New Service Development in Firms
1. Introduction
While there is a developing reservoir of research literature and information regarding the elements that different effective service administrations from ineffective ones, not much research at the level of the firms could have taken place previously (Harmancioglu et al., 2009). This isparticularity associated with that of the miniscule research regarding the conditions which various service provisioning organisations are necessary to be in possession of for the purpose of ensuring new service development (NSD) in the urgent manner (Froehle and Roth, 2007; Johne and Storey, 1998). A particular or coincidental achievement does not infer any NSD ability; rather this requires a dependable practice after some time(Schreyo¨gg and Kliesch-Eberl, 2007). Rather than the current prescriptive research on NSD, this study research looks to comprehend the elements that bring forth the degree to which business organisations take part in NSD and "to further discredit the view that new administrations occur because of instinct, vigour or out of sheer luck"(Menor et al., 2002, p. 135).NSD application performance measure could be observed as an intersection of the quantity of new services as well as the service success rate and the financial contribution which NSD could under take regarding the operations of the large business organisations(Barczak et al., 2009; Griffin and Page, 1996; Storey and Kelly, 2001).NSD is realized by the hierarchical setting of the services and business administration firm. It comprises the "operant" assets of any business organisation which develop the imperative condition to persuade and empower the process of NSD to occur(Chandy et al., 2003; Madhavaram and Hunt, 2008).While there is a developing assemblage of imperative research examinations into the components that which outline the process of differentiating the effective new services from unsuccessful ones, there is an absence of ground level research in particular (Harmancioglu et al., 2009).Specifically, there has been scarce research investigation into the conditions that service based organisations need to set up to attempt the development of new service delivery mechanisms under the framework of New services Development (NSD) in any case(Froehle and Roth, 2007).Three key operant assets which are brought forward in the innovation based theories could be identified as the hierarchical culture of the concerned organisations (Barney, 1986; de Brentani et al., 2010),its specific and strategic alignment (Paladino, 2009), and its capacities (Day, 1994). Be that as it may, these components are probably going to create diverse NSD results. A particular or unintentional achievement does not suggest the efficacy of NSD capacity; rather this requires a dependable practice after some time (Schreyo¨gg and Kliesch-Eberl, 2007). Rather than the current prescriptive research on NSD, this examination looks to comprehend the components that drive the degree to which service based organisations take part in NSD and “to discredit the view that new services happen as a result of intuition, flair and luck” (Menor et al., 2002, p. 135). The performance execution of the processes of NSD is seen as an intersection of the quantity of new services, the success rate of any such service proposition and the financial commitments of NSD regarding the overall performance of the business operations (Barczak et al., 2009; Griffin and Page, 1996; Storey and Kelly, 2001). NSD is achieved by the organisational contextual operations of the service provisioning organisation. These are the "operant" assets of any business organisation that formulate the imperative conditions to persuade and empower NSD to occur (Chandy et al., 2003; Madhavaram and Hunt, 2008). The coverage of any service involves an extensive variety of various and frequently complicated undertakings, with the goal that it is to a great degree extremely difficult to build a thorough meaning of service utilisation (Schreyo¨gg and Kliesch-Eberl, 2007). Zeithaml et al. (2009, p.4) depended on a straightforward and broadened definitive interpretation of any service that could characterise the same to incorporate “…all economic activities whose output is not a physical product or construction, is generally consumed at the time it is produced, and provides added value in forms (such as convenience, amusement, timeless, comfort, or health) that are essentially intangible concerns of its purchaser”(Zeithaml et al., 2009).Kasper et al. (2006) had demonstrated that there are some features which are common in numerous interpretations of services. These build their meaning of service provisioning and characterize that services are initially elusive and are perishable in a relatively rapid manner since the action of purchase happens as a major aspect of an intelligent procedure oriented towards ensuring the consumer loyalty, yet this collaboration does not generally prompt material ownership. It is maybe the NSD capacity of any business entity which shapes how and why firms can vary in their capacity to undertake NSD activities. Abilities are unpredictable sets of aptitudes and collected information that empower firms to arrange operational undertakings and make utilization of their resources to shape complex yet favourable circumstances. The NSD capacity of any particular business organisation exhibits the ability and perfection of excellence which it possesses including other factors which are associated with the emergent products and services. It is realized by time and investment of resources which lead to the formulation of implied and expressed knowledge about NSD and the processes which accompany the processes (Storey and Kahn, 2010).
2. Aims and objectives
Capabilities of marketing and product promotion can enable business organisations to detect and react to changes of the market, for example, to marketing moves of competing organisations, innovative development and contingency management, empower the firmsto better organise their organisational management processes to use the capacities and assets of ancillary organisations and processes for creation of values, encourage firmsto foresee and envision the prospective as well innate and exhibitive necessities.
These, thus, can provide assistance in development of the both innovative products or utilize existing productswith new highlights and ascribe to fulfilboth the requirements of current clients and new clients to guarantee the stability, survivability, and evasion of shocks from new entrants of the market rivalry in light of new advances and new offers.The researchexploration work intends to build a multifaceted comprehension of how market based product promotional abilities could be utilised in a cohesive manner to institutionalise NSD within the automobile business. In an according manner, the accompanying factors are the primary destinations of the present research function as have been specified beneath:
The concerned research process is reflective of the significance to build better understanding regarding the strategic processes of marketing which could be utilised for new service development (NSD). The research study strives towards the formulation of the perception regarding the mutual influence amongst the practices of definite marketing and the development and instating of NSD.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Capabilities
The job of advertising in empowering firms to accomplish and keep competitive advantage and at last superior and prevalent performance is one of the primary research inquests which are considered by the researchers of marketing strategy to provide credible answer to. The Resource-Based View (RBV) of the business organisation contends the superior and prevalent performance and feasible competitive advantage completely depend significantly upon the value, rarity, inimitability and non-substitutability (VRIN) of the endowments of the resources(Barney 1991).In any case, dynamic abilities (DC) theoretical hypothesis contends that basically having expansive supplies of VRIN assets could never be adequate to accomplish maintainable competitive advantage; rather, after some time, the capacities empower the proficient improvement and organization of VRIN assets which could provide assistance to a few business firms to perform superior than other organisations(Eisenhardt and Martin, 2000; Helfat et al., 2007; Teece, 2009).Abilities are intricate packs of aptitudes and information inserted in organisational procedures that change available internal and external resources and assets into important and valuable outputs(Day, 1994)(Day, 1994). Since abilities are primarily formulated after some time and could transformed into integral components of the hierarchical organisational procedures and schedules (Grant 1996), they are troublesome for market based competitors to monitor and emulate. These factors empower business firms which have important capacity to realise reasonable and preferred advantageous positions their market based business opponents.As limits are ordinarily made after some time and relegated to a completion process which gets embedded in definitive methods and schedules (Give 1996), they are troublesome for rivals to emulate and monitor, in this way this enables firms that have vital capacities to acknowledge functional favoured outlook over their foes(Grewal and Slotegraaf, 2007). The existing literature on marketing activities could highlight the suggestions that marketing and product promotional capacities are particularly significant (Shervani, and Fahey 1998)and are not to be imitated (Morgan et al., 2009) and non-substitutable in formulation of competitive advantages which could be sustained through superior performance demonstration on part of the companies under consideration (Krasnikov and Jayachandran 2008).
2.2 Marketing Capabilities
Capabilities of marketing couldattest to the ability factor of any organisation to utilize its accessible assets to comprehend and satisfy client needs in a manner which could be superior to its opponents (Day 1994). They are the blend of procedures that a firm uses to characterize, create and convey an incentive to its objective clients by consolidating, changing, and sending its accessible assets (Morgan and Slotegraaf, 2011).In the accompanying section, I will undertake the proper review of the literature on promoting marketing abilities from three points of view: (1) the grouping of marketing capacities; (2) the estimation of marketing abilities; and (3) the antecedents, moderators and consequences of marketing abilities.

