Impact of Fast Fashion on Trends
1. Introduction
1.1 Background of the study
Fast Fashion
The fashion industry is in a state of continuing flux and increasing competition. There was new steam, which is called ‘fast fashion’ in the fashion industry since in the early 2000s. It has made many differences in the fashion industry and changed the fashion system as well. It was a revolution in the industry, and it was really good news to the customer. It put over stimulating customer’s desire for fashion (Bhardwaj and Fairhurst, 2010).
Fast fashion system and business method
There are so many fast fashion brand and still emergence as well. The market uses a different brand strategy with an existing fashion brand. So, I will study about ZARA as an example. It has around 1.600 stores in 58 countries; it is a benchmark model in the industry. Through the brand study, it will understand easily and illustrate about fast fashion’s system and business. I will focus on the production as well with showing the difference with other fashion brand system (Caro and Martínez-de-Albéniz, 2015). Also, I am going to analysis the system of fast fashion in conjunction with SWOT. Additionally, through observing these industries, I will see how they use consumer behaviour and psychology for their business.
Side effects of fast fashion and future
The fast fashion industry has grown quickly with the mass production system, and it kept growing by leaps and bounds. However, it brings many side effects. Also, they were not concerned about sustainability. The matter has brought up, and they start to solve it. However, there is still a big problem, especially in the environmental and ethical sector. I will examine the problems (McNeill and Moore, 2015). As I mentioned above, there are many side effects. So I will study what are side effects of fast fashion and how we can solve the problem of it for the future.
1.2 Rationale of the study
The present is aimed to determine different aspects of fast fashion with reference to business operations ZARA, a leading fashion brand within fast fashion. The main reason behind the selection of present research topic is that there have been several studies carried out about fashion industry in the context of consumer behaviour, demand of luxury products, growth of the luxury industry, promotional strategies of different fashion brands and many more (Karaoglu and Inan, 2018). However, this present investigation evaluates a distinct overview of the fashion industry, which is called Fast Fashion, in which companies are offering cheap and trendy clothes through mass production. Brooks (2015) has disclosed that fast fashion has encouraged the mass production of clothing that has created a wide range of sustainability-related issues as a result of the exploitation of resources. Therefore, the present study has examined different aspects of fast fashion such as emergence and growth of fast fashion industry as well as the business methodology used by fast fashion companies like Zara. Fast fashion is being addressed as an important cause of different environmental issues so as the present investigation is found very effective for presenting a systematic overview of fast fashion.
2. Aim And Objectives
Fast fashion
Fast fashion meaning
How to emerge fast fashion
Fast fashion system/business method
How they retail fast fashion
The study of ‘ZARA’ as an example of fast fashion
Customer behaviour
Side effects of fast fashion and future
What is the problem in the industry?
The way of sustainability work
How we can develop the model of fast fashion for the future

3. LITERATURE REVIEW
This paper divided into three sections. The first section gives the definition of fashion, its background and its differentiation from other markets. The second section examines the way of operating fast fashion through brand analysis of ‘ZARA’ which is a representative example of fast fashion. In the third section looks at the question of the problem of fast fashion, the sustainability trend of current companies, and the direction of fast fashion in the future.
3.1 Fast fashion’s meaning and Background of emergence
Simona Segre Reinach (2005) has put forward a definition of fast fashion, which is that the author analyses modern fashion as Haute Couture, Pret a Porter and Fast Fashion. It is described as Haute Couture is a luxury fashion that distinguishes the class, and Petra porter focuses on the modernity that fits the lifestyle. Fast fashion has been described because whimsy is the key and to instantly satisfies new temporary things. In addition, the hierarchy of the concept has been diminished, and various cultural strata have emerged since modern times. Therefore, fast fashion can be defined as a newly emerging fashion phenomenon for the public to quickly detect the pace of change. Now, rather than wearing clothes differently according to class, people began to dress as a way of expressing their personality. Public began to become more sensitive to the trends and having the desire to express through fashion style. These phenomena really suited to the concept of fast fashion. These historical events have transformed the economic and trade interactions of countries around the world and thus have made a major difference in the pattern of production and manufacturing of the apparel industry. There is considerable literature on the book, which is called ‘The Fashion Reader: Second Edition’. In the book, Author described the history of the emergence of fast fashion and showed the change process of the manufacturing system. Welters and Lillethun (2010: 107) mentioned that: The map of Europe changed dramatically at the end of the 1980s and beginning of the 1990s with several events, including the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989, the reunification of East and West Germany in 1990, the official dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, and the subsequent end of communism in most of Eastern Europe. Meanwhile, amid continued attempts at negotiating peace in the Middle East, the 1991 Gulf War increased tension between the United States and Iraq. The United States and the European Community led the world in the movement toward a liberalised global economy. In 1993, Canada, Mexico, and the United States signed NAFTA (North America Free Trade Agreement). In 1995, the World Trade Organization was created to promote further trade agreements. Apparel makers in industrialised countries outsourced manufacturing to developing countries where lower wages were paid.
