Communication in Mental Health Care
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Overview of the study
Mental Health is referred to the behavioural, cognitive and emotional state of well-being in which all the individuals required to have the potentiality for coping with stress experienced normally in life and can work in a productive as well as fruitful way along with would be able to contribute properly in the social community. The individuals who are treated in the mental health settings are often seen to lack psychological well-being and mental ability to cope with life and participate normally in the community. In this setting, proper communication is required to be established by the support workers so that they are able to develop an effective relationship with the service users to understand their specific needs and demands to ensure satisfactory care to the service users. The development of effective relationship through communication in mental health setting is also essential for the support workers so that the service users trust them and avoid creating barriers in accepting care from them. In mental health settings, the support workers require to have proper non-verbal and verbal communication skill to properly show support to the service users. Thus, to understand the way these natures of communication are used by support workers in mental health settings the project has been formulated.
1.2 Background of the study
The support workers in mental health settings establish effective communication through non-verbal and verbal methods with the service users. This is done to ensure enhanced care experiences to the patients as well as increase the self-confidence of the support workers to offer proper care without barriers or conflict from the service users (Stanyon et al. 2016). However, in many mental health settings, it is been reported that proper communication is not being established by the support workers that are creating hindrance in offering satisfactory care to the service users (Vermeir et al. 2015; Stensrud et al. 2012). This is because without the development of effective communication in the mental health settings the support workers are unable to understand exact needs and demands of the service users which are making them incompetent in framing satisfactory care services. Moreover, lack of communication leads the support workers unable to receive complaints from the service users which they have with their services making the support worker unfit to understand the way they are to create changes in their service providing ways to satisfy the service users (Alsawy et al. 2017). Therefore, this study is framed to identify the detailed methods of communication used by the support workers in mental health settings along with the issues and hindrances faced by them that are making them unable to establish effective communication. Moreover, the topic is being explored so that theoretical knowledge developed from practical healthcare environment can be provided to the support workers in mental health settings to understand the methods of communication and its importance of use at the settings along with the barriers to be faced and the way they can be resolved.
1.3 Research Rationale
According to the report of Parliamentary and Health Service Ombudsman, after analysing more than 200 mental health complaints received five common failings has been identified out of which poor communication with the patients and their family by the support workers is one of the failings. The failure of communication is proved from several complaints one of which is where a woman with a history of bipolar disorder reports that her baby was taken from her without any form of communication made by the support workers that result her to cause immense distress (www.ombudsman.org.uk, 2018).
The inability to execute effective communication by the support workers in the mental health settings has become an issue because it has created an increased error in care for the service users. This has resulted service users to experience dissatisfaction with the care provided to them, in turn, has resulted in creating conflict between the service users and the support workers (Price et al. 2018). In the study of Furnes et al. (2018), it is reported that the lack of use of effective communication methods by support workers between themselves in the mental health settings has created hindrance for them to determine and have confidence to deliver proper care to service users. This is because through open communication methods with experienced health professionals the support workers were previously able to determine the nature of specific care for mentally-ill individual in a proper manner. Thus, the lack of proper use of communication method by the support workers in the mental health settings has become an issue as it is posing hindrance for them to offer care with confidence.
The inability of the support workers to use proper method of communication has presently become an issue as it is determined by the NHS as one of the causes among many for causing 271 deaths in the mental health setting between 2012 to 2017 in the England and Wales (www.theguardian.com, 2018). This indicates that issues with communication implementation by support workers have become a vulnerable cause in mental health settings as it has resulted not only in improper care but also in deaths. Thus, this study is being developed to shed light on the methods of communication used by the support workers in mental health settings and the barriers faced with the implication of the methods that are creating hindrance in care for service users.
1.4 Research Aim
The aim of the study is to identify the methods of communication used by support workers in mental health settings and its impact on patients as well as on support workers along with the barriers faced with the implementation of the methods and the way they can be reduced to ensure effective communication development in the mental health settings.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1 Introduction
In this chapter, the critical analysis of the communication methods used in mental health settings by the support workers is to be executed to understand its impact on the services as well as on themselves. In relation to this, different theories and models are to be used to develop a logical understanding regarding the impact of communication and the barriers faced with its implementation in mental health settings. Further, an effective framework is also to be developed to determine the rationale related to the study.
2.2 Concept of communication in mental health settings
Communication is referred to as exchanging or imparting of data or information through writing, speaking or another medium to others (Aggarwal et al. 2016). In mental health settings, communication is made to let the service users have proper answers regarding the queries they have regarding the care service provided. This is because through communication the support workers are able to inform the service users about the benefit of the acceptance of the care services being provided to ensure their well-being (Fisher et al. 2016). The communication in mental health settings is also made between support workers so that they can consult with one another to determine the best way of providing any complex care in an easier manner to ensure greater satisfaction and well-being of the service users (Elhai and Frueh, 2016).
2.3 Factors that influence communication in mental health settings
The psychological instability of the service users in mental health settings due to their illness leads them to be unable to properly understand messages and make decisions for their care through verbal communication (Munson and Jaccard, 2018). This, in turn, influences the support workers to use non-verbal mode of communication in which they try to get information from the service users regarding care through analysis of their expression, body language and others. Moreover, it also influences the support workers to use verbal mode of communication with the family members of the service users in talking decision regarding their care. The past experiences of the service users influence the communication with the support workers. This is because in the past the service users may have been ignored or abused or harmed while making communication due to the fear of which they presently avoid to create interaction with the support workers through any method of communication used by them (Paternotte et al. 2015). The misinterpretation of the messages provided by the support workers to the service users through verbal or non-verbal method of communication influences interaction between them in the mental health settings (Lyngstad et al. 2015). This is because misinterpretation may lead the service users avoiding further participation with the support workers in making interaction. The cultural diversity influences communication in mental health settings by making the support workers use different method of communication for individual patients according to their cultural orientation (Ross et al. 2016). This is because the cultural perspectives differ among all the culture based on which the support workers are required to use specific communication mode for the patients for successful interaction.
