Impact of IoT on Health and Society
Introduction
Interest of Things (IoT) is seen as a billion of smart, connected “things” more like a “universal global neural network” in the cloud, or on premise that will encompass every aspect of our lives, and its foundation is the central intelligence that is embedded within the device. IoT is the internetworking of physical devices, vehicles and other objects, which comprises of an embedded system with actuators, sensors, and network connectivity that enable to collect and exchange data.
The IoT allows objects to be sensed and/or controlled remotely across existing network infrastructure, creating opportunities for more integration of the physical world into computer-based systems, and result in improved accuracy, efficiency and economic benefit. The IoT is a rapidly increasing and promising technology, which becomes more and present in our everyday lives. Furthermore, the technology is an instance of the more general class of cyber-physical systems, which also encompasses technologies such as smart grids, smart homes, and smart cities. The creativity of this new era has no limit, with amazing potential to improve our day-to-day lives.
IoT has found its way into homecare by redefining the concept in a positive way. The biggest advantage that IoT offers for homecare is that the patients can be monitored in the comfort of their own home. Sensors can be installed on different type of apparatus and through the data that is gathered this allows the monitoring of the patients by either the carer or doctor so they can analyse the patient if there are any health concerns or issues.
The critical concern when it comes to Internet of Things entails the coverage on the societal understanding, the impact IoT has in the medical, and health related purposes and the subsequent benefits. To most consumers, IoT is an avenue that carries with it the potential of delivering solutions, which are thought to dramatically improve health, energy efficiency, security and education among many other areas. To most enterprises, Internet of things is thought to underpin significant solutions said to enhance decision-making as well as productivity across the retail, manufacturing, health, and agriculture among other sectors. Dimitrov (2016) insists that a good background of internet of things lies behind the machine-to-machine solutions, which is regarded as a subset of IoT. Key findings made by Dimitrov (2016) indicate that the definition of IoT is moving towards the wireless networks used in connecting devices while limiting direct human intervention. In the year 2013, most of the machine-to-machine solutions are said to have accounted for at least 2.8% of the entire global mobile connections, which amounts to 195 million. Such achievements have also attracted efforts towards development of control systems, wireless sensor networks, and automation among other areas.
While discussing the wide applications of IoT, it also good enough to focus on the impact it has in medicine and healthcare. Alqahtani (2018) who touched on the communication shares a significant preamble as well as sensing devices together with their respective software. This comes after taking into consideration the IoT solutions, which are taking different dimensions due to dynamics seen in different sectors. A snippet of such solutions has highly been shared by the IoT enabled healthcare research, which carries with it the most valuable implications as much as preventive care is concerned. Medical, and more so healthcare, applications, in the face of IOT, foster enhancement of the quality of services while trying to reduce costs. Kulkarni and Sathe (2014) assert that in the face of Internet of Things, it is possible to track most of the health parameters such as body temperature, blood pressure and even the blood glucose among many others. Most of the measurements can be attained in real time with the help of the wireless sensors. This has attracted the attention of developers who eye for better data processing technologies as well as advanced technologies, which never go without IoT application.
Rghioui et al. (2014) believe that in the face of advancing technologies, the real focus leans in favour of the medical IoT which is regarded as a system which constitutes health monitoring devices. This means that most of the health parameters can remotely be recorded using a back-end system, which later analyses data while providing the most appropriate feedback to the professionals. Medical IoT system is regarded as a complicated set-up that carries with it varieties of systems as well as mechanisms that constitute smart sensors, cloud computing, network gateways, clinical information systems as well as big data among other components. Perhaps, the true impact IoT in medicine can be felt through the growth of enabling technologies, which help professional in making the right decisions. First, identification technology is part of IoT that allows the authorized node to generate data before assigning the unique identification number (UID) to every node the identification technology is significant in terms of creating relations across a number of identities in the relevant digital domain (Darshan and Anandakumar 2015). The second enabling technology under IoT in the medical and healthcare area includes the communication technologies. The IoT networks are said to carry heterogeneous transmission rates, frequencies, as well as standards needed in transferring data. With this, IoT has served as a regular means of long term and short-term communication via such technologies like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and ultra-wideband. Other technologies include location technology with the help of real time location systems, sensing technology as well as cloud computing.
