The Dynamics of Forex Markets
Chapter 1:
Introduction
The flow of money and its rates are the bloodstreams of an economy. Economic strength differs from country to country, and its currency and exchange rates tell us many things about the economic situation of that country. The foreign exchange, FX or forex market is the market in which currencies are traded. It is a decentralized market what is open 24 days where a currency value is determined by supply and demand like any other commodity. According to BIS (Bank for international settlements), global FX markets averaged $5.1 trillion per day in 2016, what makes Forex is the biggest and most liquid of financial markets globally. If you require assistance with understanding these concepts for your studies, seeking economics dissertation help can provide valuable insights and support.
Historically, Britain has the largest share of the forex market, with about 40 per cent of all transactions taken place in London. The abolition of all foreign exchange controls in Britain in 1979 was instrumental in the development of the forex market. Vast numbers of stakeholder are involved in this market, which is directly involved due to financial evolution and its importance. They are including the country's central bank, commercial bank, institution, broker, individual, etc. Because of the involvement of multiple stakeholders and their interest, decision, or situation have a significant impact on these markets and create opportunity and volatility.
Constant related global news and update of countries economic indicator give a fresh strategic reason for the trader to involve in this market and make the market very interesting. Information of its factor gives the trader more confidence to understand the expected movement for supply and demand. Even though the retailer combined the only fraction of this massive global market but still a considerable number of people have an interest in the foreign exchange market. Traders get involved in the short term, or long term trading in a different currency based on their strategy and wants to find the opportunity in the market by speculation of future price or value of the currency.
Background of the study
Currencies are traded in pairs, thus forecasting future movement in the price of a currency pair or foreign exchange rate of an individual currency is very challenging. There are many factors, directly and indirectly, affecting the exchange rate.
In early 1960, Eugen Fema developed a theory with a concept that-“prices of financial assets reflect all relevant information. Therefore, price on average accurately, that means the financial market is efficient. A direct consequence is that an active investor cannot continuously beat the market and a passive investor can achieve the same profit on average as the action does. Overall, market values are always accurate, and the future price is randomly depending on randomly incoming news (information)
However, speculator plays an assumption based on the resources they have and try to beat the market in order to maximise their profit or to be on the right side of the trade. If a trader did not make money, they would not last long, and this market would not expand as big as it is and as attractive as it is now. A scientific explanation of what and how much movement can occur in currency against another's is a very complex task and academics are arguing about market efficiency theory. The question of how much foreign exchange market gets affected by macroeconomic fundamentals news and prediction is unknown.

