The Power of IoT Sensory Capabilities
Introduction:
The Internet of Things (IOT) comprises of interrelated computer devices which has opened up so many possibilities according to (Statista, 2019) in year 2019 there are around 26.66 billion connected devices that already exist in the real world and they project that by year 2025 that it will increase fivefold this shows how much our human lives, livestock, agriculture, transport, health and services will inevitably rely in some way or the other on these small smart devices to collect share and analyse data just to make life a little easier. The sensory capability is the most important aspect of the internet of things (IOT) this allows to and gives the tremendous capability of integrating different sensors to collect different types of data whether it’s a temperature reading or a gas detection model the possibilities are just endless this gives this idea a big advantage by being able to combine different monitoring or detecting or even scanning capabilities gives it an advantage and making it the next most important thing. Different devices can integrate with different services such as smart administration, smart environment, industries, energy, transport, smart office and residential buildings, smart security, and health.

Saying this the (IOT) does come with its own challenges and threats. The first challenge we need to look at is to develop and design some sort of smart device that is useful to use in transport which is intuitive easy to use and most important make their trip a seamless trip. This will enable passengers to self-check in without the need to have to produce the ticket to the train conductor; this will help both passengers and the train conductor by giving the responsibility to the passenger in order to validate their seat seamlessly with the added features. The second challenge which is the most important is the threat that is introduced to possible security breaches in these smart devices also increases the more connections we get the more vulnerabilities’ we introduce.
Design and implement a prototype device that allows train customers to check in their tickets validate it with 2FA authentication by entering a pin number sent directly as a text message, the device then turns a red light to green if the seat allocated is the right one. This device will have a heart monitoring device connected to the users arm to monitor heart beats and a panic button that would be directly connected to the train managers handheld device.
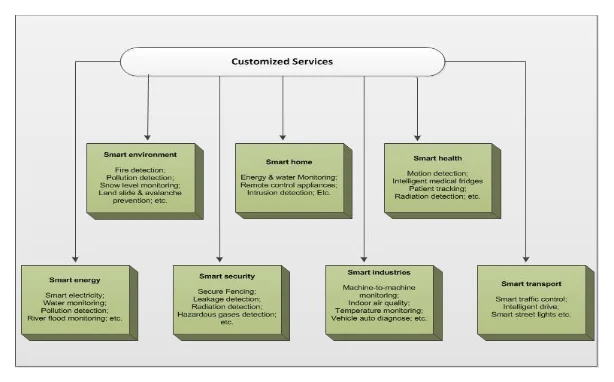
Abdelhadi, and Akkartal (2019) define internet of things as the network of physical objects such as instruments, devices, buildings, vehicles and trains which are integrated with electronics, software, circuits, sensors, software and network connectivity; enabling these object to gather and exchange data. Besides, the internet of things also enables various objects not only to be detected but also be controlled by remote controller along a given network infrastructure which then creates a golden opportunity for more direct manipulation of the physical world into computer systems; to provide the users with more accuracy in handling the tools and effectiveness especially in time management.. Kevin Ashton (British technologist) conceived the concept of Internet of Things in the year 1999 describing it as a system in which the physical world is linked together through ubiquitous sensors (Endsley, 2016). Since its conception, Internet of things has fostered communication without necessarily being there physical human interventions or contact. This study takes cognizance of how IoT has taken a large share in the realms of transportation, automotive and healthcare industries (Ashton, 2009; Atzori et al., 2010). Despite the fact that IoT technologies are in their initial stages of development, some conspicuous observations have already be made in incorporation of objects with sensors in the internet. Poslad et al., (2018)’s study that a working IoT system will always have its drivers which will requires the availability of infrastructure namely standards, protocols, communications and interfaces. As the spectrum of IoT continually develops and evolve so does the number of connected gadgets increases. It is estimated that by the year 2010, more than 10.5 billion mobile connections will be attained, which will bridge the digital and physical world, and indeed enhance life quality and productivity of enterprises, persons and people (Poslad et al., 2018). The internet of things is a characterization of various impacts on the sphere of human life. The internet links people together through not only business prospects, but also social communication. The emerging trends in IoT seeks to connect systems and machines together through actuators and sensors to ensure meaningful information and data from these systems are collected and an appropriate course of action to foster human efficiency and productivity.