According to Darshan and Anandakumar (2015) argued that the attention of medical IoT system is given more to sensing technologies. Most of the sensing technologies are regarded as the on-the-ground devices known for performing a critical role of taking measurements, monitoring as well as collecting the required data. For instance, the invention of oximeter in the 1970s served as the major tool for diagnosis. It helped physicians in monitoring the blood oxygen saturation as well as the patient’s heart rate, which are considered as critical parameters across the emergency services. Further attention is equally given to remote e-health monitoring, which has the capacity of providing patients’ real time information (Alqahtani 2018). IoT essentially has marked a significant transformation in the clinical laboratory industry, health insurance industry, and healthcare as far as medical related fields are put into consideration. IoT, through these transformations, allows patients, doctors, and other parties such as guardians, parents, families and even nurses to be part of the entire system. This has led to development of significant databases, which are patient centred and largely involves substantial flexibility as regards the patients’ medical conditions. The emergence of better and newer types of the dynamic information, as a result of IoT, has seen significant application of the sensor-based solutions which include mobile apps said to track the consumer behaviour, wearable and biosensors among other connected health devices (Darshan and Anandakumar 2015). In addition, IoT serves as a critical component in handling chronic diseases as well as control and prevention of diseases. This is possible under the framework of remote monitoring realized through powerful wireless solutions.

Consideration of IoT in medicine largely comes with significant benefits considered by professionals. According to Coetzee and Eksteen (2011) assert that IoT is cost saving as a result of improved asset utilization as well as process efficiencies. Asset utilization comes with the essence of tracking the assets while making use of sensors. This helps in getting the real-time insights on the condition of assets, because of the increased visibility, and the supply chain. The same viewpoint can be applied to improved productivity and efficiencies as far as medicine and healthcare related services are concerned. With aging comes poor memory or poor eyesight, so there is a growing concern that number of patients who need constant help is on the rise. Timing is critical for some patients as this can have a knock-on effect on their health condition so taking a certain medication in order to prevent this is a must; therefore, developing and designing an automated pill dispenser will be the solution for monitoring loved ones. The aim of this study is to build a Smart Pill Box (Dispenser) to remind the user to take the medication and include a monitoring mechanism. In order to make a useful smart pillbox it had to be easily integrated with the recent sweeping smart technologies. While at the same time it had be fit for the elders and their limited knowledge and experience to implement the ease of use. Size and portability were also an important fact that we had to keep in mind. For it to be called smart, its connected through a wireless network, which enables it to be connected to the internet for future applications and integration, also its distinguished by the wide range of the Wi-Fi instead of a Bluetooth or any other communication protocols, and remove the need for wired connections. Through that same network it is connected to the mobile phone making use of a mobile application, this will allow the carer or doctor to administer dosages and timings accordingly without having to actually be present at the site also set alarms for notifications.
Will also include a buzzer with a LED blinking red to warn that it is time for the medication intake.
This model can aid in helping elders to take their medication at the right time with the right dosage
Aim
To create and design a smart pill dispenser prototype, intended to help people (users) that are under monitored medication and suffering from memory loss due to illness or stress. The smart pill dispenser is an Internet of Things device, which helps patients under such condition to control the tablet intake trough an Android application by proper guidance or by another person.
The pill dispenser device is integrated with the Android application to receive notifications related with the pill intake and to send alerts.
Motivation
Technology plays a big advantage in people’s health life. Now they are capable to live longer than previous generation with the help of advanced technology. This fact makes it possible for the elderly population to grow but also as a consequence for increasing the population puts a pressure on the traditional healthcare systems, to provide quality care for a growing population for a long period of time. There are many advantages to grow old at home but the main concern is safety in not doing self-harm (Medgadget, 2019).
Take a deeper dive into Vitamin D Deficiency and Health Risks with our additional resources.
The motivation for developing the proposed prototype device came from the desire to help people in need as it is scientifically proven that a lot of people experience memory lapses due to the fact that they are ill or engaged in a very stressful environment. Each person is affected differently, for some patients loss of memory often increases with the age, on others for the fact that life is to stressful for them (WebMD, 2019).
