Comparative Analysis of Smoking Cessation Treatments
Introduction:
The present research is conductedin order to determine the impact of various treatments on the smoking habits of the people and this process affects the smokers. For this purpose, the trial was performed to compare a pharmaceutical drug (varenicline), nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) patches, e-cigarettes, and placebo e-cigarettes (no nicotine). After the trial was completed, a follow-up was organised after a gap of six months. The present report tries to analyse the data collected from the trail and the follow-upin order to determine which, if any, treatment is more effective at helping people to quit smoking .Other than to understand what factors are affecting smoking cessation process. this research also highlights the importance of seeking healthcare dissertation help for comprehensive insights into such topics.
Aim of the research
The primary aims and objectives that this study proposes to achieve are:
To understand the effects of various treatment of smoking cessation process
To understand different methods better assessment of nicotine dependence.
To understand all the factors that are affecting the smoking cessation process.

Context of the research
The background of the research is to understand different effects of the smoking cessation treatment. For this, pragmatic randomised controlled trial of smoking cessation products have been started. The trial compared a pharmaceutical drug (Varenicline), nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) patches, e-cigarettes, and placebo e-Cigarettes (no nicotine). Six-month follow-up has been completed and it is now your job to analyse the data and write a scientific report for the Principle Investigator of the project.
Research questions
Which treatment is most effective? The primary aim of this study is to determine which, if any, treatment is more effective at helping people to quit smoking.
Is a clinical diagnosis or self-reported information a better assessment of nicotine dependence?
Are the results for self-reported cessation similar to those for serum nicotine level? And do the treatments appear to be as effective when this variable is considered (as a secondary outcome)?
Which treatment, if any, should we recommend for use in clinical practice?
Method
Participants
As per the data, there were a total for 791 participants. 40.1 percent (317) of the participants were male while remaining 59.9 percent (474) of the participants were female. People who were aged had 18 years or older, smoked five or more cigarettes per day for the past year, wanted to stop smoking, and could provide consent were eligible for the study via multiple clinics around the country. Then they were referred for undergone any of the four smoking cessation treatment.Choosing of the therapies were randomised between Varenicline, NRT patches, active e-cigarettes, placebo e-cigarettes. Data collection was done by research assistants. All applicants provided informed consent about their participation and the whole study was permitted by the King’s College London Human Research Ethics Committee. At randomisation, the following data were collected on each participant:
Study Design
The study was quantitative in nature. The data was collected and the design of the questionnaire is one of the most difficult and strategic work to do. This experiment used a between-subjects design. To interpret the effects of various treatment of smoking cessation process, the independent variable was different types of intervention as this is randomised in nature and dependent variable is nicotine level serum that is found after testing. Regression analyse was also done where in the same context. To interpret different methods better assessment of nicotine dependence, paired t test was also done.To understand all the factors that are affecting the smoking cessation process, logistic regression was performed to analyse relation between the nicotine levels of serum and self-reported cessation. Self-reported cessation,categorical variable, is the dependent variable here. The nicotine levels of serum is the independent variables for assessing its effect on the dependent variable.