There are many factors that moves the forex market, including but not limited to Supply and demand, Central banks/ government decision, Economic performance, Credit ratings, Sentiment, Foreign affairs, Political stability.
Research Objectives
After 1973 the collapsed of Breton Wood System foreign exchange rate Forecasting become very volatile. Many business decisions and government foreign policies based on finance are depending on the future exchange rate.
The investor needs to calculate the spot and forward exchange rate to dictate foreign transaction volatility. Pilbeam (2013), said policy-makers and Economists are concerned about the implication of foreign exchange rate changes in the global market and take action on their balance of payment based on real, nominal and effective exchange rate.
The objectives of this research project are to understand the foreign exchange rate behaviour on the development of news and economic factor in large. Forex market runs around the clock 24 hours, and also every day there are many economic data releases some have a significant impact on the weight of the currency some could be light depending on the expectation and market sentiment. Some of the economic data releases contain the figure what directly affect the market movement. The purpose of this research is to investigate identify, and market reaction with data outcome as economic event unfold throughout the day.
Chapter: 2:
Literature Review
Money is the main bloodstream in the economy. Eun and Resnick (2004) said money represents purchasing power. Produced domestic product convert into money and give the ability to exchange it for foreign goods and service for essential daily and business life. How much product a certain amount of money can buy it depends on its weight or exchange rate or the ability against a foreign currency if it is about buying from abroad. Because of the different value of the same currency amount of product or same item can cost a different amount in a different country. For example, a product may cost 10 pounds in the United Kingdom, and if you want to buy that product from Spain you cannot buy it with 10 euro as pound and euro rate are not same. If 1 pound is equal to 1.10 euro, than to buy a 10-pound worth of product we will need 11 euro. The rate of that currency or exchange rate brings the solution to convert money and its value to different currency.
There are many literature reviews about the exchange rate, market movement speculation and economic model for the foreign exchange rate. They all tried to identify the forex behaviour forecasting. Like any other market participants, we can divide the foreign exchange market player into three main categories they are investor, speculator and trader. They all might have a different strategy in place, but the ultimate goal is to maximise the profit. It is said to finance start with investor .there are an individual investor and institutional investor depending on whose investment are involved. Traders are the athletes in the market. They are always focused on the market and keep searching for opportunity. On the other hand, the speculator is the one who use their insight and intuition to predict future market movement or value. It is assumed all investment in a way speculative, hoping market will react to traders favour in an uncertain market environment however What makes speculator different then a gambler calculates the risk taken and expected a return on investment.
Different scholars have a different view of a speculator. Not everyone has a similar attitude about the matter. Olser (1995) think Speculators activity could be a source of a random walk. However, as we can understand, speculation can be informed and stabilising force. On the other hand, Keynes (1930) and Hicks (1946) believed-the role that speculation plays in facilitating financial market transactions by providing liquidity that allows hedgers and other market participants to find counterparties without the need for large price concessions swiftly. Informed and Uninformed Speculation plays big rules in the forex market. Example of it could be we see big movement happen when the expected result turns out to be wrong. Black (1986) claimed that the interaction of informed and uninformed activity was essential to the smooth functioning of financial markets. Noise, he stressed, was the “the arbitrary element in expectations”.
De Long et al. (1990) provide a model where speculative noise constraints informed traders from benefiting from their knowledge. In a way, speculator provides liquidity in the market and assumes the market risk and play essential rules. Not all scholar have a positive attitude towards speculator, Friedman (1953) said though speculator can be informed and uninformed informed speculator making a profit by trying to buy when the price in low intrinsic value and sell it high, limiting volatility and driving loss-making uninformed speculator out of business. Keynes (1936) shows a negative view of speculation by regarding it as a myopic, sentient-driven activity, dominated by the desire to “beat the gun” or “outwit the crowd”. Sometimes they can create a speculative bubble by increasing demand. Most speculators rely on short term trading strategy. As a result constant market factor update and news feed oil the wheel of continuous trading flow.
Meese and Rogoff (1987) proved a random walk beats any attempt to predict exchange rates with macroeconomic models, especially in the short term, and out-of-sample period. The argument about speculation and importance of speculator in the market is on-going among scholar; however, we can stress speculation must be an essential factor in the financial market. We can also say the main two concepts of speculation random and disruptive and informed and beneficial in the market. Informed and beneficial information should be the one what market trader would look for in order to adjust them self with the markets actual value.
The basic principle of the efficient markets hypothesis is that current market prices reflect the total knowledge. So, any new information must be spread to the market quickly and thoroughly so that they can adjust the prices instantly as the information flows. A most important source of information currently is news what reach among the trader worldwide. Historically we have seen the increasing number of news channel throughout the glove, and they are continually updating the financial and related information to the public.
So the big question arises, do the news create an opportunity for speculator? If so, how much and what extend as the market is continually updating with the latest information. I tried to find out what other scholar thought about it and what extent they have found any potentially exploitable trading patterns.
Historically Scholar tried to understand through their investigation about the potential effect and how the reaction of the market comes over data release. The debate and research are ongoing. Among the many researchers, Jagerson and Hansen (2011) think economic announcement and other news events as a wild card in this market. Even though no one knows when the news will explode in terms of market reaction, but long term understanding how different Currencies trend to react to particular news events can be used in the trading strategy. As a result, forecasting or speculation is a big part of the currency move. News and macro-economic data are widely used to test for informational efficiency in the market. Few scholar analysis shows efficiency in the spot foreign exchange market. Like Laakkonen, (2009) found that macroeconomics news significantly affects exchange rate often resulting in a jump the rate of the currency, and it also increase the volatility. Hogan and Melvin (1994) investigated that US trade balance news on exchange rate levels and volatility. They found a significant impact of US trade balance on the JPY/USD.
Ito and Roley (1987) examine news on inflation, industrial production and money shocks from the US and Japan they also experienced the impact of the news especially unexpected data news give market more movement and quite rapidly. Hakkio and Pearce (1985) investigated on seven exchange rates. They have used data similar to that of Hogan and Melvin (1994) and Ito and Roley (1987). Their study shows too exchange rates respond quite rapidly to US money supply innovations, but not to other types of US news. Evans and Lyons (2007) found in their investigation arrival of macro news can account for more than 30% of daily price variance. They had two account features of their analysis for that finding first They used a broad spectrum of macro news schedule, and unscheduled announcement market participants observe second they allowed the arrival of news to affect prices indirectly via its impact on the volatility of order flow. Their analysis of intraday data shows that order flow contributes more to changing FX prices in the period immediately following the arrival of news than at other times.
Almeida, Goodhart, Payne, (1997) believed macroeconomic news announcements have sort term effect on the exchange rate; in the long run, their effects are rather insignificant. Leonard, Linda and Adam (2008) found that new economic data affect asset price such as stock, bond, foreign exchange market. However, they found out few announcements have a more significant impact on the market than others, such as nonfarm payroll, GDP, and manufacturing report. They also found out in their analysis direction of this effect give a suggestion that stronger than expected result rise in the exchange value of the dollar. Edison (1996) stressed that Reactions to macroeconomic indicators are not always linear, and positive surprises can lead to negative impacts and vice-versa. How much impact experienced varies in different currency pair as the true value of the currency may not affect straightway.
Chaboud et al. (2004) found that the exchange rate responds very quickly to the unexpected component of data releases also News releases cause the volume to raise, and to remain elevated for a more extended period. According to their finding after the release price usually suffers the most significant changes within the first 20 minutes, and the unusual volatility activity is dissipated up to two hours. This is due to market participants urge to adapt their positions as fast as possible to the new information (Rezania, Rachev, Sun and Fabozzi, 2010). Ederington and Lee (1993) found announcements are responsible for most of the observed time-of-day and day-of-the-week volatility patterns they think the bulk of the price adjustment to a major announcement occurs within the first minute and volatility remains substantially higher than normal for roughly fifteen minutes and slightly elevated for several hours.
Market reaction to the economic data may not get the same importance with time example Brexit vote news over take unemployment data or us presidential election vote over its non-farm payroll data. That is why (Harris and Zabka, 1995; Thawornwong and Enke, 2003) said in their view about variables or Macroeconomic indicators importance change over time and have different impacts during regressions or expansion periods (Andersen, Bollerslev, Diebold, Vega, 2004). Harris and Zabka (1996) investigated daily data on six currencies to examine the impact of statistics contained in the US Employment Report on foreign exchange markets. From their finding conventional regression analysis shows a clear positive relationship between dollar appreciation and employment surprises.
Many models are built using quoted data, which is less precise than actually executed one (Rezania, Rachev, Sun and Fabozzi, 2010). Toberlechner and Shockin (2004) done a survey and found that financial markets may be less about the actuality of economic facts than about how information is perceived and interpreted by market participants and that technological advances have dramatically increased the speed and the amount of available market information. Their result was based on a survey of over 300 traders and journalist. Ramon P.DeGennaro and Ronald E.Shrieves (1998) investigated in public and private information release and their relationship in foreign exchange market volatility. They believed both information sources are effective, and effect is significant in volatility. They also found that unexpected quote arrival positively impacts foreign exchange rate volatility is consistent with the interpretation that an unexpected quote arrival serves as a measure of informed trading. Foreign exchange market also traded in high frequency. In order to exploit the opportunity, there should be more volatility needed in the market so that more trading can take place.
Dirk Eddelbuettel and T Mccurdy (1998) found a significant relationship between frequency of news and volatility. They think when there is a lot of economic news come during that period spot exchange rate become more volatile with market participants' explanations for observed volatility clustering. In a study by Harvey and Huang (1991) on the forex market movement found out in the hour of US economic data release are the busiest compared to any other time in the day. The author found this anomaly comparing the announcement day and non-announcement day of similar time frame. Impact of the data in price adjustment happens quickly. Ederington and Lee (1993) and Ederington and Lee (1995) Analysed that majority of the volatility response is also very short term, and Prices adjust within a very short space of calendar time. Post-release volatility also observed by JPY /USD pair in a study by DeGennaro and Shirieves (1995) at the time of us announcement large increase in volatility inter alia, DeGennaro and Shrieves (1995), Payne (1996a) and Almeida (1996) found Extensions of existing time-series volatility models in the spot FX market. If one tries to justify the efficient market hypothesis model by Fama (1965) who believe price should fully reflect all information, and price is unpredictable Samuelson (1965).