Memory loss is often associated with first sign of Alzheimer; in the past loss of memory was the normal symptom that were associated with aging; however scientists believe that this is the first signs that can affect a person’s ability to carry out their daily activity (Alzheimer's Society, 2019). According to Dr. Armond B. Neel Jr. (2015) article, sometimes the side effects of medication could impact a patient’s memory especially by the antianxiety drugs (benzodiazepines). There are many factors when a patient has long-term illness and is in need of regular medication that can impact normal memory function so the intake of pills must be monitored. Forbes statistics shows that a large number of medical innovations and improvements that have changed the wellbeing of patients around the globe have been accomplished by placing Internet of Things devices into the patient’s life (Forbes.com, 2019). IoT technology has evolved rapidly making possible that more devices to be equipped with the ability to share date with other device. Over the last years, IoT devices such as pill dispenser had a big impact in the field of personal healthcare, which is the alternative for the traditional hospitalisation (Health and Care, 2019). Most people with chronic diseases must take a wide range of medication on a period of time in order to stabilise their condition. Keeping track of the right pill every day has become a daily challenge for the elderly people, making it difficult for them to remember which medication has to be taken at the correct time or confusing the medication by not being able to distinguish one from the other. This problem will be a big concern for the members of the family or for the carer.
The proposed solution of a pill dispenser will be the key that can offer comfort and safety for both, the user and family and not ending up taking the wrong dosage or medicine that can cause several health problems. Due to the fact that many elderly people, which suffer from Alzheimer’s or partial memory loss, choose to be cared at home not in hospital, pill dispenser can provide for the user and the carer the required assistance. According to the analytical research by FMI (Future Market Insights), which estimates that smart pill bottles will have significant growth till 2028 and many users will adopt such technology that can be a lifesaver for humanity. Dementia care is the key application areas for the smart pill dispensers, according to the research due to the fact that 80% of sales are accounted by dementia afflicted or aging patients (Dailychronicle24.com, 2019). On the market there has been few models of pill dispensers but many of them have issues such as they are too expensive or too complicated to be used by elderly people.
Chapter 2: Literature review
In the world of healthcare, technology has become very essential. Medical engineering's build vast devices that have incorporated IoT. The IoT sensors play a big role in meeting the requirements for any device, due to the fact that can measure any possible changes and record every difference in the habitat. As follows, pill dispenser literature review will have the purpose to exemplify and highlight other projects related with the proposed project and bring up the benefits and limitations that they have faced. The study of Internet of Things attracts a significant research of IoT applications in healthcare and its evolution. According to Ibarra-Esquer et al. (2017) regarded IoT as being intelligent as well as an invisible network fabric that generate an embedded technology, which has the capacity of communicating either indirectly or directly via the internet. Ibarra-Esquer et al. (2017) insisted that Internet of Things must have emerged in the 1990s where internet connectivity is said to have started proliferating the enterprise networks as well as consumer markets. However, the connectivity is said to have been low at the time as a result of low performance associated to network connection. Ibarra-Esquer et al. (2017) asserts that in the 2000s, it is believed that internet connectivity came out as a norm for mos of the applications.This means that at this time, internet connectivity became common across most of the enterprises. Chase (2013) noted that the world currently deploys around 5 billion smart connected things with forecasts attracting more than 50 billion connected devices before the year 2020. Chase (2013) indicates that the term IoT came in place in the year 1999 after it was introduced b Kelvin Ashton. While this looked impossible,the current technology trend reflects a significant growth of IoT after its implementation. Ibarra-Esquer et al. (2017) argues that implementation of IoT added a fresh way for the smart cities, emergencies, logistics, and security. Kulkarni and Sathe (2014) believes that history of IoT, especially in healthcare, mus have started way back in the year 1974 with the term described as an embedded computer system. At the time, this would incorporate a large system whose key function was never data processing. The systems in healthcare were implemented with the help of such devices like single board computers and microcontrollers among others.However,the devices have significantly gained momentum since the affordable use of the prototyping platforms such as Lego Mindstorms, Arduino and Raspberry Pi among others. It was until early 1990s where Mark Weiser thought of ubiquitous computing, which was later thought to be pervasive.The fundamental backbone behind ubiquitous computing entails the advances made by the embedded computing technologies as well as ubiquitous networks on a significant scale of several computers. Ibarra-Esquer et al. (2017) insisted that this concept closely resembled the actual IoT in which Weiser indicated the significant challenge of designing the operating system, which could host a software that can exploit essential capabilities of networks. Mainetti et al. (2011) indicated that by mid-1990s, sensor nodes began developing several technologies such as digital electronics and wireless communications. These are regarded as tiny modules which have the capacity of sensing data, which could be transmitted over the network. Significant numbers of the sensor nodes pave way for implementation of sensor networks which attracted applications in a number of areas. This further attracted significant platforms like localization, cloud technologies, nanotechnology and big data. Internet of things in healthcare started taking its current shape in the year 1999. The scope widened to attract website of alliances, development of magazines and IT related organizations. Further attention to IoT is captured by Istepanian et al. (2011) who focused on the establishment phase that ran from the year 2009 to 2011. During this phase, the concept began changing towards network.This could meant that IoT could play a significant role of bridging the gap between the representation of information technology and physical world. An increased attention towards healthcare has further attracted advances in communications, microelectronics and information technology. The gap between the physical world and the virtual one continuously bridged by a number of technological developments. Developments in IoT refers to capabilities in identification, cooperation, communication, addressability, actuation, sensing and embedded information processing as well as novel user interfaces.