2.2.1 Marketing Capabilities: Classification
Abilities to undertake proper marketing, for example, sensing the proper market conditions, linking with the customers and the clientele, useful abilities to organise product promotion have been connected to different positive hierarchical organisational outcomes (Mitrega et al., 2012). Such capacities can either be utilized to shape amarketing strategic methodology which would prompt predominant process operational execution or might be of strategic or operational value, along these lines adding to the value formation process. Keeping in mind the objective to help our proposition that promoting capacities for instantaneous and effective market based success achievement, it is necessary to provide the review of the key literature in this regard.In an investigative study which had been performed by (Nath et al., 2010) the objective was to decide the impact of useful capacities of any specific company (marketing and operative activities) and broadening approaches (product/ service and international diversification) on by and large budgetary and financial operational execution. The outcomes showed that marketing and promotional capacity is the central determinant for unrivalledbudgetary operations and furthermore, the realisation that market-driven firms are probably going to have much preferable business operations over an organisation concentrating totally on operational abilities (Nath et al., 2010). It is maybe the capacity of NSD application of any business organisation that shapesthe rationale of the firms regarding contrasting their capacity to authorize NSD oriented operations. Capacities could be considered to be groups of aptitudes and amassed information which empower firms to facilitate exercises and make utilization of their resources to shape complex and favourable circumstances. The NSD ability of any business organisation reflects the skillsand greatness as well as the peripheral capabilities at extensive service operations and developments. It is achieved by time and investment of resourcesin a formative manner to formulate implied and express knowledge based learning regarding NSD and the forms which accompany the same(Storey and Hull, 2010).As the thought of promoting capacities is still generally new to the marketing discipline (Morgan, 2012), researchin this context is primarily extremely fragmentary. Be that as it may, the literature on the marketing processes shows a few different ways to undertake the service and product promoting capacities. For instance, Day (1994) takes the market introduction viewpoint and characterizes capacities as outside-in, back to front and encompassing abilities and recognizes detection of marketing opportunities and client connecting as the most essential outside-in abilities for market driven organisations. Day (2011) expands his previous classification order by proposing three subsets of marketing abilities:(1) Static promoting capacities which incorporate particular/practical abilities and cross-functional capacities; (2) Dynamic market operational activity promoting capacities, for example, the capacity to reconfigure and enhance existing product and services advertising abilities; furthermore, (3) Flexible and adaptivemarketing capacities which manage careful market based learning processes through practical and logical experimentations and dynamic communications with network based operative factors. In an alternate methodology, Vorhies, Morgan, and Autry (2009) categorise the marketing and operational abilities into two classifications: specialized capabilities and architectural capabilities.Particular and specialised capacities allude to the practically engagedfocus of functionalities, procedures and schedulesrelated with that of the marketing mix, for example, evaluation of the pricing, advertising and management and marketing strategy administration, while architectural capabilities such asplanning of marketing strategy and operational abilityto manage procedures and schedules which could organize and facilitate the specific marketing abilities of the organisation and the related asset inputs. Undertaking the perspective of hierarchical capabilities, Vorhies, Orr, and Bush (2011) additionally expanded this differential structure of research by recognizing and distinguishingfist and second tier of marketing process capacities:The initial tier of client centred marketing abilities incorporate client relationship services administration and brand administration capacities; second-tier service promoting abilities incorporate advertising explorative and investigative abilities that either create or enhance first-arrange advertising capacities. Morgan (2012) has provided a more broad scientific categorization by characterizing marketing abilities not just by their ascending order based nature, yet additionally by the diverse levels at which they exist: individual, group, organization and inter-organizational, in this manner giving the most far reaching structure to comprehend different service and product promoting capacities so far clarified in the writing.
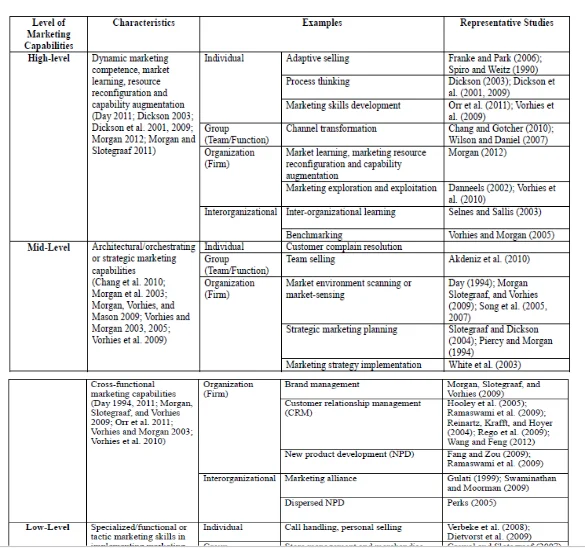
Table 2 shows that prior research has mostly focused on low-level marketing capabilities characterized by firms’ basic, specialized or functional marketing processes in implementing marketing mix (4Ps) activities such as pricing and marketing communications. Research on individual-level specialized marketing capabilities has mainly focused on employees’ skills in the sales and customer service area (Verbeke et al. 2008). Relatively little attention has been paid to group-level marketing capabilities in the extant literature. Only recently have marketing scholars begun to pay attention to mid-level (mainly firm-level) marketing capabilities characterized by architectural/orchestrating and cross-functional capabilities (Vorhies, Morgan, and Autry 2009) such as marketing strategy planning and marketing strategy implementation, brand management, customer relationship management (CRM) and new product development capabilities. But research on the mid-level marketing capabilities is still relatively scant and thus there are numerous calls in the literature for more research in this area (Morgan and Slotegraaf2011). Not very many research scholars have concentrated on investigating larger amount, dynamic promoting skills related with reconfiguring assets and upgrading current showcasing capacities. Precedents of such larger amount promoting capacities are advertise learning abilities (Morgan 2012), the market process controlling abilities as well as undertaking of proper exploitation processes, between hierarchical learning capacities, and benchmarking, and also some individual-level higher-arrange abilities like versatile offering and process thinking aptitudes. Such larger amount promoting capacities are hard to watch, however are generally thought to be a definitive wellspring of upper hand in unique situations (Danneels, 2002) as they enable firms to refresh their lower-arrange showcasing abilities ceaselessly, and subsequently defeat way conditions and maintain a strategic distance from "competency traps" (Danneels 2002; Walk 1991). In this study process investigation undertaking, the attention would be on market projection based resource building capacities and market-based resource utilizing abilities. The reason is that the writing proposes that building long haul advertise based resources and creating trade streams out the here and now are required for firms to appreciate prevalent execution (Ambler and Roberts, 2006). Market-based resource building capacity alludes to an association's capacity to utilize its accessible assets to construct market value projection based resources (e.g., mark administration ability, client relationship administration ability and store network administration ability) (Morgan, Slotegraaf, and Vorhies, 2009). Market-based resource utilizing capacity alludes to a company's capacity to utilize accessible assets to create here and now money streams from its market-based resources.
Looking for further insights on Enhancing Service Quality through Self Machines? Click here.
2.3 The concept of New Service Development
The launch of the Journal of Product Innovation Management (JPIM) in 1984 resulted in a dramatic growth in the study of new service development (NSD). Over the 27-year period since then, the study of NPD has evolved and increased in sophistication in terms of categories, models, and techniques. In fact, signs of a maturing discipline have been uncovered (Page and Schirr, 2008). Johne and Storey (1998, p.184) stated that “…the words new service development and new product development are often used interchangeably”. In fact, it is well known that service characteristics are different from physical products’ attributes. Intangibility, inseparability, heterogeneity, and perishability (Zeithaml et al., 1985) show how new services should be treated differently from new tangible products. Tatikonda and Zeithaml (2002) pointed out that the outputs of product and service and their development processes are different due to these four characteristics. For instance, while tangible goods are produced prior to consumption, services are mostly produced and consumed at the same time. The early articles on NSD focussed on success factors and innovation in the financial service sector.Nonetheless, based on an analysis of 27 years of research into NSD, Papastathopoulou and Hultink (2012) proposed that NSD needs to progress further by focusing on neglected aspects such as organizational issues, product/market fit factors, and service-dominant logic. Although researchershave realized the importance of service development in recent years, morestudies are required to build an integrated body of knowledge.
