The Rise of User-Controlled Social Media
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Background
Over the recent times, the use of internet has been faced with major changes as realized through the emergence of the user-powered and controlled technologies. The range of use runs from blogs, social networking sites to the notable video sharing, thereby forming a collection of technologies that would collectively form the social media. The influence of social media is felt across the world as people show an increasing commitment to internet access and the use of social media platforms (Smith 2009). Everyone, around the world, currently feels the impact of the media tools as they increasingly become part of the emerging media. Based on the arguments raised by Smith (2009), the predominance of such players like twitter, YouTube and Facebook constitute the mainstream tools that strongly describe the structures, functions, and purpose of social media. Recent studies conducted by Nielsen (2011) indicate that 4 out of the possible 5 internet users would frequently make a visit to the social networks, which are substantiated as the first online destination. Any average consumer would therefore find it easier to generate content via the internet platform, which is an area that was reserved for the specialist in the recent past. The dynamics seem to have empowered the consumers who feel at par with their leaders in the society and companies as well (Grégoire et al. 2010).
The business world has equally enjoyed the dominance of internet and social media, which have been counted as tools that drive the success of companies (n.d, 2010). Managers have alluded to the fact that social media has offered many companies a competitive space, which they never used to have before. However, a good number of these companies are yet to realize the opportunity that has been introduced by social media. Based on the key observations across industries, there has been great disparity in the way companies integrate applications based on the company size and interests. While 84% of the largest companies, as indicated in the Fortune Global Rankings, would make use of at least one social media platform, it is only 15% of the Small enterprises have capacity of accessing social media in Canada (Burson-Marsteller 2011; Cefrio 2011). The findings are commendable in companies that carry 5-19 employees where 13% of them make use of the web 2.0 applications. This follows the dominance of the business-related aspects that integrated in the use of social media in most of the companies. The use of social in the managerial context and functions of the business follows the critical component of corporate communication, which is a component that has a critical influence to the performance of the business. Businesses have used this component of social media to enrich promotions, marketing, and relationship management and brand awareness.
Social media platforms are increasingly becoming convenient areas where businesses would easily reach out to their target consumers. Social media platforms are increasingly becoming convenient areas where businesses would easily reach out to their target consumers. This means that when Very Small Enterprises (VSE) fails to make use of the social media, they stand to lose on many things including the ease of customer reach among other consequences (Castronovo and Huang, 2012). The notable imbalance across the usage of social media between large companies and micro-businesses is likely to be the prime reason as to why more consumers would be attracted to larger companies compared to the small businesses. Such an imbalance can introduce ripples in the economy due to the large number of VSEs that re not willing to embrace change.
The gap between small and large firms in their use of internet might yield the explanation of the reluctance seen among business owners as far as the implementation of modern marketing I put into consideration (Pacitto and Tordjman 2000). The resistance is more pronounced among Very Small Enterprises with business owners having the perception of additional costs that yield fewer benefits in the end. According to the VSEs owners, implementation of the new marketing models, such as the ones that incorporate social media and the wide internet use, may only put the company at risk of losing track, values, vision and the quality of the relationship the enterprise would have built with the customers or clients (Pacitto and Tordjman 2000). However, most researches have failed to expound on the key reasons that must have led to the widening between large and small firms in the market. Ideally, the management systems of the VSEs are poorly structured and provide a true personality associated to the owner-manager (Cyr et al. 2011). It is always a big challenge to profile most of the VSEs because their typology essentially reflects more personal as well as psychological traits of the respective entrepreneurs (Laufer 1975; Stewart Jr and Roth, 2001). Due to this, most of the VSEs are informal and even unconscious of the market dynamics, which are presumed to affect the large companies that dominate the market (David Carson and Gilmore, 2000; Julien, 2005; Maclaran and McGowan, 1999; Weick, 1979; Jennings and Beaver, 1997).
Based on the details on the behaviour of the VSEs in the market, it should be noted that there is a research gap that revolves around determination of the reasons behind the insignificant rate of penetration of social media across small businesses. The precise literature has already indicated that the relationship between the VSEs and social media has rarely been explored. The same goes to the perceptions and representations of the owner-managers that ruin the urge to adopt some of the social media tools for business use. Based on the close relationship between management activities and the managing owner of the VSEs, it is important to inquire more about how social media can evoke managers of the VSEs. Subsequent analysis would out personal representations and the impressions developed around the social media tools, as far as the insignificant use of social media among the VSEs is put into consideration. This triggers a reflection of the research gap that fosters the discovery of deep representations, as well as perceptions behind the significant concept of social media as related to the managerial traits of the VSEs. This resonates with what the VSEs stand to lose in case they ignore making use of social media as a significant marketing tool in their businesses.
1.2 Problem statement
From the background information, it can be noted that VSEs are reluctant in making use of the social media as a marketing tool in the business. However, most of the social media platforms are inexpensive to use and have a significant market reach, which would subsequently improve the profitability of the business. While large business are fond of social media tools like Facebook and twitter, VSEs tend to shy off most of these tools citing expenses and time consumption that goes along with it. Ideally, a significant population of the world own personal social media accounts at no cost, which means that reluctance noted with VSEs is a subject of perceptions, and not justifiable factors within the business environment. While the structures and operations of the VSEs carry the blame, the research remains wide enough concerning the connection between VSEs and marketing, the notion of internet use among the VSEs owners and the perceptual argument of social media use in the context of marketing. Therefore, concentration on perception of VSEs owners is a subject of interest and attracts a research process that would be established in this context. This goes alongside a focus on the research aim that carries the idea behind the research.
1.3 Research aim and Objectives
The main aim of this research is to explore the perceptions, as well as deep representations of social media as noted in the resistance by VSEs managers. This is supported by the following objectives.
To determine the gap of modern marketing practices in the Very Small Enterprises
To examine reasons as to why VSEs owners avoid social media tools
To explore the perception of cost and inconvenience of social media among the VSEs owners
To highlight the representations of social media by VSEs in their respective business
To determine reasons as to why social media representations are necessary to soothe the attitude of the VSEs owners
1.4 Scope and limitations
The research will narrow down to exploration of perceptions and the evident representations of social media through the resistance put up by the VSE managers. In conducting the research, the context will narrow to the modern marketing practices that are never realized by the VSEs, and reasons as to why the VSEs have a high tendency of avoiding most of the social media tools. The scope will further expound on the perception of cost as well as inconvenience of using social media as identified with the VSEs owners. This will further rely on details of the social media representations as used in most VSEs within relevant business environments. Lastly, the research will further take note of the reasons that make social media representations more necessary than social media tools as preferred by the VSEs owners. In achieving this, the research will be limited to secondary data research that will observe the preconceptions of owner-managers. This is possible through the help of systematic reviews that narrate key observations from other research processes bearing dissimilar contexts. Systematic reviews are normally qualitative in nature and always expound on the narrative description of either behaviour or experience. Systematic reviews make it possible for any researcher to discover the representations, as well as perceptions of the VSE owners-managers concerning application of the social media tools in the business world.
1.5 Structure of the thesis
The thesis adopts a comprehensive structure that is distributed in chapters. The first chapter presents an introduction of the entire thesis. A background that narrates relevant details attached to the research topic accompanies this. The chapter also states the problem statement while specifying the objectives that build up the research aim. The second chapter presents a literature review where definition of concepts linked to social media is put into context. The review will further be extended to researches that focus on both social media and the business context, and how the two platforms can be integrated to produce meaningful conclusions in the course of the research. The same goes to the attention given to the VSE, which is an area that needs more details for the purposes of understanding and expounding on the research objectives. The third chapter presents the method to be used, which revolves around the applicable structures of qualitative research method, which equally unearths significant tools that build the research process. First, the chapter will have to justify the choice of the qualitative method over other methods before presenting brief details on the significant use of systematic reviews in the context.