Darwish et al. (2017) asserted that from the year 2012, IoT turned into an extension of the internet and the physical realm. This is remarkable extension is attached to smart objects as systems started bringing the user information in a secure way. According to Yuehong et al. (2016), the most important bit of the long history and evolution of IoT entails its application in healthcare. This has paved way for significant medical applications which include elderly care, chronic diseases, remote health monitoring and fitness programs The evolution of IoT healthcare services has attracted significant changes in healthcare in the 21st century, which counts as part of the IoT evolution since the dawn of the new millennium. Based on the research conducted by Yuehong et al. (2016), the IoT evolution is marked by healthcare services. Some of these services include the Ambient Assisted Living, which is a system that carries the potential of solving personal healthcare challenges. The AAL systems are believed to facilitate an ecosystem of computers, wireless networks, medical sensors and software applications linked to healthcare monitoring. Another service include m-Health Things, which attract a new concept believed to match functionalities of IoT and m-health. The two platforms are thought to define the new as well as innovative future linked to 4G health applications. Other services include adverse drug reaction, wearable device access, semantic medical access, embedded gateway configuration and embedded context prediction among others. On the other hand, Baker et al. (2017) believes that IoT is essentially afresh field in the world of healthcare. Some of the pioneering works have been directed towards development of healthcare IoT systems at the centre of evolution. Based on this, most of the IoT systems have been directed towards diabetes management and rehabilitation through the AAL. Notably, IoT has been at the centre of the design of many systems while ensuring secure communication. Some of these systems, according to Baker et al. (2017), include the wearable healthcare systems, which are essentially linked to the Internet of Things technology. In this system, for instance, designers would use pulse sensors which are essential in reading vital sign upon detection of the wide range of the emergency conditions. Some of these conditions are not limited to vasovagal syncope, pulmonary embolism and cardiac arrest. Again, the respiratory rate sensors which are known for monitoring sensors. With more attention drawn towards IoT in healthcare and the smart pill dispenser prototype, studies aligned to user centred design approach and its importance in the design process. As mentioned before, IoT supports the design process of the systems, which still remains relevant for the smart pill dispenser. According to Chammas et al. (2015), the user centered design is regarded as philosophy as well as a process, which puts a person at the significant centre while focusing on cognitive factors said to come in play during the people’s interactions. The user centred approach has attracted more attention over the recent years. A number of methods as well as tools felt necessary within organizations for the purpose of comprehending the user and task requirements. The user centred approach attracts the idea of electronic interfaces made possible through software engineering. Chammas et al. (2015) also talks more about the interaction design in which the design triggers users to incorporate the relevant product, which can be a system or an app to the routine where necessary. While talking about the user centered design approach, most of the researchers would preferably talk of the interactive design which is known for handling problems while using available material.