Procedure
After the collection of data, at first descriptive analyse was done to understand the data and visualizing it properly. The primary aim of the data is to interpret the effects of smoking cessation programme. For fulfilling the aim, it is essential to know that the participants have ever tried to quit smoking and they are already motivated for quitting smoking was needed to know that’s why data was analysed.In order to motivate participants to quit smoking, different participants underwent different treatment namely; pharmaceutical drug (Varenicline), nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) patches, e-cigarettes, and placebo e-cigarettes (no nicotine). For comparing and determining the effectiveness of different treatments by mean (Kim, 2014), Chi-square and one-way ANOVA testing was performed. In one-way ANOVA, null hypothesisisthatthere is no statistically significant difference between the four treatments and alternative hypothesis is thatthere is statistically significant difference between the four treatments.The Chi-square test was performed so as to determine whether there any difference in the effectiveness of the treatment and self reported smoking cessation status of the participates (McHugh, 2013). Then regression was performed to verify the dependency in between dependent variable (Serum level nicotine of nicotine) can be explained by the independent variable (type of intervention).To compare clinical diagnosis and self-reported information as a better assessment of nicotine dependence paired t-test was performed (Stephanie & D. Wilkerson, 2008) in between two pairs as there is the two types of clinical diagonosis process with respect to HSI. The first pair of the paired T test is between DSM V and HIS where null hypothesis is there is no statistically significant difference betweenDSM V and HIS and alternative hypothesis is that there is statistically significant difference between DSM V and HSI. The second pair of the paired T test is between DSM R and HISwhere null hypothesis is there is no statistically significant difference betweenDSM Rand HIS and alternative hypothesis is that there is statistically significant difference between DSM Rand HSI. Reliability test was performed also to understand the reliability (Tavakol & Dennick, 2011) of clinical diagnosis. Kappa test was also performed for checking the reliability of DSM V mode of clinical diagnosis of nicotine dependency. Same test was also performed for validating the self-assessment report of high smoking index in the context of other two clinical diagnosis method. To determine if the results for self-reported cessation similar to those for serum nicotine level was 1 sample t-test was performed to determine whether the results for self-reported cessation similar to those for serum nicotine level which is 2.0 mg/ml. To fulfil the secondary objective of the question, binary logistic regression was performed to analyse relation between continues independent variable the nicotine levels of serum and categorical dependent variable self-reported cessation. For recommending proper clinical process result of ANNOVA and chi square of type of intervention variable was analysed in the context of cost of different treatment and proper treatment was recommended according to it.
Results
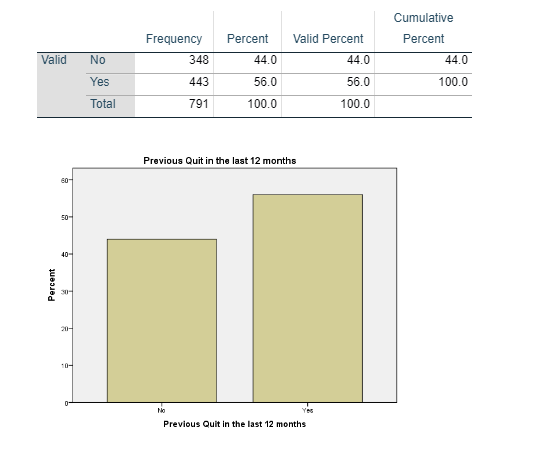
The collected data shows (Figure 1) that out of 791 participants, 44 percent of the participants, that is, 348 participants had tried to quit smoking in the last 12 months. On the other hand, 56 percent of the participants, that is, 443 have not tried to quit smoking in the last 12 months.
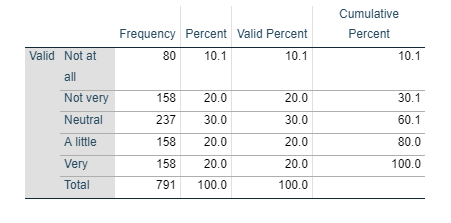
The survey data also shows (Figure 2) that out of 791 participants, 10.1 percent of the participants never had a quitting motivation, 20 percent of the participants are not very motivated for quitting, 30 percent of the participants are not sure whether they want to quit smoking or not, 20 percent of the participants are bit motivated to quit smoking, and the remaining 20 percent of the participants are highly motivated to quit smoking.
In reply to the question that whether the participants are living with other smokers, 40.1 percent of the participants said that no they are not living with other smoker, while the remaining 59.9 percent of the participants agreed that yes they are living with other smokers (Figure 3) .
In response to the Cessation Training Program, 82.2 percent of the participants disagreed that their clinic does not have any cessation training program. Only 17.8 percent of the participants said yes that they do have cessation training program provided that the clinic they visit (Figure 4).
To determine which treatment is most effective at helping people to quit smoking
ANOVA table (Figure 5)compares the impact of the categorical variable intervention on Serum level Nicotine of Nicotine. The four categorical variables were a pharmaceutical drug (varenicline), nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) patches, e-cigarettes, and placebo e-cigarettes (no nicotine). The table shows that the p-value or the significance value of the analysis comes out to be 0.175, which is greater than 0.05 (Dahiru, 2008). It means that obtainable null hypothesis is accepted and the alternative hypothesis is rejected. That is, there is no statistically significant difference between the four treatments. All the treatments have a similar impact on Serum level Nicotine of Nicotine.