2.3.1 Typologies of new service
The extant literature proffers numerous different typologies of new “products”. A well-known new product classification, Booz’s et al. framework (1982), showed six categories of new tangible products based on two dimensions of newness: newness to the firm and newness to the market. Rooted in Booz’s et al. work, many research studies have proposed different classifications for new product innovativeness. While innovativeness from a product perspective is well established, only a few such categories can be found in the service literature. Lovelock and Wirtz (2001) identified seven new service categories ranging from simple style changes to major service innovations. Based on internal skills and market entry strategy, Kasper et al. (2006) described three different new services: new to the world, new to the market, and new to the organization. Zeithaml et al. (2009) devised six new service options running the scale from major or radical innovations to style changes. A number of studies have classified a hierarchy of new services categories focusing on the financial service sector. For example, Gadrey et al. (1995) proposed four different financial service categories: innovations in service products, architectural innovations, modifications of service products and innovations in processes and organization for existing services. Cooper and de Brentani (1991) offered three types of financial service innovation: synergy, newness to the firm, and innovativeness of service product. To provide empirical evidence, Avlonitis et al. (2001) explored different innovative types of services in financial companies. Their study revealed six distinct service innovativeness types, represented in the form of a continuum depending on the degree of innovativeness: new-to-the-market services, new-to-the-company services, new delivery processes, service modifications, service line extensions, and innovative service repositioning. An examination of new service categories indicates that the innovativeness classification of new services is slightly different from the types developed in new product research.
Continue your exploration of Historical Development of Enterprise Agility with our related content.
2.3.2New service development process
It has been discovered that a precise procedure for growing new administrations affects new administration and firm execution (de Brentani, 1991). However, just a couple of formal NSD models have been proposed by researchers (Alam, 2006). NSD process comprises of thought ideation, idea advancement and assessment, business investigation, benefit improvement and assessment, advertisement based market testing and commercialization. Arbors' work depends on the Booz-Allen (1982) procedure of NPD. Where Nooks (1989) contrasts is in his worry with a business technique or a long haul vital heading for the firm as a piece of the NSD procedure. While Nooks (1989) extended the NSD procedure to cover key advancement, Cowell (1988) wound up engrossed with operational stages. He expressed that NSD techniques ordinarily comprise of thought age, thought screening, idea advancement and testing, business examination, improvement, testing, and commercialization. He included screening as a stage of the NSD procedure. He focused on that there are no regular criteria for all associations. Indeed, Easingwood (1986) found that screening procedures can go from formal to casual methodology. Scheuing and Johnson (1989) outline the most extensive procedure for NSD utilizing a review of sixty-six budgetary administrations. Their work incorporates fifteen stages. The process focused on new administration structure and gave points of interest of the procedure. In spite of the fact that the NSD model's 15 phases are more extensive, Tatikonda and Zeithaml (2002) expressed that means are once in a while skipped or led at the same time. From an abnormal state perspective, they portrayed that the administration improvement process comprises of three full scale organizes: the front end, the back end and item presentation. They assembled vital situating exercises, thought age and idea advancement into the front end. The back end includes the picked benefit idea usage, and item acquaintance exercises relate with the actualized benefit for use by the clients. All the more as of late, Alam and Perry (2002) formulated 10 phases of NSD in light of the contextual analyses of 12 monetary administration business perspectives. They intended to distinguish key phases of the administration improvement process and attached them to a client contribution point of view. Regardless, their model does not cover the post-benefit dispatch survey arrange which helps assessing the accomplishment of new administration goals. Table 2 has provided the actual crossover effects of the past investigations and demonstrates a 9-exercises NSD process. These exercises educate the improvement of the surviving exploration examination.

2.3.3 New services: definitions
Administrations encompass an extensive variety of frequently exceptionally complex exercises, with the goal that it is to a great degree hard to develop a thorough meaning of administrations (Bryson and Daniels, 2007). Zeithaml et al. (2009, p.4) depended on a straightforward and extensive meaning of administrations that characterizes the process of incorporation of the elements of "… every financial action whose yield is definitely not a physical item or development, is for the most part expended at the time it is delivered, and gives included an incentive in frames, (for example, accommodation, delight, immortal, solace, or wellbeing) that are basically impalpable worries of its buyer" (Quinn et al., 1987 referred to in Zeithaml et al., 2009). Kasper et al. (2006, p.57) demonstrated that there aresome regular highlights in numerous meanings of administrations. They build their meaning of administrations, and characterize that administrations are initially immaterial and moderately rapidly short-lived exercises whose buy happens as a component of an intuitive procedure went for instigation of consumer loyalty, however this association does not generally prompt material ownership. Lovelock and Wirtz(2011, p.37) offered an exhaustive definition: "Administrations are financial exercises offered by one gathering to another. Frequently time-based, exhibitions achieve wanted outcomes to beneficiaries, objects, or different resources for which buyers have obligation. In return for cash, time, and exertion, benefit clients anticipate that incentive from access will products, work, proficient abilities, offices, systems, and framework; however they don't ordinarily take responsibility for of the physical components included" (Lovelock and Wirtz, 2011). The research process examination in existence could be considered to contain couple of formal meanings of NSD. New administration advancement is characterized in numerous terms, however a standout amongst the most exhaustive definitions is proposed by Van Ark et al. (2003) who guarantee that NSD is another or significantly changed administration idea, customer association channel, benefit conveyance framework or innovative idea that independently, yet probably in blend, prompts at least one renewed benefit works that are new to the firm and change the administration/products offered available. They additionally require fundamentally new innovative, human or hierarchical capacities with respect to the administration association. The meaning of NSD proposed by Van Ark et al. (2003) appears to cover just extreme advancement. As indicated by the NSD definitions clarified over, the typologies of new administration and the NSD procedure examined in the before area, this exploration characterizes NSD as: The general procedure of technique advancement, thought ideation and evaluation of the same processes, idea advancement and assessment, business examination, benefit improvement and assessment, testing, commercialisation, and post-dispatch assessment of new administrations of which the results are either incremental or radical administration developments offered either to customers and additionally to organizations.
2.3.4 NSD performance
New service performance has been consistently reported as a multidimensional construct (Cooper et al., 1994; De Brentani, 1991). Its successful measurement can be evaluated at the project or at the programme level. While the project level refers to individual new services, success at the programme level is determined based on performance over a period of time. Highly successful NSD development efforts produce multiple benefits (Menor and Roth, 2008) which can be divided in terms of financial and non-financial criteria. The financial performance dimension normally includes sales, market share, profitability (Cooper et al., 1994), growth targets and cost efficiency (Hsueh et al., 2010). Non-financial dimensions of service innovation performance generally consist of speed (e.g. the speed of the NSD process), service quality, effectiveness (e.g. the number of new service products developed annually), relationship enhancement (e.g. customer loyalty) and corporate reputation (Cooper et al., 1994). Less innovative firms use solely financial performance measurement, while truly innovative firms employ a number of softer internal dimensions (Storey and Kelly, 2001). Cooper et al. (1994) identified three performance dimensions: financial performance, relationship enhancement, and market development and obtained data on 173 new financial services. Financial performance aims to assess 1) the level of sales 2) market share, 3) total sales, 4) profitability objectives, 5) large market share, 6) high level of profitability and 7) long term performance. They also evaluated new service outcomes based on relationship enhancement in terms of the loyalty improvement of existing customers, positive impact on the company’s perceived image, increases in profitability of other products, and increased opportunities to introduce further new products. The last dimension is market development which consists of taking advantage of the opportunity to open up a new market to the company, supporting the company to change its image, and increasingsignificantly the number of new customers to the company. De Brentani (1991) provides an in-depth perspective of performance measurement. She surveyed the NSD of 115 Canadian companies in a broad range of business service industries. She asserted that there are four main determinants of new service performance: sales performance, competitive performance, cost performance, and other boosters. Afterwards, De Brentani (1991) proposed four new performance dimensions: proficiency in NSD, project synergy, market characteristics, and the nature of the new service provision. Later on, De Brentani and Cooper (1992) found five key factors to measure new financial services: product/market fit, quality of execution of launch/marketing activities, synergy, service expertise, and product advantage. De Brentani’s previous research using four key measurements shared similar elements with the five new financial service measurements. It showed that these researches aimed to measure new service performance and characterise new service projects in terms of the nature of the NSD process, the market, and the internal corporate NSD environment. Storey and Kelly (2001) investigated how service firms evaluate their NSD activities and proposed three measures of new service performance. Financial, customer and internal measures are employed to assess the performance at the individual new service level and at the programme level. Profit, sales, ROI, market share and costs are financial performance indicators employed at both levels. As with the financial measures, usage and sales growth are used to assess a new service at the project level only. To measure the customer dimension, customer satisfaction, new customers,market feedback, customer retention and competitiveness are employed to verify the success of new services. Lastly, internal measures of new service projects and programmes comprise future potential, efficiency, strategic fit and the development process. Contact staff feedback is added into internal measures at the project level, while success rate is added into the internal success dimension at the programme level. Johne and Storey (1998) argues that the performance of service development should be measured at two levels. First, there are performance measurement variables of service development involving financial measures, competitiveness measures, and quality measures. Second, there is a summary of measures of success as part of the development process in the form of criterion cost, effectiveness, and speed.New service performance has been consistently reported as a multidimensional construct (Cooper et al., 1994). The performance of service development, in this study, is measured at two levels: the overall performance and the process itself. There are four key indicators at the overall performance level. First of all, sales and market share or financial performance is applied to measure whether the outcomes exceed sales and market share objectives. For competitive performance, it focuses on the superior service performance to competitors. Next, other booster is the indicator used to measure whether or not the performance hasenhanced sales, customer use and the profitability of other services. The last indicator is cost performance which determines whether or not the firm can achieve cost efficiencies.There are three measures of success in the NSD process: criterion cost, effectiveness, and speed. Criterion cost refers to costs relating to developing new services, while effectiveness focuses on the number of developed new services and their degree of success. Finally, speed is the indicator used to evaluate how fast is the development time in terms of how long it takes from concept to service launch time.