The interactive design also finds more categories, which includes the genius design, activity centered design, user centred design and system design. In the 1980s, Chammas et al. (2015) noted that most of the computer scientists and designers behind human-computer interaction started on the practice question of designing the systems that used to be left for the engineers. However, in the subsequent years, software designers started a movement that concentrated more on the users than the computer. The movement could be referred to as the User-Centred Design, which is largely regarded as being based on ergonomics as well as usability knowledge that finds the needs of the users. The UCD approach attract similar us of the procedure, the standard design guides as well as documenting for future projects.Notably, the ISO 14598 predecessors are known to have facilitated the significant translation of the USD approach known to complementary to significant software development methods. The approach is believed to be used across the system life cycle while explaining activities of the design and clarifying the user-centred design principles. A significant number of principles are thought to be considered in the course of developing any interactive system. First, it is required that the project should essentially be based on the significant understanding of the users, tasks and the environments. In relation to smart pill dispenser,the UCD approach demands that the design should take into consideration significant aspects linked to the project. The second principle entails users who need to be involved in the development process. The user engagement, in this case, is regarded as a valuable resource attached to knowledge as far as the context of use and solutions are put into consideration. The third principle demands that the project need to be conducted as well as refined via assessments while focusing more on the users thereby minimizing risks of the system. Notably, the design needs to address the absolute user experience. The project team should also involve the multidisciplinary perspectives and skills. This means that team members need to emerge from separate areas with required views, experiences, and skills. A discussion on the user centred design approach aligned to Internet of Things is fronted by Leppänen et al. (2016) who noted that already some efforts have been made to facilitate the coexistence of as well as interactions between Internet of Things and human beings. The ecosystem avails human-to-things interactions with two key objectives. First, the ecosystem aids at improving the significant quality of the user experience as well as enhancing the collaboration. Human and things are expected to initiate bidirectional interactions in smart spaces. The realization of the interaction between internet of things and use-centred design approach, as seen in the SandS project, indicates tools meant to personalize the significant behaviour of the smart things. This is evident in the opportunistic IoT which is known for making use of the human social behaviour as the mediator of communities with unconnected objects. Leppänen et al. (2016) further denotes that the interaction between IoT and user-centred design approach is more evident in social IoT known for designing machines which can communicate with other machines on the basis of an autonomous established social relationship. On the other hand, social web of things is known for reusing the web architectures for the purposes of integrating most of the heterogeneous devices and the social networks. Besides, the NFC and RFID are regarded as powerful technology enablers known for connecting the digital and the physical worlds. This can intuitively connect most of the smart objects with human beings.
Endsley (2016) believes that in designing the smart pill dispenser, it is necessary to have a user-centred design mindset, which recognizes the essence of making use of applications and the design process. In this sense, Endsley (2016) seemingly asserts that the USD approach, in the presence of IoT, prompts the designer to first focus on the customer’s needs. As it would be for the smart pill dispenser, the User Centered Design approach equally provides a common language for the stakeholders, designers as well as the end users. This is evident in the case of the Lunar Rover Mission carried out by NASA which is said to have used the integrated user centered design. In addition, UCD approach attracts measurement as a significant part of the design process (Terninko 2018). This is because measurement creates a mechanism which helps in understanding what is needed and what is to be improved. Apparently, the UCD approach would only attract simple sketches which are simple to understand. A flow structure as well as navigation can highly support the main tasks. In addition, UCD approach is fundamental in attracting such technologies like IoT for the purposes of creating smart spaces. Niting Bange et al. proposed a basic pill dispenser that helps the patients to take the medication on time, by notifying them through an alarm clock. The device was made of an Arduino controller, GSM model, 4x4 matrix model keypad, RTC module, LCD display and an alarm system. There are also significant limitations for this system and the most critical that need to be mentioned is that the system does not automate the pill dispenser mechanism and it doesn’t keep record of the pills dosage (Ijarece.org, 2017).
In the first case of the pill dispensers they had limitations such as the fact that is not automated, Sahil Upadhyay et al. comes up with a better version of a pill dispenser by making it automated. The automated pill dispenser is GSM based and has the purpose to assist the users with an age over 60, who tends to forget the periodical pill intakes. The notifications that are generated based on the consumption of the pills are sent towards family members or carrier trough an SMS. The model uses GSM communication to provide interaction between machine and human. The limitation of the system is that it has issues with the network when communicating between modules. In addition, the system is imitated in terms of portability (Pdfs.semanticscholar.org, 2019). Andrea Mondrag'on et al. proposed a better version of an automated pill dispenser. The device has the feature to attract the attention of the user when he/she misses the time to take the medicine. The system consists of 2 devices. One is the pill dispenser, which is a fixed device and the other one is a mobile device that can communicate with the fixed device in order to capture information and notify the user. The limitations of this system are that it does not provide evidence to monitor the pills intake and also is limited in terms of portability and weight. IOT is the most emerging technology evolving day-by-day bringing new features, making individuals to research and try to bring new improvement versions of the device. Videet Parekh, Chris Pinto et al. developed a pill dispenser device called "Avion", which uses a combination of an LCD display and a mobile application that remind elderly people to take the pills at the right time. The device has different trays that allow to be filled with different tablet size. The limitations of the project are that the application cannot distinguish or know which pill the dispenser will provide for the user and also the application can't give a solution when the person forgets to take a pill (https://www.ijser.org, 2016).
