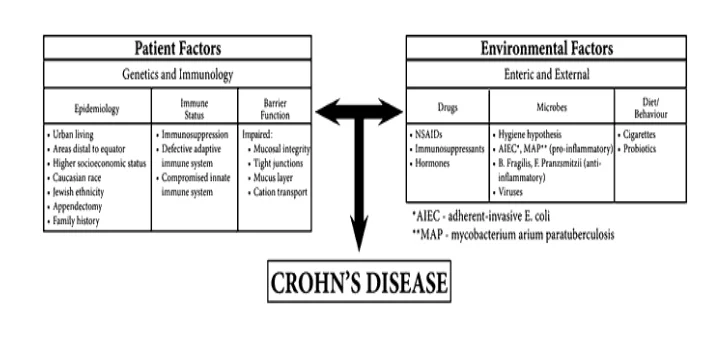
The etiology of Crohn’s disease
The hypothetical constructs, formed currently, regarding the etiology of Crohn’s disease, is indicative of the mutual influence of both the factors of environmental and patient related factors. The factors related to the patients could be understood to be the variables of epidemiological observations as well as demographical studies, status of immunity which could be observed within the patients and, ultimately, the functioning of the intestinal epithelial barrier. The environmental factors could be understood to be both enteric and external in nature. Such factors are identifiable as, enteric pathogens (bacteria, viruses, and fungi), and drugs (Springer, Cham 2015).
The immune system and Crohn’s disease:
Crohn’s disease described as an autoimmune disease. The immune system has a serious role in the progression of the disease. Apart from this, the specific disease could be understood to be engendered through various factors such as the environmental ones and these contribute in the disturbance of the mucosal barrier as well as having detrimental impact upon the balance of gut microbiota. Apart from these, such factors also are responsible for the stimulation of the immune system within the human body. The immune system generates effective responses to the stimuli of injury which could be received at individual cells as well as to the influence of the microbes infiltrating the immune system through the utilisation of the molecular processes which involve secretion of IgA, Toll-like receptor (TLRs) mediated recognition and autophagy. In this context, the most significant cellular components could be identified as the epithelial Paneth cells, macrophages and dendritic cells. With the detection of any antigenic insult, the immune system which is innate to the pathological conditions of the patient, initiates the pro-inflammatory cascades and also triggers the adaptive immune system. This directly contributes to the occurrence of inflammation. The damage to the cells as well as the progressive inflammation in the innate and adaptive immunoactivities is generally caused by the dysregulation of the process.

In CD, with the detection of any antigenic insult, the immune system which is innate to the pathological conditions of the patient, initiates the pro-inflammatory cascades and also triggers the adaptive immune system. This directly contributes to the occurrence of inflammation. The damage to the cells as well as the progressive inflammation in the innate and adaptive immunoactivities is generally caused by the dysregulation of the process. (Springer, Cham 2015)
Innate immunity:
With the recognition of the signature of the molecules, the activation of the responses from the innate immune systems takes place. This occurs in the form of a luminal pathogen through the format of a pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP) or in the intracellular process through the manner of damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) which could directly result in the injury to the cells. The majority of the inflammation-inducing pathways get triggered with the recognition of the pattern recognizing receptors (PRRs) which are primarily located on the effector cells. Such responses are primarily mediated by receptors and are also involved in the formulation of the samples of the intestinal microflora of the individual under consideration and could as well contribute to the prevention of the dysbiosis or “bacterial imbalance.” The indications could outline the reduced diversity of intestinal microbiota and Dysbiosis and this could as well be related to the CD patients whenever the comparison could be undertaken concerning the healthy controls.