2.4 Model of Communication
2.4.1 SOLER model of communication
The SOLER model is used by the support workers in the mental health settings while communicating with the service users to ensure establishment of productive non-verbal method of communication. The SOLER model informs that the support workers are to sit squarely, has open posture, lean towards the service users, make eye contact and relax (Quiddington, 2018). The sit squarely is important for the support workers to indicate their positive posture which reflects the service users that the support workers are attentive to listen to them. The open posture in the non-verbal method of communication is used by the support workers to show they are concerned and interested regarding the well-being of the service users (Barker and Williams, 2018). The leaning towards the service used to indicate the service users that they are being attentively listened to by the support workers. The making of direct eye contact with the service users during non-verbal communication makes the support workers indicate they are focusing on the concerns they are reporting to them. The relaxing attitude in non-verbal communication is required by the support workers to avoid being anxious and show negative body language towards the service users (Treloar et al. 2018). The support workers by abiding with all these aspects of non-verbal method of communication are able to show value to the service users which makes them fruitfully communicate with them verbally in the mental health settings.

2.4.2 Transactional Model
The transaction model of communication is referred to the model in which the communication is made in a two-way direction (Glanz et al. 2015). This model of communication is used by the support workers in the mental health settings to successfully implement verbal method of communication. This is because two-way of communication development in verbal method of communication helps the support workers in the mental health settings to understand the needs and demands of the service users, as well as they, are able to deliver valuable information of care services to the service users. It is done with the intention to develop care practices that offer satisfaction to the service users and the support workers are able to include decision of the service users regarding their care to lower conflict while providing care in the mental health settings (Mikesell et al. 2016).
2.5 Theory of Communication
2.5.1 Peplau's Interpersonal Relations Theory
The Peplau's Interpersonal Relations theory informs that interpersonal competency is to be developed by the support workers to assist the service users in any work required for regaining their well-being and healthy life. The theoretical principles indicate that the interpersonal competencies to be developed by the support workers in health settings are leadership, motivation, flexibility, patience and others (Calohan et al. 2016). The support workers in mental health settings according to the theory developed flexibility to execute any method of communication. This is because without being flexible they cannot use the method of communication and the way it is to be established as per the wish of the service users which would result in creating improper interaction and information sharing between them (Deane and Fain, 2016).
2.5.2 Dyadic Interpersonal Communication theory
The Dyadic Interpersonal Communication theory informs the face-to-face interaction of mutual ideas between two people (Pietromonaco and Collins, 2017). The support workers use dyadic theory in the mental health settings as it helps them to get live feedback regarding their care through the facial expression and body language of the service users (Howland et al. 2016). It makes them take immediate actions to resolve any complication. Moreover, the use of theory assists the support workers to focus on the voice of the service users to understand the extent of satisfied or dissatisfied they are with their services making them alert to understand the importance of the situation in a proper manner (Carson, 2017). In mental health settings, the development of an effective relationship between the support workers and service users are required to fruitfully provide care and improve the well-being of the service users (Pincus, 2018). The use of this theory offers this opportunity to the support workers as well as helps them in showing value and ensures maintaining confidentiality of service user’s information in mental health settings.
2.6 Concept of support workers in mental health settings
The support workers in mental health settings are the one who is entrusted to offer assistance to the service users with their immediate needs like dressing, maintaining hygiene, washing and others (Fekadu et al. 2016). This is because the mentally-ill individuals due to loss of proper emotional and psychological condition experiences hindrance with executing daily activities. The support workers are responsible for monitoring the health condition of the patients as well as report patient assessment to the health professionals. They also perform the duties to maintain medical information and records of the patients and are entrusted to provide support and information to the families of the service users regarding their care and health (Ross et al. 2015).
2.7 Factors influencing communication by support workers in mental health settings
The lack of proper training is seen to act as key factor that may influence support workers in the mental health setting to experience hindrance in properly performing their duties (Hollis et al. 2017). This is because without training the support workers do not have the efficiency and skills required in the practical field of mental health settings to perform their duties appropriately. The presence of background noise acts as key factor that disrupts the development of effective communication by the support workers in mental health settings (Ambrose-Miller and Ashcroft, 2016). This is because noisy environment interferes in the pathway of the service users while informing their personal information to the support workers making them avoid executing further communication. Moreover, the noisy environment makes the service users feel vulnerable that while communication their personal information may be made public as they have use higher tone of voice to interaction to let the support workers understand the information. This is another reason which negatively influences communication to be established between service users and support workers in mental health settings. The increased use of complex medical terms by the support workers while developing information with the service users leads to create hindered communication. This is because terms are unable to be understood by the service users which make them interpret the messages in a wrong manner creating disrupted communication (Scheff, 2017).
2.8 Model for support workers in mental health settings
2.8.1 Integrated Healthcare Model
The Integrated Healthcare model is referred to the approach in which people-centred health systems are used by promoting the comprehensive delivery of quality care services that are designed as per the multi-dimensional needs of the service users which is provided with the help of coordinated effort of multidisciplinary team of care providers (Marais and Petersen, 2015; Petersen et al. 2016). The model is used by support workers in the mental health settings to determine through consultation with the multi-disciplinary team for exploring the suitable methods of communication for service users for establishing fruitful communication. This is done with the intention to improve their ability in making successful communication to identify the needs of service users and create change in their service delivery ways to ensure effective satisfaction to the service users.
2.8.2 Collaborative Care Model
The Collaborative Care Model has the approach of integrating primary care providers along with care managers and psychiatrist to monitor the health of the mentally-ill patients and provide care to them (Watkins et al. 2017). The model is used by support workers in making communication with service users in the mental health settings as according to the approach mentioned in the model the support worker consult with the psychiatrist and care managers to identify the best method of interaction with the patient. This is because the psychiatrist has better knowledge regarding the psychological condition of the mentally-ill patients and the way they are going to respond to which nature of communication to be executed in the best manner. The Collaborative Care Model is also used as it helps the support workers to keep the service users in the middle while making decision regarding any care or method of communication to be used to gather or deliver information successfully (Marais and Petersen, 2015).
2.9 Theory for support workers in mental health settings
2.9.1 Psychodynamic Theory
The Psychodynamic theory emphasises on identifying the unconscious psychological process and contends that is developed from previous experiences in the childhood which are crucial for developing the present adult personality (Lopes and Cutcliffe, 2018). The theory is used by the support workers in the mental health settings to identify the reason behind the behaviour and feelings portrayed by service users while making communication and offering care. Thus, it helps support workers to understand the subconscious mind of the service users. It is beneficial for them to understand each method of communication are to be established by them to get fruitful results which are sharing of information between them and the service users.