Many researchers and scientists have brought improvements for the proposed IoT device but also, they face limitations and challenges. Maheswar Rao Kinthada et al. proposed the latest system called "eMedicare" which has the purpose to act as a pill monitoring system. The device offers assistance for the patients with memory loss and also notifies the carrier if the pill is not consumed through messages or phone. The biggest limitation that faces such a system, which promises a lot, is that is limited in number of the pills that can be monitored at the same time (www.academia.edu , 2016). Based on the findings and previous developed projects, a survey table will be made to bring up the main issues, which will help me to focus on the improvements when the device will be developed.
Table of literature survey
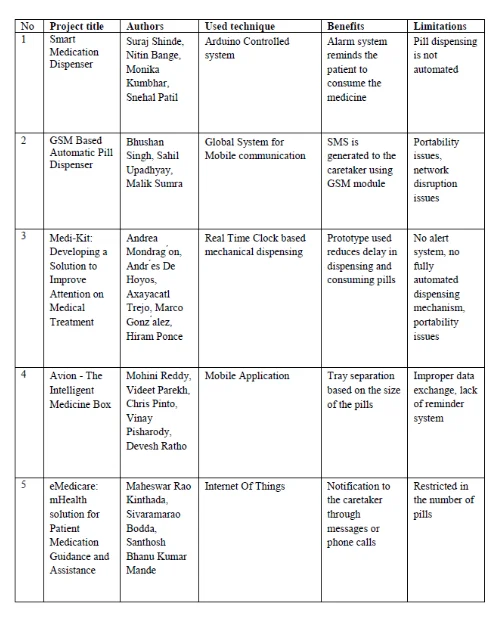
The survey led to the conclusion that there are devices that can meet some requirements, but also every improvement version leads towards a new limitation. The automated pill dispenser is a new advancement that needs improvement and offer simple features for the elder user with the purpose of making them understand how to use it. Also, the features must meet user's memory loss requirements in notifying them through voice alarms, or mobile app when the intake of the pill must be made or when is missed. Another important improvement is related with the intake of too many pills. Therefore, the device should contain a feature that doesn’t allow the user to overdose.
Process
After critically review the existing pill dispenser devices, the information will be collected and based on that, a questionnaire will be made and presented to the target audience in order to collect data that will have as main objective to help in gathering the required features for the device. The outcome from the collected data will be interpreted and analysed to bring up the weaknesses in other devices and focuses on the improvements.
The prototype device will be connected with an Android app through Wi-Fi, which lets the device inform the user when:
The medication intake must be made.
The medication is missed.
medication
The device will have sensors that will emit voice and lights notification at a particular set of time for alerting the user that it is time to take the medication.
In addition, the device will be user friendly and offer feature that will be easy to understand.
Security implementation
Understanding the device lifecycle play an important role in security implementation because each layer must have specific security features.
Firmware checks trough-emended passwords for checking that no tempering has been made.
Use certificate-based encryption
Encryption the communication between the device to Internet and to app and from device to user. (HTTPs, AES, etc.).
API security
Software up to date
Develop secure application for the device.
Provide user documentation for the device.
Objectives
The dissertation aim is to analyse types of smart pill dispensers and base on that to create and develop a device that will overcome the limitations.
Objective 1
Review the existing literature and identify the challenges.
Objective 2
Understanding how IOT is used in this area to support potentially better health care by addressing effective medication management, through literature research.
Objective 3
To investigate user requirements for helping in design of the IOT pill dispenser and analyse the results and future potential.
Objective 4
Design and develop a user centred pill dispenser to help improve the care and wellbeing on people with long-term health issues.
Objective 5
Research and find solution for security improvement. Analyse the interaction between human and the device.
Resources
To create the prototype device, I will use the following resources:
Northumbria online library and books.
Journals and articles
Android studio for developing the application for the prototype.
Arduino platform for programming the prototype
Access to "Things Speak" platform to allow the collection of the data from the sensors and be stored in a Cloud channel.
Time can be a constrain, if the data can be gathered as soon as possible then the prototype can be built to meet the requirements. Allocating a time for each task and follow the schedule of the activities strictly should not be a constraint.
Ethical considerations
The questioned users will be informed of the purpose of the project and they will be aware of the benefits and risk of participating. The participants will have the legal age and they will never be exposed to risks such as dignity and emotional distress. All their data will be confidential, and no user will be named in the project. Note: Northumbria online tool will be used in creation of the questionnaire. The tool has disclaimers, which protect the user data and gain their consent by assuring anonymity.