Take a deeper dive into Leadership in Modern Business Challenges with our additional resources.
In the same way, Taplin (2014) has evaluated that the garment industry has always been a low capital and labour-intensive industry. Furthermore, the industry has been characterised by low entry barriers and standardised production for a mass market. From the beginning of globalisation, outsourcing has begun to grow in developing countries because of the advantage of cheap labour, less regulation and taxes. Outsourcing of apparel production changes consumers to have attention to Fast Fashion, which has a combination of the latest high fashion content and inexpensive price(Linden,2016). It means that the fashion company’s business management method also shifted from product-focused to customer-focused approach to product access. As of now, the fast fashion business is under management. In the late 1990s, the concept of fast fashion emerged as characterising an upheaval of fashion, and some of the companies started to use it as a form of consumption(Muthu,2018). Some of the successful global owners such as Forever 21, H&M and Zara realised that movement of business and started the mass production targeted to young people in the world.
2.2 Fast fashion’s retailing through the study of Zara
‘sell high-fashion look-alikes to price-conscious consumers’ (J.N. Smith 2008:54). To understand the fast fashion system, this part outlines an approach to fast fashion retailing system through the brand study of Zara and sees the difference with other markets. Zara is a fashion brand established in 1975 by Amancio Ortega and Rosalía Mera. It is the main brand of the Inditex group which is the world’s largest apparel retailer and has owned brands such as Pull&Bear, Oysho, Stradivarius, Massiomo Dutti, Bershka, Stradivarius, Zara Home and Uterqüe. The company manages over 2,220 stores in 88 countries. Zara is the pioneer of fast fashion based in a highly responsive supply chain. (Zhelyazkov, unknown) Zara wants changes in management mechanisms. Welters and Lillethun, an authority on The Fashion Reader, affirms that the key point of success is to respond quickly to changing fashion trends and volatile customer demands.

Zara has produced new products twice in a week to around 1670 stores in the world. It means they have made more than 10,000 new designs every year. It takes only two weeks from design stage to sales floor (Petro, 2012). Several seamstresses are ready for making samples immediately, and because of a rapid-response production system, the design part meets every day to discuss colours, patterns, and fabrics to bring new designs to the store as soon as possible in two to three weeks (Welters and Lillethun, 2011). As we can see in Fig 1, compare to the traditional Apparel Industry that spends time a few months from design to production. Otherwise, Production Timeline for Zara’s Fast fashion that takes just in 6 weeks is remarkably short.
3.3 Problems with fast fashion
As per the study of Kim, Park and Glovinsky (2018), it has found that fast fashion has emerged with various sustainability issues. This is because more than 2000 gallons of water are required for growing cotton for just a pair of jeans. Further processing of garments such as dying, bleaching and many more has also increased the level of water footprint as well as environmental pollution. Zhan (2017) has determined that fast fashion retailers are managed their operations as per the current fashion trends. Therefore, factories do not have appropriate time for systematically managing different business operations in the form of designing, production and distribution so as companies have failed to manage significant attention on the quality of products that could be considered as an important element of the organisational sustainability issue. The investigation of Heuer and Becker-Leifhold (2018) has determined that there is huge exploitation addressed within the fast fashion manufacturing industry because workers have enforced to work extra hours within less pay. For lowering the cost, organisations have avoided appropriate safety norms and quality standards. These factors have played a critical role in managing organisational sustainability. The research of Garcia-Torres, Rey-Garcia and Albareda-Vivo (2017) has focused on determining tools and practices for handling sustainability issues in the fast fashion in which companies are focusing on the recycling of old clothing as well as wastage so as fashion firms are able to facilitate new clothing range in low prices. This approach has found very effective for handling future trends in fast fashion in a positive manner with consideration of environmental safety (Linden, 2016).