Fama also defined three forms of market efficiency -weak, semi-strong and strong form. In his theory strong form version as market price will fully reflect all information so there will be no opportunity for the trader to benefit out of it but as we know every currency traded as pair there are more significant news, and factor derive the supply and demand and anomalies like trader perception cannot be explained by the theory. In the foreign exchange market context, every time news and significant data release market need to adjust the rate quickly, and speculator and trader must swing from expected information to unexpected reality assuming the market is efficient. However, last few decade efficient market hypothesis been much-criticized basis of imperial evidence suggesting anomalies in the market. Abnormal behaviour of market reaction to individual data or information is much standard. Presence of intraday pattern is the example of anomalies.
Admati and Pfliederer (1988) found more intensive trading happen in at the beginning and end of the trading day together with higher price volatility. Wood et al. (1985) found that market movement in the opening and closing of the exchange time is higher. Strawinski and Slepaczuk (2008) found evidence of intraday patterns in the Warsaw Stock Exchange. Shiller (2000); and Akerlof and Shiller (2009) thought that there are strong and many reasons for the presence of anomalies in financial markets. In his view irrational behaviour of investors (animal spirits, the herd instinct, mass psychosis, and mass panic) is inconsistent with the EMH paradigm Schwert (2003) did study providing evidence of abnormalities which are inconsistent with asset pricing theories.
Armin Shmilovici, Yoav Kahiri, Irad Ben-Gal, Shmuel Hauser (2009) used Universal compression algorithms to detect recurring patterns in financial data for prediction. These researchers presented a universal Variable Order Markov (VOM) model to test the weak form of the Efficient Market Hypothesis. Even though they found the pattern in the market, but the model turns out to be a not profitable trading strategy. Francis Breedon and Angelo Ranaldo (2010) research on ten years of high-frequency FX data and presented evidence of the time of day effect in FX market returns through a significant tendency for currencies to depreciate during local trading hours.
Guillaume et al. (1994) found in their survey Stylized facts concerning the spot intra-daily pattern in foreign exchange markets. Muller et al. (1990) provided some early evidence of cross-sectional patterns in intraday fx data.
Chinn and Meese (1995) found poor forecasting performance for the short-term and better results in the long-term forecasting performance in their fundamental exchange rate models Dua and Ranjan (2014) researched on few univariate exchange rate models like a random walk, monetary model and various extensions. He found in a projection of one year and less than one year, vector autoregressive (VAR) and Bayesian VAR framework generally outperform the random walk based on forecasts. Ghalayini (2014) researched in ARIMA models and found that the PPP theory explains the main part of the euro/dollar exchange rate, and in this case, the interest differential of the fundamental variable explains only a small proportion of subsequent changes in exchange rates model. They showed that the existence of co-integration between the exchange rates and various fundamental variables supports the monetary model as a long-term relationship.
Rezania, Rachev, Sun and Fabozzi, (2010) talked about Many models what built using quoted data, which is less precise than actual executed one). Others also searched for different approaches to explain forex behaviour. Hirschleifer (2001) talked about the use of Psychology Finance model. Evans and Lyon, 2005; Love and Payne (2006) talked about a successful approach using microeconomic variables showing trading importance in price discovery. The author thought order flow plays a principal role and increase predictability in comparison to traditional macroeconomic models.
Lo, Mamaysky and Wang, (2000) talked about using Technical Analysis in model construction to bring some additional information. On the other hand, also Schneller and Vanstone (2010) suggested that the trading system method gives an alternative way to understand currency behaviours based on macro-economic news.
Chapter 3
Research Methodology
Introduction
Foreign exchange market composes of the diverse element. Individual, small firms, banks, brokerage firms, multinational corporations, private investors and government all have a relationship with this market. However, the factor that determines the rate movement is a complex economic function. There are many economic factors that move the rate of the currency creating supply and demand we can identify main component factors include economic development, the central bank decision on money controls, domestic and foreign policy from government, and so on.
Fundamental Analysis and Technical Analysis are used as main trading methodology. Vanstone and Finnie, (2009) argued that "A general criticism of using trading systems is the absence of a formal methodology describing the procedure for the development as well as the benchmarking of results."
The main target of study is forecasting exchange rate behaviour after macroeconomic news releases in order to research that the study uses some simple strategy based on the price movement calculation. The focus of the strategy is to see if there are any relationship among the macroeconomic news and forex market movement through a trading system approach, for a better understanding of their effects and systematically capture the direction of trade.
The research methodology consists of some systemic approach, including identifying the key economic data release, their immediate effect in market movement, the calculation in pips movement, expected vs actual forecasting differences, cross-comparison of the currency pair etc. It tried to find the expected outcome through the economical instrument (Robson, 2011). In the end, the study established the relationship among the trend, affect and market movement if there is any.
Research Hypothesis
The main purpose of conducting this research was to determine if the macro-economic factors have any influence over the exchange rates. Here data from World Bank regarding exchange rates of UK and US from 1960 to 2018 was collected. This study tests the following two hypotheses.
H0 – There is no significant impact of macro-economic factors on exchange rate.
H1 – There is significant impact of macro-economic factors on exchange rate.
Research Type
The meaning of research type refers to the kind of data or information included in the study and the way the information is being processed or analysed to accomplish the objectives. There are mainly two kinds of research types; qualitative and the quantitative research types. The qualitative is the one where the researcher has the freedom to include the data which is subjective in nature and combine it with the exploratory research design. Here the researcher aimed to focus on obtaining in-depth information about the subject matter (Silverman, 2016). On the contrary, quantitative research type is the one which deals with the objective information, and it compliments well with descriptive research design. The quantitative research type is very accurate in nature as it discusses the subject matter on the basis of numerical facts and statistical data. The objective of the study is to analyse the Forex and exchange market where the quantitative research type was highly suitable. With the help of quantitative research type, the descriptive techniques were put into application, and it helped in establishing the link between different variables (Gioia, Corley and Hamilton, 2013).
Data Collection
The purpose of data collection revolves around gaining the maximum knowledge about the topic and generating a sufficient amount of information in a logical and structured manner so that the analysis can be conducted and research objectives can be attained. The effectiveness of data collection is very important with a view of enhancing the credibility of the study else the wrong interpretations and results can be presented by the researcher. Here in the current scenario, the secondary sources of data collection were being put into application due to the nature of research objectives (McCusker and Gunaydin, 2015). As the study is quantitative in nature, so the researcher has selected certain variables which are related to the discussed topic and enable to develop an understanding of the final results. Here the secondary data is being gathered from the website of World Bank from where the numerical data is being gathered, from 1960 to 2018, to support the quantitative study. Five variables, where inflation, interest, GDP and unemployment are the independent variables and exchange rate is the dependent variable, are:
Inflation: The inflation rate of any country becomes the reason behind the fluctuation of currency, and it affects the exchange rate.
Interest: one of the most important data is the interest rate for the day trader. Surprising monetary decision by the global central bank, especially main eight major central banks, FED, ECB, BOE etc. it can move the market potentially immediately and forcefully. One of the main reasons why it is important to trades is that the higher the rate of return, the more interest in incurred on currency invested (Mackenzie et al., 2012).
Unemployment: this economic indicator shows the number of percentages of the total workforce is out of the job and actively looking for a job in the previous month. Higher than expected reading is taken as negative for the currency and lower than expected taken as positive for the currency.
GDP: GDP shows the health of the economy. It measures the national income and output for a given period of time in a country. The report is published monthly, quarterly and yearly, usually depending on the country. GDP can be used to compare the size of an economy. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the annualized change in the inflation-adjusted value of all goods and services produced by the economy (Robson, 2011). When GDP goes up, the economy is growing – people are spending more and businesses may be expanding. GDP result come out positive than expected result, currency, in general, goes up, and if the GDP come negative currency lose its value as over economy not performing well.
Exchange rate: It represents the value of one currency against the value of another currency of a particular country or group like EU.
Data Analysis
In this section data collected from World Bank regarding UK and US’s exchange rate from 1960-2018 is analysed. The study is quantitative in nature and is combined to the descriptive research design so in the current scenario the applied technique was descriptive statistics and regression analysis. The data analysis was done with the help of statistical tools and regression analysis techniques (Silverman, 2016). The regression analysis technique was done to understand the impact of macroeconomic factors (independent variables) on exchange rate the dependent variables. Further, IBM SPSS software was used to analyse the data, along with descriptive statistics, regression analysis and coefficients.
exchange rate= α+ 1*inflation rate+2*interest rate+ 3*unemployment rate+ 4*GDP
Reliability and Validity of the Study
The results of the study were highly reliable as it includes the implications of statistical tools and regression analysis technique which enhances the chances of accuracy in the research results. Further, the reliability is high because the researcher has focused upon gathering the data from the platforms like the World Bank’s website and other reliable and reputed sources (Gioia, Corley and Hamilton, 2013). The validity of the study is high as researcher has gathered the most recent information which ensures the validity of the results as per current situation or market scenario.
Chapter 4
Data Analysis and Results
Introduction
The foreign exchange market is being termed as the most diverse element that plays critical role in influencing investment and business transaction. It includes brokerage firms, multinational corporations, private investors and government all have relationship with this market. This section of present investigation is aimed to evaluate several factors and macro-economic elements that encourage currency rate fluctuations (McCusker and Gunaydin, 2015). For analysing the relationship among multiple variables, the present has considered the different tools statistical tools for analysing a range of data such as inflation rate, GDP, interest rate, unemployment and currency exchange rates of UK for assessing their correlation and attainment of research objectives.
Interpretation of Findings
Graphical Analysis

