Social Media: Opportunities and Risks
Social media offers a huge potential in advancing learning and education as well as advancing communication, developing talents, and enhancing social interaction and engagement. For young people and children, social media platforms open doors to explore more, learn new skills, access learning materials and information, socialising, and connecting with peers either within same geographical area or far away. However, despite these positive elements, the platforms have been marred with negative effect such as bullying, abuses, cyberattacks, hacking, threats, and hacking. For parents and teachers seeking to leverage the social media platforms for the benefits of their children and learners, the negativity acts a huge barrier.
Findings and Discussion
Outline of results
Initially, the data was to be collected using both questionnaire ad interview. However, due novel COVID-19 pandemic and restriction imposed by the government, the data collection process followed on an online questionnaire. The design of the questionnaire questions was informed answering the questions of in what way the social media benefit the children and young people and challenges faced in navigating through social media. The participants invited to participant in participating in filling the online questionnaire, comprised on teachers, educators, parents, and guardians. The participants were directed through a provide link to the Google forms where the questionnaire was being hosted. Out of the initial population of 150 participants, those who responded to the invitation were 131 individuals.
Demographics


From the table above, majority of respondents were female (51%) with male being 42% of the respondents. In terms of age group, those within 35-44 formed the majority (47% of the respondents) then followed by individuals indicating being in the 25-34 age cohort (28%). The 45-60 age group also formed a significant part of the respondents (18%). On marital status, 71 (54%) participants indicated being married while 23% (30) saying being single. Eleven percent said being separated and 6% indicating living with partner. The questionnaire also included a question on the education level of the participants. Majority of the participants (51%) indicated that they held a university level education while 32% saying they had college level education. Nine participants (7%) saying they had attained post-graduate education level. Only 13 individuals (10%) said they had secondary level education. On the question on how the participant related/ role held, 63% of the respondents said were parents and 16% saying being guardian. Sixty participants were either teachers include head teacher while 5 being staff members and 6 indicating having educators’ role. Therefore, from these, it can be seen that participants were made up of different group of people with various roles and responsibility in relation to early child learning and development. As such, the opinion and view held by each individual will provide an insight into the wider perspective on perception held on social media.

Social media Familiar and Use
Continue your journey with our comprehensive guide to Emerging Tech in Maritime Industry.

According to the respondents, Facebook ranked highest in familiarity (69%) then followed by Twitter (57%). Instagram, TikTok, and Snapchat also ranked high where 31%, 29%, and 9% of the participant saying being familiar with the platforms. According to the Statista (2021), the most popular social media platforms based on the number of users include Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, QQ, WhatsApp, and WeChat. Twenty one individuals said being familiar with MySpace while eight said Tumblr

Use of Social Media


From the figure 3.2, the most respondents (50%) indicated accessing social media twice a day then followed by those who said to logging into the platforms at least five times a day (43 individuals). Twenty-nine participants indicated to being logged into the sites most of the times. On the other hand, only 6 participants saying not often do they use the platforms while 7 indicating using only once a month. From this data, it is evident that most individuals constantly use social media (using at least once a day).
Influence of Social Media
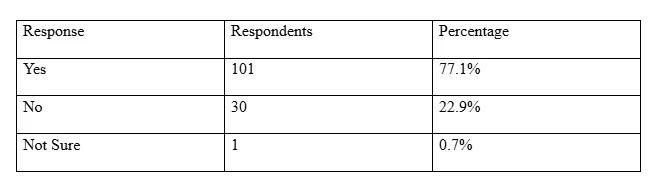
The questionnaire included a question on using the social media platforms for the good of a society. From table 3.3, majority of the participants (77%) held a view that social media has a potential of being used to advance social good. On the other hand, 30 participants (23%) saying the social media cannot be used positively.
Group Most influenced by Social Media