IoT has extensively influenced human lives in a positive way especially by fostering sustainable and efficient patterns of energy consumption at homes and offices (Pinochet et al., 2018; Crooks, 2018; Ismail, 2018). Additionally, smart meters have continued monitoring the presence of inhabitants in homes and offices while shutting down energy-consuming gadgets when none is using them. IoT has also contributed to the actualization of building ambiances meeting different tastes and interests of inhabitants. Intelligent houses programmed to save energy make life convenient, and reduces costs in energy related bills. Alarm clocks are now connected to traffic apps, heating systems synced with external temperature sensors; and connected to cost evaluators. Better security through constant surveillance in homes and streets have all contributed in spicing human life with thrilling delicacies which make life convenient and comfortable. Poslad et al., (2018) pointed out two crucial areas of IoT applications affecting currently society first information and analysis and secondly, automation and control. In the sphere of information and analysis, the studies emphasize how decision making processes abilities have been elevated through receiving better and more updated information from networked objects, for more accurate analyses regarding to situational awareness, tracking, and sensor-driven decision analytics. In automation and control, information transmitted from processed data and analysis is refined more for the betterment of their efficiency and related-decision making processes. Despite the positive significances affiliated to Internet of Things, there are various regulatory and technological challenges in need of redress, which have affected humans. Mhamane and Shriram (2018) maintained that the most important area which needs attention is in relation to data ownership such as privacy, security and sharing information. The application of IoT in the area of commerce is subject to certain limitations as far as information privacy is concerned. Poslad et al., (2018) consider the element of security and privacy as major impediment inhibiting full acceptance of IoT. The technologies may contribute to breaching of users’ privacy rights as in cases of home and office surveillance. Unauthorized access of information related to people’s finance, and personal information severely compromises personal privacy. This challenge can be reinstated through acute data governance strategies and governance. The Internet of Things has solved many challenges related to urban transport. The IoT device has significantly reoriented the transport sector by reducing the time and fuel commuters spend in finding a parking spot (Alsafery et al., 2018; Bajkowski, 2019). Many countries, which have adopted these IoT technologies in transport sector, have allowed the users to view available space from their own smartphones, and make payments through e-wallet. The users are then able to drive directly to identified places without necessarily loitering to find space for packing. Start-ups using this technology can communicate with commuter and offer them relevant information on location of the bus or a train, and the available seats in them.
Additionally, information related to route can be communicated, for decision to be made by commuters as whether to take alternative means or wait. Internet of things is playing a pivotal role in in the domain of Bus Rapid Transport Systems (BRTS) in various countries. In many cases, upon the arrival at bus station, passengers are offered with information concerning current location of the bus; and the anticipated duration it will take to arrive on stage (Shah, 2019; Kathuria et al., 2016). The passengers are then able to decide whether to wait or look for alternative means. In the transport domain, Internet of Things has capacitated vehicle management. Car breakdowns, which in many cases are unpredictable, expensive, and inconvenient, can be curbed through vehicle management system that continuously obtains statistics concerning vehicle performance. Upon anomalous detection, attention is brought to the vehicle owner who in turn fixes the problem in time. Essentially, this has improved vehicles’ life expectance, minimized accidents and fuel.
Aim
The Aim of this proposal is to create and design a ticketing system prototype device with the intention of checking the passenger’s ticket. The ticketing system is an IOT device that will represent the trends in smart transportation. The main purpose for developing this prototype device is to make passengers’ traveling more convenient, safe and most of all keeps passengers at ease especially if they have any health issues. The prototype device will be used in sleeper trains, domestic trains it will have an integrated pulse sensor to monitor the heart rate during the passenger’s sleep and a panic button in case of emergencies
This method gives the customers some free and quiet time without getting disturbed for the ticket inspection,
This also provides us with valid points
Easy to use intuitive and provides safety for passengers who suffer of any illnesses
Security
Self organization: by allowing passengers to organise and plan their journey effectively.
Self-control: by having all your details of your ticket on your handheld device it allows some point of control
Time saving: the ability to purchase e-tickets online and sent to your smart device eliminates the need to print out physical tickets. Thus allowing the passenger to travel freely without any ticket delays.

Background
Motivation
Digitalisation is a convergence and the ongoing development of connecting physical and virtual worlds this has allowed companies to integrate IOT, Cloud infrastructures, automation and the collection of big data seamless whether it’s by plane, ships, cars or trains used in transportation or the movement of big loads in the freight business.
According to a recent study conducted by (PIERIEGUD, 2018) the adaptation of technology and transport.