From 1962 till 2018, the value of exchange rate underwent a lot of fluctuation. Significant changes happened between years 1980 to 1988. During this period the exchange rate rose significantly, while it fell sharply during the year 2008 when the financial crisis took place.

Value of interest rate was highest from 1978 to 1980, after which it fell sharply. However, it rose again during 90s, but by the year 2008 it started to fall starkly, indicating that the value of interest was among the lowest after its rise in the 90s. Since the year 2010 there has virtually been no change in the value of interest rate.

During the year 1974, the inflation rate was the highest. However, the debacle of the 2008 financial crisis played a crucial role in decrease in value of the inflation rate. It has improved only after the years 2016 and declining slightly in 2018.

Unemployment fell starkly after 1996 and continued to fall till early 2000s. The graph above also shows that after 2010 unemployment rate started to increase considerably, meaning a significant portion of the society was left unemployed, especially after financial crisis in 2008. The data here also suggests that the unemployment rate is declining at a fast rate.

From the graph, it is clear that the GDP rates are improving at a healthy and steady rate. Fluctuation and changes have been a common occurrence in the value of GDP throughout the years.
Descriptive Analysis
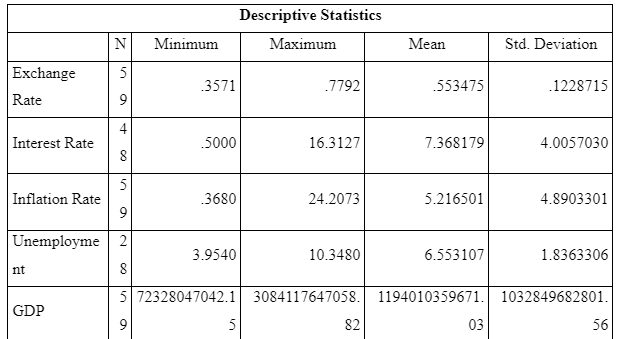

From the table above, the minimum value of the exchange rate was 0.3571, while the maximum value was 0.7792. Mean for exchange rate was 0.55. The minimum and maximum value for interest rate was 0.50 and 16.31 respectively; the mean was calculated to be 7.368. The minimum value of inflation rate was 0.3680, maximum value was 24.20, and the mean was 5.21. Similarly, maximum value for unemployment was 3.9540; maximum value was 10.3480, and the mean was 6.55. The minimum value for GDP was 727328047042.15, maximum was 3084117647058.82, and the mean was 1194010359671.03.
Correlation Analysis
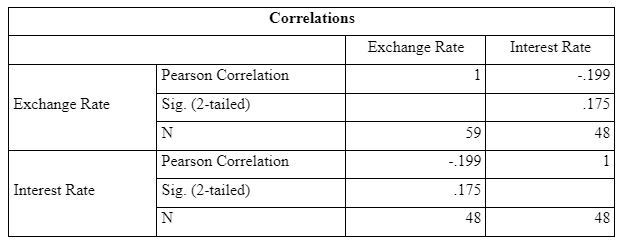
The p-value is coming out to be 0.175 is more than the critical alpha value of 0.05. This shows a non-significant negative association between the two variables; exchange rate and interest rate. On this basis, it can be said that a change in interest rate will result in a non-significant negative change in the exchange rate.
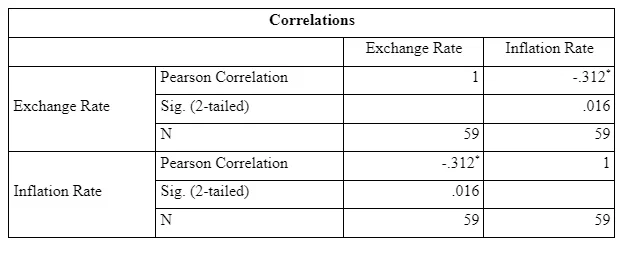
*. Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed).
The p-value is coming out to be 0.016 is less than the critical alpha value of 0.05. This shows a significant negative association between the two variables; exchange rate and inflation rate. On this basis, it can be said that a change in inflation rate will result in a significant negative change in the exchange rate.
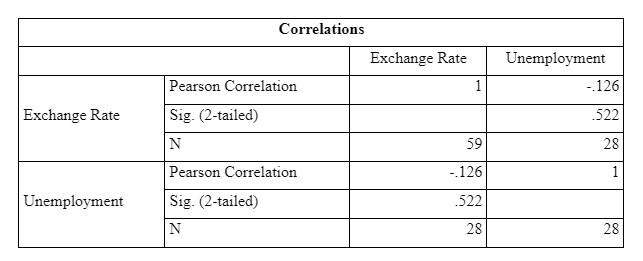
The p-value is coming out to be 0.522 is more than the critical alpha value of 0.05. This shows a non-significant negative association between the two variables; exchange rate and unemployment. On this basis, it can be said that a change in the unemployment rate will result in a non-significant negative change in the exchange rate.
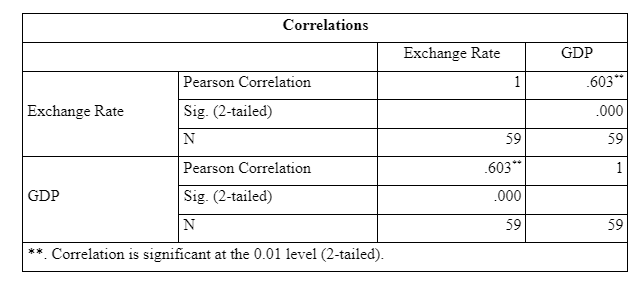
The p-value is less than the critical alpha value of 0.05, which means there is a significant positive association between exchange rate and GDP. Therefore, there is major relation between the two variables. Moreover, the results obtained here indicate that change in GDP variable will significantly affect the exchange rate.