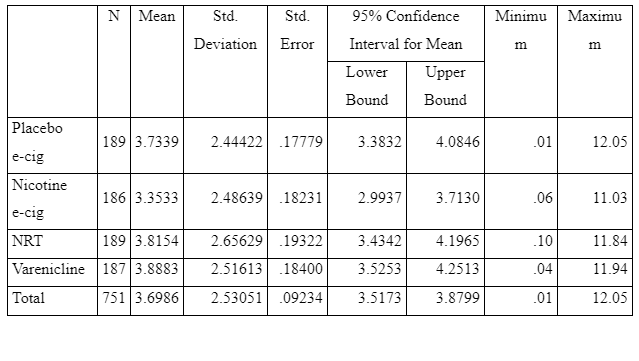
Though it shows that there is no statistically significant different between the nature of treatment, but it does not tell anything about the mean of Serum level Nicotine of Nicotine of the four tests. This mean can be compared trough the figure 6. As per the figure, the mean for the pharmaceutical drug (varenicline) is 3.8883, nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) patches is 3.8154; e-cigarettesare 3.3533, and placebo e-cigarettes (no nicotine) is 3.7339. This clearly shows that there is not much difference between all the four treatments. Serum level of nicotine (smokers who have abstained from tobacco products for at least two weeks should have a serum nicotine level less than 2mg/ml. As per report the mean of e-cigarettesare 3.3533mg/dl is less than others and near to 2mg/ml, which depicts that e-cigarettes is little more effective than other methods.
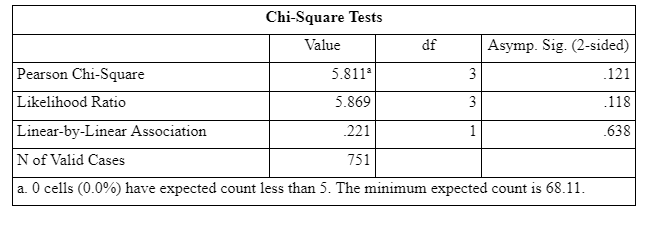
The Chi-square test was performed so as to determine whether there any difference in the effectiveness of the treatment and self reported smoking cessation status of the participates. From the chi-square test, it can be said that since the p-value or the significance value of the test comes out to be greater than 0.05, there is statistically no significant difference in the effectiveness of different treatment on the self reported smoking cessation status of the participants. The table shows (Figure 7) depicts the result of chi square test between self-reported smoking cessation statuses from the view point of each treatments’ effect:
Placebo e-cig treatment 69 participants agreed that they did not have more than five cigarettes in the last six months
Nicotine e-gig treatment 78 participants agreed that they did not have more than five cigarettes in the last six months
NRT treatment 57 participants agreed that they did not have more than five cigarettes in the last six months
Varenicline treatment 71 participants agreed that they did not have more than five cigarettes in the last six months
From this chi square test it can be interpreted that there is almost no significant difference in these treatments like pharmaceutical drug (varenicline), nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) patches, e-cigarettes, and placebo e-cigarettes (no nicotine). But however ,Nicotine e-gig treatment is become somewhat successful than other treatments as the data is almost not biased and number of participants are more who agreed that they did not have more than five cigarettes in the last six months.
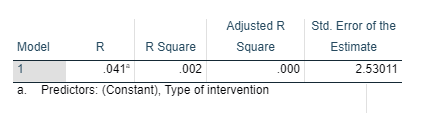
The model summary (Figure 8) provides the value of R and R2 values. The Rvalue represents the simple correlation and is 0.41 which depicts positive correlation between Serum level nicotine of nicotine and type of intervention. The value of R square is 0.02 which depicts that’s only 0.02% of dependent variable (Serum level nicotine of nicotine) can be explained by the independent variable (type of intervention).
This table (Figure 9) indicates that the regression model predicts the dependent variable not well. As the significance value of the analysis is .266, more than 0.05 which depicts the regression model statistically does not predict the outcome variable. Hence it can be interpreted that only type of intervention variable could not able to express the Serum level nicotine of nicotine. Other factors further can be analysed for getting a significant regression model. Further study can be done on that.