2.9.2 Cognitive Theory
The Cognitive theory is referred to the psychological approach which attempts to explain the behaviour of the human through understanding of their thought process. Thus, the theory assumes the thoughts as the primary determinants of the behaviour and emotion reflected by the individuals under any condition. The cognitive theory is being used by the support workers to establish effective communication with the service users as it helps them to understand the reason of the abnormal behaviour executed by the service users during the communication and the way the issues are to be resolved to establish effective communication (Kehle-Forbes et al. 2016).
2.10 Impact of methods of communication used by support workers in mental health settings
The verbal method of communication used by the support workers in the mental health settings helps them to develop feedback and share information with service users and between themselves within less time (Burgio et al. 2018). This is effective for the support workers to make quick changes in the care services and delivery of any extra care service to the service user at the earliest resulting in better care delivery to the patients in mental health settings. The verbal communication by the support workers provides them chances of clearing in any doubts regarding the care needs and demands of service users (Percy et al. 2016). This aspect of the communication is effective to provide quality care to the service users in mental health settings as fewer errors are faced in delivering care as the support workers have clear concept regarding any complex needs of the service users. The verbal communication method allows the support workers to persuade and control the decision regarding care services by the service users (Wallin et al. 2016). This is effective as the service users who do not initially accept to consider certain care services from the support worker even being essential for their well-being are able to be persuaded through verbal communication by the support workers to ensure improved health of the patients at the end.
The non-verbal communication helps in representing the information in an easier way through the use of audio, visual and other means of non-verbal communication (Lavelle et al. 2015). This is effective for the support workers to let service users effectively understand the way complex care services are provided to them, in turn, assisting the service users in making better decision regarding their care. The non-verbal communication is referred to act as complement to the verbal communication (Pompili et al. 2016). This means that the support workers are to develop proper non-verbal communication to ensure they can also successfully verbally communicate with the service users.
2.11 Challenges with communication faced by support workers in mental health settings
The lack of confidence of the support workers while using any method of communication act as challenge for them in developing fruitful interaction with the service users (Caswell et al. 2015). This is because lack of confidence results the support workers to stammer and maintain improper body language that makes the service users feels lack of value while communication, in turn, making them avoids interaction. The lack of privacy while using any method of communication act as challenge for the support workers in establishing successful interactions with service users (Hollands et al. 2016). This is because without privacy the service users feel vulnerable to be abused or harmed which led them to avoid making further communication with the support workers. The improper use of voice tone creates challenge for the support workers in establishing fruitful conversation with the service users in mental health settings. This is because higher voice tone makes the mentally-ill individuals feel disrespected and verbally abused which leads them to avoid further communication with the support workers (O’Brien et al. 2018). The emotional disturbance of the service users creates challenge for the support workers to establish any methods of communication in mental health settings. This is because emotional disturbance leads the mentally-ill service users lose psychological balance which leads them to be incapable to effectively participate in any communication that makes the support workers face hindrance in delivering the proper meaning of the message or information to them (Isobel and Delgado, 2018).
2.12 Gaps in Literature
In executing the review of the literature, various gaps were found in the studies. The literature analysed were unable to provide detailed information regarding the way various communication methods are used by the support workers in the mental health settings. Further, there is lack of information on the detailed choice of the communication methods according to which the support workers prefer one over another in the mental health settings. The studies analysed were unable to offer information regarding the way strategies are to be used in different methods of communication by the support workers to develop successful interaction with the service users and themselves in the mental health settings. There was also lack of information on the way various methods of communication is to be executed by using technologies by the support workers to develop better communication in the mental health settings. Thus, this informs that the study requires greater insight into the methods of communication used by support workers in mental health settings to develop effective communication.
Chapter 3: Methodology
3.1 Methodological Approach and Design
In this study, instead of inductive approach the deductive research approach is to be used. The deductive research approach helps the researcher for developing information on the basis of existing model, theories and concepts that are related to communication methods in mental health settings (Sullivan et al. 2017). Thus, it is to be used as it helps the researcher to conduct the study with less error and collected validated results regarding the communication methods used in mental health settings. The inductive approach have been preferred to be use in studies where the study requires new theories to be developed and since no new theories in this study can be developed thus it is not to be used (Isobel and Edwards, 2017). The descriptive design is to be used in the study because this design helps the researcher to include negative and positive aspects of the study topic and develop information critically in the study. The exploratory and explanatory designs are not to be used as they are used in studies where research objectives or aim are not defined (Itzhaki et al. 2015; Guetterman et al. 2015). However, in this study research aim and objectives are clearly mentioned and thus they are not to be used in the study.
3.2 Search Strategy
The search strategy informs about the plan to be used by the researcher to gather relevant information for solving the encountered problem in the study. In this study, the case study research strategy is to be used as it provides clear understanding regarding any complex case in the most effective way. The advantage of using case study method is that it helps the researcher to collect data from practical situation by analysing the participants in real-time (Semrau et al. 2015). Thus, using the strategy is going to help in adding value to the study. Moreover, the case study method is useful for this study because it improves communication with the participants, ameliorates analytical thinking and helps the researcher develop tolerance for various views on the same subject that is in this study is identifying various methods of communication used in mental health settings by the support workers. The limitation of using case study strategy is that it includes observation and perception of the researcher only and there are chances that the researcher may be missing different aspects that are to be focused one completely (Ng and Weisz, 2016). Thus, this may led to develop partial collection of information regarding the study topic. The case study strategy is to be used to collect information about the experiences of support workers in using different methods of communication while working in mental health settings. Moreover, the strategy is to be used for understanding regarding the way different health professionals are using communication methods in mental health settings to interact with the service users. The case study is to be conducted in three specialist wards which are wards for people with learning disability, people suffering from dementia and rehabilitation mental health ward present within a single mental healthcare unit.
3.3 Research Question
The research question is to be formulated for the study by using PICO tool which is the technique usually used for executing evidence-based practice to identify answers related to the key question of the study. As commented by Bourne et al. (2018), clinical questions are to be developed in such a way so that it is directly related to the clinical problem and facilitates to develop proper answers regarding the key problems identified in the study. Therefore, this study used PICO framework tool to develop the research question. The PICO stands for problem, intervention, control and outcome (Siegfried et al. 2018). The Problem informs to mention the identified issue in the medical field which in this study is issues in using methods of communication by the support workers in the mental health settings. The Intervention informs about the area of interest of the researcher which in this study is strategies or ways to conduct different methods of communication by support workers in mental health settings. In this study, no comparative or control group was used. The outcome informs about the results or impact on the patients which in this study is improved use of communication methods by support workers to develop effective communication in the mental health settings.