In the above table, the correlation between different variables was presented. Herein it can be observed that p-value for inflation rate and GDP was less than the critical alpha value of 0.05. This means there is a significant association between inflation rate, GDP and interest rate. Similarly, a significant relationship between inflation rate, interest rate, unemployment and GDP was observed, while, unemployment did not have a significant association with inflation and GDP. Further, the p-value for GDP, interest rate, inflation rate and unemployment was less than 0.05, which showed a significant association between the said variables. Also, the above table confirms that there is no issue of multicollinearity as there is no strong association between any of the independent variables.
Regression Analysis
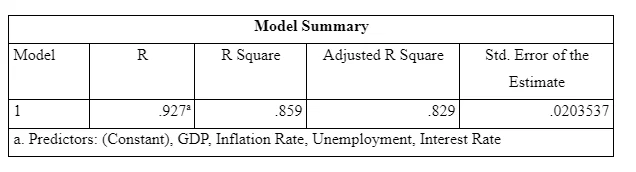
As per regression analysis the regression coefficient, R Square, is coming out to be 0.859. This shows that with a 100% change in the independent variables, there will be an 85% change in the dependent variable. Now, whether this relationship is statistically significant or not can be seen from the ANOVA table below.

As per ANOVA, F(4,23) = 28.927; p = 0.000. As p-value is less than the critical alpha value of 0.05, this shows that there is a significant association between the dependent variable and independent variables.

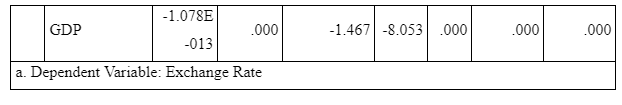
As per the above coefficients table, the p-values of interest rate and GDP is less than the critical alpha value of 0.05. This means that the interest rate and GDP have a significant impact on the dependent variable of exchange rate. On the other hand, p-values for inflation rate and unemployment rate is more than the critical alpha value of 0.05, meaning that these variables do not have a significant impact on the exchange rate, i.e. the dependent variable.
Data Analysis
The present study is aimed to evaluate the foreign exchange trading opportunity in the economic factor. In this regards, it has paid significant attention to different economic indicators that are playing important role in influencing the exchange rates within country. In this regards, this investigation has paid significant attention to the five most important variables such as interest rate, GDP, unemployment rate, inflation rates along with exchange rates (Basher, Haug and Sadorsky, 2012). For analyzing the outcomes, currency exchange rates have been addressed as dependent variable and remaining four factors have been termed as independent variables that are playing important role for influencing the exchange rate and also offering wide range of foreign exchange opportunities. As per the analysis of previous years data of UK exchange rates, it has found that UK government has recorded significant up and downs in foreign exchange which can be termed as an important indicator of overall efficiency of economy along with the health of economy.
In this context, the study of Fan and Yan (2010) has stated that economic announcement and other news events have been addressed as a wild card in the foreign currency exchange market. Even though no one knows when the news related to political and economic decisions could be termed as an important cause of the market reaction. However, the evaluation of currencies trend and results of different news events can be used as a trading strategy. As a result forecasting or speculation is big part of currency move. News and macro-economic data have been addressed as most common tool which has been applied for testing the informational efficiency in the market. However, Aminov (2011) has analyzed the efficiency in the spot foreign exchange market and found that macroeconomic news is significantly affecting exchange rate often resulting in a jump the rate of the currency and it also increase the volatility.
The present investigation has examined the correlation of exchange rates with various independent variables such as GDP growth, inflation rate, interest rates and unemployment rate. In this regards, the researcher has carried out a quantitative analysis of data of more than 20 years for determining the correlation among different factors. In the present investigation, researcher has determined the correlation between national GDP of UK and exchange rates. While performing the quantitative, researcher has found the positive relationship between national GDP and currency exchange rate in which the value of p= 0.00 that is lower than the ideal value of p=0.05. Therefore, the relationship between GDO and currency exchange rates is statistically significant that indicate that GDP of country seems as key economic indicator that could influence the efficiency and market trends in currency market because GDP trends are recorded as key performance indicator and influence the perception of investors (De Castro and Fernández, 2013). In this context, the study of Shiau and Luo (2012) has supported the findings of present investigation in which author has stated that GDP is termed as most appropriate indicator for analyzing the health of the economy. This is because this approach seems a very useful tool for measuring the national income and output for a particular period of time in a country. The report is published by the government agencies on the monthly, quarterly and yearly usually depending on the requirements of country. In this regards, author has examined that GDP can be used for managing a systematic comparison of the size of an economy.
Furthermore, the investigation of Olweny and Shipho (2011) has found that Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is also measuring the annualized change in the inflation-adjusted value of all goods and services produced by the economy for predicting future GDP values. When GDP goes up, the economy is growing – people are spending more and businesses may be expanding. GDP result come out positive than investors would find the increase in the currency value, and if the GDP come would find downward trends then currency loses its value as over economy not performing well.
For analyzing the fluctuations in the foreign exchange rates, the present study has also examined the correlation between interest rates and currency rates. In order to determine the correlation between two variables, the present investigation has addressed that the p-value is 0.000 that is lower than the 0.05 so as it can be stated that the association between interest rates and currency exchange rates is statistically significant. Therefore, there is a statistically significant negative correlation emerged between lending rate and exchange rate. In the context of present case, the findings of research of Arouri, M. E. H., and Nguyen (2010) has supported in which scholar has found that interest rate has emerged as one of the most significant data that influences the decisions of day trader in currency market.
It has addressed that the monetary decisions taken by the global central bank especially main 8 major central banks along with central banking authorities of UK have influenced the market potentiality immediately and forcefully with reference to current market trends. Therefore, it can be stated that fluctuations in interest rates are being termed as one of the main reason why it’s important to trades is that the higher the rate of return, the more interest in incurred on currency invested. On the other hand, the study of Ahmed and Zlate (2014) has stated that lending and deposits rates within-country influence public and corporate spending along with investment trends. These factors could have direct impact over the import and export operations within country. Therefore, different individuals have addressed significant fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates. Interest rates have been addressed as most critical factors in the context of current market trends in order to promote the business cycle and spending of different people that could have direct impact on international money market trends along with trading activities in the currency market (Gilbert, 2010).
The present research has considered the inflation rate as an important variable that encourages exchange rates. The analysis of correlation between two variables has disclosed the negative correlation that shows that change in inflation is encouraging the currency exchange rates along with trading activities within the foreign currency market. On the other hand, the investigation of Sierzchula et al., (2014) has opposed the findings of present investigation. This is because researcher has stated that inflation rate based on Consumer Price Index (CPI) influences trading and pricing of currencies in the money market. The researcher further stated that CPI measures the average value of change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a market basket of consumer goods and services. In the USA the bureau of labour statistics (BLS) reports the CPI on a monthly basis and in the UK office for national statistics (Zamalloa et al., 2011). CPI measures inflation in the economy, and it is considered the best monthly measure of inflation And Federal Open Market Committee and trader pay high attention to core data of CPI. Therefore, the Higher than expected reading would be taken as positive for the currency and lower than expected would be taken as bearish for the currency. The rapid increase in CPI figure or rising price in the basket could force central bank interference to keep the price stability and changes in interest rate decision. All these factors would have direct impact for encouraging the change in exchange rates.
On the other hand, Sari, Hammoudeh and Soytas (2010) have stated that inflation rates within the country are having very less and no impact the trading in currency market markets because these factors are not stimulating the currency rate on significant manner. The inflation rate is being seemed as internal elements of the economy of country. The study of Sari, Hammoudeh and Soytas (2010) has stated that unexpected quote arrival and news related to macroeconomics positively impact foreign exchange rate volatility is consistent with the interpretation that unexpected quote arrival serves as a measure of informed trading. It has addressed that foreign exchange market is also traded in high frequency. In order to exploit the opportunity there should be more volatility needed in market so that more trading can take place. However, inflation rates are not creating any kind of quick volatility during the different trading operations and other practices. Therefore, it can be stated that inflation rates are having partial implications on the currency exchange rates along with trading operations in the foreign exchange market.
The current study has also considered the role of employment or unemployment rate for influencing the currency exchange rate. In this regards, it has focused to identify the relationship between unemployment rates of UK and currency market trend. The analysis of a wide range of information has stated that the p-value is 0.522 that is higher 0.05 so as it has addressed that the association of relationship is statistically insignificant between the variables. On the other hand, the findings of Basher, Haug and Sadorsky (2012) have opposed the outcomes of present investigation in which researcher has determined that unemployment rate seems an important economic indicator. This economic indicator determines the number of percentages of the total workforce that are out of the job and actively looking for job in particular time period. The author argued that higher than expected reading would lead negative impact the currency values and lower than expected would be treated as positive outcomes for the currency that indicate that unemployment rate is having direct relationship with currency figures (De Castro and Fernández, 2013).
However, Shiau and Luo (2012) argued unemployment rate of the country is not having direct impact on the currency exchange rates in the forex market because it is not encouraging currency market fluctuations directly because unemployment rate influences the income of people along with their spending and investments. Therefore, fluctuations in currency market have been emerged due to increase in market demands of different goods and services along with investment of people in currency markets. Therefore, it can be stated that unemployment rates are not having direct impact on the exchange rate, but it leads partial implications through several other economic indicators (Olweny and Shipho, 2011).
In the context of the present study, researcher has addressed that exchange rate of currency is not influenced by a single economic indicator because it has been termed as an important outcome of various economic indicators. Arouri and Nguyen (2010) argued that different economic indicators are mainly correlated with political stability within country. The author further determined that foreign investors are always focused to consider a stable economic environment and wanted to avoid political unrest before investing money in the country. Foreign demand has been addressed an important cause of exchange rate rises and falls as well. Therefore, the political and economic decisions have played a major part in the economic growth as a result economic situation that could encourage a strong currency or depreciation in the currency.