In the last four years railway companies have been pressurised to begin the digital transformation (DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION: A ROADMAP FOR BILLION-DOLLAR ORGANIZATIONS , 2011)
A research has been conducted that looks into the challenges faced (Yongjun, et al., 2012).
In this research the authors used RFID in order to identify the person now with the creation of smart devices and smart environments with much easier and user-friendly interfaces among the high demand for such systems to make our journeys easier, safer and more secure.
Looking at the possibilities that these smart devices can offer us as users of the rail transport system my motivation is to create a device that would eliminate the process of providing physical evidence of the tickets while the system also monitors the user’s well-being while he/she travels
Having to produce tickets has become some sort of an issue as we delve into the world of digitalisation we are moving towards the e-ticketing systems some might prefer to book online but never the less printing physical paper copies will inevitably be a thing of the past. So we can use the already existing systems of barcoded e-tickets to create a seamless check in process easy for all passengers to use just by scanning the barcode.
According to a recent case study that concentrated on health care using the internet of things (Case study on Health care Using Internet of Things, 2016) the IOT devices consist of many sensors receivers and actuators by using the available technology we can further advance the IOT device to capture health abnormalities by improving health and safety of the passengers.
This solution is so flexible we can scale it up and add more features as and when we want because we are utilising the use of the IOT devices to connect different sensors together we can easily add more features. Idea: is to develop a device that can scan the barcode on the ticket in order to check the passenger is occupying the right seat which turns a green light on which confirms that the customer has already done that. This will help the train inspector by not having to ask for the tickets. This also stops disturbing passengers especially if they are asleep and monitors old or sick passengers heart rates that triggers a notification to the train manager for assistance and will also have a panic button for any other emergencies.
Literature review
Application of Internet of Things has grown drastically in the recent past. The International Data Corporation (IDC) maintained a perception that the transport sector is the biggest beneficiary of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies. Smart IoT is accelerating the rates of innovation and transformation in transportation and infrastructure areas. Application of smart, and connected sensors alongside smart intelligence and big data analytics have enabled the collection of knowledge, making accurate predictions and helping in making improved decisions in transport safety. Obaidat et al., (2019) contended to the immense contributions of IoT to the areas of smart infrastructure maintenance, smart traffic management, smart car technology, and smart driver advisory systems. In this chapter, the focus will be on the concepts, ideas, theories, and discussion binding together the larger scope of the IoT particularly as presented by previous studies and findings.
Architecture of Internet of Things
Vermesan, and Friess (2013)’s studies presents IoT architecture as a composition of five layers namely; application layer, communication layer, sensing layer, infrastructure layer and communication layer; and that these layers are functionally interconnected and work as a unit. The service layer as the mastermind triggers a correct response the entire system as per the particular needs of the entire bus or train system. Based on the dynamic nature of transport sector demands, IoT technologies are on the blink of constant evolution to meet new demands. Various scholars have keenly traced the factors which inspired the need for IoT related smart technologies in the realm of transport. Venkanna et al., (2018) researched on adoption rates of IoT related technologies in trains users. Their studies shows that users could readily find trains between stations locate the position of a train relative to the nearest station but could be unable to book or extract a ticket via online. To overcome this gap, they proposed the integration of e-wallet system along with booking. E-wallet scheme constitutes one of the latest developments, which enable users to own a wallet account to use in depositing money to wallet accounts for purchasing train tickets. E-wallet scheme makes sure the user does not necessarily visit a bank for payment each time thus saving time in making payments for the acquisition of e-wallet. This IoT device is under continuous modification and improvements for more efficiency.