From table 3.4, majority of the respondents (54%) indicated teenagers are the most influence social group then followed by children (32%). Although the question did not indicate the influence is positive or negative, 83% of the respondents held that individual within the age category of Young adults, teenagers, and children were the most affected. Twelve respondents indicate older generation while 17 individuals saying older people are most influenced.
Influence of social media in a society
Table 3.5 outline the participants’ response to the question of perceive influence of social media to the society. The question was structure to be a multiple choice answer. Eighty-five participants noted that social media has enhanced entertainment the most, then followed by meeting and engaging with friends, where 48% of the respondents saying it is a platform of socialising with friends. Learning and assessing information as well as developing social skills were ranked high with 45% of the respondents saying the platforms are used to advance learning, developing social skills, and access to information.
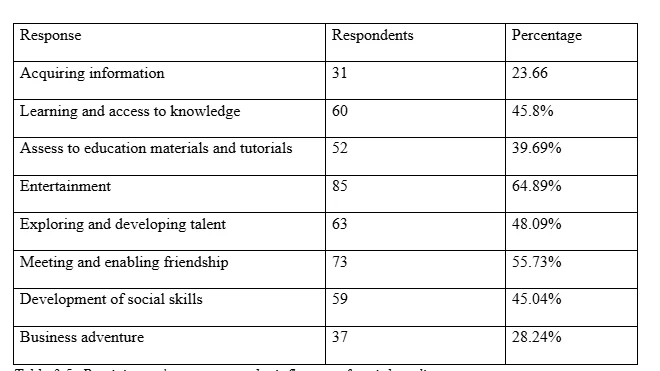
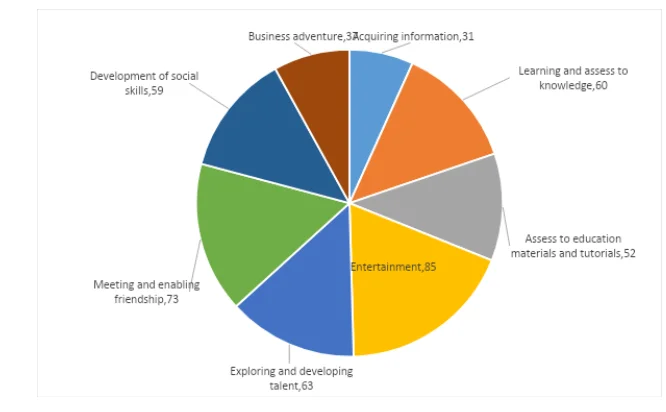
Similarly, 48% of the respondents said using social media to explore and develop talents, while 37 respondents (28%) noted use of social media to for business adventure. From the participants’ response, one can note that influence of social media transverse one area but impacting learning, entertainment, communication, socialisation, exploration of talent, and business worlds.
Biggest Social media challenges

As indicated by Table 3.6, the question on the biggest challenges faced by social media users saw majority noting cyberbullying (56%) then followed by hacking and phishing (48%), misinformation (45%), and misinformation (41%). The participants also noted identify theft (29%) and ransomware attacks (28%).

Currently, as pointed out by Rasheed et al. (2020), cyberbullying and abuses have become a big problem to the social media users. The prevalence of abusers and bullies in the cyber space has prompted some scholars calling for immediate addressing the problem because of the psychological effect it has on the bullied and abused (Yao et al. 2019; Hani et al. 2019). As noted by Van Hee et al. (2018), cyberbullying can comprise of sending mean message, racially and sexual abuse, pranks, using offensive and explicit language, threatening and manipulation, and stalking.
Use of Social media by the most vulnerable group from Cyberbullying and abuse

As indicated by table 3.7, the majority of participants (61%) held a view that the most vulnerable individuals in a society should not be allowed to access and use social media platform. Whereas, 44 individuals (33%) noting all be allowed but access and use to be moderated. On the other hand, those holding that these vulnerable group to be allowed were 28 (21%). Twelve individuals said not sure.