3. Methodology
3.1. Research design
The configuration of the research process depends on the exploration inquiries and targets and in addition by being reliable to the examination rationality as recommended by Saunders et al. (2009). The examination is to utilize the subjective investigation with a specific end goal to demonstrate the significance of showcasing capacities with regards to NSD execution. For this reason, the pilot contextual analysis in the car business, for example, BMW has been chosen to inspect the connection between market based operational abilities and NSD related operational execution procedures. As has been indicated by this, the arrangement of unstructured inquiries have been assigned and circulated to the important respondents, for example, deal supervisors, overseeing executives and CEOs through semi-organized meeting. The motivation behind the pilot test is to refine the survey so that the respondents would not have to be in a position where they would have to confront any issue concerning the inquiries and to wipe out further issues in recording the information. Furthermore it causes the creator to check the dependability and legitimacy of the information to be gathered (Saunders et al. 2009). Pilot test guarantees that the gathered information will be useful in noting the investigative inquiry or research questions (Saunders et al. 2009). The quantity of individuals required to pilot test the survey relies upon inquire about inquiries, examine targets and size of research venture and for the most regarding the undertaking the survey of the students, the numerical value for a pilot test is 10 (Saunders et al. 2009). In this way the creator led the pilot test by circulating the survey questionnaire to 10 respondents in BMW. Moreover, the auxiliary information from the organization has been gathered and contrasted with the information recording document the respondents. This could provide assistance to the research process to have similar investigation which gives a rule to supervisors of the administration organizations n the BMW to analyze the most essential advertising rehearses that impact on NSD execution emphatically. For sure, this could be accomplished by the emotional judgment of the respondents and cross examination with auxiliary information, for example, organization report which improve the reliability based factors and authenticity of the research process based investigation. At long last, the philosophical presumption of the examination as for the exploration targets has been defended in the accompanying segments.
3. 2. Philosophy
3.2.1 Epistemological position
Social scientists have developed several paradigms which offer different ways of looking at human social life in order to understand social behaviour (Babbie, 2005). Philosophical issues are central to the view of research design which can affect the quality of the research (Easterby-Smith et al., 2002). The reason is that reseachers’ choice and particular use of methodology and methods are based on assumptions or on their theoretical perspective (Crotty, 1998). This suggests that a philosophical position informs the researcher about the techniques used to gather and analyse data, as well as the research strategies or the choice of research methods used to achieve research objectives.There are a large number of research techniques and methods. Each research method has its own philosophical assumption on how to conduct research. There are several philosophical traditions in social science research such as relativism, positivism, social construction, feminism, interpretive social science (Crotty, 1998; May, 2001; Easterby-Smith et al., 2002), yet positivism, interpretative social science, and critical social science represent fundamentally different viewpoints and alternative assumptions about social science research (Neuman, 2000). While positivism is the most widely used approach, critical social science is less commonly seen in academic work (Ibid, 2000). Each approach and the assumptions underpinning them are described in the following sections.
3.2.2 Positivism
The central notion of positivism is that the reality of the social world is external, with the assumption that knowledge should be measured through observation of this external reality (Easterby-Smith et al., 2002). According to the positivist perspective, meaning is already inherent in the objects under consideration, and this is independent of any consciousness of the objects (Crotty, 1998). This means that objects in the world previously have meaning; thus, people are required to discover the meaning by verifying knowledge grounded in empirical data. When applied in the research context, positivism aims to explain people’s behaviour in terms of cause and effect, as well as predict such behaviour (May, 2001). Moreover, data or facts should be observable and measurable by using some kind of instrument; hence, the researcher sometimes is required to reduce data to make it operational (Mats and Kaj, 2000). In addition, the researcher remains detached and neutral in order to conduct value-free research which finally leads to confirmation of data/facts through an empirical test (Neuman, 2000). Perceptual notions impact the plans of research and administration of the processes of management of different working conditions. The practical people contend that specialists should make the most productive utilization of the two ideal models in understanding social wonders (Creswell, 1994, p.176). Hence, to address examine questions, this examination laid on Creswell's model (1994) of consolidated plan, overwhelming less predominant outline. In the prevailing less overwhelming plan, the investigation exhibits a solitary predominant worldview with one little part of the general examination drawn from an elective worldview. He expressed that the writing and hypothesis in predominant plan would be utilized in a methodology reliable with the prevailing worldview. He alluded to Morse (1991) who expressed that task must be hypothetically determined by the quantitative strategy fusing a corresponding subjective part. Consequently, to accomplish the goals of this exploration, positivism underlies the examination strategies for this investigation. In positivism, the effect imparted by the research specialist is restricted in the procedures of theoretical construct arrangement, idea operationalisation and research configuration (Yates, 2004).This implies the analyst must be free of what he/she is considering. Positivist research centres around the examination of connections between different components (Israel, 2005). This examination means to look at the advertising abilities in NSD process. This fits the supposition of the causative rationale that is to recognize clarifications regarding the causes. The various implications which could be associated with that of the factor of Positivism, the progression of any research project is completely incumbent upon the theoretical constructs as well as the logical derivations of the conclusions in this regard. This leads to the generalisation of the research outcomes through the factor of deliberation regarding the probability, from a statistical standpoint of various situations and opportunities to emerge (Easterby-Smith et al., 2008). With the suggestions related with positivism, investigation procedural advances through theories and derivations could be achieved, while the outcomes can be summed up through likelihood The motivation behind positivism is "… to create speculations that can be tried and that will in this way enable clarifications of laws to be evaluated" (Bryman, 2001, p.12) or purported deductivism. Positivist research likewise centers around the creation of general articulations which hold crosswise over various settings (Yates, 2004) which can be estimated utilizing scientific verification. This exploration intends to clarify the causality of showcasing capacities and NSD by testing the RBV hypothesis. Additionally, it plans to utilize contextual analysis approach which will make it conceivable to propose suggestions. Thusly, this research process exploration could be accommodated within the positivist suppositions.
3.2 Research scope and unit of analysis
In the present study, the research scope is related to the context of NSD in the automotive industry. The BMW in the UK has been selected due to importance of marketing practices that enhance the NSD performance of the company in the recent turbulent business environment. The unit of analysis is mainly focused on the sales managers and directing managers of the company that deal with entire NSD process, new and existing customers.