This chapter can go wide to incorporate the research design, research type, data collection tools, data analysis and sampling processes if necessary. The fourth chapter presents the results of the interviews while carrying out a deep analysis, as well as interpretation of comments as declared or articulated by interviewees. This chapter further gives room for identification of themes and central metaphors that are likely to evoke speeches concerning the concepts behind social media. The same goes to social media representations and perceptions the VSEs owners are likely to have as specified in the research process. The final chapter delves into drawing the conclusion of the research. This includes providing a summary of the content or main sections of the research, before taking a stock of different contributions. In the end, the research will point out a discussion in which the context will expose both managerial and academic implications of the findings that will be realized in the course of the research. The chapter will still indicate the limitations, as well as avenues for future research where new ideas can be introduces to address fresh research gaps.

Chapter 2: Literature Review
This section presents a narrative review that attracts theoretical and methodological contributions other researches make towards the research topic. Based on this, the chapter touches on the theories, concepts, discussion, and inferences on various variables and factors fundamental to the social media, consumers, and marketing focusing primarily on the business entities within VSEs categorization.
Theoretical concepts
More researchers are attracted to conducting more studies while trying to understand significant barriers that impede businesses entities to adopt, as well as to incorporate social media marketing. Sánchez-Prieto et al. (2017) believed that the most effective way of describing perceptions in adopting technology can be achieved through Technology Acceptance Model (TAM). The model, according to Sánchez-Prieto et al. (2017), incorporates two significant constructs, which are known for predicting adoption of technology among individuals and businesses at the same time. The two include the perceived ease of use (PEOU) and perceived usefulness (PU). Notably, perceived usefulness (PU) only explores the extent to which an individual believes that making use of technology would eventually enhance job or business performance. On the other hand, PEOU defines the extent to which a person or a business believes that making use of technology needs no effort. Based on this model, Abrons (2018) notes that small business owners tend to lag behind the large and more established enterprises when it comes to adoption, as well as acceptance of the social media tools. In one of the case studies that narrowed down to cloud computing as it would be used by very small businesses and other enterprises. It could be noted that cost effectiveness was a slightly significant factor that contradicted a large body of research. However, the same case study still indicated that low financial barrier would be perceived as important to most small businesses as far as social media marketing is put into consideration. On the other hand, there was no evident relationship between the use of internet and the PEOU. However, both extrinsic and intrinsic motivating factors played part in predicting the use of social media across most of the small businesses. Perception of external control has been floated for a long period of time with very small business owners fearing loss of control of the entire business. Pando-Garcia et al. (2016) noted that social media could equally have its own drawbacks as seen in a case study of accountability in the travel sector.
2.1 Social media: Modern marketing practices
Baker (2016) indicated that businesses would spend a lot of money training employees aimed at propelling it and emerging as the best salespeople across the market. Only few studies have data regarding the connection between training and the overall performance of the business in the market. Recently, business entities have focused on methods as one way of retargeting the sales while boosting the performance of the company. The dominating talk in the industry would include internet practices, as incorporated in modern marketing, where businesses would take advantage of internet marketing tools to enhance the growth of the business. Coviello et al. (2017) further notes that while businesses are expected to take advantage of internet as a modern marketing, most of them have shied off thereby denying their consumers a chance to enjoy a change in the marketing experience. This has led to dominant gaps witnessed among the start-up companies that may end up lacking enough data, which is needed in understanding, as well as building the product or service as desired by the target customer. Across modern marketing, it is worrying that most of the very small enterprises do not have a clear and established sales process. The latter normally gives room for aligning the company towards the qualities of the desired products, concrete customer, demand and even the delivery time. The VSEs are only comforted by becoming more scalable without making mileage in adopting change. This is one modern marketing mistake, which includes failure to prioritize the actual customer and an effective sales process, which would yield a better perspective on the way consumers would make use of a service or product. Broadly businesses that have tried to create content have stood a better chance of understanding the piece of information that is needed by the potential market, as well as understand the problems they face. This means that businesses stand a better chance of controlling the consumer experience through attracting, engaging as well as selling to consumers. For instance, platforms like social media are good for connecting people through creation of good marketing content as they give room for creating a small video of the product, which can go viral the moment it is put on such a tool like Facebook. Good videos are likely to be shared to over 5 million people where at least 500,000 people would develop interest in the product.
Julien (2018) noted that large businesses are simply making use of internet, dubbed a free resource, to scale business performance and raise the bar that has made the small and VSE businesses to give up on putting a better fight. While studies fail to link E-marketing to marketing performance associated to large businesses, the expansion of research has already explored on the broader concepts attached to e-commerce and other uses of internet within the business environment. Julien (2018) pointed out that small businesses have ignored the paramount relationship between performance and e marketing without realizing that the future is still characterized by the E-Business penetration. This advantage has been embraced by large businesses with the positive relationship between E-Business and performance leading to relationship development, business efficiency, sales performance, as well as customer satisfaction. E-marketing, as a component of modern marketing, is said to be dominant across the USA companies with studies covering the period from the year 2002 to 2005. The findings have been due to high rates of internet use in North America, which has 252 million users which forms around 16% of the total internet users as the per research conducted in 2009. In essence, US-based companies are taking advantage of this platform to implement E-Marketing, which is also more pronounced in New Zealand, Australia, United Kingdom and United States itself. While internet and the wide area of modern marketing used to be platforms for the developed countries and more established companies, the trend has changed as more users are attracted to social media, and other areas that are hosted on internet. Africa which used to lag behind has shown positive growth over the last 5 years as youths embrace internet and mobile technologies. While such changes would have served as an opportunity to most of the small business enterprises, most of them have left have left it to be swept by the large multinational companies, which are perceived to have enough resources and more time to invest in modern marketing platforms. On the other hand, in modern marketing, it is always advantageous for the business to understand the characteristics of the market that suit the products or service provided by the company. However, this is not always the case with VSEs, which end up focusing on the mass market, instead of narrowing down to micro market. This follows an assumption that targeting mass market assures the business of a product segment. Such assumptions can equally be linked to another gap area in modern marketing, which involves lack of attention on content marketing. Coviello et al. (2017) categorically stated that radios and televisions would end up costing a lot of money but fail to yield substantial returns on the capital a business would have spent on marketing. While businesses seek better alternatives, VSEs would pay no attention to content marketing and would work on rare strategies that make a firm grow. While VSE s would have an equal advantage of creating a blog and reap from good content, they fail to do so and therefore miss out on the significant platform of developing online presence, as well as create awareness of the product, or the entire business. The obvious advantage modern marketing gives a business revolves around content marketing.
2.2 Influence of social media tools on businesses
Modern marketing, internet marketing, and E-commerce are strongly thought to be fields dominated by large business enterprises. However, internet has strongly been regarded as a free resource that has to be used by everyone who has interest. For instance, opening Facebook accounts is almost free and even operating is relatively free. The most disturbing area is why small businesses should avoid making use of the free resource, which would serve as an advantage to their businesses once implemented. The blame goes to the business owners who carry a different perception about the use of social media in their respective businesses. Fuchs (2017) argued that businesses especially very small must have carried different assertion concerning benefits of social media in their respective businesses. First, they are thought to fight for immediate results, which may not be realized from social media platforms, which require time before investors or business owners could reap from them. The use of social media has been perceived as a lagging process that entails attraction of a community of fans attached to a brand. This can take a long period before realizing the connection social media has towards business performance. Fuchs (2017) indicated that social media is always a long-term strategy, which may not be convenient for seasonal small businesses.
The struggles of big companies like Apple, Samsung and Coca-Cola in handling the harmful effects of trust, security and trust issues that emerge from social media has served as a threatening lessons to other businesses primarily VSEs. Smith and Zook (2012) argued that while social media is used in promoting a brand, it has an equal capacity of trust, data security, platform intrusion, and privacy issues. Companies, including the large ones, are gradually taking precautionary measures in reducing the exposure of personal data. For instance, trust has emerged as one of the critical issues in the dimensions of privacy and transactional security. It is a critical component placed at the centre of customer loyalty to the company and the social media marketers. Most of the consumer-generated reviews, tags and images might serve as a critical platform that determine the online choices to be made by customers. It is quite damaging to most of the marketing campaigns when a business receives negative responses. Most of the unhappy customers, and even industry competitors, would take advantage of the freedom to launch attacks, post disparaging pictures, videos, and comment. In such a case, business owners increasingly develop an attitude of social media as a destructive tool, which is enticing and captivating in the first place, but leads to as a threat and inconveniences once it is embraced and integrated in the business. Within VSEs business ecosystem, Zeitel-Bank and Tat (2014) alluded to the fact that the business owners have a growing attitude of social media as a complications and a challenge, which can kill the dreams of a young business that is making efforts of penetrating into the market. Most of them have indicated that social media is a waste of time due to the dire commitment to management of the networks, responding to comments, posting the product information and sometimes responding to awkward questions. Zeitel-Bank and Tat (2014) further notes that businesses that do not have an established service to run social networks may find it hard to compete in the market. Apparently, social media marketing calls for time investment, which might be a rare resource to very small enterprises running a tight schedule, small profits and a non-established market segment. Most of the VSEs do not have reports on their market segment, a business plan or even business forecasts because all these details are seen as expensive for an enterprise that is running on no economies. In addition, social media is an open platform that supports anonymity, which is a vice that is likely to support negative feedbacks or defamatory information which can ruin the future of the business.