The final research question framed by considering the framework tool is that: What are the ways in which different communication methods are to be used by support workers in mental health settings to reduce challenges experienced in making communication?

3.4 Sampling Technique and Participant Group
The participant group selected for executing the study are senior nurse, ward manager, support worker, service users and support workers who are involved in providing services to them in the mental health settings. In probability sampling, the participants are seen to be selected on random basis where selected participants represent the population as a whole (McChesney et al. 2015). The sampling technique is used for selecting participants for the quantitative data collection where out of total 200 support workers, senior nurse and service users in each ward 100 are selected. In non-probability sampling technique, the selection of the participants is done on the basis of the purpose of the study where all the selected individuals do not represent the population as whole (Drabble et al. 2018). This sampling technique is used for selection of participants for qualitative study where total of 3 support workers and 2 ward managers in each ward are selected.
3.5 Data Collection Technique
The study is going to use mixed data collection technique for gathering information regarding the different communication methods and the way they are used by support workers in mental health settings. As asserted by Loi et al. (2015), quantitative collection of data involves the gathering of numeric data. The method is used as it helps the researcher to collect wider amount of data within short amount of time. This avoids the researchers to encounter error for determining average ration of data. As argued by Rabelo et al. (2016), qualitative data collection includes gathering of information about the perception, feelings and expression of the participants. This helps the researcher to understand the thoughts and views of the participants regarding the study topic. In this study, both quantitative and qualitative data collection technique is to be used so that the limitation of using one method is cancelled by the benefit of another method. In collecting quantitative data, close-ended questionnaires are to be used that is to be provided to the participants through person and internet. In collecting qualitative data, open-ended questionnaires are to be used for interviewing the selected participants of the three wards so that they are free to inform about their concept regarding methods of communication used in mental health settings.
3.6 Ethical Consideration
In order to ensure ethical considerations, the researcher is going to take initial permission from the gatekeeper of the mental health unit for conducting the study by informing in details about the way data is to be collected and way they are to be used. The Data Protection Act 1998 is to be followed by the researcher which informs that no data of any individual is to be made public or used without the prior permission of the owner (www.legislation.gov.uk, 1998). A consent form is to be provided to each participant in the three wards where the reason behind executing the study and the way the data to be collected from them along with the way the collected information is to be used is to be mentioned in details. This is required to help the participants take an informed decision regarding their participation. Moreover, no participants are to be forced to participate in the study and each of the participants is provided with the will to leave the interview and avoid answering any questions at any time during the execution of the study.
Chapter 4: Findings and Results
4.1 Quantitative Results
1. Which method of communication is appropriate to be used to successfully interact in the mental health settings?

2. Which type of communication is used by you to interact with the service users in the mental health settings?

3. Which type of communication is used by you to interact with other support workers in the mental health settings?

4. Which factors influence the choice of method of communication to be used in mental health settings?

5. What challenges or barriers are faced by you while using any methods of communication in mental health settings?
6. How far do you agree that proper methods of communications are fruitfully used in mental health settings?
4.2 Qualitative Results
1. Frequent method of communication used in mental health settings
The participants of the learning disability ward inform that verbal accompanied by proper non-verbal method of communication is mainly used by support workers in communicating with the service users. One of the participants informed that "I communicate verbally any information to the service users in an empathetic manner by maintaining positive body language and lower voice tone because service user’s learning inability makes them unable to understand written communication in proper manner all the time”. Another participant in the Dementia ward informed “I use verbal accompanied by non-verbal communication because these methods of communication help me develop proper relationship with the service users to make them comply with me to accept care services in an easier manner. Moreover, written communication is time-consuming and requires longer process comparison to verbal or non-verbal communication”. The ward manager in the Rehabilitation ward informed: "I use written communication to interact with support workers to let them know their duties and way to perform them”. One of the support workers in the same ward reported: “While communicating with service users to prefer using verbal communication method over written method as it offers us more scope to talk and understand the needs of them at personal level”. Thus, the collected transcripts inform that verbal and non-verbal method of communication is frequently used by support workers in all the specialists wards in mental health settings to communicate with service users and written communication method is mainly used for formal interaction between staffs.
2. Skills used for verbal and non-verbal communication method in mental health settings
One of the support workers in Rehabilitation ward informed: "While I use verbal method of communication I try to speak with confidence, focus on my body language and practice humility”. However, another participant in the Dementia ward informed: "In our ward to communicate effectively in verbal mode, I consider one should have effective listening skill and patience as well as need to use simple words”. In Learning Disability ward, one of the participants informed: "I try to be authentic while speaking and consider keeping direct eye contact with the service users and focus on the gestures made by me and service users while communicating non-verbally”. A participant from the Dementia ward mentioned: "I try to be friendly while using verbal method of communication and in non-verbal method that is accompanied with verbal communication I consider keeping proper facial expression, eye contact and low voice tone to interact”. Thus, the information indicates that support workers in mental health settings keep focus on facial expression, listening, eye contact, gestures, posture and tone of voice while using non-verbal communication method. However, in verbal communication method, they focus on words used, practice humility, confidence, focus on body language and others.
3. Impact of different communication methods in mental health settings
One of the participants informed, "Communication is essential between us and service users as it helps us to get clarified regarding their needs and demands of services". Another participant in Learning Disability ward informed: "Making fruitful communication with service users helps me to avoid unnecessary conflict with them and resolve their confusion regarding any care creating ease in care delivery”. The other participant in the Dementia ward informed: "Communication helps us build close relationships with the service users to create familiar health environment for them”. Thus, it indicates that communication in mental health settings is important for the support workers to create ease in delivering services and provide quality care to service users.