3.3 Research strategy
Different from quantitative research, which seeks regularities and common properties at the event level, qualitative research studies social events and their causal mechanisms in order to reach their actual causes (Saunders et al. 2009). It investigates how generative mechanism works and describes the interaction between the powers that produce a social phenomenon (Danermark, et al., 2002). Although sampling is also needed in this type of research, Danermark et al. (2002) argued that sampling in qualitative research is strategic and the sample is very specific and purposeful not as big and representative as possible and it does not aim to have a statistically representative sample but a sample of typical member(s) in an endeavour to discover all, or as many as possible, of the properties that a typical member has. The subjective research approach receives distinctive ontological and epistemological positions. Right off the bat, subjective research embraces the interpretive epistemological introduction to pass judgment on what learning is and how to get this information and the reason for such an introduction is, to the point that the use of logical methodology for concentrate social wonders isn't fitting (Easterby-Smith et al., 2008). Subsequently, analysts need to get rich information to completely comprehend the social wonder through communication with particular individuals in the focused on populace and afterward comprehend and decipher the got information inside their social constitution. This exploration approach likewise embraces the useful ontological introduction through contextual analysis and world class meet where the truth of a wonder is the after effects of social development between the collaborating social factorial characters (Danermark et al., 2002). There is now an increasing awareness that using both quantitative and qualitative methods of research may have a contribution to make to a research project (Wood and Welch, 2010). To address the research questions described in introduction, this research makes use of cases study approach, a qualitative research method which help to develop questions and hypotheses for further inquiry (Yin, 1993). Data from the case study which is the automotive industry was analysed to justify and complement the theoretical propositions.
3.4 Data collection method
3.4.1 Pilot case study
The process of undertaking Pilot study regarding the contextual case based investigation, could be considered as a system of utilisation of strategic approaches for the purpose of better formulation of the scope of the study. Apart from this, the Pilot study is also meant to be utilised as a specific instrument for the purpose of collection and utilisation of information regarding the formulation of research understanding concerning the operational dynamics which could permeate the topic under consideration (Eisenhardt&Graebner, 2007). This is considered as a research inquiry process, which is empirical in nature and is oriented towards the investigation of any phenomenon which could be concurrent in terms of emergence. The utilisation of multiplicity of sources is significantly necessary in this regard to accumulate sufficient measure of evidence (Yin, 2003). In this context, it could be highlighted that the most significant yet salient aspect on the case study based approach is centered on the analytical unit. This contextual unit could be considered to be any business organisation, any individual, specific industry or even any particular project(Rayan et al., 2002).. This could be performed through the utilisation of singular or multiplicity of cases. It incorporates accumulation of information methods such as archived records of previous researches, meetings and interview sessions, information evaluation and survey based questionnaire formulation. This enables the researchers to gather extensive and effective information reservoirs with profound relevance of knowledge about the topic which could be under the scope of analysis (Yin, 2003). Contextual cases based investigative study can be conducted for various purposes and can be utilized in exploratory research examinations, it can construe the proper delineation and could be utilized in an effective manner for building the perceptual hypotheses to furthermore assess the developed recommendations and to properly investigate the theoretical speculations (Eisenhardt&Graebner, 2007). Contextual cases based investigative study is viewed as a great research approach because of the application of the concept of triangulation that implies taking into account the various existing alternate points of perceptions and utilizing differentiated data and information accumulation techniques from various literary and other documented as well as primary sources so that this could contribute in the constitution of greater depth and specific value of the accumulated research information (Yin, 1994). In spite of this, it has a primary disadvantage in correlation with quantitative research process strategies which engender the theoretical research process into over generalisation which could supersede the context of the considered cases for research purposes.
3.5 Reliability and validity
The factors of reliability and maintenance of specific quality allude to the measure to which the utilisation of the information and data research and accumulation systems or strategic examination of the research could lead to the specific and intended outcomes (Saunders et al. 2009). The concern in such cases are mostly oriented towards the considerations of reliability which takes into account the degree to which the findings and conclusions of the research precisely address the factors of what could be the actualities regarding the research process and the associated circumstances, and furthermore, the conclusive findings are integrally related to the actualities of the research findings and not merely perceptual notions which could not be verified through definite or exploratory research tasks (Saunders et al. 2009). Regarding the actual aspects concerning such studies, the principle issue which could emerge for the approaches related to cases study based research could be identified as the challenges of utilisation of different ranges of research choices for gathering of Qualitative information, for example, through the utilisation of semi-structured interviews, through the interviews which are generally not structured at all, important and archival documents derived from the companies under consideration and participation of the research respondents in an active manner in the overall research process and observation of such processes from an academic standpoint. Likewise, every one of these strategies is connected to avail the most maximised and thoroughly examinable and verifiable data through various styles of inquiries. The contextual analysis and case study based pioneering approach is understood to be considered as one of the efficient and productive methodical techniques which could be applied for the purpose of accumulation of Qualitative information. Thus, the corresponding research project is oriented towards the utilisation of all of the available strategic methods of research which could enable the Researcher to imbibe the study with the classical benefits of research values such as the validation process success achievement, maintaining the factor of reliability and ultimately conform to the generalisation prospects which could lead the study towards the necessary and intended outcome. The utilisation of the semi-structured methods of interviews would be a central aspect to this research and the associated questions would be provided to the participants of the company under consideration through electronic mail. In this regard, the personnel of significance who could be taken under consideration could be acknowledged to be the Chief Executive Officer, the Deputy Chief Executive Officer, the General Manager and other personnel who could be selected on the basis of their seniorities and who could be employed for a certain measure of time by the company under consideration in this research project. The various deliberations in this regard are indicative of the structural format through which the selection of research respondents and the data collection and analysis method pertaining to the research process could be performed. The included factors would be the case study based initial tests through the later structure of the partially developed formulations of the interviews could be determined and the primary data sources would be the research respondents as well as the information from the market segments where the company under consideration could be operating (Ellonen et al., 2009). The proper recommendations regarding the gathering of more relevant and conclusive research data could be envisaged through the evaluation of various secondary sources of research data such as the statistical records and reports and updates published by the company under consideration on a annual basis and through the various sources of data derived from the local and regional as well as international press such as articles published in the leading and trustworthy newspapers. These data would be effective in reinforcement of the case study based conclusion derivation since a correlation and corroboration of data and information could be undertaken from the perspectives of both the primary as well as the secondary data which could supplement the research information which could evident in the transcripts of the research questionnaire based interviews(Adam & Healy, 2000). This could as well contribute to the formulation of generalisation which is primarily constricted on behalf of the fact that the generalisation prospects could not be undertaken from a limited numbers of case study based analysis which is available in this project undertaking. The utilisation of the electronic mail base questionnaire and methodical interviews could yield greater benefits in this regard.
3.6 Unstructured questions
The following table describe the main research questions which are based on the objectives of the study. The research questions have been designated and rolled out to the relevant respondents in the BMW Company in the UK.