To compare clinical diagnosis and self-reported information as a better assessment of nicotine dependence
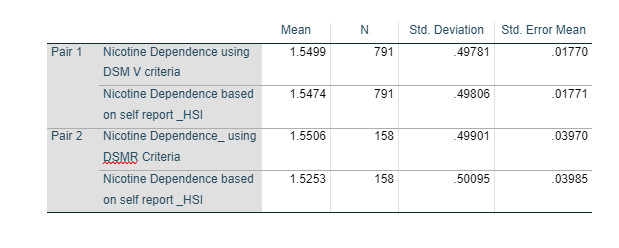
Figure 11 shows the mean for both the criteria. As per the table, mean for DSM V is 1.5499 and DSM R is 1.550 while the mean for HSI is 1.5474 and 1.5253 respectively.
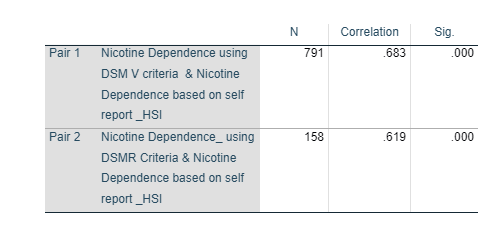
Figure 12 shows that there is a positive association between DSM V and HSI as the correlation coefficient comes out to be 0.683 (Mukaka, 2012). Also this table shows that there is a positive association between DSM R and HSI as the correlation coefficient comes out to be 0.619.
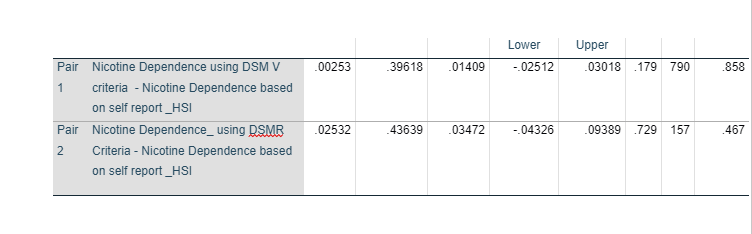
Figure 13 shows that there is a mean difference of 0.00253 betweenDSM Vand HSI. Further, the t-value comes to be 0.179 with a p-value of significance value of 0.858. P-value or the significance value of the analysis comes out to be 0.858, which is greater than 0.05. It means that obtainable null hypothesis is accepted and the alternative hypothesis is rejected. That is, there is no statistically significant difference betweenDSM Vand self-reported information.
Figure 13 also shows that there is a mean difference of 0.02532 between DSM R and HSI. Further, the t-value comes to be 0.729 with a p-value of significance value of 0.467. P-value or the significance value of the analysis comes out to be 0.467, which is greater than 0.05. It means that obtainable null hypothesis is accepted and the alternative hypothesis is rejected. That is, there is no statistically significant difference betweenDSM R and self-reported information.
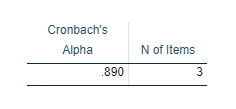
Reliability test between DSM V and HIS (figure 14),DSM R and HIS (figure 15), DSM V and DSM R(figure 16),DSM V ,DSM R and HIS (figure 17) had done and Cronbach’s alpha values (Tavakol & Dennick, 2011) were resulted 0.812, 0.765, 0.924 and 0.890 respectively. This indicates a high level of internal consistency in all 3 three diagnosis procedure including two clinical diagnoses with this specific sample. This proved that clinical test are reliable.
The reliability of the clinical diagnosis DSM V:
Cohen's kappa (κ) is such a measure of inter-rater arrangement for categorical measures when there are two raters scale. So Cohen's kappa (κ) test can be performed to determine inter-rater arrangement of DSM V with two other method: DSM R (clinical diagonosis) , HSI (self-report assessment).
The result of kappa measurement between DSM V, one method of clinical diagnosis with HSI, other method of self-assessment was reported .683 ( Figure 22) which denotes that there is almost 68% similarities between two clinical methods for assessing nicotine dependency. .61 to .80 value of kappa result interpret that two agreement can be treated as substantial agreement (McHugh, 2012). So it can be depicted that two clinical diagnosis method DSM V and HIS have significant resemblances in detecting nicotine dependency.