Chapter 5: Discussion
The data collected from the case study informs that verbal communication method is most appropriate to be used by support workers to fruitfully interact followed by non-verbal method of communication. The written and visual communication skills are less frequently used method of communication as per the information. This is evident as 39% reported verbal communication and 27% reported non-verbal communication compared to 15% reporting written and 11% reporting visual method of communication as the appropriate method of communication to be used in making communication in mental health settings. In the reviewed literature, it was informed that verbal method of communication was essential to be used in mental health settings by the support workers as it helps them to fruitfully communicate care information regarding patients to the family members as well as to service users (Burgio et al. 2018). This is essential to create informed decision regarding care intervention to be offered to service users for the improvement of their mental health. Moreover, literature also supports verbal method of communication to be essential in mental health settings because it helps the support workers to persuade service users to accept complex care without less conflict due to better clarification of the way the care is to be provided (Wallin et al. 2016).
The literature supported non-verbal method of communication to be used along with verbal communication as proper non-verbal communication is mentioned to improve the strength of verbal interaction made by the support workers in the mental health settings. However, the literature lacked to mention any aspect of written communication method being appropriate to be used for interacting in mental health settings. One of the reasons may be that the written communication method use requires proper mental perception and psychological condition of both communicator and listener. In mental health settings, often the service users lack proper mental perception or psychological condition to understand written message (Folker et al. 2018). Thus, the method may not be thought to be appropriate for use in mental health settings for communication between support workers and service users.
The quantitative data collected from the case study research is that support workers prefer to use face-to-face, oral and written communication to communicate any information between one another. However, the support workers prefer to use face-to-face communication as the key type of communication to interact with the service users. This is evident as participants in the study informed that 30% preferred face-to-face, 27% preferred oral and 29% written type of communication to interact with other support workers but nearly 41% of support workers reported they prefer to use face-to-face communication as the key type of interaction to communicate with service users in mental health settings. In the previous studies, it is mentioned that face-to-face communication by support workers in mental health improves social contact and reduces risk of depression, anxiety and inappropriate behaviour of the mentally-ill individuals (Chan et al. 2016). This is because it allows the service users to build proper rapport and trust by directly communicating with the support workers. In the study of Ruesch et al. (2017), it is informed that written communication is hard to be understood properly by the mentally-ill people as they are psychologically able to develop the meaning of the information making the support workers avoid using it in develop agreement regarding care in the mental health settings.
The support workers prefer to communicate face-to-face with other support workers because it offers them to share information more accurately within minimum time (Tsoh et al. 2016). Thus, the support workers during confusion can be able to ask for immediate help or assistance through this type of communication in mental health settings for controlling any situation in such a way so that it does not create chaos. The written communication type is equally important for the support workers to interact between themselves because it helps to get detailed information about any aspect which they require to offer quality care to the service users. The written communication often include previous patients record and treatment process, details of providing care services and others which when shared between support workers provides them greater scope and knowledge in executing complex mental health care intervention in an appropriate manner without any confusion (Dreison et al. 2018).
The support workers inform that the method of communication to be used is based on certain factors. It is evident as 21% reported patient’s psychological condition, 25% type of message, 19% urgency and secrecy and 18% reported relationship factor influence them to choose the method of communication to be used by them. The messages regarding patient’s health condition are often communicated by support workers in written format that are collected by them on daily basis to health professionals which are required by the professionals to understand the progress of the patients (Beidas et al. 2015). This is because in this way detailed information regarding patients can be shared by the support workers in the mental health settings which they require to execute to ensure from the health professionals regarding the way they are to change their services accordingly if needed. However, the urgent messages are often seen to be informed through verbal communication method. This is because it is the fastest way of communicating the information in mental health settings where immediate actions are often needed as mentally-ill patients may act in weird manner all of a sudden due to any psychological imbalance in the brain.
The relationship acts as effective factor in choosing the method of communication in mental health settings. It is evident as often information between the health professionals or managers or higher officials is shared with the support workers in written method compared to verbal interaction. This is because written method of communication ensures detailed sharing of information without confusion and it is formal in nature (O'Brien and Cadwell, 2017). However, informal relationship that usually exist between support workers and service users verbal and non-verbal method of communication is chosen as they are regarded as effective way of developing interaction between one another. The psychological condition of the patient also influences choice of communication method because mentally-ill individuals are often seen to be unable to understand written information as a result of their deteriorated mental condition. It is evident as individual with inborn mental health issues such as autism is often unable to understand proper meaning of written information (Griffiths et al. 2017). However, they effectively understand verbal communication and thus the method of communication to be used is based on psychological condition of patients.
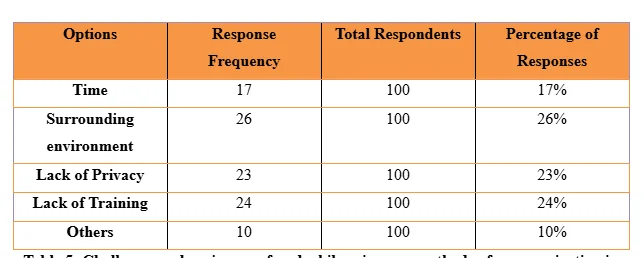
In the gathered quantitative data from the case study, 17% reported time, 26% reported surrounding environment, 23% lack of privacy, 24% lack of training and 10% other issues as barriers in making effective communication. The lack of time in making communication leads the support workers experience hindrances to properly understand the needs of the service users in mental health settings and issues with communicating the service users about care provision to influence them to accept the care intervention without conflict (Caswell et al. 2015). Thus, time acts as a key hindrance in making successful communication between support workers and service users. As mentioned by Brophy et al. (2016), lack of training of the support workers to make effective communication act as barriers for them to use communication methods successfully. This is because without training the support workers do not have required skills to identify and use proper methods of communication in mental health settings to establish fruitful interaction.
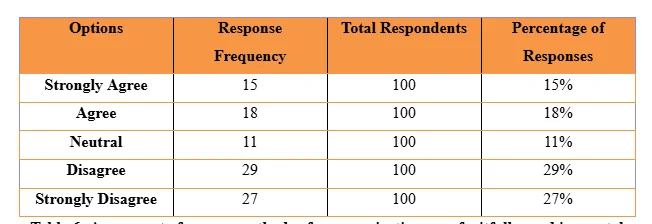
In the literature, it is already mentioned that the surrounding environment which is noisy in nature creates barriers in communication by the support workers as they are unable to interact with confidence and deliver messages successfully to service users (O’Brien et al. 2018). The previous literature also supports that lack of privacy creates barriers in using methods of communication successfully by support workers as the service users in this situation who are mentally-ill are seen to avoid cooperation to interact out of fear or abuse or harm due to revelation of personal data (Hollands et al. 2016). Thus, the barriers are seen to be valid in nature and proper strategies are required to be implemented to resolve them. The study reveals that 29% disagree and 27% strongly disagrees that proper methods of communication are being fruitfully used in mental health settings to execute interaction. Further, only 15% strongly agreed and 18% agreed that proper communication methods are fruitfully used in mental health settings. It informs that increased interventions are required to be taken for support workers to make them efficient to fruitfully use any method of communication in mental health settings. This is because many participants in the study who are support workers are seen show that they disagreed rather than agreed with the fact they are able to use any method of communication properly in the mental health settings. The fact also supports the problem identified in the study that in mental health settings in true manner issues with using proper methods of communication still exists.