Automatic Ticketing and IoT
Studies show that the development of Automatic Ticket Vending Machine was inspired by the urge to decongest long queues in obtaining tickets in major cities and increase efficiency in the transport sector. In this system, the users ought to register on the website and fill in fundamental details such as destination, source, return date, and date. Upon the entry of the details, a QR is generated which the user use as a ticket for travelling. On the peripheral side of the ticket, the QR code is scanned to attain information related to the user, and validate get validated. For the purposes of security, the ticket is only checked and the message generated to the intended user (Poslad et al., 2018). In the domain of ticketing, Gupta (2016) stated that the operational features are the same. The distinction lies on the sense that tags are linked with special cards, which are owned and carried by passengers. The reader of the cards gathers the information from them. The RFID technology in ticketing system allows passengers to tag off or tag on and be charged automatically based on the number of zones travelled. Conventional tickets are printed and sealed. A study by Poslad et al., (2018) demonstrated that the application of automatic ticket systems allows proponents such as transport authorities to not only save time but also personnel costs, and instil fare collection. Besides, these systems require less maintenance costs and less fraud-induced losses; which highlight their significances. Sandhya, and Sudha (2018) contended that automation is keynote in the reduction of crime, excess work, and time in the whole transport system. Radio Frequency Identification harnesses the low end electromagnetic spectrum which is not deleterious; just like the radio waves. As the radio tunes into various frequencies, so does the Radio Frequency Identification readers and tags tune to the same frequency to communicate. Utilizing radio waves to identify and trace a person, animal, or product by using RFID tags integrated on them, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has been integrated into trains and buses for purposes of tracing them while informing customers on stage about relative estimations to arrive on stage. RFID system comprises of microchip with antenna (tag) and reader with an antenna. As stated by Domdouzis et al. (2007), a typical RFID tag constitutes incorporated circuit for storing and synthesizing information; and for modulating and demodulating Radio Frequencies (RF) signal. RFID tag also comprises of an antenna for the purposes of receiving and transmitting signals. Technological engineers have applied the concept of RFID in transport sector, especially in bus identification, where the tags are attached to the bus. Besides RFID, technologists have actualized the use of AWS. The AWS IoT enables us to connect and manage devices alongside facilitating the construction of IoT applications. Besides, AWS IoT platform renders much more efficiency in connecting gadgets into the cloud, and fosters easy collection, storage and analysis of large volumes of data streaming from connected gadgets (Oppitz, and Tomsu 2018).
Oppitz, and Tomsu (2018) attributed credits to Radio Frequency Identification tickets on the basis that they are complex to duplicate as opposed to magnetic tickets; which therefore minimizes chances of fraud. Additionally, radio waves permeate through most non-metallic objects hence can be integrated in encased non-metallic materials for the purpose of enhancing durability. Smart ticket terminal lack moving parts, which minimizes tear and wear; making Radio Frequency Identification terminals reliable while reducing maintenance time-ratios. Reduced memory size equally the ticket price which incites customers to switch to them. Oppitz, and Tomsu (2018) in their work define E-ticketing as a transport payment system which is based on the application of information and communication innovations. On the other hand, Mallikarjuna, Reddy, and Sailaja (n.d) define it as “a contract in digital format, between the user and service provide….” which has the ability to also offer the verification and authentication and of passengers. An E-ticket has therefore can hold huge amount of information which is electronically coded; thus many commuters do not necessarily carry printed tickets. E-ticket technology helps commuters to book long journey tickets. Upon the completion of booking, a confirmation mail is sent to the passenger containing the ticket information which ought to be printed. M-Ticketing was conceived on the same spirit as E–Ticketing to help passengers obtain travelling tickets from the touch of their phones. End-to-end encryption based on Biometric Saas is one of the reliable management systems developed to counter common identity theft and meet the ever-increasing security demands in various domains such as government, forensic and transportation, security, finance, education, healthcare and public justice (Jaiswal 2018). The program concerns with information security; rendering it integrity, confidentiality ensuring it availability in all forms at given time. Systems based on biometrics have gradually evolved to ensure they provide information security services. The capacity to provide personal identity is crucial in identity management systems, based on the premise that surrogate representations of identity including use of identity cards and passwords may become unreliable or insufficient. In the field if engineering, Jaiswal (2018) maintained that biometric recognition is mainly attached with the establishment of individuals’ identities according to their measurable behavioral or biological traits. Biological traits may take forms of finger prints, eye, hand geometry, ear or face; while behavioural traits may take forms of signatures, gait and keystroke dynamics. Biometric authentication is characterized by improved levels of accuracy, but its inadequate scalability and accessibility by current biometric technology; alongside high cost incurred in actualizing the same have inhibited its adoption rates. Elemental costs incurred in the implementation process are reduced by the application of a low-cost IoT device such as Raspberry Pi. The attraction of Raspberry pi ascends its affordability and the computer’s small size. Raspberry is applied to develop a biometric system based on its ability to link with fingerprints or cameras through USB ports. Additionally, raspberry pi constitutes an Ethernet port which fosters internet connectivity. This study ventures into this technology based on its cost effectiveness, ability to connect with wireless internet adapters and indeed abilities to be housed on the cloud as a software-as-a-service (SaaS).