The result of kappa measurement between DSM V, one method of clinical diagnosis with DSM R , other method of clinical diagnosis ,was reported .859 (Figure 21) which denotes that there is almost 86% similarities between two clinical methods for assessing nicotine dependency. .81 to 1.00 value of kappa result interpret that two agreement are almost perfect agreement (McHugh, 2012). So it can be depicted that two clinical diagnosis method DSM V and DSM R give almost same result.
Any kappa more than .60 indicates adequate agreement among the raters scale so confidence can be placed (McHugh, 2012). From the result of both test, it can be depicted that DSM V, clinical diagnosis method is reliable as the result of this assessment technique have almost significant to high level of similarities.
The validity of self-reported assessment (High Smoking Index)
For checking the validity and the reliability of High smoking index, same kappa analysis can be performed in the context of other clinical diagnosis test. Obtaining a clinical diagnosis is more expensive that’s why the reliability check is needed. If the reliability self-reported assessment of High smoking index was proved, the expensive diagnosis method would not be needed then.
The result of kappa measurement between DSM V, one method of clinical diagnosis with HSI, other method of self-assessment was reported .683 ( Figure 22) which denotes that there is almost 68% similarities between two clinical methods for assessing nicotine dependency. .61 to .80 value of kappa result interpret that two agreement can be treated as substantial agreement. So it can be depicted that two clinical diagnosis method DSM V and HIS have significant resemblances in detecting nicotine dependency.
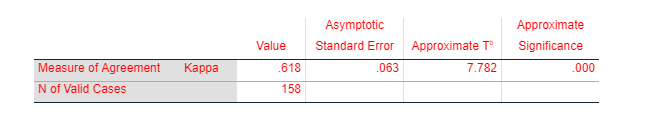
The result of kappa measurement between, HSI , method of self-assessment with DSM R , other method of clinical diagnosis ,was reported .618 (Figure 23) which denotes that there is almost 62% similarities between two clinical methods for assessing nicotine dependency. .81 to 1.00 value of kappa result interpret that two agreement are significant. So it can be depicted that two diagnosis method of nicotine dependency, HSI and DSM R give significant result.
Both clinical diagnosis method show 60%-70% similar agreement with self-assessment report which means 30%-40% variations are there. However, having 40% of the trial estimations being wrong would be an extremely serious quality problem for a clinical laboratory. Any kappa value under 0.60 indicates insufficient agreement between the raters and little confidence should be showed. If kappa value just crossed 0.60 value then high confidence cannot be shown so it can be concluded that the result is significant. As this is a clinical procedure, so it cannot be concluded that the reliability of HIS is too high to be used in future instead of other two clinical diagnosis method of clinical dependency.
To determine if the results for self-reported cessation similar to those for serum nicotine level
The results of the analysis of 1 sample t-test are reported as the mean of self reported cessation comes out to be 3.6986 with a standard deviation of 2.53051 and standard error of 0.09234 (Figure 18).
Figure 19 shows that the one sample t-test comes out to be 18.359 with a mean difference of 1.69861 between self-reported cessation and serum nicotine level. Further, the significance value or the p-value comes out to be 0.00 shows that there is significant statistical difference between the self-reported cessation and serum nicotine level.
However for better understanding the variable nicotine level of serum, logistic regression was performed mainly for evaluating relation between the nicotine levels of serum and self-reported cessation and some other factors are also taken. Thetable (figure 20) contains the Cox & Snell R Square and Nagelkerke R Square values, which are both methods of calculating the explained variation. These values are sometimes referred to as pseudo R2 values (Adwere-Boamah, et al., 2015). Therefore, the explained variation in the dependent variable based on the model ranges from .07% to .09%, depending on whether to reference the Cox & Snell R2 or Nagelkerke R2 methods, respectively. Hence it proves that variable nicotine levels of serum is significantly different from the self-reported cessation as the dependent variable self-reported cessation only show 07% to .09%, variation when the independent variable nicotine levels of serum is added to the model.