Design Consideration
Several issues are taken into considerations before starting the design process. Each compartment should house pills and capsules. Software must be reliable and enable recording current medication and future medication dispensation. An LED display is to be provided to indicate the working condition and to provide pertinent instructions. Provision for visual and audio notifications is to be provided. Proper storage is to be ensured for quality of medicine.
Hardware concept design
Speaker: The Speaker is provided to give a beep sound to warn the patient regarding the time to take the tablet.
Led: The Light emitting diode display will be a simple red light; it provides information such as power on, flashing as he speaker beeps to have the attention of the user and emergency indication. It also provides pre-selected precautions to the patient concerning the medications being currently dispensed.
Arduino:
Software concept design
Android: is the platform in which the application will be developed with the purpose of allowing user to control the pill dispenser. Also, the app will inform the user about the pill intake that must be taken at a time.
Things Speak: Is the analytics platform that will allow the doctor to see the patient’s live data(instant), which are streamed in the cloud and to closely keep it under the radar being able to predict or stop a harmful situation.
Flow Diagram



Comparation between 3 soluttions according to research.
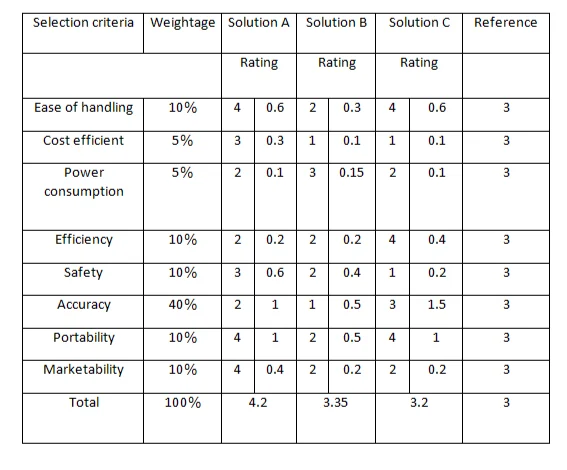

Main usability features.

OFMC checker.
OFMC is a model checker, that combines two ideas for analyzing security protocols based on lazy, demand-driven search. The first is the use of lazy data types as a simple way of building efficient on-the-fly model checkers for protocols with very large, or even infinite, state spaces. The second is the integration of symbolic techniques and optimizations for modeling a lazy Dolev–Yao intruder whose actions are generated in a demand-driven way(Basin, Mödersheim and Viganò, 2019).

References
- (Suraj Shinde, Nitin Bange, Monika Kumbhar, Snehal Patil, “Smart Medication Dispenser”, International Journal of Advanced Research in Electronics and Communication Engineering, volume 6, Issue 4, April 2017)
- (Bharat Bhushan Singh, Sahil Upadhyay, Malik Sumra,”GSM Based Automatic Pill Dispenser”, International Journal of Engineering Science and Computing, April 2017, vol.7,issue no.4 )
- Terninko, J., 2018. Step-by-step QFD: customer-driven product design. Routledge.
- Endsley, M.R., 2016. Designing for situation awareness: An approach to user-centered design. CRC press.
- Brown, T. and Katz, B., 2011. Change by design. Journal of product innovation management, 28(3), pp.381-383.
- Leppänen, T., Milara, I.S., Yang, J., Kataja, J. and Riekki, J., 2016, October. Enabling user-centered interactions in the Internet of Things. In 2016 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC) (pp. 001537-001543). IEEE.
- Baker, S.B., Xiang, W. and Atkinson, I., 2017. Internet of things for smart healthcare: Technologies, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Access, 5, pp.26521-26544.
- Porkodi, R. and Bhuvaneswari, V., 2014, March. The Internet of Things (IoT) applications and communication enabling technology standards: An overview. In 2014 International Conference on Intelligent Computing Applications (pp. 324-329). IEEE.
- Mainetti, L., Patrono, L. and Vilei, A., 2011, September. Evolution of wireless sensor networks towards the internet of things: A survey. In SoftCOM 2011, 19th international conference on software, telecommunications and computer networks (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Ibarra-Esquer, J., González-Navarro, F., Flores-Rios, B., Burtseva, L. and Astorga-Vargas, M., 2017. Tracking the evolution of the internet of things concept across different application domains. Sensors, 17(6), p.1379.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