Nadaraja and Yazdanifard (2013) pointed out that most of the VSEs owners would not want to risk their businesses because of negative feedbacks, propaganda, negative reviews, fake news, and conman-ship, which are common among large business enterprise believed to have the capacity of handling or containing negative forces. In the study of small enterprises in United Kingdom and United States, Nadaraja and Yazdanifard (2013) noted that social media has converted most consumers into advertisers and marketers, which provides them with an opportunity of creating a negative pressure on the company, and services or products provided. The negative pressure emanates from the way a company presents the products or services online, the quality of the commodities, the interests of the competitors and the ill motives of the rumourmongers. Due to this, most of the VSEs owners decide to pull back citing the challenge of impressing both the enemy and the friend while observing the growth of the business. On the other hand, privacy concerns have resulted in public relations fiasco across major social media platforms leading to brand image erosion among other things. As much as social media companies try to work on the privacy policies, violations are extremely high due to subsequent propagations that are instigated by anonymous figures. While using social media, companies seemingly operate on a threat and a time bomb that is likely to explode the hopes and the future of the company. Therefore, the VSEs owners have an unending fear of loss and extra expenses in case they pursue the use of social media in their daily operations. Perhaps, most of them would try to avoid social media because the awaiting repercussions that can to kill the business, and dismiss the achievements that might have been attained through struggles.
2.3 Influence of social media on VSEs’ financial operation cost and management
According to Abrons (2018), social media marketing has an influence on the consumer trust because it accounts for around 37% of all the purchasing decisions encountered in the business world. Abrons (2018) further notes that small businesses are known for accounting for over half of the private sector workforce in United States. However, it is still worrying that most of the small business owners have consistently expressed their fear in adopting concrete strategies that embrace new technologies such as mobile and internet. In a case study conducted in Chicago, Illinois, the author discovered that the perception of cost, as well as inconvenience amounts to the evident reluctance witnessed among the VSEs owners. While social media tools would be necessary for earning small businesses a competitive advantage, most of them have shown laxity and lack of interest citing lack of money, personnel, as well as sufficient time. Pando-Garcia et al. (2016) realized that online tools such a TripAdvisor shifted accountability and business control towards consumers through development of the emergent notions of collective knowledge and group wisdom at the same time. Consumers tend to provide a service and seem to patronize the business by leaving favourable views. However, this role should be left for the business itself given that most of them fear when customers hold them to account on some issues that would not have popped up if social media tools were never used. TripAdvisor and other sites are said to have an influence on the perception of the public as the visibility of organization continue increasing in the face of social media tools. ideally, most of the VSEs owners believe that they might more inconvenienced by putting the business in the hands of the customers as chances of reputational risk escalate. Ott and Theunissen (2015) noted that ambient and conventional publicity is likely to trigger negative publicity as the reputation of the business is damaged with negative information spreading through social media platforms. The perception and the attitude behind reputational risk is the one that seem to discourage small business owners from adopting social media marketing. A part from reputational risks, Ott and Theunissen (2015) added that social media marketing is difficult to measure. While businesses find it easy to deduce the associated costs of social media marketing, as well as the modest expense of using social media, most of the efforts from social media are quite elusive.
It is a big challenge to evidently link the profits to all activities and investments directed to social media. Other measures that have introduced in line with social media include the brand perception, users in a given website and the social media user behaviour. As much as the indicators might show significant relevance to a possible performance of social media, it is still unclear for one to establish to extent to which such indicators are likely to translate into business value. The concept of perception of cost and inconvenience has received more attention from other scholars and researchers. This include Brivot et al. (2017), who pointed out that the VSEs owners seem to be discouraged by the disadvantages of social media that are more aligned to costs and inconvenience. First, Brivot et al. (2017) pointed out those chances of an improper relevant network is likely to sink more investments without necessarily yielding profits for the business. This goes alongside improper structures that can support the course of social network, the components and elements associated to the trends and manage or tailor the structure of the social media tools towards the market needs. Secondly, most of the VSEs do not have a better platform, as well as relevant skills that are more inclined towards customer relationship management. Businesses should understand that social media platforms are not just meant for posting videos and pictures of the product. Social media platforms should provide ground for good relationships with stakeholders including customers. Polite responses, patience, and significant expressions form the paramount pillars of building relations. In addition, time consumption has equally been cited as a limiting factor in adopting social media. The latter requires more time investment, which is a requirement that can rarely be met by the VSEs owners. Forging relationships with customers and other stakeholder is equally a significant component as far as loyal customers are put into consideration. However, social media managers have argued that keeping such relationships is relatively expensive. On the other hand, Brivot et al. (2017) adds that social media is a significant platform, which is equally delicate and vulnerable at the same time. A critical component attracts business performance and, in equal measures, invites negative reviews that can torment or spoil the business image. Businesses would try to ignore negative feedbacks and delete disapproving opinion, which are actions that limit or impede development of strong ties between the business and customers.
2.4 Social media on consumer relationship management
While most researchers are attracted to the fact that most of the VSEs owners are not embracing the use of social media tools, it is still evident that the same businesses are making use of representations of social media. Tran (2015) believes that even the very small business are embracing the elements of customer relationship management (CRM), which determine the historical transactions, the insights of customer life cycle and the sales process. Instead of direct adoption of social media, VSEs have started realizing the need of social CRM. The latter constitutes an approach that embraces the role of the market or customers as far as the definition of the brand, service or product is put into consideration. Employees are part of the wide structure of social CRM in that they strongly tap into internet technologies while enabling the business to benefit from efficiency and productivity of their talents. Another representation revolves around innovation where social technologies are said to be paramount in deriving thoughts, insights, as well as ideas on the ways of serving the clients or customers in the market. Innovation is a platform that cannot be avoided by individuals, groups, very small businesses, SMEs, and large business enterprises. A venture into World Wide Web (WWW) offers an opportunity to share information, recommendations and even collaborate with the central purpose of transforming lives. Furthermore, Lai et al. (2017) showed that VSEs and their respective owners cannot absolutely deny the use of social media. Facebook is not only a cheap platform to businesses but also individuals who have a common interest aligned to business, social interaction and any other concerns that could be expressed openly. Lai et al. (2017) argued that VSEs cannot absolutely deny making use of social media even if the use is not meant for profitable gains as noted or construed in the business goals. Most of the VSEs would employee at least 5 employees or more. Lai et al. (2017) further noted that a group of 5 people forms a community that can forge a unique culture, behaviour and even a set of beliefs that can be shared on such platforms like group Whatsapp, online communities on Facebook and hangouts, a feature introduced in Gmail. While the use of all these platforms may not directly involve the elements of business performance, employees would automatically develop a tendency of discussing their experiences, routines and even better moments, which may heavily touch on their work lives.