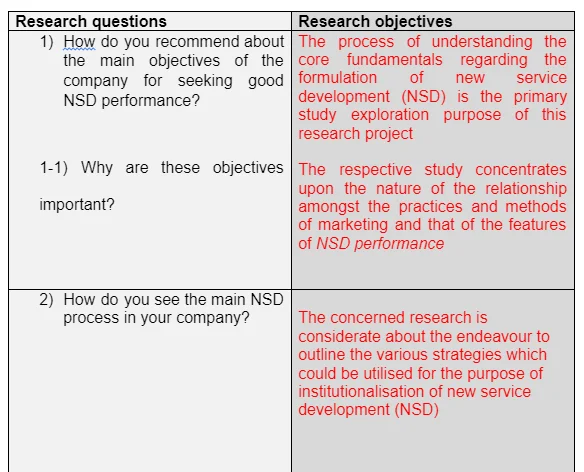
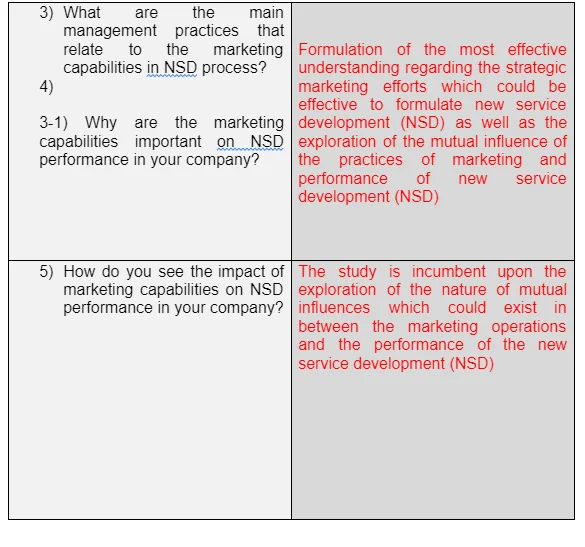
4. Results and discussions
In the concurrent times, the company of BMW could be considered to be in a position which could fetch the coveted overall affirmation as the leading sports vehicle manufacturing organisation with considerable brand market value. The perceptual image of the company within the customer base is an extraordinary one. The company is considered to be in a niche of itself where it could provide an effective amalgamation of productive work environment and efficacious structure of management and operations. Organisational vision could be considerately perceived to be a psychological perceptual aspect which permeates the general consciousness in individuals and in organisations it provides the most illustrative objective background to the existing work scenario management structure. The business environments of both internal as well as the external measures are responsible for the formulation of organisational vision. The declaration of the statement of vision by BMW could be subjected to simplification methods which could be redundant and yet, the rationale could be readily comprehended in this regard. The actual manner of the vision statement could be comprehended as the formulation of uniqueness through utilisation of various factors including the management of diversity of operations as well as resources and formulation of better leadership capabilities through risk management. The vision statement could as well be an indication of the deliberations of working conditionalities as well as the operative philosophies associated with this business organisation. BMW places stock in offering exceptional things embedded with premium quality obliging the necessities and requirements of a specific market portion of clients and their inclinations. Considerable upgrades have taken place at the business association of BMW regarding the product offerings which the company could offer and each such product offering includes the investment of specific resource and novelty development procedure derived results which could set the organisation apart with impeccable product value and could as well enhance the public perception towards the same. The structure of management and organisational control which is prevalent at the company of BMW concentrates upon the particularities of work process efforts which could be utilised for the purpose of quality and competitive effect enhancement by exploring the entire range of different avenues of success achievement. This process coincides with the other developments at the manufacturing and engineering sector of the business process development through the consideration of the newly developed technological novelties as well as the time tested methods through which the company under consideration could plan for both the shorter and longer terms for the purpose of profit maximisation through value addition to the products it offers. By and large, the vision proclamation of BMW is one of a kind and down to earth that makes a significant distinctive reasonable picture sponsored by service administration and broadening of operations. Thus, it could be better understood that BMW could be considered to be, arguably, the most valuable as well as the leading sports and utility vehicle manufacturer on the current global scenario. In this context, it could be considered that the specific highlighting of this particular statement of purpose may propose the objective of the business organisation achieve the coveted position of being the best automobile vehicle manufacturing organisation in the automobile engineering and manufacturing sector of the world. Nonetheless, the business organization is at the pinnacle of the list of companies which could offer greater innovation based product and service inventory to finally become the most effective and numero uno automotive vehicle manufacturing organization as far reach, acknowledgement of the acceptance and revenue generation.
4.1 Values and Objectives in BMW
The adequacy of the items and administrations related with the BMW could understood to be the outcome of the advancement of differential items which this organization has possessed the capacity to produce over the time as it has for the longest time been itching to beat the closest market equals in the current and the imminent market situations through perception of the interior and also the outer business conditions in presence and under forthcoming improvement. The goals of BMW incorporate
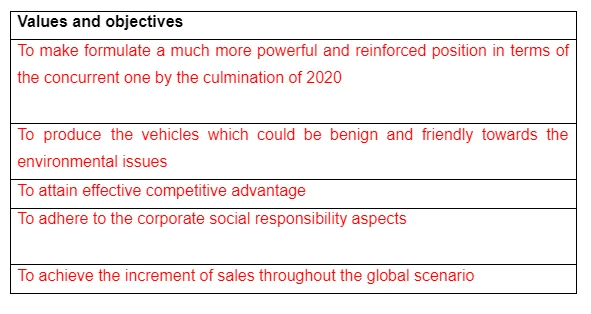
Up to the year of 2020, the BMW Group has outlined the overall intent to fortify the current position inside the market of the global automobile products through increment of the sales operations upto the volume of at least two million vehicles on a yearly basis. Apart from this, in addition to the organisational operational effort towards the ensuring of the growth of the existing business prospects, the BMW Group has also specified the intent to invest profusely in the various futuristic technologies which could involve the concepts of vehicles of higher sophistication and ground breaking technologies such as automatic driving and revolutionary suspension introduction mechanisms.
4.2 Marketing capabilities in BMW
Communication Structure
The related and specific structure of organisational communication which is observed at BMW is deliberate as well as centered towards operational efficacy, for the purpose of development of the most effective data sharing and communication process. BMW has been the organisation which has considerately put forth wide assortments of technical novelties that are required to ensure that every form of data management and communication streamlining could be associated with within the overall working architecture of such a system. The structural communication of the company of BMW is particularly inclusive of the newspapers, internet, intranet, video and audio journals. Apart from this, the business organisation undertakes particular efforts to provide adequate means of data and information to the various customers through audio-visual presentations and through image sharing. The social mobility which could be exhibited by the customers of BMW has been at the core of attention of BMW for a long time regarding the luxurious vehicle sales market. The effectiveness of the communication is particularly specific since this could perform the responsibility of formulation of the most effective brand image from the company under consideration and could as well provide the company with the reputation which could be similar to that of a reliable and value oriented service condition.
Identity and Vision
Definitely, BMW is one of the most noteworthy and advantageously positioned automobile manufacturing business organisations, offering wide varieties of automobiles to clients in an international perspective. The personality of BMW as a superior automobile producer that could provide the most effective and extravagant products of the automobile market, works alongside an interest of genuineness and quality which works effectively to convince a large number of clients throughout the entire global context. This character has compelled the relationship to develop a broad and sensible vision that turns around uniqueness through arranged assortment and activity. The character of a particular relationship in the market and among the customers helps a significant measure in making a motivating force in arranging of missions, vision and targets. The identity is made through sheer quality and validity and that happens over some stretch of time through wide assortments of segments in the constrained and furthermore over the broadened plan. BMW constantly drives itself to keep up the brand character based identity recognition that it has earned during the time by offering new and innovative items to its devoted and potential customers on a worldwide level close by keeping a tab on the vision in the shorter and in addition in the more extended terms.

Sustainability
The supportability and additionally practicality report of BMW gives the best possible enlightening information on how the affiliation expect ecological and social commitments close by relating the same with the achievement accomplishment of the organization both in the shorter and longer spans. The maintainability reports of BMW incorporate esteem and trust and fuse society and natural conditions in a thorough way. The manageability report of BMW reliably offers straightforwardness and game plans which make it one of the extraordinarily regarded and pined for car fabricating associations all through the world. As per the Dow Jones Sustainability Indexes, which takes into consideration the 'monetary, ecological and social performance' of 2,500 organizations, BMW is the best performing association out of car items and this has made BMW to be highlighted in the majority of the six diverse List Documents since the time of 1999 as an exceptional association. Each recommendation today is assessed against the corporate target of supportability and reasonability. At the most important organization level, BMW set up a Maintainability Board in 2009. This board, which incorporates the specific faculty of the company administration, chooses the imperative game plan for sensibility issues. This unit undertakes discussion twice a year to outline the strategies and activities proposed at the operational level. According to BMW Gathering, the goal is "to make manageability a fundamental piece of the whole esteem chain and its hidden procedures to make an additional incentive for the organization, the earth and society." BMW is a "Super Division Pioneer" because of its work with eco-friendly advancement, for instance, its class-driving effective elements innovation, elective vehicle ideas and green reusing practices both in the vehicles and in the assembling techniques. BMW basically assumes that reasonable convenience should reinforce individual fulfilment and monetary change while, meanwhile, constraining any potential mischief to nature including that of the curtailment of emissions of Carbon dioxide.