On interviewing individuals in the three separate wards, it is identified that they usually use verbal communication followed by non-verbal communication method to deliver information and interact with the service users. This is evident as the support workers in the Dementia ward as well as in Learning Disability ward informed they frequently use verbal communication method accompanied non-verbal method of communication. In the study of Frain and Abdalla (2017), it is mentioned that the verbal and non-verbal communication are inter-related as while verbally interacting one has to focus on the gestures, voice tone, expression, body language and others which are aspects of non-verbal communication to establish effective interaction. This is because without maintaining low voice tone, positive body language and other aspects of non-verbal communication the support workers would not be able to execute verbal method of communication as the value and respect to the service users cannot be established. Thus, this information also proves the fact presented by support worker at the Learning Disability ward regarding inter-relatedness of verbal and non-verbal method of communication.
The people with learning disability are seen to experience issues with understanding written information as they are often unable to read or perceive the meaning of the information (Booth et al. 2017). The learning disability people prefer verbal and non-verbal method of communication as they are mostly done in a one-to-one way and executed face-to-face. This offers the individuals have efficiency to make meaning of the information by directly interacting during any confusion with the communicator to understand the information. Moreover, the verbal and non-verbal communication offer scope to the support workers of the learning disability individuals to make them understand care information at their own pace by continuously repeating facts in different way. It is done with the intention to make the patients understand and be able to make own decision regarding care as well as communicate their personal needs and demands to ensure quality care delivered from the support workers (Irwin and Sheridan, 2019). Thus, these facts inform that verbal and non-verbal communication is justifiably effective methods of communication being used by the support workers in the learning disability ward.
The participants in the Dementia ward also informed that they used verbal method of communication followed by non-verbal communication method to communicate with service users. As mentioned by Alsawy et al. (2017), dementia patients often lack proper cognitive ability and experience low speed of understand and thought. This leads the individuals to be unable to understand complex ideas and information on their own. In relation to this, written information regarding their care is difficult to be understood by the dementia patients as in written information they are unable to understand the facts on their own due to the hindered cognitive ability (Drummond and Simpson, 2017). However, in verbal and non-verbal method of communication, the person to whom the information is to be communicated and the communicator are present face-to-face where they interact according to their ease and have scope to develop clarification regarding any hindrances with understanding any message or information (van de Rijt et al. 2018). Thus, the verbal and non-verbal communication is useful methods to be implemented in the Dementia ward as the support workers would be able to successfully interact with the service users without hindrances.
In the Rehabilitation ward, the ward manager informed that they use written communication to interact any information to the support workers. As asserted by Brunner et al. (2017), written communications are precise and detailed in nature. This indicates that the support workers in the ward would have detailed information in evidential and permanent form to be used to deliver care and in time of confusion they can read the written information thoroughly to avoid making mistakes in offering care. Thus, the written communication method used between ward manager and support workers in mental health setting can be determined to be effective mode to communicate proper information in a fruitful way.
The interview of the support workers and ward manager in the case study scenario inform that to effectively execute verbal communication one require to speak with confidence, practice humility, use simple words and others. The use of simple words in verbal communication ensures engagement of the listener as they are able to understand the information being shared verbally making them provide response that leads in establishment of successful two-way communication (Hynninen et al. 2016). The practice of humility in verbal communication in mental health settings is essential for the support workers to make the service users build trust over them and confidently speaking makes the service users perceive that true information is being shared with them regarding their care (Quirke et al. 2019). This indicates that the mentioned skills are essential to be required to make the service users comply and establish effective verbal communication with the support workers in mental health settings.
One of the participants in the Dementia ward informed that friendly nature is one of the skills being used by the person while using verbal communication. The dementia patients are often seen to be depressed and are abused as well as isolated from society due to their psychological health condition. Thus, in this situation, friendly interaction leads the service users feel being valued and cared that makes them share further details regarding their health with the support workers (Machiels et al. 2017). Thus, the friendly skill is essential in verbal communication in the mental health setting to make the service users easily share personal information with the support workers to help them understand the key needs to be fulfilled to offer quality care to the patients.
The participants from the three specialist mental health ward informed that skills required to be focussed on in non-verbal communication while it is made accompanied with verbal communication method are eye contact, body language, facial expression, tone of voice, posture and others. The direct eye contact with the service users in mental health settings during interaction helps the support workers to indicate that they are being properly listened (Pompili et al. 2016). This leads the support workers show value to the service users which in turn makes them share detailed information regarding their health that helps the support workers to understand the nature of care to be provided. Moreover, using lower tone of the voice in mental health settings by the support workers makes them show respect to the service users while communicating. The positive body language such as leaning to listen to the service users in mental health settings informs that the listener (support workers) is paying attention to the information shared by them which makes them motivated to share further personal health data (Downs and Collins, 2015). Thus, the mentioned skills identified by the support workers in the mental health settings are evident to be used in proper manner to successfully execute verbal and non-verbal method of communication.
The use of proper communication method is essential in mental health settings because one of the participants who are support worker in the Dementia ward mentioned that successful interaction makes it easier for them to understand the needs and demands of service users. This is also evident from the literature where it is mentioned that direct communication with service users makes them reveal their personal health condition and specify needs to be fulfilled (Burgio et al. 2018). Thus, communication is essential in mental health settings as clarification of needs of service users makes the support worker understand the way the services are to be designed. The use of proper communication led the support workers in the study report that they can avoid conflict in providing care to the service users in the mental health settings. This is essential as conflict in providing services leads service users avoid accepting care from support workers that may at times makes support workers experience hindrance to provide care. This leads to develop ethical dilemma and creates impact on to adversely affect service users’ health as proper care intervention cannot be provided to them (Windle et al. 2019). Thus, communication is essential in mental health settings to impact on to create effective care intervention for service users without any forceful activity by the support workers.