While this may go unnoticed by the employer, it is apparent that employees caged in a certain bubble passing strong messages to the customers through the quality of products. Some of the employees would even go to an extent of sharing their personal experiences on different avenues and platforms that may not be disclosed to the VSEs owners. In one case study on VSEs in Finland, it could be noted that while business owners showed no interest in social media, their employees gradually dragged them towards using some of the tools by openly sharing their personal experiences. This forms the informal representation of the use of social media through employees, who form a critical pillar of the business performance as far as the structures of the business environment are put into consideration. Yan and Musika (2018) further alluded to the fact implementation of social media by the VSEs owners may take indirect forms while ensuring that communication retains a superficial level. Yan and Musika (2018) took note of three significant approaches that are helping the VSEs to presume the use of social media in realizing best business performance. The first one is mindful adoption where the business would embrace the technology, ride on other platforms, and benefit from it from the implementation process. Mindfulness can be realized through identification of value metrics, deployment of relevant platforms, assignment of the governance responsibility, ensuring accessibility of the social media applications and management of risks. Secondly, VSEs are collectively taking note of community building, which aims at expansion and development of fresh commercial opportunities.
More investments have already been channelled towards the literature of the community as far as business interests are put into consideration. The emergence of social media communities and online user innovation communities has provided significant platforms for crowdsourcing of data. This has been achieved on either small scale or large-scale platforms that are developed based on the business requirements, the available resources and the goals linked to profitability of the enterprise. Lastly, businesses are continuously working on the absorptive capacity where the enterprise acquires, explores, and alters the form of knowledge said to be acquired from the external sources. Some of the VSEs believe that CRM processes can allow them to recognize, acquire and accept knowledge that can influence employees and the customer services as far as traditional and modern social networks are put into consideration. The absorptive capacity is gradually helping the VSEs to understand the use of social media and the essence of embracing virtual environments as far as internal knowledge is put into consideration.
Chapter 3: Conceptual framework
A conceptual framework largely represents a synthesis of literature that explains a phenomenon. The framework map the course of the entire study as noted through prior knowledge and observations. In this case, the research narrows down to examination of representations and deteriorated perception of social media by VSEs owners. According to Jabareen (2009), defined the framework as a network drawn linking constructs and concepts with assumptions of knowledge on nature of reality and way things are with consideration of how things work. Theories and constructs linking the social media usage, applicability, and viability within business ecosystem range from the technology acceptance, perceived ease of use, and perceived usefulness taken from consumers and businesses perspective. In light of this study into the perception and representation of social media, such theorized concepts on population encompassing of multifaceted phenomenon of social media cupped within users perception, consumers attitudes, influence on businesses, and influence of socio-economic in contemporary business environment, ethics, social media tools, and modern marketing. Resnick et al. (2016) further insisted that anything related to social media and micro enterprises touches on two key platforms, which include technology, marketing, and consumer behavior. In modern societies and business environment, technological advancement has grown into one of fundamental if not necessity to respective daily operation and connectedness to a wider community. Similarly, business entities and individuals have seen a huge influx of new technologies. According to the proponents of the technology acceptance model (TAM), users presented with number of technologies have choice and accept through consideration of some factors that include the belief that integrating or use that particular technology will ultimately enhance his/her input and output (Rauniar, et al., 2014; Weerasinghe, and Hindagolla, 2018; Wamba, 2014). Similarly, the user has to consider the use of proposed technology would be free of effort (Hansen et al., 2018; Wamba, 2014). According to Rauniar, et al. (2014), housing this two variables of usefulness and ease of use suggest influence of user’s perception and take on the extent to which the proposed technology will have on improving his/her performance as well as the effort either financially or structure need. Wirtz and Göttel (2016) argued that factors harboring TAM aids in predicting users’ acceptance as well as influence technology will hold measured by degree of adoption and usage. For instance, in broader perspective, social media hold significant influence in business performance due to connectivity, marketing, and ability of consumer to review and provide their view on the products and organization in general. In essence, the TAM (perceived usefulness and ease of use) is considerably high.
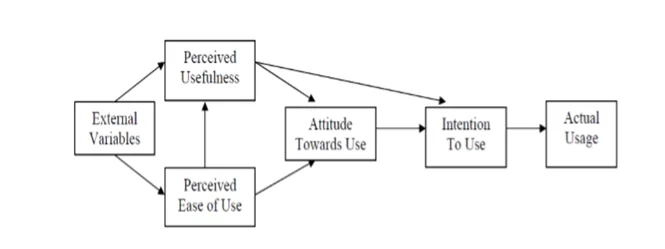
Numerous studies exist that explored the relationship between technology and social ties ranging on the influence of social media on decision making, consumer purchasing behavior, information exchange, marketing, consumer relation, and business take of social media. But limited studies have considered factors around its perceptions and representation particularly on very small businesses (VSEs). As such, this study followed the following framework in attempt to relate actual usability and influence social media platforms hold to VSEs capturing in particular the factors influence attitudes (perception) and intention to uses of social media platforms taking from VSEs’s point of view (Pando-Garcia et al. 2016). The intention of use was driven widespread popularity of social media acting as a core factor in consumer purchasing decision, relating to consumers, and dominating current marketing strategies in business ecosystem construing that user attitude and usage behaviour taken from perspective of VSEs’ owners is fundamental to development and growth of this businesses.

Apart from the conceptual overview of the very small enterprises and how they are intertwined with the micro enterprises, it is worth looking at the social media representations, which is a significant concept in this research. Rost et al. (2013) posit that representation is a common concept across the media industry. Whether the representation is conscious or unconscious, it equally builds sense in the media channels. It is of essence to note that representations mostly appear in the course of developing social media communication, which is developed from human networks. The latter enforces information sharing, cooperation and even communication. Barnett (2003) further indicated the fact that social media users stand a chance of building an entity or identity while portraying a target that incorporates ideas, groups, topics, brands and products. The description is based on the fact that media represents a certain target inclined along the value and ideological dimension. The dimensions can easily be translated into images across the public mind. Best example is where advertisements on large numbers of beer would portray a party. On the other hand, perfumes are easily connected to sexy ladies.

On a general case, representation is never born and it simply reflects the identity or the image created for the public. Representation can be created as well as constructed. In media industry, representations would mean human networks that are constructed under the influence of social media platforms, or tools that carry characteristics similar to social media. In most cases, the VSEs owners would tend to avoid social media tools, but end up using tools that are close to social media. Dobson (2016) argues that one of the dominant case of social media representation is the use of social customer relationship management, which is commonly denoted as social CRM. The simple definition of social CRM encompasses a business strategy and philosophy that is substantially supported by a technological platform, processes, social characteristics and business rules. Social CRM is largely designed for the purposes of engaging clients or customers in a more collaborative conversation for the interest of gaining a mutual value across the transparent and trusted business environment. In simple terms, social CRM is a significant fusion of customer relationship management and social media. It covers such concepts like CRM, communities, relationships, customer value, strategy, social networks and the communication technology among other things. Social CRM slightly moves away from social media tools based on a number of reasons.

First, it has been framed as a tool that guides the business towards adoption of a personalized marketing strategy. This constitutes the unbound ability of creating the custom content based on accessibility to reliable as well as qualitative social user data. This paves way for the precise audience segmentation. Secondly, it is a gateway to social customer service as far as construction of the brand advocacy is put into consideration. Lastly, social CRM gives room for social engagement with the prospects as the business is more engaged towards listening to the sentiments with regards to the characteristics and the nature of the product or service facilitated by the business. In this regard, the research finds it meaningful in incorporating the TAM model with indications of the alternative routes provided to micro enterprises which are shying off the direct use of social media. Greenberg (2010) agrees with the fact that adoption of the TAM, model at the center of social media representation and the behaviors of the micro enterprises owners, brings in the idea of relationships and conversations and not just the premier focus on customer information and data. This implies that researchers are not just looking at the importance of social media platforms but also the slightest customer engagement and communication between the business and customers noted with very small enterprises. The notion is not far from the perceptions behind the use of social media. Malthouse et al. (2013) paid more attention to the sustainability and development of social media and social media representations across the very small enterprises. Both the social media and social media representations are grounded on the aspect of social networks, which starts from the interactions between the business and the customer. However, the advantages of social media do not surpass the fear most of the VSEs owners have towards the information technologies. A simple case study provided by Trainor et al. (2014) looked at the business landscape of Turkey and a landmark of social networks in the face of business performance. Based on the findings of Turkey’s business landscape, it could be noted human or social networks is the highly valued concept when compared to the vast social media use and the dominance of the tools. Given that the small and micro enterprises account for over 70% of the businesses in the market, most of them do not appreciate the impact of social media. A large portion of the enterprises have gone forth embracing social networks that are both reasoned as being traditional and modern.