4. METHODOLOGY
This section determines a combination of different research method and data collection process to attain research objectives. In this regards, some important element of research methodology are mentioned below:
4.1 Data collection method
The present study is tired to evaluate different aspects of fast fashion such as current trends in the fashion industry, consumer behaviour, growth trends and sustainability issues of fast fashion. In this regards, the researcher considered both primary and secondary sources of information. The collection of primary data was performed through an online survey about Fast Fashion by sharing the link of the survey through SurveyMonkey that was being addressed as a most effective platform for assessing response about the subject matter (Mackey and Gass, 2015). This survey provided significant assistance for analysing consumer’s behaviour towards the fashion industry so as researcher got a range of data about personal demographics, purchase pattern, interest, brand preference and many more. By assessing appropriate responses, the researcher would be able to found appropriate research findings in the context of the subject matter. In the collection of primary data, special attention has been paid on young age participants because fast fashion has gained significant popularity of among young age buyers as a result of low price and trendy clothes (Silverman, 2016). On the other hand, the researcher also considered secondary sources of information in the section of literature that included online books, journals, internet articles, past studies and business reports of Zara. All these tools were played a critical role for assessing in-depth understanding of different elements that are influencing the fast fashion industry such as emergence and growth of the industry, problems based on environmental safety and other factors (Taylor, Bogdan and DeVault, 2015). By taking information about business strategies of Zara, researcher tired to evaluate current industry trends which have been followed by different companies for dealing with sustainability-related issues. The secondary sources helped the investigator in evaluation views, perception, findings of other authors, business theories and many more about the subject matter.
4.2 Data analysis method
In the context of the present study, the researcher considered both primary and secondary sources of information in which collection of primary data was carried out by considering questionnaire and the section of literature review considered different secondary source of information for analysing different elements of Fast Fashion. In the present qualitative study, the researcher has focused on exploring a wide range of information about the subject matter so as the thematic analysis was selected by the researcher for analysing findings of primary and secondary data (Bresler and Stake, 2017). In the context of thematic analysis, the investigator created different themes with reference to the questionnaire and other secondary sources of information. Thematic analysis was addressed as a great tool for analysing the research findings which had gained different sources for the generation of appropriate results with consideration of research aim and objectives. The thematic analysis found very effective for analysing the views of participants by using chart and diagrams so as reliable results could be produced to attain research objectives (Taylor, Bogdan and DeVault, 2015).
5. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
5.1 Results (Thematic analysis)
For analysing views participants, thematic analysis is carried out below in which different themes are created as per the aim and objectives of the study:
Theme 1: Gender plays important role is the fashion industry
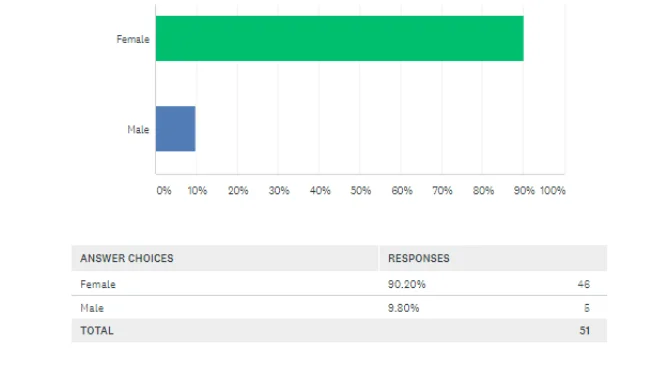
As per the above chart, it has found that the involvement of female consumers is significantly high in the fashion industry. This is because 90.20% of participants within total respondents were female. Therefore, it can be stated that the interest of female consumers is having a significant impact on the whole fashion industry.