The establishment of effective use of communication methods in mental health settings lead the support workers build close relationship with the service users. This essential as the literature informs that close relationship building between the service users and support workers help them to build rapport and feel ease in providing care services to the patients with fewer objections from the service users. This is because close relationship makes the service users trust the support workers regarding the care services provided ensuring successful care delivery (Strøm et al. 2016). Thus, the information indicates that executing effective communication leads the support workers to build trust and provide services with ease in the mental health settings. Moreover, it ensures the support workers to keep the health of the patients in control by providing satisfactory care as per their needs and demands.

Chapter 6: Conclusion
61. Conclusion
In the mental health settings, communication is important for the support workers in framing better services for the service users. However, this study indicated that in many instances in the UK the support workers in the mental health settings are failing to implement proper methods of communication that has result the service users to complaint against their care. Moreover, this lack of proper use of methods of communication by the support workers in the mental health settings in the UK is reported to cause few deaths. Thus, the study was framed to highlight the different methods of communication being used in mental health settings by the support workers and the barriers regarding them being faced that has resulted in raising the communication issues and deteriorated health condition of the patients in the settings. The exploration of the methods of communication used by the support workers in mental health settings informs that verbal and non-verbal method communication is being frequently used by them. However, the written communication method is mostly used for sharing information between support workers and ward manager in the mental health settings. Moreover, it is informed that the choice of the method of communication to be used by the support workers in mental health settings is based on the urgency of the message, relationship with the individual to whom the message is to be communication, patient’s psychological health and others. The study also informed that lack of time, surrounding environment, lack of training and other issues are creating challenges for support workers to implement successfully different methods of communication in the mental health settings. In order to avoid these barriers and to ensure successful implementation of communication methods by the support workers in the mental health settings, few recommendations are provided.
6.2 Recommendations
Communication Training: The support workers are to be provided training for using different methods of communication in an appropriate manner in mental healthcare settings. This is because the training is going to help the support workers properly analyse the situation to identify the exact method of communication suitable for the situation to be used. Moreover, communication training is essential to improve the communication skills of the support that are essentially required to successfully implement any method of communication.
Improve environment: The environment in which the communication is being taken is to be properly managed by the support workers in the mental health settings. This means that it is suggested the support workers ensure that the environment where they are making communication with service users are totally private. It is required so that the service users’ feel their privacy is properly maintained which would make them feel free to share information under any method of communication used by the support worker to gain information required by them. Moreover, it is suggested that the surrounding environment where the communication is being made by the support workers is noise free so that both the support workers and service users can concentrate in each other to make successful communication in the mental health settings.
6.3 Limitations of the study
In this study, the first limitation experienced was that the research was executed in single mental healthcare settings that lead to create issues with generalising the results for other mental healthcare institution. The use of open-ended questionnaire in interview has resulted to create limitation in controlling over the length of response to be provided by the participants. The other limitation of the study was that less time is provided to compile and present the information due to which much vital information may have been missed to be properly presented in the study. The lack of money created limitation in the context that may paid journals and articles could not be accessed that were intricately related to the research topic due to which many vital data may have remained uninformed.
References
- Stanyon, M.R., Griffiths, A., Thomas, S.A. and Gordon, A.L., 2016. The facilitators of communication with people with dementia in a care setting: an interview study with healthcare workers. Age and ageing, 45(1), pp.164-170.
- Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., Hallaert, G., Van Daele, S., Buylaert, W. and Vogelaers, D., 2015. Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice, 69(11), pp.1257-1267.
- Stensrud, T.L., Mjaaland, T.A. and Finset, A., 2012. Communication and mental health in general practice: physicians' self-perceived learning needs and self-efficacy. Mental health in family medicine, 9(3), p.201.
- Alsawy, S., Mansell, W., McEvoy, P. and Tai, S., 2017. What is good communication for people living with dementia? A mixed-methods systematic review. International psychogeriatrics, 29(11), pp.1785-1800.
- Furnes, M., Kvaal, K.S. and Høye, S., 2018. Communication in mental health nursing-Bachelor Students' appraisal of a blended learning training programme-an exploratory study. BMC nursing, 17(1), p.20.
- Aggarwal, N.K., Pieh, M.C., Dixon, L., Guarnaccia, P., Alegria, M. and Lewis-Fernandez, R., 2016. Clinician descriptions of communication strategies to improve treatment engagement by racial/ethnic minorities in mental health services: a systematic review. Patient education and counseling, 99(2), pp.198-209.
- Munson, M.R. and Jaccard, J., 2018. Mental health service use among young adults: a communication framework for program development. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research, 45(1), pp.62-80.
- Lyngstad, M., Hofoss, D., Grimsmo, A. and Hellesø, R., 2015. Predictors for assessing electronic messaging between nurses and general practitioners as a useful tool for communication in home health care services: a cross-sectional study. Journal of medical Internet research, 17(2), p.e47.
- Treloar, A., Stone, T. and McMillan, M., 2018. Learning about mental health nursing: Linking threshold concepts to practice. Journal of Problem-Based Learning, 5(1), pp.21-28.
- Mikesell, L., Bromley, E., Young, A.S., Vona, P. and Zima, B., 2016. Integrating client and clinician perspectives on psychotropic medication decisions: developing a communication-centered epistemic model of shared decision making for mental health contexts. Health communication, 31(6), pp.707-717.
- Deane, W.H. and Fain, J.A., 2016. Incorporating Peplau’s theory of interpersonal relations to promote holistic communication between older adults and nursing students. Journal of Holistic Nursing, 34(1), pp.35-41.
- Pietromonaco, P.R. and Collins, N.L., 2017. Interpersonal mechanisms linking close relationships to health. American Psychologist, 72(6), p.531.
- Pincus, A.L., 2018. An interpersonal perspective on Criterion A of the DSM-5 Alternative Model for Personality Disorders. Current opinion in psychology, 21, pp.11-17.
- Ross, L.E., Vigod, S., Wishart, J., Waese, M., Spence, J.D., Oliver, J., Chambers, J., Anderson, S. and Shields, R., 2015. Barriers and facilitators to primary care for people with mental health and/or substance use issues: a qualitative study. BMC family practice, 16(1), p.135.