Chapter 4: Methodology
4.1 Research Approach
A research on the performance of the very small businesses has attracted a different version of the modern marketing practices. The same attention given to representation and perception of social media by VSE owners attracts the analysis of the appropriate research approach to be adopted. A research approach is simply a procedural plan that consists of the broad assumptions which are necessary in concluding the course of the research (Woo et al. 2017). Three approaches are always considered depending on the nature of the research. These include the deductive approach, inductive approach and abductive approach. The deductive approach would largely tests the validity of any noticeable assumption. The approach starts with simple facts, referred to as hypotheses, which have to be supported or rejected in the course of the research. The basis of deductive reasoning is the premise, before proceeding to the inference. On the other hand, the inductive approach does not involve development of the hypotheses. The approach starts from the aims, research questions and objectives as the genesis of the research process. Notably, the perception and representations of social media by the VSEs owners constitutes a research process that is constructed on the research aim and objectives (Tjora 2018). Building from this inductive approach is best suited for exploring the gap of marketing practices seen across the VSEs, the reasons that make the VSEs owners to avoid social media tools, perception of cost and inconvenience of social media across the VSEs owners and highlighting the representation of social media in the respective businesses.
4.2 Research Method
The wide perspective and a range of findings and interests linked to social media use across the structures of the very small business conveniently attract the use of a research method. A research method is simply a systematic plan that can be used in conducting research. Most of the sociologists would largely draw from the quantitative, qualitative, and mixed method research as the three platforms that establish the grounds for a collection of tools to be used in a research process (Mackey and Gass 2015; Silverman 2016; Taylor et al. 2015). The qualitative research is largely an explorative research that garners the understanding of the phenomenon through reasons, motivations, and opinions. It is used in availing insights linked to the research problem and helps in developing ideas concerning the research aims and objectives linked to social media use and the perception of the VSEs owners. However, the aim of this research was to explore the views and perspective of VSEs’ owners concerning social media seeking avenues and descriptive areas, which can be linked to the research objectives. The research presents a marketing phenomenon, which can be addressed by use of the quality of the opinions, attitudes, and behaviours among other variables (Kratochwill 2015). This means that a qualitative method is more convenient and appropriate in presenting a platform for the research process to be adopted in the context. In addition to offered convenience in conducting human interactions due its respective complexities, the approach enable this study to probe deeply into perception and representation indulged by social platforms with respect to VSEs (Mackey and Gass 2015).
Nevertheless, the qualitative method still suffers from poor strategies in time management due to the prolonged periods of transcription, identification of themes, and analysis of the field notes. Regardless of the drawback, qualitative research remains convenient and effective in conducting the research due to sociable structures noted with the VSEs owners, and the notable characteristics of the social media platforms.
4.3 Research Design
Research design largely denotes the strategy chosen for integrating significant components behind a study in a logical and coherent way. This ensures that that the research takes note of the research problem while forging a blueprint meant for collection, measurement as well as analysis of data. In discovering the meaningful representation, as well as perception of social media by the VSEs owners, the research has a pool of options with regards to the research designs (Marczyk et al. 2017). First, the action research design follows a cycle where the exploratory stance is effectively adopted. This brings in the essence of understanding the problem before producing an interventional strategy. The action research design fosters pragmatic as well as solution-driven research, which is better than simply testing various theories.
4.4 Data Collection Method
This is an essential part of the research that adopts key tools to be used in collecting data. Given that this is a qualitative study, qualitative tools would be more convenient are assembling necessary details concerning the subject under study. Some of the tools include interviews, questionnaires and surveys, case studies and document records, observations, focus groups, ethnographies, and oral history. In this context, the research finds the necessary use of systematic reviews, noted from the document records, which provide the recent and historical accounts of social media use, and the perception of the VSEs owners. A systematic review involves appraising previous studies and synthesizing findings either quantitatively or qualitatively using a systematic approach in collecting secondary data. It plays to the advantage of the empirical association where valid conclusions are effectively and sufficiently based on the findings. In attempt to attain research objectives in a manner that captured all the variables and research questions, this study followed qualitative approach collecting data from secondary source through systematically reviewing existing articles (Bernard et al. 2016). The secondary data collection method encompassing careful planning and documenting various articles capturing a wide data from previous structured and reviewed studies related to research topic. Ideally, adopting this data collection mechanism was informed by assumption that the field was extensive explored previously by vast number of researcher, hence time saving and cost-efficient accessing secondary data rather that collecting directly from VSEs owners and directly involved parties.

Notably, the research captured key findings from the documented records, which will mostly constitute journal articles published over the recent times (Taylor et al. 2015). The adoption of systematic reviewed was largely due to a number of advantages the tool provided to this research. Systematic reviews are largely comprehensive in that they attract the process of social research as one way of expressing the attitude, opinions and the behaviours that can be noted across common settings. However, systematic reviews would still suffer from limited representatives, which make generalization impossible in any research. Systematic reviews bear no fixed limits and would depend on a situation and dynamics that regulate the outcomes (Mackey and Gass 2015). Regardless of the shortcomings, case studies would offer a significant support to the research process by providing pieces of evidence that can be aligned to the research objectives.
Selection of material
In articles identification, keywords were keyed into the following databases namely EBSCO, Google Scholars, Proquest, ScienceDirect, Scopus, Sage Journals, JSTOR and Emerald. Fundamentally, the search was conducted based on research objectives and following core variables. Key words included modern marketing practices, very small enterprises, social media tools, cost and inconvenience of social media, social media representations and manager/owner attitude. Additional, the search focused on components related to modern marketing, social media tools, influence of social media tools, social media- owners relationship, representation (with social media), consumer relation via social media, and VSEs’ perception of social media platforms. Secondly, the process included searching for documents by first selecting the year of publication, limiting the article search to those published after 2007.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
While research method and data collection method form the critical components of the research process, the sampling procedure is equally important. This means that a criterion was set up to establish the articles to be selected from possible a vast number returned from databases search. what can be selected to contribute towards the research. There are many sampling procedures that the research is likely to encounter (Gorny and Napierała 2016).

4.7 Data Analysis
Data analysis is regarded as a process meant for inspecting, cleansing, transforming as well as modelling data with the central purpose of discovering significant details, support key decisions and inform on the conclusions. While figures would be noted in some of the cases studies sampled for this research, the presumption is that the data collected will be qualitative, and therefore call for the qualitative data analysis techniques (Agresti 2018). The research took advantage of the content analysis, which is known for being the research technique meant for replicating, making valid inferences, and interpretation of the textual materials. It includes evaluating the data and information captured by selected articles and documents focusing on texts, graphics, and even oral communication from each then working towards making sense of such data (Hounslow 2018).
4.8 Ethical Consideration
The research makes use of secondary data, which means that there be no or limited interaction with human characters. However, ethical concerns are still necessary whether a research is using primary or secondary data. While weighing out on the burdens and benefits, it can be noted that secondary data maximizes the value of data collection. it substantially reduces the burden that would have been felt by the respondents, and provides of replica of the findings (Stemler 2015). However, the major concern of this study on elements within ethics was accuracy, relevance, and reliability of data, findings, and discussions by making sure all data and information either data collected or review articles (captured under literature review) were collected and appropriately indicated and references. This was essential in ensuring validity and accuracy of literature.
Chapter 5: Data and Findings
Findings
The aim of this study was to explore the representation and perception of social media within VSEs taking the perspective and takes of the owners on such factors of social platforms as modern marketing practices, social media tools, cost, and inconvenience of social media, social media representations, and influence of social media on operation and market of VSEs. In strive to attain this aim and stipulated objectives, this study followed qualitative approach employing systematic review of existing literature. Keywords were keyed into search engine and databases such as Google scholar, JSTOR, Science Direct, Emerald, EBSCO, Sage Journal, and ProQuest. The result of the search id outlined in the table below capturing the number of articles returned by each database in relation to the searched keywords with inclusion and exclusion criteria taken into consideration.