Crisis and Risk Communication
All of the business concerns have to encounter crisis in the shorter and furthermore over the more drawn out timeframe that impact the business association under thought. It winds up being crucial to manage the emergency which could be strongly close by being set up to direct them. BMW's emergency and hazard open correspondence has helped the association in the past in leaving the over the top circumstances in a feasible and similarly more secure process in view of their informative correspondence sufficiency measure that was useful, instructive and coordinate. The emergencies and hazards are studied at standard between times in BMW utilizing effective and practical systems could involve the following
Assessment of the risks and crisis points on a regularised basis The formulation of the models of actions regarding the contingencies and crisis situations The constitution of a department specifically trained for the purpose of management of crisis Provisioning of such training of crisis management to each of the departments Management of proper transparency regarding the handling of crisis situations Maintenance of the public image and governance based reputations
BMW could be understood to be in the position which imbues the impression of being the leading organisation in terms of quality throughout world. The business related perception of the BMW as a standout amongst the most amazing and most desired business associations and product offerings as well as providing the most qualitative working environment is regarded to be a significant quality and a great degree of respect is accorded to it all through the world. In any case, this perceptual picture is correspondingly reinforced by the social organization that has offered an edge to the relationship close by making useful character in the market bolstered by the undertakings and exercises which are embraced to persuade the overall population to make a prevalent subjective future through the offering of extraordinary and equal chances to countless people everywhere throughout the world. Exactly when BMW placed assets into another plant at Hams Halls in the West Midlands, the association was standing up to troublesome issues in enlisting right people for the right movement. There was absence of capable work that compelled BMW to compose activities to define the modernisation procedure of the limited schools by offering critical information sources and getting ready crucial and viable automated equipment to help the assembling tasks. Close by that, BMW has in like manner thought of Car Institute that concentrates upon the decrease of the imperatives related with that of the deficiencies of the workforce faculty who could be adequately gifted in regards to the whole operational points of view of the car fabricating industry.
External Communications
Both the internal as well as the external process of communication assumes a critical responsibility in selecting the ultimate outcomes regarding the efforts of any business entity as far as reception and sending of data could be concerned throughout the entire global scenario. The processes of internal as well as the external communication instruments are the most significant elements on which the company of BMW deliberately operates. In this context, the influence of the external communication operational process is of immense significance in terms of the maintenance of the proper measure of information exchange with the global scenario which also involves the consumers and the competitive elements. The processes of electronic commerce as well as electronic business methods could be considered to be the elements which could enhance the necessary communication with those of the other business organisations as well as with those of the customers and the consumers in an effective manner. The capability of the BMW in maintaining the necessary presence through information sharing with the application of both Internet and Intranet could be outlined through the existence of approximately 58 different regional Web based applications throughout the 30 national perspectives which could provide the necessary backdrop through which better information sharing could be effectively undertaken. The unit for global operations which is located at Munich is responsible for the maintenance and control of the entire range of websites. Another factor could be outlined with the maintenance of team which is comprised by approximately 1000 authors who are also extremely dedicated and this dedication is reflected through the consistent updating of the current affairs regarding the operations undertaken by the company of BMW. Apart from this, the company of BMW as well undertakes the utilisation of various other communicative instruments such as advertisements, journals and other specific publications pertaining to the delineations of the automotive industry as well as the regularised automobile exhibitions through which the company could maintain effective communication with the entire world. Enhancement of the communication prospects throughout the entire world both in the short and longer time periods could be understood to be a critical factor regarding the entire operational undertakings observed by the business organisation under consideration. The element of external communicative correspondence of BMW might be named also organized, cognizant and brought together as a result of the manner in which data is controlled by the global operational unit. The company, nonetheless, has extensive channels of communication which are comprehensively controlled and utilised from a single point based approach in a logical manner in terms of the effective transparency as well as the avoidance of the problematic issues regarding the filtration based complications which could affect the circulation of the overall information within the organisational realm of the company under consideration.
Stakeholders
The response of the stakeholders is good enough as far as acquisition of relevant and straightforward data utilizing innovation in a proficient and powerful way. All the important data is passed to the providers, clients and investors utilizing internet, intranet, diaries, yearly gatherings and press. The general methodology of BMW in being straightforward with the partners so as to formulate positive perceptions on behalf of the company.
4.3 The relationship between marketing capabilities and NSD performance
The capability of the any business organisation concerning the NSD abilities could be considered to be the excellence as well as the proficiency through which the new services could be consistently developed. The NSD capacities are indicative of the development of greater effective information, knowledge as well as expertise within the field of operations including the differential sill sets, various assets which could be complementary to each other and the improvement of institutionalised routines concerning NSD(Barney, 1991). However, the dearth of any effective expertise regarding the utilisation of procedural management skills to undertake NSD operations could be identified to be one of the primary constraints to utilisation of innovation (Kelly and Storey, 2000). Execution is thus necessary to be accelerated and expedited through the utilisation of operational expertise and experiences gained from such operations, reduction of costs of development and decrease of all of the mistakes and ultimately to develop the solutions which could be superior in nature(Kyriakopoulos and de Ruyter, 2004; Montoya-Weiss and Calantone, 1994). The proper possession of NSD capability could enhance the efficacy as well as capability index of any business entity and could as well assist in the undertaking of innovation management activities so that both quality and quantity of NSD could be multiplied. The research within the BMW organisation concerning the application of NSD had brought forth multiplicity of factors with strategic importance regarding the impact of NSD on the performance level of the automotive industrial operations including those of the BMW. These outcomes have contributed to the development of the primary and underdeveloped research literature which have been developed on the applications of NSD and have been utilised for the purpose of providing effective and empirical evidence concerning the practicality of NSD as well Hauser et al., 2006). The significant strategic elements and factors which could be identified as the core components of success for NSD were mostly left unrecognised by the previously conducted research process. Several of the strategic and critical factors are highlighted and underlined through the study regarding the capabilities of marketing which could be outcomes of the managerial convictions regarding the efficacies and elements of purpose regarding the driving components of the NSD performance matrix at the organisational working scenario of BMW. Then adoption of a strategy to undertake key development of the services has been considered and analysed from multiplicity of standpoints.Goldstein et al. (2002) asserted that the service administration based conceptual idea could introduce key strategic purpose into the planning and designing of the services. Thisresearch paper contends that the "missing connection" in research process of NSD could be considered to be the strategy of service development. The context of business in the existing service spectrum and product offerings could encompass the utilisation of such a strategic element which could include the utilisation of the value which could be under utilisation of the contextual element of the customers, the resources which could be accessed internally by the organisation under consideration as well as the internal capabilities which could be brought forth by the service system. These could all be augmented through the application of the projection of the company image as well as the entire strategic spectrum of the business process of the organisation under consideration (Johne and Storey, 1998). The observations could as well lead to the realisation that the resources and the skills and expertise which are necessary for the development of new services as well as the delivery of such systems concerning the services in existence could be accommodated within the spectrum of assets, offerings and resources of the business organisation under consideration. This could as well be effective from the perspective of the effectiveness with which the new service offering could provide the necessary assistance to fulfil the requirements of customers through formulation of value of products and services which could be effectively perceived by all of the clientele. The outcomes of the evaluation fo the secondary data collection and evaluation concerning the company under consideration are reflective of the significance of the co-creation of customers which is mostly differed from the perspective of the managerial personnel regarding their particular viewpoints.