Theme 2: Age of people influence their perception about the fast fashion
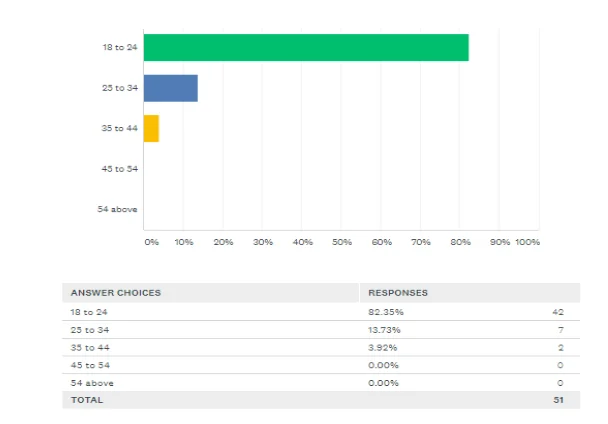
The above chart is showing the age group of participants in which majority of 42 out of 51 participants are associated with the age group of 18 to 24 years. Therefore, it has found that individuals associated with young age are having a significant interest in current fashion trends, trendy clothes and appearance so as it could be considered as an important element for the growth of fast fashion.
Theme 3: Most preferred product category

The above diagram was showing responses of participants when they were asked about the most preferred product category while selecting fashion and clothing range. In this context, the option of Fast Fashion was addressed the highest preference because 30 out of 51 participants selected a particular option. Furthermore, luxury mid-range products were gained the second most popular and were being selected by 22 participants as a second option.
Theme 5: Most preferred brand in Fast Fashion
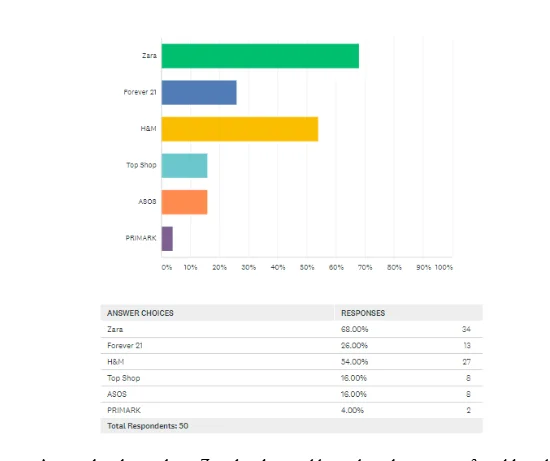
As per the above chart, Zara has been addressed as the most preferred brand in the context of Fashion. Zara was selected by 68% participants at first position then H & M got the second position with 54% responses and Forever 21 maintained third position with 28% preference. Therefore, it has addressed that Zara gained significant popularity in the context of Fast Fashion because the company is offering a wide range of products in great quality with pricing.
Theme 6: Reasons behind the selection of Fast Fashion brand
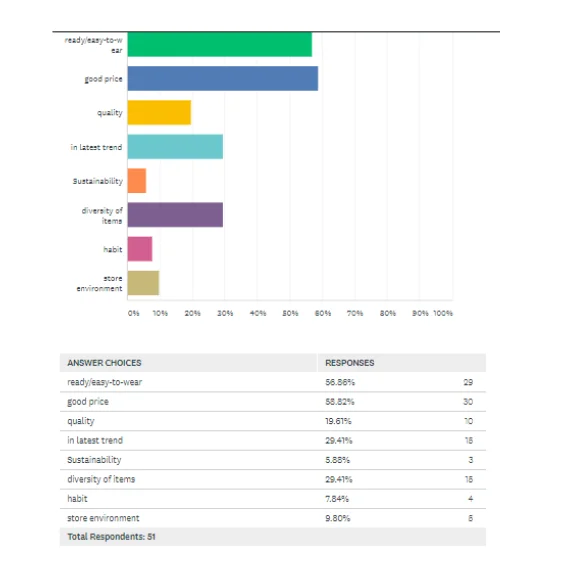
When the participants were asked about the most important element that influenced their purchase decision in the context of the fashion industry, then the researcher has addressed two options which have gained highest preference that includes a ready/easy-to-wear and good price. Further assessment of the above chart is determined that products with latest trends and diversified product portfolio have kept the second position in the context of most important motivators which could influence purchase decisions of consumers within the fashion industry.