Stringent measures towards addressing negative influence of social media
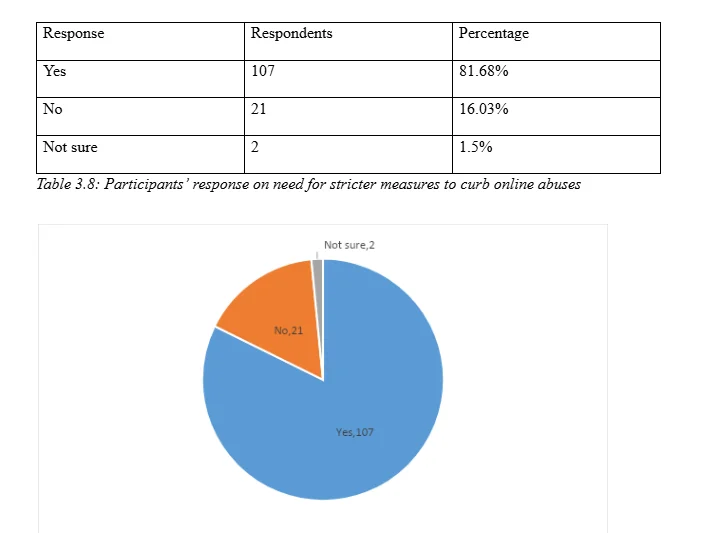
The questionnaire included a question on whether more stringent measures are need in order to address the negative influence such as cyberbullying, abuse, and identity theft. The response shown in Table 3.8 indicate significantly high number of individual hold the need for formulating and implementing stricter measures in order to reduce if not curb the abuse and bullying in the social cyber spaces.
An effective approach to addressing social abuse and cyberbullying
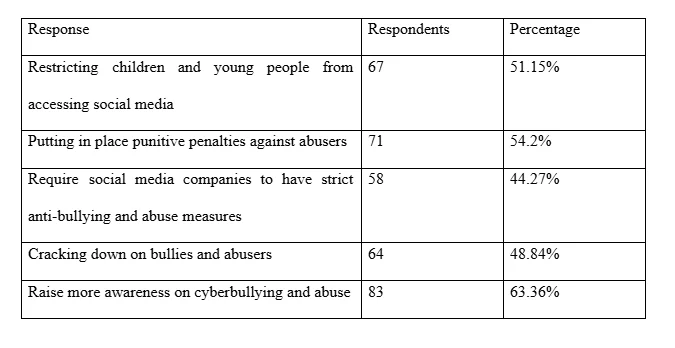
On the question of an effective approach of combating cyberbullying and abuse, the participant held various views. Majority of participant (63%) saying there is need to raise awareness on cyberbullying and abuse whereas 71 individuals holding that strict measures that a punitive are needed. Others indicated the need for restricting children and young people from accessing and using social media as intervention and preventive measures (51%) while some participant saying companies and governments should formulate and implement regulations towards anti-bullying and abuse.

In a study on preventive measures and intervention approach on cyberbullying, Espelage and Hong (2017) argued that rapid evolution of social media and supporting technology complexity bring complexity in regulating and intervening cyberbullying. However, not just regulatory bodies but a collaborative approach among parents, lawmakers, enforcers, media, and teachers is need to address the issue. Although studies do not have a concrete approach to how, they do agree on the need for to intervene and prevent cyberbullying and abuses (Tanrikulu, 2018; Sorrentino et al., 2018; Agatston, and Limber, 2018). Some scholars have called for inclusive approach where both parents/ guardian and teachers take part in development and implementation of measures, others pointed to encompassing the larger society through more awareness through media and calling out cyberbullying, while other hold requiring social companies and government to implemented strict anti-bullying and abuse regulations (Cuesta Medina et al., 2020).
References
- Agatston, P. and Limber, S., 2018. Cyberbullying prevention and intervention: Promising approaches and recommendations for further evaluation. In Bullying prevention and intervention at school (pp. 73-93). Springer, Cham.
- Cuesta Medina, L., Hennig Manzuoli, C., Duque, L.A. and Malfasi, S., 2020. Cyberbullying: Tackling the silent enemy. International Journal of Inclusive Education, 24(9), pp.936-947.
- Espelage, D.L. and Hong, J.S., 2017. Cyberbullying prevention and intervention efforts: current knowledge and future directions. The Canadian Journal of Psychiatry, 62(6), pp.374-380.
- Hani, J., Nashaat, M., Ahmed, M., Emad, Z., Amer, E. and Mohammed, A., 2019. Social media cyberbullying detection using machine learning. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 10(5), pp.703-707.
- Rasheed, M.I., Malik, M.J., Pitafi, A.H., Iqbal, J., Anser, M.K. and Abbas, M., 2020. Usage of social media, student engagement, and creativity: The role of knowledge sharing behavior and cyberbullying. Computers & Education, 159, p.104002.
- Sorrentino, A., Baldry, A.C. and Farrington, D.P., 2018. The efficacy of the Tabby improved prevention and intervention program in reducing cyberbullying and cybervictimization among students. International journal of environmental research and public health, 15(11), p.2536.
- Tanrikulu, I., 2018. Cyberbullying prevention and intervention programs in schools: A systematic review. School psychology international, 39(1), pp.74-91.
- Van Hee, C., Jacobs, G., Emmery, C., Desmet, B., Lefever, E., Verhoeven, B., De Pauw, G., Daelemans, W. and Hoste, V., 2018. Automatic detection of cyberbullying in social media text. PloS one, 13(10), p.e0203794.
- Yao, M., Chelmis, C. and Zois, D.S., 2019, May. Cyberbullying ends here: Towards robust detection of cyberbullying in social media. In The World Wide Web Conference (pp. 3427-3433).
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