Chapter 5
Conclusion
The present is focused to understand the foreign exchange rate behaviour on the development of news and economic factor in large. Therefore, the present investigation has paid significant attention to the different factors or economic indicators of country such as inflation rate, interest rate, GDP and unemployment along with its impact on the currency exchange rate. In this regards, researcher has concluded that selection of different variables of economy of country has found very effective for determining foreign exchange rate behaviour. These variables have offered great support to researcher for attainment of study objectives with an appropriate manner (Ahmed and Zlate, 2014).
This study has concluded that different constants related global news and update of countries economic indicator have been addressed as important motivator and offered a fresh strategic reason for the trader for being an important player of this market that would make this market very interesting. However, the analysis of different variables has addressed that information is termed as key element for encouraging the currency market up and downs. This is because different factors based on the information have provided the trader with more confidence for developing an appropriate understanding of the expected movement for supply and demand (Gilbert, 2010). Even though the retailer combined the only fraction of this massive global market but still a considerable number of people have an interest in the foreign exchange market.
As per the aim of the investigation, researcher has paid significant attention to wide range of secondary data. These data are focused to determine the relationship among multiple variables or economic indicator that are having huge impact on exchange or currency rates along with trading activities in the forex market. For this purpose, researcher has collected a range of data-based in different economic indicators such as inflation rate, interest rate, GDP growth, unemployment rate and exchange rate of UK. In this regards, this present study has concluded that data related to UK macroeconomics indicators has offered great support researcher for generation of appropriate research outcomes. This is because Britain has the largest share of the forex market and more than 40% of all transactions taken place in London.
The abolition of all foreign exchange controls in Britain in 1979 has been instrumented after development of the forex market. Vast numbers of stakeholder are involved in this market, which is directly involved due to financial evolution and its importance (Zamalloa et al., 2011). However, the analysis of various theories of currency market fluctuations and different economic indicators has concluded that exchange rates in currency are not influenced by a single economic indicator. This is because it is influenced by several factors and government decisions.
To assess different factors of exchange rate fluctuations and trade activities, the present study has focused on four key independent variables such as interest rate, GDP growth rate, inflation rate and unemployment rates. As per the findings and views of different past studies, it has addressed that all selected independent variables are having direct and indirect impact on the currency rates up and down along with investment pattern in forex market (Sari, Hammoudeh and Soytas, 2010). However, the analysis of different data related to four selected independent variables such as interest rate, GDP, inflation rate and unemployment rates with reference to data related to exchange rate has identified interest rate and GDP rates as key motivator of exchange rates. These economic indicators lead direct impact on the trading and investment decisions of both internal and external investors so as there is significant up and down addressed in currency rates. Therefore, it can be concluded that interest rates and GDP could have direct impact over the foreign investment within country and it plays critical role for encouraging the demand for the currency. However, the alteration in demand for foreign exchange services leads to significant fluctuations in exchange rates in UK.
The section of research methodology holds critical importance for any and all types of studies. It is considered as one of the most basic yet important aspects that has a significant impact on the overall success and effectiveness of the research process. In current study, the researcher used quantitative design (Fan and Yan, 2010). In this design the scholar used different statistical tools and methods to analyse the data collected from various sources. Through quantitative approach the researcher was able to focus on assessing the various factors that influence exchange rates.
In this study, the data was collected from secondary sources. The main reason for selecting this source was the fact that over the numerous studies has been carried out on the subject matter. Thus, there is an abundance of information available through various sources. Herein the researcher relied on using past research investigations available in form of journal articles, books, online articles and others. Inflation, interest rate, unemployment and GDP were the independent variables used by the researcher while exchange rate was the dependent variable for the current research (Aminov, 2011). Quantitative and statistical methods of data analysis were used by the researcher to analyse data collected from the secondary sources. Herein descriptive statistics and regression analysis were used. Through these methods, the researcher was able to conduct the research process in a better and effective manner, which further helped in enhancing overall efficiency and effectiveness of the current study.
Reference
Ahmed, S., and Zlate, A. (2014). Capital flows to emerging market economies: A brave new world?. Journal of International Money and Finance, 48, 221-248.
Almeida, Alvaro, Goodhart, Charles and Payne, Richard (1997), The Effects of Macroeconomic 'News' on High Frequency Exchange Rate Behaviour. ESRC Research Centre Discussion Paper 258
Aminov, R. I. (2011). Horizontal gene exchange in environmental microbiota. Frontiers in microbiology, 2, 158.
Arouri, M. E. H., and Nguyen, D. K. (2010). Oil prices, stock markets and portfolio investment: Evidence from sector analysis in Europe over the last decade. Energy Policy, 38(8), 4528-4539.
Basher, S. A., Haug, A. A., and Sadorsky, P. (2012). Oil prices, exchange rates and emerging stock markets. Energy Economics, 34(1), 227-240.
Black, Fischer. 1986. Noise. The Journal of Finance 41: 529–43.
Ca’ Zorzi, M, J Muck and M Rubaszek (2015), “Real exchange rate forecasting and PPP: This time the random walk loses”, An earlier version was published as ECB Working Paper No. 1576, 2013
Chaboud, Alain, Chernenko, Sergey, Howorka, Edward, Iyer, Raj S.K., Liu, David and Wright, Jonathan H. (2004), The High-Frequency Effects of U.S. Macroeconomic Data Releases on Prices and Trading Activity in the Global Interdealer Foreign Exchange Market. FRB International Finance Discussion Paper No. 823
Chinn, M.D., Meese, R.A (1995) Banking on currency forecasts: How predictable is change in money? Journal of International Economics, 38(1-2):161-178.
De Castro, F., and Fernández, L. (2013). The effects of fiscal shocks on the exchange rate in Spain. The Economic and Social Review, 44(2, Summer), 151-180.
DEGENNARO, R., and R. SHRIEVES (1995): “Public Information Releases, Private Information Arrival, and Volatility in the Foreign Exchange Market,” Unpublished Paper
Eddelbuettel, Dirk and T Mccurdy. “The Impact of News on Foreign Exchange Rates : Evidence from High Frequency Data ∗.” (1998)
EDERINGTON, L., and J. LEE (1993): “How Markets Process Information: News Releases and Volatility,” Journal of Finance, 48(4), 1161-1191.
EDERINGTON, L., and J. LEE (1995): “The Short-Run Dynamics of the Price Adjustment to New Information,” Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis, 30(1), 117-134.
Ederington, Louis & Lee, Jae. (1993). How Markets Process Information: News Releases and Volatility. Journal of Finance. 48. 1161-91. 10.1111/j.1540-6261.1993.tb04750.x.
Edison, Hali J. (1996), The Reaction of Exchange Rates and Interest Rates to News Releases. FRB International Finance Discussion Paper No. 570.
Evans, Martin D.D. and Lyons, Richard K. (2005), Understanding Order Flow. NBER Working Paper Series, Vol. w11748, pp. -, 2005.
Fan, W., and Yan, Z. (2010). Factors affecting response rates of the web survey: A systematic review. Computers in human behavior, 26(2), 132-139.
Ghalayini, L. (2014) Modeling and forecasting the US dollar/euro exchange rate. International Journal of Economics and Finance, 6(1):194-207.
Gilbert, C. L. (2010). How to understand high food prices. Journal of agricultural economics, 61(2), 398-425.
Gioia, D. A., Corley, K. G., and Hamilton, A. L. (2013). Seeking qualitative rigor in inductive research: Notes on the Gioia methodology. Organizational research methods, 16(1), 15-31.
Guillaume, Dominique M., Michel M. Dacorogna, Rakhal R. Dave, Ulrich M. Muller, Richard B. Olsen, and Olivier V. Pictet (1994). From the bird’s eye to the microscope: A survey of new stylized facts of the intra-day foreign exchange markets. Discussion Paper DMG.1994-04-06, Olsen & Associates, Zurich
HAKKIO, C. and D. PEARCE (1985) “The reaction of exchange rates to economic news”, Economic Inquiry 23, 621-635.
Harris, Ethan S. and Zabka, Natasha M (1995), The Employment Report and the Dollar. Current Issues in Economics and Finance, Vol. 1, No. 8, November 1995.
HARVEY, C., and R. H u an g (1991): “Volatility in the Currency Futures Market,” Review of Financial Studies, 4(3), 543-569.
Hirshleifer, David A. (2001), Investor Psychology and Asset Pricing. AFA 2001 New Orleans Meetings.
HOGAN, K. and M. MELVIN (1994) “Sources of meteor showers and heat waves in the foreign exchange market”, Journal of International Economics 37, 239-247.
ITO, T. and V. ROLEY (1987) “News from the US and Japan: which moves the Yen/Dollar exchange rate?”, Journal of Monetary Economics 19, 255-277.
John Jagerson, S. Wade Hansen (2011) All About Forex Trading: McGraw Hill Professional, united states .
Keynes, John Maynard. 1936. The General Theory of Employment, Money and Interest. London: Macmillan
LAAKKONEN, H., (2009). Essays on the asymmetric news effects on exchange rate volatility. Helsinki: University of Jyvaskyla
Lo, Andrew W., Mamaysky, Harry and Wang, Jiang (2000), Foundations of Technical Analysis: Computational Algorithms, Statistical Inference, and Empirical Implementation. NBER Working Paper Series, Vol. w7613, pp. -, 2000.
Love, Ryan and Payne, Richard G. (2006), Macroeconomic News, Order Flows and Exchange Rates. Working Paper.
Lui, Y.-H., Mole, D
Mackenzie, J., Tan, P. L., Hoverman, S., and Baldwin, C. (2012). The value and limitations of participatory action research methodology. Journal of hydrology, 474, 11-21.
McCusker, K., and Gunaydin, S. (2015). Research using qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods and choice based on the research. Perfusion, 30(7), 537-542.
Meese, R A and K Rogoff (1983), “Empirical exchange rate models of the seventies: Do they fit out of sample?”, Journal of International Economics 14 (1-2), 933-48.
Meese, Richard A. and Rogoff, Kenneth (1983), Empirical Exchange Rate Models of the Seventies. Do they fit out of sample? Journal of International Economics 14 (1983) 3-24.
Muller, Ulrich A., Michel M. Dacorogna, Richard B. Olsen, Oliver V. Pictet, Matthias Schwarz, and Claude Morgenegg (1990). Statistical study of foreign exchange rates, empirical evidence of a price scaling law, and intraday analysis. Journal of Banking and Finance 14(6), 1189–1208
Olweny, T., and Shipho, T. M. (2011). Effects of banking sectoral factors on the profitability of commercial banks in Kenya. Economics and Finance Review, 1(5), 1-30.
Osler, Carol L. (1995), Short-Term Speculators and the Origins of Near-Random-Walk Exchange Rate Behavior. FRB of New York Staff Report No. 3.
Pilbeam, A (2013). International Finance. 4th ed. London: Palgrave Macmillan. p3-200.
Rezania, Omid, Rachev, Svetlozar T., Sun, Edward and Fabozzi, Frank J. (2010), Analysis of the intraday effects of economic releases on the currency market. Working Paper Series in Economics No 3, August 2010.
Rezania, Omid, Rachev, Svetlozar T., Sun, Edward and Fabozzi, Frank J. (2010), Analysis of the intraday effects of economic releases on the currency market. Working Paper Series in Economics No 3, August 2010.
Robson, C. (2011). Real world research (Vol. 3). Chichester: Wiley.
S (2010), The Efficient Market Hypothesis and its Application to Stock Markets. Hamburg: GRIN Verlag
Sari, R., Hammoudeh, S., and Soytas, U. (2010). Dynamics of oil price, precious metal prices, and exchange rate. Energy Economics, 32(2), 351-362.
Schneller, Warwick and Vanstone, Bruce James, (2010) Predictable Responses in Currency Markets to Macroeconomic News: A Trading System Approach. 23rd Australasian Finance and Banking Conference 2010 Paper.
Shiau, W. L., and Luo, M. M. (2012). Factors affecting online group buying intention and satisfaction: A social exchange theory perspective. Computers in Human Behavior, 28(6), 2431-2444.
Sierzchula, W., Bakker, S., Maat, K., and Van Wee, B. (2014). The influence of financial incentives and other socio-economic factors on electric vehicle adoption. Energy Policy, 68, 183-194.
Silverman, D. (Ed.). (2016). Qualitative research. Sage.
The use of fundamental and technical analyses by foreign exchange dealers: Hong Kong evidence. Journal of International Money and Finance, Volume 17, Issue 3, 1 June 1998
Vanstone, Bruce J. and Finnie, Gavin (2007), An Empirical Methodology for Developing Stock market Trading Systems using Artificial Neural Networks. Working Paper.
Zamalloa, C., Vulsteke, E., Albrecht, J., and Verstraete, W. (2011). The techno-economic potential of renewable energy through the anaerobic digestion of microalgae. Bioresource technology, 102(2), 1149-1158.
Appendix