5.2 Discussion
The present study is focused on examining different aspects of Fast Fashion that has gained significant popularity among young age individuals for accomplishing fashion needs. The analysis of a wide range of information in the context of fashion industry trend has found that gender plays a critical role for influencing the perception of people because female consumers have felt more attracted towards trendy clothes (Linden, 2016). In a similar way, people belong from a young age have paid significant attention to the current fashion trends. In this context, Simona Segre Reinach (2005) has determined that the demographics of an individual have been considered as an important motivator for determining the level of interest in fashion trends. It has addressed the young age people do not have an appropriate source of earnings so as they cannot afford high-end luxury clothes. These factors have been addressed as great motivators of Fast Fashion industry. This is because companies related to Fast Fashion are offering trendy clothes at comparatively low prices. Therefore, the participants in the presents study have considered the Fast Fashion Clothing as the most preferred product category because this industry has gained significant success through low-cost trendy clothes (Caro and Martínez-de-Albéniz, 2015). Therefore, it can be stated that the personal demographics of an individual are playing an important role in influencing the decisions related to the selection of clothing range. In the present study, Zara and H & M have been identified as the most preferred brands in the field of Fast Fashion because these brands are offering a wide range of clothing products at great price. Further analysis of business strategies of Zara has determined that Zara has formulated a rapid response team for assessing current trends in the fashion industry and their implementation of production units so as the company has gained great success in the field of fast fashion (Bhardwaj and Fairhurst, 2010). The findings of a study of Brooks (2015) have supported the above argument in which pricing, quality and design of clothing products have been addressed as most critical factors which are influencing the purchase decisions of consumers and Fast Fashion. Therefore, Fast Fashion has gained lots of business opportunities in the context of cheap and trendy products and top brands like Zara, Forever 21, H & M and others have gained significant success by accomplishing the interest of consumers. It can be stated that business policies of companies have offered great support in business expansion in Fast Fashion Industry (McNeill and Moore, 2015).
The assessment of primary data has found that young age individuals are significantly attracted towards ready to use wears which are available at great prices. Therefore, low-cost pricing strategy within trendy clothes of Fast Fashion has played enhanced its market share in the overall fashion industry. Garcia-Torres, Rey-Garcia and Albareda-Vivo (2017) have determined some negative arguments against Fast Fashion in which the growth of Fast Fashion is being considered an important cause of various sustainability issues. In this regards, a systematic analysis of a wide range of information about Fast Fashion has derived that reduction in pricing of clothing is being termed as a most critical factor for influencing the demand of distinct clothing range, but it could be termed as an important cause of environmental pollution and other sustainability issues. For example, increased demand cloth has enhanced the demand for cotton and other materials, and around 2000 gallons of water is required for growing cotton to meet the requirement of a pair of genes. In addition to that, other cloth manufacturing operations such as dying and beaching have increased the level of environmental pollutants (McNeill and Moore, 2015). Further sustainability issues have addressed in the field of employee management within Fast Fashion because companies have tried to reduce the cost by paying less to workers and reducing the quality of clothes. In addition to that, companies are not following appropriate safety norms for the safety of workers at the workplace, and it can be termed as an important issue within sustainable business operations.