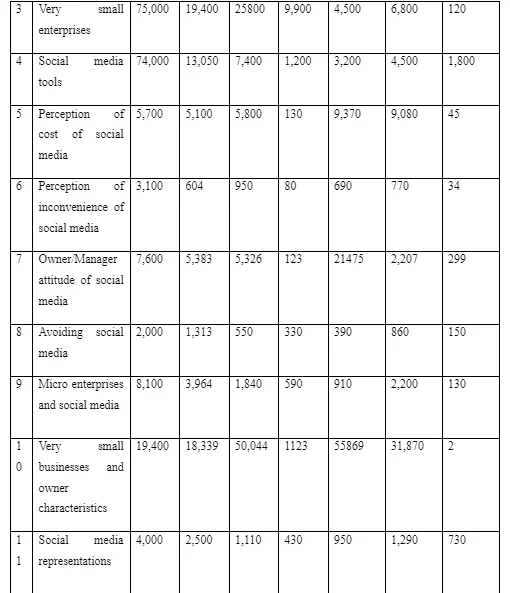
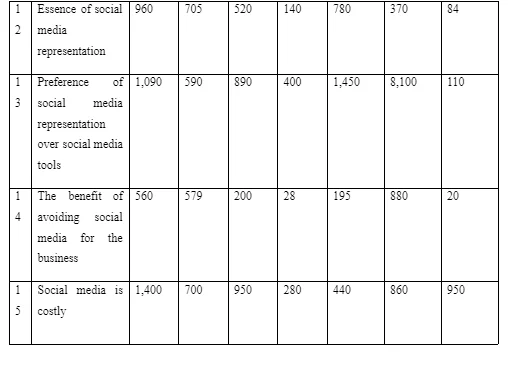
From the table above, the number of identified articles was astronomically high. Therefore, it demanded for a structure systematic approach that aided in selecting relevant and valid documents from huge number available without any bias and objectivity. After a series of reviewing through article titles, abstract, findings, research approach, and conclusion, duplicates as well as articles with near similar variable and ideas were eliminated coupled with others deemed less relevant and valid to the large research objectives and aim. The result was identifying and selecting only 15 articles within the specified inclusion and exclusion as well as capturing core study objectives and perceived being able to provide extensively answers to pre-stipulated research questions. The selected were further categorised to reflect core indicators of perception and representation of social media that include modern marketing practices, avoidance of social media platforms, reasons to why VSEs avoids integrating social media tools into their operations, and representation of such tools in VSEs ecosystem.
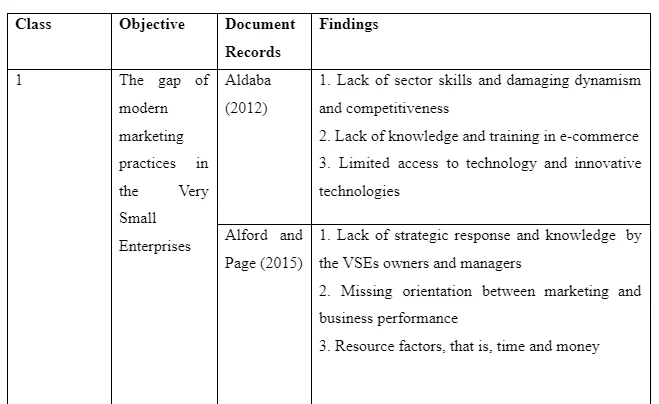
5.1 Findings on the gap of modern marketing practices
This section attracted a relook at the modern marketing practices that are missing among the very small enterprises. The following findings are as tabulated below.

5.2 Findings on the reasons as to why VSEs owners avoid social media tools
This part takes into account possible factors and reasons that make the VSEs owners to avoid significant social media tools. The findings are as shown below.


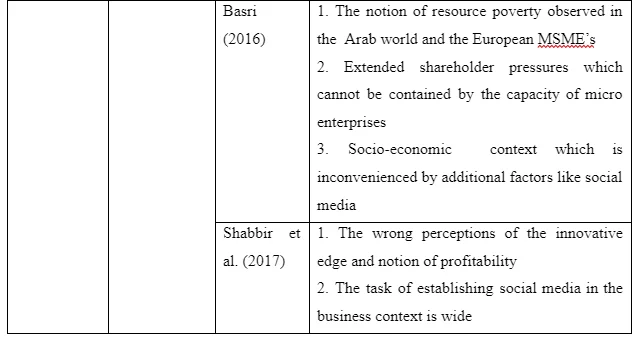
5.3 Findings on the perception of cost and inconvenience

5.4 The representations of social media by VSEs in their respective business
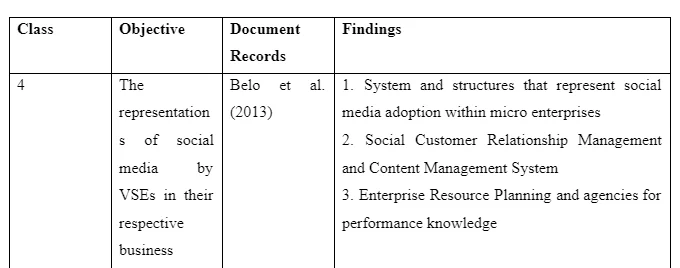
The findings on representation of social media and the analysis are as indicated below.

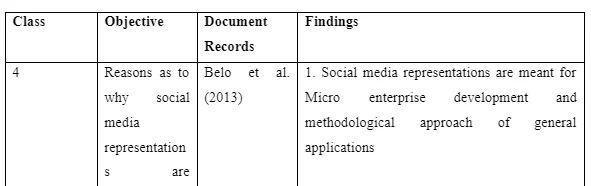
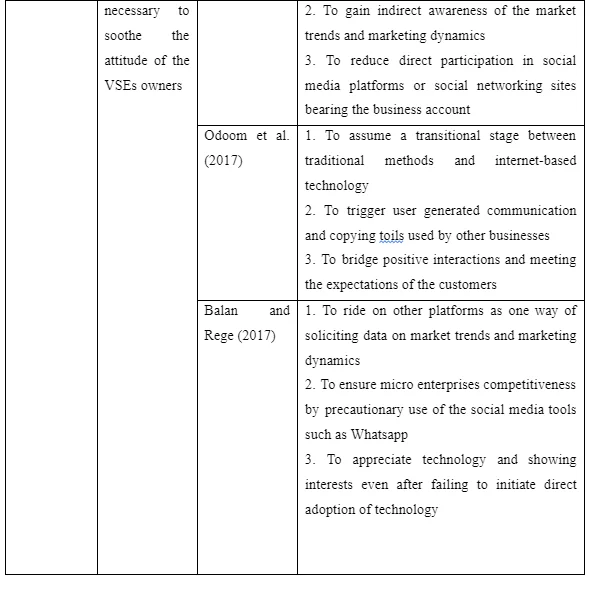
5.5 Reasons as to why social media representations are necessary to soothe the attitude of the VSEs owners
Chapter 6: Analysis and Discussion
This chapter expounds on the findings and data by adding details and concluding on the objectives stated earlier.
6.1 The gap in modern marketing practices
From the findings in the table, it is evident that most of the very small enterprises, or micro enterprises, do not make use of the modern marketing practices. Among the three case studies, it can be noted that most of the VSEs owners do not have the appropriate knowledge and proper skills that allows them to embrace the Web 2.0 applications. In the case study of Botswana, the case is even worse due to lack of the appropriate ICT infrastructure and the absence of the government support. Resources have also been noted as the impeding factor that widens the gap between the VSEs and modern marketing practices, which are heavily characterized by mobile and internet technologies. The findings also agree with those stipulated in the literature review, which cited the connection between business performance and training. The gap of marketing experience among most of the consumers has been blamed on VSEs, which have shown reluctance in adopting significant internet marketing tools. This means that the sales process is always interfered with because consumers are ahead of the business as far as mobile and internet technologies are put into consideration. This means that the VSEs are missing out on the advantage of using the Web 2.0 management skills, reengineered business processes and innovation among others. The evidence remains that adoption of modern marketing tools is still limited. Most of the VSEs in United Kingdom found it challenging to maintain a consistent digital presence as determined by the Federation of Small Businesses. In 2014, it was determined that over 75% of the VSEs expressed no interest and never used social media, which is a clear indication of the marketing gap as far as modern tools are put into consideration. While micro and small enterprises account for 92.4% of all the enterprises across the European Union, the missing adoption of the ICT initiative is seen as a threat to the industry as far as marketing and technology are put into consideration.