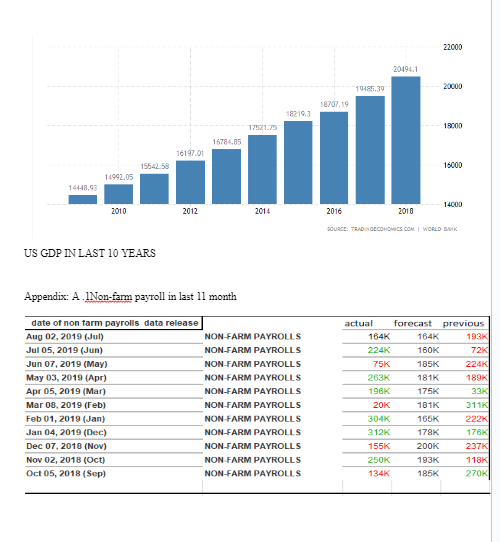
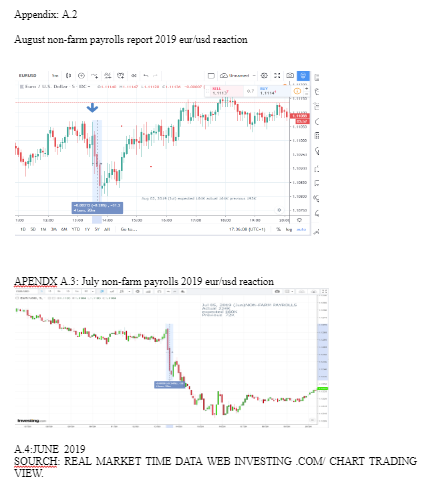
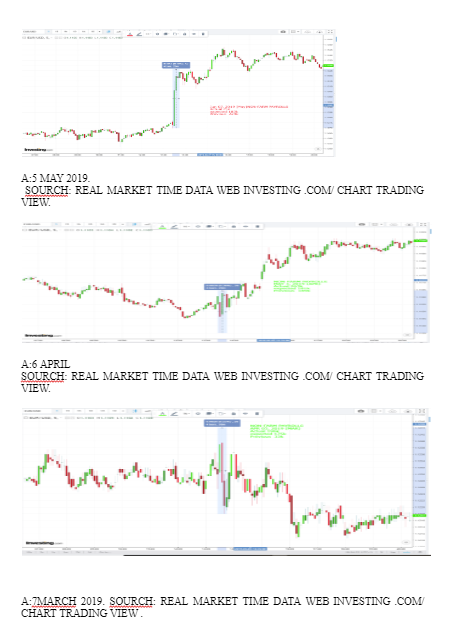
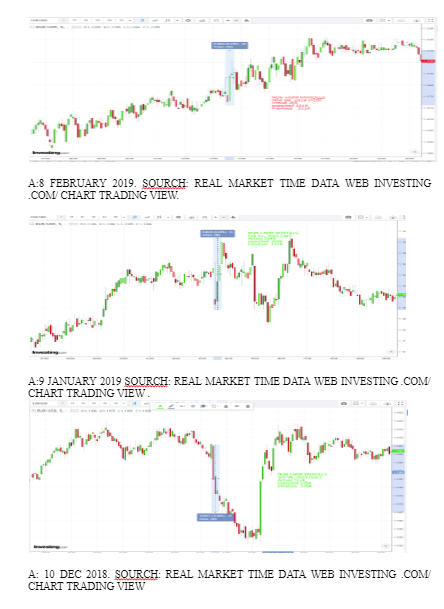