6. CONCLUSION
This study has aimed to carry out a systematic investigation on Fast Fashion in which investigator has paid special attention to the growth of fast fashion, the impact of consumer behaviour, the role of business strategies and assessment of sustainability issues identified in Fast Fashion. In this context, the present study has concluded that Fast Fashion has gained significant success and growth within the contemporary fashion industry because it offers trendy clothes at a low price as compared to other luxury brands that are playing a critical role in the attainment of distinct needs and interest of people. This is because fashion trends and personal demographics of an individual have played important role in influencing the purchase decisions in the context of clothing products (Linden, 2016). While performing different activities in the present investigation, it has found that aim and objectives of the present study are appropriately aligned with each other so as it can be concluded that researcher has found significant support from reliable objectives during the collection of a variety of data about the subject matter. In this context of the present, objectives have developed in an appropriate manner and covered all factors associated with Fast Fashion. As per the nature of the present study, the qualitative research method is being termed as an appropriate tool for controlling different aspects of theoretical investigation. In this regards, the researcher has considered both primary and secondary sources of information that have offered great support in the assessment of a wide range of information. It has concluded that survey through an online questionnaire has enhanced the effectiveness of the primary data collection process because the researcher has addressed a wide range of responses from different individuals which are situated in different remote locations. It saves the wastage of time, and the researcher has taken a sample size of 51 participants that is appropriate in the collection of a variety of information related to Fast Fashion. In addition to that consideration of secondary sources of information has enhanced the effectiveness of research outcomes because it provides a basis for conducting an in-depth study about the subject matter in the section of literature review. By grouping the information which has been generated from primary and secondary sources, the effectiveness of research finding has been enhanced to meet research goals with an appropriate manner (Petro, 2012). This research methodology is being identified very useful in covering all research criteria by providing appropriate results through direct survey and literature review. The assessment of different results with reference to research objectives has concluded that demographics of young age individuals, as well as fashion industry trends, have been addressed as important motivators for the promotion and growth of Fast Fashion. Further discussion has derived business strategies for different fashion brands such as trendy cloth and low pricing have encouraged the demand for Fast Fashion Clothing. In this context, the majority of respondents have provided a positive response in the context of Fast Fashion because it has attained their fashion needs (Zhan, 2017). It has addressed that Zara has gained significant growth with its proactive mechanism for managing frequent production of clothes within a very short time span. It has addressed that Fast Fashion is being termed as an important cause for encouraging various sustainable issues such as environmental pollution, improper human resource practices within working units, lack of appropriate quality and many more that could lead negative impact on the future growth of Fast Fashion.
As per the findings of the present, the researcher would be able to perform a further investigation to determine different tactics for dealing with sustainability issues within Fast Fashion sector that would enhance understanding of different approaches and tactics for managing the environmental safety and fair business practices (Welters and Lillethun, 2011). Apart from that researcher needs to consider the approach of cloth recycling in the context of Fast Fashion as an important topic of further investigation through which researcher will be able to enhance its understanding about cloth recycling and reduction in the cost of products.
REFERENCE
Bhardwaj, V., and Fairhurst, A. (2010). Fast fashion: response to changes in the fashion industry. The international review of retail, distribution and consumer research, 20(1), 165-173.
Bresler, L., and Stake, R. E. (2017). Qualitative research methodology in music education. In Critical Essays in Music Education (pp. 113-128). Routledge.
Caro, F., and Martínez-de-Albéniz, V. (2015). Fast fashion: Business model overview and research opportunities. In Retail supply chain management (pp. 237-264). Springer, Boston, MA.
Garcia-Torres, S., Rey-Garcia, M., and Albareda-Vivo, L. (2017). Effective Disclosure in the Fast-Fashion Industry: from Sustainability Reporting to Action. Sustainability, 9(12), 2256.
Linden (2016) An Analysis of the Fast Fashion Industry. Senior Project Submitted to The Division of Social Studies of Bard College Zhelyazkov (unknown) Agile Supply Chain : Zara’s case study analysis. BA. Strathclyde University Glasgow
McNeill, L., and Moore, R. (2015). Sustainable fashion consumption and the fast fashion conundrum: fashionable consumers and attitudes to sustainability in clothing choice. International Journal of Consumer Studies, 39(3), 212-222.
Subramanian Senthilkannan Muthu (2018). Fast Fashion, Fashion Brands and Sustainable Consumption
Taplin, I.M (2014). Global Commodity Chains and Fast Fashion: How the apparel industry continues to re-invent itself. Competition & Change, 18(3), 246-264.
Taylor, S. J., Bogdan, R., and DeVault, M. (2015). Introduction to qualitative research methods: A guidebook and resource. John Wiley and Sons.
Zhang, J. (2017). Decision models for fast-fashion supply and stocking problems in internet fulfillment warehouses.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