Ling et al., (2017) conceived the blend of cloud and Raspberry Pi as an emerging trend in IoT. The IoT enabled objects sensed and controlled remotely across a given network architecture, thus motivating opportunities for direct manipulation between computer-based systems and physical world; and in due process inducing opportunities efficiencies, economic gains and precisions. According to Sandhya, and Sudha (2018), the Internet of Things has reinvented identity management systems biometrically to facilitate opening of not only bank and email accounts but also homes, cars, and personal health databases.
Privacy and Security concerns
Many theoretical studies demonstrate that password-based authentications are subject to attacks including dictionary, brute force, sniffing, phishing, and surfing and key-logger invasions. Human-induced traits also add additional challenges to password bases authentication, as in through sharing confidential passwords to friends and family members. Kaiwartya et al., (2016) demonstrated the main causative agents of password challenges such as unique organizational needs and memorability issue. The scholars’ study concluded that human computer interactions logistics have the capacity to address password-related challenges (Schmidt et al., 2000; Karat et al., 2009). Sandhya, and Sudha (2018) empirically studied security and password memorability constraints, and concluded that amongst the various biometrics of face, finger, eye, voice, hand, signature, DNA; the face biometrics was the leading in terms of compatibility evaluation conducted by the Machine Readable Travel Document (MRTD). The possibility of all electronic interfaces and the associated human-optimization capabilities they bring have been facilitated by software engineering. Interfaces are useful, and easy to use because of their interaction design that triggers users to integrate the system or app to the normalized routine; or even when necessary to complete intended tasks. Poslad et al., (2018) categorize interaction design as naturally contextual and that the interaction aims at solving of problems under special occasions using the available material. User-centered design is important in this study based on the fact that it demonstrates how user participation in every phase is crucial. According to Endsley (2016), the User-Centered Design is founded on the precepts of usability knowledge and ergonomics to identify the users’ needs. The scholars define user-centered designs as a “project-oriented to interactive systems development”. The ISO 9241-210 proposed the application of User-Centered Design as a way of influencing acceptance and productivity of interactive designs while reducing errors and time incurred in supporting, training and producing projects. The adoption of User-centered Design will also inspire this study to inspire best users’ experiences, and address the development of systems which are inclined to specific consumers’ needs and preferences; through the application of ergonomic criteria and the knowledge on user techniques. Endsley (2016) stated that User-Centered Design increases efficiency, improves human wellbeing sustainability and accessibility while putting into account the various impacts interactive systems can bring forth in the realms of human health, user performance and safety. ISO defines user experience as the ‘perceptions and responses resulting from the use or anticipated use of a product, system or service" Poslad et al., (2018). Other studies present user experiences as the affections, beliefs, emotions and anticipations occurring before, during and after the consumption of a given technology. The pursuits to employ User-Centered Designs is therefore impeccable in promoting easy and faster adoption rates of our project based on the premise of that the approach takes into considering diverse needs, preferences and interests.
Mr. Godson Michael D’silva, Mr.AnoopKunjumonScariah, Mr.Lukose Roy Pannapara and Ms. Jessica John (Verma, 2018).
The Proposed the idea of the ticketing system for trains for the suburbs regions. He used this method and added the ability of the authentication and authorisation process by using smart cards. The idea of using a smart card was a total innovation that allowed passengers to maintain a balance for the purposes of travel from source to destination, they used this idea by adding the ability of the AWS public cloud services. This allowed the capture of the RFID sensors which sent data through the Raspberry PU device and publishes the event or journey costs to the cloud. This also allowed monitoring crowd analysis in real time in turn makes it cost effective with all features included
Md.FoisalMahediHasan et. Al (Verma, 2018).
Proposed and RFID based ticketing system on busses and other transport systems.
This system mainly concentrates on consistency among various and a number of bus agencies.
Which allows the uniform access of passengers on their daily routine roots via an automated server that is updated in real time every time passengers board these busses just by carrying the RFID enabled passes.
KirtiDhiman, Er. And CK Raina (Verma, 2018).
Proposed an IOT module which includes a QR code that is generated when the passenger purchases the ticket. The passengers receive a message to their mobile phone with all the details of the journey with times, dates, and seat numbers that is used to validate and verify the ticket.
Vijaysanthi. R et. Al. (Verma, 2018) .