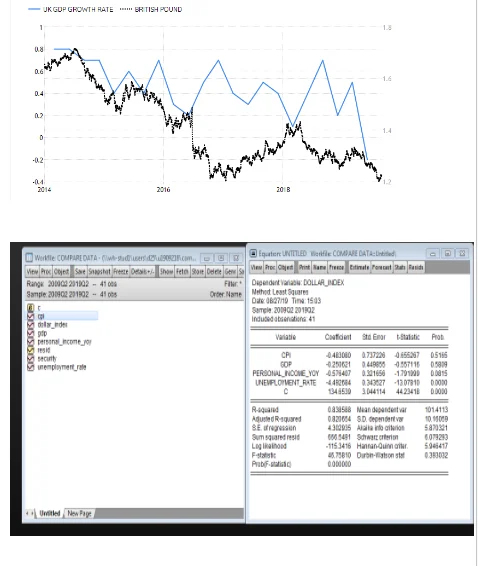


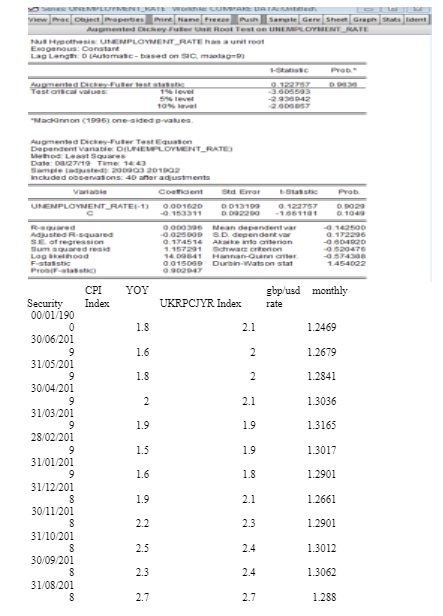








Looking for further insights on The Dynamics of Britain's First EU Referendum? Click here.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