6.2 Avoidance of social media platforms
There are many reasons that have been cited in the course of realizing a negative attitude noted with VSEs as far as adoption of social media tools is put into consideration. The perception of challenges, limited benefits, lack of resources, the attitude of owners, lack of the appropriate skills, issues of security and private concerns are all aligned to reasons as to why the VSEs owners have a negative attitude towards the adoption of social media, and other mobile and internet technologies are put into consideration. Four dimensions can describe the reluctance of VSEs owners in adopting social media tools. The dimensions include individual, organizational, technological, and environmental. Based on the individual dimension, the manager or owner personality or characteristics have an influence in the course of adopting the new technology in the market. The decision made by the owner or manager determines the course of acquiring the e-commerce infrastructure, financial commitments, and the technological developments to be adopted in the functions of the business. This means the reluctance noticed with the managers or owners have an equal impact on the capacity of the VSEs or micro enterprises to adopt the new technology and the dominant social media tools. Besides, the level of e-commerce and ICT knowledge subsequently reflects the level of appreciation of e-commerce and technology embraced in the market. Only 11% of the micro enterprises in US and Canada understand the impact of technology and the e-commerce opportunities in the market.
Most of the owners and managers of the VSEs end up ignoring most of the technological platforms because they do not understand the constituents and even ways of using such platforms. Some of them lack the creativity as well as the zeal of acting beyond the routine environment, which is a case observed in most of the developing countries. In addition, organizational factors are paramount in influencing the decision made by VSEs owners and business managers. The idea of privacy, trust, and security is still paramount as far as the feedback and the image the business gets from social media tools are put into consideration. The lessons VSEs owners learn from the use of social media by medium-sized and large enterprises seem to have threated the micro-enterprises in pursuing the same course. The tendency of trust and security is always low especially where social media tools are used as part of the determinant factor of the business functions and operations. The same case applies to cost implications and financial ability, which are two areas that are feared by most of the VSEs owners. The perceived limited benefits from social media to the growth of the VSEs have been regarded as part of the negative attitude the owners have towards social media. Some of the VSEs lack the understanding of the exact benefits e-commerce and social media tools have towards the respective businesses. The negative mind-set has further made most of the VSEs owners to believe that social media is a waste of time and resources.
6.3 The perception of cost and inconvenience
The observation of reluctance among the VSEs owners has attracted the attention of researchers and scholars who look beyond the perception of the growing entrepreneurs. However, the uses of the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) where two key areas are observed. These include the perceived usefulness (PU) and the perceived ease of use (PEOU). Findings on stringent financial commitment, side effects of the Community of Practice, resource poverty and the wide business context of establishing social media has raised the idea of the rate of perceived usefulness as noted with most of the micro enterprises. The inconvenience within the socio-economic context and external pressures are placed under the perceived ease of use, which is rated low as far as micro enterprises are put into consideration. The perceived usefulness, as explained before, takes note of technology as the paramount tool that would lead to business and job performance. Financial commitment or lack of the financial resources has made social media to look costly for the VSEs owners. Observations made across the European MSMEs noted that financial constraints lead to cost consideration as well as investment prioritization as investors try to limit the burden behind systemic innovations. Most of the micro enterprises, or the VSEs, have continuously missed on the opportunity of building up significant financial reserves.
The challenge has always been the immediate cash needs that cannot be postponed. This makes costs as well as risks linked to investments in social media tools and other technologies sound like a heavy burden to the very small enterprises, or micro enterprises as used in some contexts. It is even worse when the VSEs owners perceive social media as an inconvenient area that may not have any positive impact in the business. Based on the examination of the socio-economic context, the study of the 1330 Latin American micro enterprises and 7662 European micro businesses fostered the welfare of the respective countries. In the lower welfare countries, the cultures and the public welfare traditions form the explanation of the business context and their performance in the market. Best explanation of such scenario can be linked to the analysis of the intrinsic and extrinsic motivating factors. Public and social controls are external controls where social media has been perceived as a tool that can snatch the VSEs owners their control. Such powers are seen to be channelled to customers who end up having a voice in the operations of the business. For instance, unfavourable views would always paint a bad image of the business and ruin its visibility.
6.4 The representations of social media
Most researchers are of the view that VSEs are never embracing or appreciating the significant use of social media tools and the subsequent platforms. However, based on the findings, it is undeniable that micro enterprises are to some extend making significant use of the social media representations. This means that social networks are still necessary even when they adopted in an unnoticeable way. Micro enterprises or the VSEs have put in place the systems and structures that represent the adoption of social media as far as the entrepreneurial culture is put into consideration. To some extent, the micro enterprises have adopted social CRM, Enterprise Resource Planning, and Content Management Systems, which have introduced miniature platforms meant to nurture new ideas while improving the prevailing ones. Integration of the CRM functions in line with the social networks prompts the use of open sources and the available communication channels. CRM guarantee the option use while taking note of the essence of expanding the market, working on the social networks and enjoying the consultative services that are normally solicited from the external sources. The same attention is given to small-scale adoption of social media through the Community of Practice. This is possible through employees who have individual accounts where they can share their experiences and attitudes. Across the community of practice, it should be noted that the owners may be or may not be aware of the on-going interactions and social networks, which may have an equal impact on the business performance. Besides, VSEs owners are fond of analysing tweets meant for different business accounts, which are not directly related to the business. Such owners may have their personal twitter accounts but are not willing to associate the platform with the business. In such a case, the VSEs owners would be making the indirect use of the social media, or any relevant technology. The recent emergency of Whatsapp is lately putting every employee, owner and other stakeholders in the online communities, which may have limited membership that are closely connected to the business.
6.5 The significance of social media representations
Different businesses would front different reasons in the course of explaining the use of Communities of Practice, small scale adoption of social media, indirect use of Facebook and Twitter and social CRM. Several reasons have been floated in the course of explaining why such social media representations are necessary. Almost 100% of the VSEs are making use of the social media representations as one way of hiding their direct identity, or as one way of reducing their digital presence. Direct use of social media increases the visibility of the business thereby making it more susceptible to reputational damage. Therefore, most of the VSEs owners prefer social media representations rather than the social media platforms as it would be the case with medium sized and large business enterprises.
Chapter 7: Conclusion and recommendation
Summary of the findings
The research walked through a process that consistently looked at the deteriorated perception of VSEs owners and preferred social media representations. The research identified and selected 15 articles and journals aligned to the research objectives acting as source od data. This provided the wide perspective of why VSEs owners have reservations to the idea of adopting social media tools into their businesses structures. In the course of defining the research process, adoption of the qualitative research method helped in understanding the meaningful use of the systematic review. A whole process of researching, identifying, assessing, and selecting led to the finest findings that could be assigned to each objective established at the start of the research process. Over the process, the research delved deeper into the gap of modern marketing practices realized across the micro enterprises, attitude of VSEs towards social media tools, the perception of cost and inconvenience, social media representations and reasons as to why they have received more preference.
Based on the first objective, the gap of modern marketing practices is evident because of lack of skills and knowledge, lack of the ICT infrastructure, financial commitments, resource poverty and lack of the appropriate government support. Secondly, VSEs owners avoid social media because of the manager or owner characteristics such as attitude, decisions, and attitudes, organization factors like privacy, security and trust issues, environmental factors like stakeholder pressure and other extrinsic factors. It could still be found out that VSEs owners are putting more preference on social media representations like social CRM, Communities of Practice and small scale adoption of social media. Notable, the VSEs owners believe that social media representations limit on the visibility of the business, which makes the enterprise less susceptible to reputational damage among other inconveniences.