Proposed a fingerprint authentication system using the Biometric authentication using a GT-511c3 and a raspberry PI on IOT, the fingerprint is collected by an optical sensor that sends data to the cloud. The process is to use the fingerprints for authentication, which is stored in a file server, then the webserver performs the verification process utilising the POST method in return sends back reports based on match score along with the finger index ID.
Dhvani. K et. Al. (Verma, 2018).
Proposed End-to-End encryption based on Biometric SaaS. By using fingerprint sensor and wifi module to integrate with raspberry PI to upload data on to Azure cloud service. This system uses different applications like ATM’s, voting systems, adhoc cards and attendance management systems. This method uses fingerprint and face detection systems that are automatically uploaded to the cloud fully encrypted.

Process
From the existing investigations a critical review has been largely available for research taking this in to count and using it as a base to start with.
An online questionnaire that targets travellers in order to collect ticket data for analysis
The purpose for this questionnaire is to identify and isolate requirements for this device by concentrating on the security side to assist users and protect data.
After analysis of the questionnaire a set of requirements can then be targeted taking this step will assist in the design and implementation of this device the conclusions of the questionnaire will be evaluated and a set criteria will be developed and designed for this device bearing in mind to keep costs as low as possible while keeping the functions as expected and minimising any security threats. This way we can interpret requirements and change them to a tangible device.
Tasks to be carried out:
We design a fully automated system that checks the ticket of the passenger in trains through IOT based System.
After scanning the bar code of the ticket if the passenger is allocated to this seat a green light will show to confirm that, if it stays red then this seat is not valid for that passenger.
Passengers will buy tickets in the normal manner purchase through the trainline system and all we need is a bar code to be able to use this system.
This system will introduce time saving and also environmentally friendly due to its carbon footprint we will not need any paper-based tickets any more but utilise the already existing e-tickets system.
Introduces passenger self-check in Passenger checked his/her ticket by scanning the bar code of ticket into the system.
System is used in sleeper trains and domestic journey trains.
TICKET VALIDATION: there won’t be any ticket validation but a confirmation that the ticket is allocated to the right seat we do this on the barcode issued to the passenger by only having the seat number and times.
No personal data will be needed for this confirmation
Security:
This IOT device does come with a security concern for every IOT device is a data collector some devices collect personal data and store them on the device locally and some don’t. (Fu, 2017)
This brings some challenges by making it a potential target to obtain such information.
A number of security concerns and challenges does prevent securing of these devices to insure end-to-end security in the IOT environment.
The most important challenge to date is often the resource constraint and not having enough computing resources to manage encryption which makes these devices more secure, another is that there are no agreed security standards worldwide, so manufacturers often don’t take this matter seriously.
In order to combat these issues, we need to focus on a number of things such as:
Security should be the first thing that we need to think about during the design phase
Digital certificates should be used all the time no exceptions.
API security to protect the integrity of data being transmitted.
Every IOT device has to have a unique identifier.
Hardware should be physically secured to stop tampering.
Software should be up to date as manufacturers find vulnerabilities updates get sent out. So should be a must to update to rectify these security flaws.
Consumer education of these devices.
Unique pin numbers for (2FA) multi factor authenticator
Objectives
Objective 1:
Critically investigate/review and develop the Internet of thing (IOT) device to scan barcodes on tickets for travelling
Objective 2:
Critically analyse and investigate the relationship between IOT and the human daily interactions
Objective 3:
Critically evaluate data and analyse a target group to conduct a user questionnaire and what challenges might come up.
Objective 4:
Design and evaluate a user-friendly device which is used to validate and confirm customer tickets to seats, heart rate and a panic button.

Objective 5:
Critically design and draw up a final set of recommendations and conclusion on how to make the IOT device secure.
Resources
Northumbria online library
Journals/articles
Arduino Website.
Arduino platform for programming the device.
Constraints:
Due to the very tight and limited timeframe of this project the main constraint can be time for gathering questionnaires of potential users and the coding and buying the different sensors.
Ethical considerations
This questionnaire will be target at adults who have full responsibility of their travel assuring them that this data will be anonymous and none of the content will be tied to any specific user.
Users will have full confidentiality anonymity which will be guaranteed as no names will be collected.