- Hollis, C., Falconer, C.J., Martin, J.L., Whittington, C., Stockton, S., Glazebrook, C. and Davies, E.B., 2017. Annual Research Review: Digital health interventions for children and young people with mental health problems–a systematic and meta‐review. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 58(4), pp.474-503.
- Petersen, I., Fairall, L., Bhana, A., Kathree, T., Selohilwe, O., Brooke-Sumner, C., Faris, G., Breuer, E., Sibanyoni, N., Lund, C. and Patel, V., 2016. Integrating mental health into chronic care in South Africa: the development of a district mental healthcare plan. The British journal of psychiatry, 208(s56), pp.s29-s39.
- Lopes, J. and Cutcliffe, J.R., 2018. Psychodynamic and Psychoanalytical Theory, Approaches and Clinical Relevance: Applying the Psychoanalytic Principles and Practices to Mental Health Nursing. In European Psychiatric/Mental Health Nursing in the 21st Century (pp. 75-88). Springer, Cham.
- Kehle-Forbes, S.M., Meis, L.A., Spoont, M.R. and Polusny, M.A., 2016. Treatment initiation and dropout from prolonged exposure and cognitive processing therapy in a VA outpatient clinic. Psychological Trauma: Theory, Research, Practice, and Policy, 8(1), p.107.
- Wallin, E.E.K., Mattsson, S. and Olsson, E.M.G., 2016. The preference for internet-based psychological interventions by individuals without past or current use of mental health treatment delivered online: a survey study with mixed-methods analysis. JMIR mental health, 3(2), p.e25.
- Caswell, G., Pollock, K., Harwood, R. and Porock, D., 2015. Communication between family carers and health professionals about end-of-life care for older people in the acute hospital setting: a qualitative study. BMC palliative care, 14(1), p.35.
- Isobel, S. and Delgado, C., 2018. Safe and collaborative communication skills: a step towards mental health nurses implementing trauma informed care. Archives of psychiatric nursing, 32(2), pp.291-296.
- Itzhaki, M., Peles‐Bortz, A., Kostistky, H., Barnoy, D., Filshtinsky, V. and Bluvstein, I., 2015. Exposure of mental health nurses to violence associated with job stress, life satisfaction, staff resilience, and post‐traumatic growth. International journal of mental health nursing, 24(5), pp.403-412.
- Semrau, M., Evans-Lacko, S., Alem, A., Ayuso-Mateos, J.L., Chisholm, D., Gureje, O., Hanlon, C., Jordans, M., Kigozi, F., Lempp, H. and Lund, C., 2015. Strengthening mental health systems in low-and middle-income countries: the Emerald programme. BMC medicine, 13(1), p.79.
- Siegfried, N., Draper, B., Draper, G., Porter, M., Bonaconsa, C., Hunter, J., Moeng-Mahlangu, L. and Asmall, S., 2018. A contextualisation approach to health promotion guideline development in South Africa. South African Medical Journal, 108(12), pp.1036-1041.
- Drabble, L.A., Trocki, K.F., Korcha, R.A., Klinger, J.L., Veldhuis, C.B. and Hughes, T.L., 2018. Comparing substance use and mental health outcomes among sexual minority and heterosexual women in probability and non-probability samples. Drug and alcohol dependence, 185, pp.285-292.
- Rabelo, I., Lee, V., Fallah, M.P., Massaquoi, M., Evlampidou, I., Crestani, R., Decroo, T., Van den Bergh, R. and Severy, N., 2016. Psychological Distress among ebola survivors Discharged from an ebola Treatment Unit in Monrovia, liberia–a Qualitative study. Frontiers in public health, 4, p.142.
- Chan, J.K., Farrer, L.M., Gulliver, A., Bennett, K. and Griffiths, K.M., 2016. University students’ views on the perceived benefits and drawbacks of seeking help for mental health problems on the Internet: a qualitative study. JMIR human factors, 3(1), p.e3.
- Tsoh, J.Y., Sentell, T., Gildengorin, G., Le, G.M., Chan, E., Fung, L.C., Pasick, R.J., Stewart, S., Wong, C., Woo, K. and Burke, A., 2016. Healthcare communication barriers and self-rated health in older Chinese American immigrants. Journal of community health, 41(4), pp.741-752.
- Dreison, K.C., Luther, L., Bonfils, K.A., Sliter, M.T., McGrew, J.H. and Salyers, M.P., 2018. Job burnout in mental health providers: A meta-analysis of 35 years of intervention research. Journal of occupational health psychology, 23(1), p.18.
- Beidas, R.S., Marcus, S., Aarons, G.A., Hoagwood, K.E., Schoenwald, S., Evans, A.C., Hurford, M.O., Hadley, T., Barg, F.K., Walsh, L.M. and Adams, D.R., 2015. Predictors of community therapists’ use of therapy techniques in a large public mental health system. JAMA pediatrics, 169(4), pp.374-382.
- Brophy, L.M., Roper, C.E., Hamilton, B.E., Tellez, J.J. and McSherry, B.M., 2016. Consumers and their supporters’ perspectives on poor practice and the use of seclusion and restraint in mental health settings: results from Australian focus groups. International journal of mental health systems, 10(1), p.6.
- Irwin, M. and Sheridan, T., 2019. Outcomes for two men with intellectual disability following communication support training for their workers. Intellectual Disability Australasia, 40(1), p.9.
- van de Rijt, L.J., Weijenberg, R.A., Feast, A.R., Vickerstaff, V., Lobbezoo, F. and Sampson, E.L., 2018. Oral health and orofacial pain in people with dementia admitted to acute hospital wards: observational cohort study. BMC geriatrics, 18(1), p.121.
- Quirke, O., Evans, W. and Brosnan, M., 2019. How healthcare professionals in acute settings construct identities for people with dementia. Nursing Older People, 31(2).pp.14-34.
- Windle, G., Algar-Skaife, K., Caulfield, M., Pickering-Jones, L., Killick, J., Zeilig, H. and Tischler, V., 2019. Enhancing communication between dementia care staff and their residents: an arts-inspired intervention. Aging & mental health, pp.1-10.
- Frain, J. and Abdalla, M., 2017. Teaching Clinical Communication. ABC of Clinical Communication, p.61.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