Treatment, if any, recommended for use in clinical practice

The present shows that all the four treatments, that is, pharmaceutical drug (varenicline), nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) patches, e-cigarettes, and placebo e-cigarettes (no nicotine) have similar effectiveness at helping people to quit smoking. The chi-square test and the one way ANOVA test clear shows that all the test are equally effective in abstaining people from smoking and there is no much difference between them. However, when the data is almost unbiased then Nicotine e-gig treatment is become somewhat successful than others according to chi square test. When the cost of treatment is also considered in determining the effectiveness of the treatment, it can be said that Nicotine replacement therapy patchesseem to be the most economical treatment at helping people in quitting smoking. The cost of 12 week course of Nicotine replacement therapy patches is GBP 135, whereas, the cost of Varenicline and Active e-cigarette for a 12 week course is GBP 165 and GBP 250 respectively. According to the chi square result of cross tabulation only 57 participants agreed that they did not have more than five cigarettes in the last six months where 71 participants of Varenicline treatment agreed that they did not have more than five cigarettes in the last six months. Nicotine e-gig treatment seems to be best according to test but it is most costly also where Nicotine replacement therapy patchesseem to be the most economical treatment but its effects is somewhat less than other treatment. However Varenicline treatment is not as costly as Nicotine e-gig treatment but the reported result of according to the participants, it seems to be more effective than Nicotine replacement therapy. It can be stated that pharmaceutical drug (varenicline), is the most effective treatment among all the four treatments and should be used in clinical practice.
Discussion
The above analysis was performed to determine the impact of various treatments on the smoking habits of the people. For this purpose a sample of 791 participants was selected who underwent four different types of treatments namely; pharmaceutical drug (varenicline), nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) patches, e-cigarettes, and placebo e-cigarettes (no nicotine). The primary analysis shows that all the treatment are equally affecting in abstaining people from smoking. From the result of ANNOVA and chi square, it reported that all the treatment are equally affecting more or less same. Different clinical diagonis process was analysed and result of paired t test was depicted that there was no significant difference between clinical assertion and self reported assertion. Cronbanch’s alpha also reported that the clinical diagonis are highly reliable and the results for self-reported cessation not similar to those for serum nicotine level. Kappa value was also reported from that it can be understood that DSM V, the clinical diagnosis method is reliable according to its similarity with other mode of assessment. Self-reporting assessment method of nicotine dependency through High Smoking Index (HSI) can be not be recommend for using in future instead of clinical method as it can only show similar in 60 percent cases which indicates that it resulted 40% variation with the other mode of diagnosis that’s why it cannot be relevant as 40 percent variation is regarded as extremely serious quality problem. However, when the cost of treatment is also considered to determine the effectiveness of the treatment, it can be said that pharmaceutical drug (Varenicline), seems to be the one most effective treatment among all the four treatments and it is not too much costly, so it can be recommeneded for using in clinical practice for helping people in quitting smoking.
References
Adwere-Boamah, Joseph, H. & Shirley, 2015. Predicting social trust with binary logistic regression. Research in Higher Education Journal , Volume 27, pp. 1-6.
Dahiru, T., 2008. P – Value, A True Test Of Statistical Significance? A Cautionary Note. Annals of Ibadan Postgraduate Medicine , 6(1), pp. 21-26.
Kim, H.-Y., 2014. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) comparing means of more than two groups. Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics, 39(1), pp. 74-77.
McHugh, M., 2013. The Chi-square test of independence. Biochemia Medica, 23(2), pp. 143-149.
McHugh, M. L., 2012. Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic. Biochemia Medica, 22(3), pp. 276-282.
Mukaka, M., 2012. A guide to appropriate use of Correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Medical Journal : The Journal of Medical Association of Malawi , 24(3), pp. 69-71.
Stephanie & D. Wilkerson, 2008. Application of the Paired t-test. Xavier University of Louisiana’s Undergraduate Research Journal, 5(1), pp. 1-5.
Tavakol, M. & Dennick, R., 2011. Making sense of Cronbach's alpha. International Journal of Medical Education, Volume 2, pp. 53-55.
Appendix













Continue your exploration of Comparative Analysis of Share Prices Before and After Crisis Across Different Country Types with our related content.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