Based on the findings, the study viewed lack of sector skills and damaging dynamism and competitiveness as a trigger to the gap in modern marketing practices. The same attention is given to lack of knowledge and training in e-commerce, which are key areas in the effective use of mobile and internet technologies. In addition, lack of ICT infrastructure, strict access to innovative technologies and resource factors have a significant impact in prompting the gap in modern marketing practices as far as very small enterprises are put into consideration. On the basis of the second objective that cites reasons as to why VSEs owners avoid social media tools, it can be concluded that individual factors including the manager/owner characteristics such as financial commitment and personal decisions can describe the exact reasons that impede VSEs to avoid social media. Same individual factors o alongside the resource factors, perceptions and attitude towards cost and benefits and the levels of knowhow and education as regards e-commerce and ICT. The second category of reasons resides behind organizational factors, which go alongside issues to do with trust, security and trust. Social media tools are thought to expose the business more to the out world, which can make it more susceptible. The same can be extended to the perception of limited opportunities the business can enjoy from using social media.
Other reasons can be linked to ethical challenges among other areas. On the basis of the perception of cost and inconvenience of social media, it can be concluded that investments on social media can rarely be traced, which equally means that businesses may not easily trace the returns of social media. The benefits take long to be realized by the business, which makes the business to take no notice or dismiss the impact. Lastly, VSEs owners cannot avoid social media representations. Based on this, it can be concluded that even the VSEs owners cannot avoid making use of the social CRM among other tools that bear similar characteristics to social media tools.
Limitations of the Research
The research showed strength in selecting and assessing significant articles and journals. The same goes to the establishment of the rigorous research process that led to justifiable findings. However, a few limitations could still be witnessed. First, the research leaned towards qualitative research method. This limited analysis of figures or numerical data ruined application of numerical findings. Perhaps, this must have limited the scope as far as the research indicated sporadic numerical data. Secondly, the research expound on the sampling and assessment process without pointing out a significant background.
Recommendations
Based on the findings and conclusion of the research process, it is still recommendable for the research to consider
The research should narrow down to a specific business environment in a global context such as a certain global market that reflect the global dynamics
The research should emphasize on the real-life case studies that give the key evidence to the findings while expressing the context, meaning and the possible analysis
References
Abdulkadiroğlu, A., Angrist, J.D., Narita, Y. and Pathak, P.A., 2017. Research design meets market design: Using centralized assignment for impact evaluation. Econometrica, 85(5), pp.1373-1432.
Abrons, I.M., 2018. Social Media Marketing Among Small Retail Clothing Businesses.
Agresti, A., 2018. An introduction to categorical data analysis. Wiley.
Aldaba, R.M., 2012. SME development: narrowing the development gap in the ASEAN Economic Community. Philippine Journal of Development, 39(1/2), p.143.
Alford, P. and Page, S.J., 2015. Marketing technology for adoption by small business. The Service Industries Journal, 35(11-12), pp.655-669.
Andersen, E.S., 2013. Evolutionary economics: post-Schumpeterian contributions. Routledge.
Anonymous., 2010. How social media are changing the face of business. Leader to Leader, 57. p. 59.
Baker, M.J., 2016. What is marketing?. In The Marketing Book (pp. 25-42). Routledge.
Balan, S. and Rege, J., 2017. Mining for social media: Usage patterns of small businesses. Business systems research journal: international journal of the Society for Advancing Business & Information Technology (BIT), 8(1), pp.43-50.
Belo, A., Castela, G. and Fernandes, S., 2013. How small and medium enterprises are using social networks? Evidence from the Algarve region. In Advances in Information Systems and Technologies (pp. 143-155). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Boutary, M., 2008. ICT and VSE: between proximity and modernity, in Lavoisier (dir.), Very small businesses: a management of proximity, Paris, Hermès Science.
Brivot, M., Gendron, Y. and Guénin, H., 2017. Reinventing organizational control: Meaning contest surrounding reputational risk controllability in the social media arena. Accounting, Auditing & Accountability Journal, 30(4), pp.795-820.
Cefrio., 2011. NetPME 2011: The use of ICT by Canadian and Quebec SMEs, p.134
Cluley, R. and Greenhalf, W., 2018. Social representations of marketing work: advertising workers and social media. European Journal of Marketing.
Dobson, A.S., 2016. Postfeminist digital cultures: Femininity, social media, and self-representation. Springer.
Gorny, A. and Napierała, J., 2016. Comparing the effectiveness of respondent-driven sampling and quota sampling in migration research. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 19(6), pp.645-661.
Grégoire, Y., Laufer, D. and Tripp, T., 2010. A comprehensive model of customer direct and indirect revenge: understanding the effects of perceived greed and customer power. Academy of Marketing Science Journal, 38(6). p. 738.
Hodgson, G.M., 2012. From pleasure machines to moral communities: an evolutionary economics without homo economicus. University of Chicago Press.
Julien, P.A., 2018. The state of the art in small business and entrepreneurship. Routledge.
Lai, C.H., She, B. and Tao, C.C., 2017. Connecting the dots: A longitudinal observation of relief organizations' representational networks on social media. Computers in Human Behavior, 74, pp.224-234.
Liu, I.F., Chen, M.C., Sun, Y.S., Wible, D. and Kuo, C.H., 2010. Extending the TAM model to explore the factors that affect Intention to Use an Online Learning Community. Computers & education, 54(2), pp.600-610.
Malthouse, E.C., Haenlein, M., Skiera, B., Wege, E. and Zhang, M., 2013. Managing customer relationships in the social media era: Introducing the social CRM house. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 27(4), pp.270-280.
Odoom, R., Anning-Dorson, T. and Acheampong, G., 2017. Antecedents of social media usage and performance benefits in small-and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 30(3), pp.383-399.
Pacitto, Jean-Claude et Pierre-André Julien., 2006. Is marketing soluble in the very small business? Revue internationale PME, 19(3-4), p. 33.
Pando-Garcia, J., Periañez-Cañadillas, I. and Charterina, J., 2016. Business simulation games with and without supervision: An analysis based on the TAM model. Journal of Business Research, 69(5), pp.1731-1736.
Rauniar, R., Rawski, G., Yang, J. and Johnson, B., 2014. Technology acceptance model (TAM) and social media usage: an empirical study on Facebook. Journal of Enterprise Information Management, 27(1), pp.6-30.
Rost, M., Barkhuus, L., Cramer, H. and Brown, B., 2013, February. Representation and communication: challenges in interpreting large social media datasets. In Proceedings of the 2013 conference on Computer supported cooperative work (pp. 357-362). ACM.
Shabbir, M.S., Ghazi, M.S. and Mehmood, A.R., 2017. Impact of social media applications on small business entrepreneurs. Management and Economics Research Journal, 2(2016), p.605.
Smith, P.R. and Zook, Z., 2012. Marketing communications: integrating offline and online with social media/PR Smith & Ze Zook. Philadelphia, PA: Kogan Page,.
Srinivasan, R., Bajaj, R. and Bhanot, S., 2016. Impact of Social Media Marketing Strategies used by Micro Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) on Customer acquisition and retention. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 18(1), pp.91-101.
Stewart Jr, W. H, and Roth, P., 2001. Risk Propensity Differences Between Entrepreneurs and Managers: A Meta-Analytic Review. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86(1), p. 145-153.
Taylor, S.J., Bogdan, R. and DeVault, M., 2015. Introduction to qualitative research methods: A guidebook and resource. John Wiley & Sons.
Trainor, K.J., Andzulis, J.M., Rapp, A. and Agnihotri, R., 2014. Social media technology usage and customer relationship performance: A capabilities-based examination of social CRM. Journal of Business Research, 67(6), pp.1201-1208.
Wamba, S.F., 2014. Perceived usefulness, ease of use and risk in social media adoption within workspace: an empirical study integrating assessment of unobserved heterogeneity in PLS path modeling. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth International Conference on Electronic Commerce(p. 20). ACM.
Wirtz, B.W. and Göttel, V., 2016. Technology acceptance in social media: review, synthesis and directions for future empirical research. Journal of Electronic Commerce Research, 17(2), p.97.
Wu, L. and Chen, J.L., 2005. An extension of trust and TAM model with TPB in the initial adoption of on-line tax: an empirical study. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 62(6), pp.784-808.
Yin, R.K., 2017. Case study research and applications: Design and methods. Sage publications.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