Users will be aware the overall purpose of this project. (Adrian Mcewen, 2014)
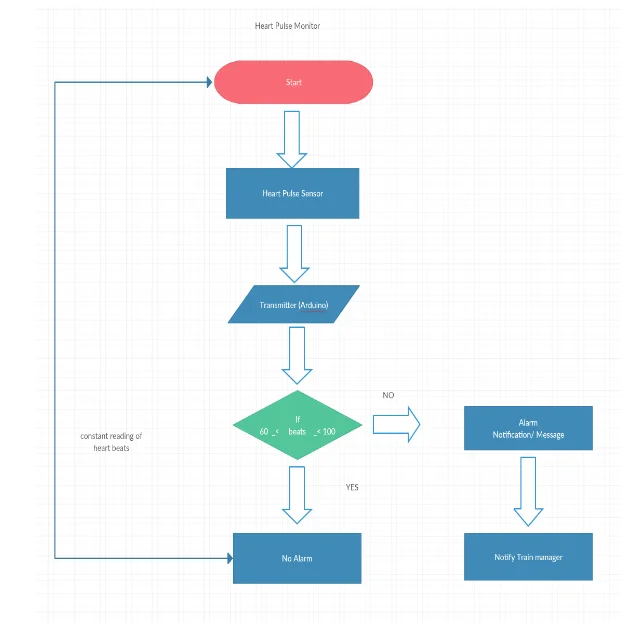
Flow Diagrams for different features
QR Code Scanner

Heart Pulse Monitor
Panic Button

Bibliography
- Adapa Sri Kumar Satya Ganapathi, 2. K. 3. K. 5., n.d. SMART RAIL RESERVATION AND VERIFICATION SYSTEM WITH UNIQUE IDENTIFICATION IN IoT USING CLOUD DATABASE. International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, Volume Volume 119 No. 14 2018, 279-283.
- AdityaGaur, B. G. S., 2015. Smart City Architecture and its Applications Based on IoT. Procedia Computer Science , 2015, , Volume Volume 52, pp. Pages 1089-1094 .
- Adrian Mcewen, H. C., 2014. Designing the internet of things. s.l.:s.n.
- Case study on Health care Using Internet of Things (2016).
- Hong Zhou1, B. L. a. D. W., n.d. Design and Research of Urban Intelligent Transportation System Based on the Internet of Things. Design and Research of Urban Intelligent Transportation System Based on the Internet of Things, pp. 572,573.
- Kirti Dhiman1, E. C. R., 2017. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer and Communication Engineering. IoT Based Ticket Checking System, 6(3), pp. 916-919.
- Domdouzis, K., Kumar, B. and Anumba, C., 2007. Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) applications: A brief introduction. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 21(4), pp.350-355.
- Atzori, L., Iera, A. and Morabito, G., 2010. The internet of things: A survey. Computer networks, 54(15), pp.2787-2805.
- Alsafery, W., Alturki, B., Reiff-Marganiec, S. and Jambi, K., 2018, April. Smart Car Parking System Solution for the Internet of Things in Smart Cities. In 2018 1st International Conference on Computer Applications & Information Security (ICCAIS) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
- Kathuria, A., Parida, M., Ravi Sekhar, C. and Sharma, A., 2016. A review of bus rapid transit implementation in India. Cogent Engineeri Abdelhadi, A. and Akkartal, E., 2019. A framework of IoT implementations and challenges in Warehouse Management, Transportation and Retailing.
- Ling, Z., Luo, J., Xu, Y., Gao, C., Wu, K. and Fu, X., 2017. Security vulnerabilities of internet of things: A case study of the smart plug system. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 4(6), pp.1899-1909.
- Obaidat, M.S., Rana, S.P., Maitra, T., Giri, D. and Dutta, S., 2019. Biometric Security and Internet of Things (IoT). In Biometric-Based Physical and Cybersecurity Systems (pp. 477-509). Springer, Cham.
- Venkanna, U., Sharma, S., Katiyar, B. and Prashanth, Y., 2018, February. A Wireless Sensor Node Based Efficient Parking Slot Availability Detection System For Smart Cities. In 2018 Recent Advances on Engineering, Technology and Computational Sciences (RAETCS) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Schmidt, A., Gellersen, H.W. and Merz, C., 2000, October. Enabling implicit human computer interaction: a wearable RFID-tag reader. In Digest of Papers. Fourth International Symposium on Wearable Computers (pp. 193-194). IEEE.
- Sandhya, K. and Sudha, T., 2018, August. Driverless Train Using IoT. In International Conference on Intelligent Data Communication Technologies and Internet of Things (pp. 1097-1102). Springer, Cham.
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