Pattern recognition receptors
Within the lumen, the Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) generally perform the recognition of the pathogen associated molecular pattern (PAMPs) which generally takes place at the surface of the virus, fungi and bacteria. The PRRs generally recognise the pathogen damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) at the intracellular space. Such observations are mostly derived from the fragments of the cells or through the sate products. These PAMP and DAMP mediated recognition processes generally result into the conditions which could be understood to be immune responses which are inclusive of the IgA and proinflammatory cytokine production and epithelial proliferation (Springer, Cham 2015) .
Genetic Factors:
One of the most significant and substantial impacts on the progression of the disease could be identified to belong to the genetic factors. Various significant genes such as NOD2, IL23R, ATG16L1and IRGM are directly related to the Crohn disease and these are also closely integrated in the functioning of the immune systems. The proteins which are generated by these specific genes, consequently assist in the responses of the immune system to the existence of bacteria within the digestive tract. The process of autophagy is influenced by these proteins and this process is utilised by the cells for the purpose of surrounding and eliminating the identified viruses and bacteria. The variability in such genes could lead to the alteration of the autophagy and could result in the disruption of the responses of the immune system towards the existence of the bacteria within the digestive system. The interaction between these genes and the environmental factors include drugs, bacteria, fungi, or virus leads to alteration the in the host immune system which affects the inflammation process and the gut mucosal integrity. Various studies have been able to recognize approximately 200 variations of the genes which could impact the conditions of risk probability regarding the Crohn’s disease. The proper understanding regarding the activities of such genes as well as the process through which these affect the immune system has still not been developed. However, it could be understood that these are mostly responsible for the alteration of the functioning of the immune systems in various manner. Whenever these genetic changes could be comprehensively considered, it could be understood that such genetic changes could be attributed the responsibility of undertaking of only a minor and miniscule percentage of development of risk potentials of Crohn disease which could be identified to be induced by different genetic factors.

Inheritance
Crohn's disease could be perceived to be condition which is prompted by multiple factors. This denotes the probable association of this with the influence of multiplicity of genes which are reflective of the influences of both of the environmental and lifestyle related factors. The presence of the autoimmune diseases within the family lineage, under variety of circumstances, could pose significant risk for the emergence of similar autoimmune diseases in the relatives and members of the families. However, the presence of any autoimmune disease within the family, in the manner of the Crohn's disease, is not a direct and assured condition for the development of the autoimmune disease in the family members. In terms of the existence of the autoimmune disease, it could be understood that the family could be affected and there could be the existence of a predisposition, genetically, within the family, which could increase the probability of any particular individual of the family getting affected by the autoimmune diseases. Thus, it could be understood that having any member affected by genetic autoimmune diseases could lead to the enhancement of the risk factor concerning the Crohn's disease.
Environmental factor:
As per the available evidence regarding enhancement of the incidence in the Crohn's disease within various developed nations, it could be understood that various studies have highlighted the fact the incidence of Crohn's disease is extensively influenced by the environmental factors as well. Amongst these, smoking could be considered to be a factor of Crohn's disease which could exacerbate this and various other environmental factors could as well be investigated concerning their association with Crohn's disease and regarding their roles in enhancing the probability of the Crohn's disease. These factors could be identified as infectious agents, diet, drugs, stress and social status. These have been evaluated in detail in the accompanying review. Apart from this, particular Mycobacteria, oral contraceptives and antibiotics could also play significant roles in the Crohn's disease. Apart from this, the likelihood of enhancement of the Crohn's disease propensities through the utilisation of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for significantly longer durations especially within female patients, could be significantly higher. The consumption of antibiotics over a significantly longer period of time could lead to the enhanced propensities of development of Crohn's disease and the associated risk. Various researchers have observed and outlined the proposition that consumables which are considerably saturated in sugar, omega-6 fatty acids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, total fat, meat, and oil could considerably contribute in the propagation and incidence of the risk of Crohn's disease. In such a case the consumption of the fibrous sustenance and fruits could reduce the risks associated with Crohn's disease.

Conclusion:
Crohn's disease is an autoimmune disease that produce an inflammation mainly the intestinal part of the body. Although there are many studies that have shown many factors about Crohn’s disease, the primary cause still has not been identified and fully understood. Researchers indicate that the pathophysiology of the Crohn’s disease is complex, however the disease result from a combination of many factors like genetic and immune system and other factors like an environmental factor that disrupt the immune system. Overall, the prevalence of Crohn’s disease has been increased over the time especially in the western countries.
References
Payam Behzadi, E. B. a. R. R., 2015. The Incidence and Prevalence of Crohn’s Disease in. Symbiosis Open Access Journals.
Ray Boyapati, J. S. G.-T. H., 2015. Pathogenesis of Crohn's disease. PubMed Centeral(PMC).
Robert J. Klein, X. X. S. M. J. W. J. H., 2010. Successes of Genome-wide Association Studies. Cell Press.
Connelly T.M., Koltun W.A. (2015) Molecular and Genetic Factors in Crohn’s Disease. In: Fichera A., Krane M. (eds) Crohn’s Disease. Springer, Cham
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