(Edvardsson et al., 2013).The importance of NSD procedural elements could be considered from the various components which are integral to the entire process. These involve the collection of information regarding the customers from the customers themselves, the evaluation of the information which could be accumulated, the development of the integration and utilisation of divergent and often incoherent data structures (Melton and Hartline, 2010). The most significant contribution, in this context, could be understood to be that of the interaction which could be identified to take place in between the utilisation of different teams for the purpose of development of operations and that of the customer co-creation. However, previous researches often ignored the fact that the utilisation of an amalgamation of these two practices is extremely significant concerning the performance matrix development of NSD and often had stressed upon the individual importance of the customer co-creation and the integrated teams for development.Lee and Chen (2009) had discovered in their study of the Information Technology based firms operating at Taiwan, that the existence of positive correlation could be an actually observable fact regarding the project performance extents concerning the teams which are meant to contribute in the integrated development plans. The corresponding study is reflective of the suggestion that it is necessary to progress further than the integrated development purpose based teams and this could be achieved through the utilisation of the knowledge and abilities of various external experts as well as through the process of integration of customers.Melton and Hartline (2010) had brought forth the suggestion that both the employees who operate at the frontline of sales and operations and the customers are to be integrated within the development based team framework. However, no previous test has outlined the impact of such integration on the overall performance scenario of NSD. Thus, it could be understood that NSD performance development could be ensured through the facilitation of sharing as well as transfer of information and knowledge amongst working team members and through better improvement of the organisational learning propositions which could be more effectively concentrated upon the entirety of the existing customer preference scenario.. The concentration of the efforts of project managers on the development of team based operational management and skills could be a beneficial proposition as per the study discourse. This could spell out the strategic processes of interaction between the execution of NSD and those of the customers.Accordingly, the administration of strategic service development and advancement of procedures and a formalized improvement mechanism ofo development of services should empower and secure comprehensive learning and the combination of various abilities and client information in the correct phase of the service administration improvement process could be effective. The effective administration of this test will spare time, effort and financial resources(Melton and Hartline, 2010). The recognized impact of the interactions could be understood to be a key research element concerning the learning of application processes of NSD, since it can clarify why the impact of client co-creation on NSD frequently does not achieve the maximum efficacy which could be ascertained through the research investigations(Edvsrdsoon et al., 2013). Previous researches have outlined that the quantity of products which could be launched into the market add to the existing value of any business organisation (Pauwels et al., 2004). Anyway Barczak et al. (2009) found no distinction in the quantity of new product items marketed between dominant organizations and less fruitful companies, recommending that the best are not being effective by sheer quantities of product launchesand this does not ensure the capacity of any company to be effective competitively.In this manner, it is both the quantity of new service administration processes and the relative accomplishment of those service administration processeswhich direct the budgetary commitment NSD makes to the firm. This work makes various imperative commitments to the base of the hypothesis supporting NSD.The primary commitment as well as contribution in this context could be understood to be the introduction of an unpredictable yet intricate model of service administration development which could delineate the impacts of various resources which could be utilised for operational purposesregarding the particular dynamics of NSD operational performance.This research investigation works in reverse aggregation regarding the NSD process performance enhancement responsibility execution into the quantity of new service administrations which could be built up, the rate of achievement and success and the budgetary commitment of NSD to the general operational process, each requiring diverse operational assets. Along these lines the researches which have been completed in the past could onlyprovide inadequate clarification regarding the catalysts of the NSD procedural activities.An entrepreneurial culture drives the quantity of new service administrations which could be developed. In an according manner a culture which could emphasise upon learning, could, drive the rate of success. The NSD capacity index which could be in existence could assume an imperative job in supporting both these parts of NSD functional operational execution. It is, however, important to note that the key aspect that drives the financial commitments of NSD is this capability extent. Contrasted with reactors each of the three factors and orientations could demonstrate the operational execution processes could benefitand the prospector is the also integral to the achievement of such success.A secondary contribution based commitment could be considered to be the observation that the quantity of new services administrations consummately and detrimentally influences the achievement rate of new service administrations. This is the first occasion that this effect has been confirmed. One purpose behind this can almost certainly be found in speculations of organisational slack(Voss et al., 2008). The development of greater and more noteworthy new services administrations is a process of intense consumption of assets which could only leavefewer assets for their viable commercialisation. A second reason can be found in the imperfection characteristicsof entrepreneurial orientations (Hughes et al., 2007). Entrepreneurial work processorientation can self-strengthen a culture of identification of opportunities in a greater manner, original ideation and heightened risk awareness as well as management of riskcan prompt higher quantities of disappointments. This proposes that services administration might be more viable in dealing with their NSD operations through the earlier selection of their arrangement of priorities of success in light of their organisational conditions.The concerned study examination demonstrates the manner in which the process of conceptualisation of NSD operational execution could be provided which could neglect to represent the various different measurements which are primarily defective. We found no immediate impact from culture or NSD ability on the monetary commitment made by NSD to the overall performance scenario of any business organisation.The third commitment at this point could be contended as the revelation that NSD capacity could direct as well as moderate the mutual influences amongstthe cultures and the performance procedureswhich could provide the exactitudes of the various problems of rigidity. Past research undertakings have suggested that current information could assist in the formulation of theground-breaking abilities which may lessen advancement because of the issues related to the rigidity of the processes (Leonard-Barton, 1992; Subramaniam and Youndt, 2005). The absence of an immediate connection between NSD ability and commitment might be a direct outcome of this issue. This research examination demonstrates that the issues pertaining to the procedural rigidity are significantly more complex than what could be expected at the first glance. In the first place, NSD ability decidedly directs the mutual influence between entrepreneurial culture and the quantity of new services administrations which could be formulated through proper development. Subsequently, a synergistic relationship exists between the business operational elements of the companies and its NSD ability with the objective that together they could contribute in the increment of the quantity of administrations which couldl be produced as well.To this effect, there is considerable enlargement and expansion of the innovation based efforts of the organisation under consideration. Then again, NSD capacity adversely directs the mutual influences between the learning culture and the achievement rate of NSD. It is this relationship that starts to influence the core rigidity based issues in this context. At considerably constricted measure of abilities, learning could greatly influence success achievement. Anyway the advantage from learning is decreased as the information and mastery of the firm could experience greater change. The extensive capacities, which could be in existence could characterize how people working within the business organisations could perceivethe NSD procedure pertaining the different interpretations which are intended to be utilised in the process which could be performed. Knowledge produced by means of learning might be stifled by previous experiences. The development of innovation efforts of the firm at that point turns out to be more unbending to this past assortment of abilities as the NSD capacity is strengthened and left underdeveloped. These discoveries indicate capacities can enlarge and undermine hierarchical activities adding value to the convenient commitment to the collection of learning on how operational assets could be developed (Madhavaram and Hunt, 2008).This could be considered to be a final element which could contribute to the understanding formulation regarding the strategic orientations and conditions which exist within the organisations from personalised perspectives. The available evidence could suggest that prospectors could perform better with an entrepreneurial culture and Analysers could do the same through a learning society. Alternately a misaligned culture can harm performance execution. For instance an entrepreneurial atmosphere concentrating on investigating new chances, undertaking risk fraught propositions could producecomprehensively misaligned orientations with defensive, reactive or even analysis basedapproaches. Without the maintenance of the effective focus, entrepreneurial endeavours are diminished without receiving any benefit of the performance based operations. This has critical ramifications for administrators. If the situations could develop the proposition that senior administration personnel see the requirement for a creative technique, for aggressive or market based rationale the performance of which could be incumbent upon the entrepreneurial approaches and the association does not have an entrepreneurial culture, then, the administration has a predicament.Does it press ahead and denigrate into performance of poor stature or does it overlook the key objective? It is positively less demanding to pick a less creative methodology than to change culture. Also, the existing work culture may abrogate the enunciated strategy based orientations, which could dissolve management administrative designs. It might be desirable over utilisation of a more moderate technique, even to the detriment of letting opportunities go by, while contributing time and effort towards steady alteration of the organisational culture. The right vital introduction additionally fortifies the impact of NSD ability on the work process execution. A high NSD ability empowered set of Prospectors could assist in thegrowthof considerably greater measure of products and services altogether.At low levels of ability and capacity developmentwithin the process of creative new administrations being produced by Prospectors may keep running into inconvenience and deferrals, consequently constraining the limit with regards to assistance provisioning to NSD. A NSD capacity additionally benefits protectors. A cautious introduction concentrated on securing existing advantages can expand on existing capacities also. We expected that analysers would profit by a NSD ability to help their profit earning rate. Anyway the other competing firms benefitted from this advantage. Analysers have the most elevated success achievement rate, despite the fact that the distinctions are not critical. It appears that expanding a success ratet past a specific point might be precarious in nature.It is conceivable that as progress rates rise at that point desires of the company could likewise rise in this way constraining the expansion in the success achievement rate (i.e. NSD based projectswhich in the past would have been viewed as being fruitful may now be seen as peripheral, best case scenario and even as disappointments). How supervisors characterize achievement and what impacts this definition is a completely another process of contemplation. Anyway it remains that methodology must be planned in light of the understanding of existing conditions of the organisations. Research findings propose distinctive pathways to NSD. It is clear that not one of the cultures is better than the as the two cultures in this regard work in various ways.Any entrepreneurial culture which could be oriented towards a prospector orientated approach could as well drive the quantity of new service processes administrations which could be developed and created and henceforth the financial contribution related commitment of NSD to general performance management. Regardless, the quantity of new services administrations compels the success achievement rate to positively expand. Along these lines there is a second avenue to NSD-driven growth development. This is through a higher success achievement rate which could be driven by an analyser orientation based approach combined with a learning society. Which way firms ought to operate relies upon existing capacities. One may guess a transformative sequential grouping of processes as firms develop and change their aggressive surroundings. At low levels of NSD ability a culture arranged towards learning might be ideal. After some time, a learning society will help in development and reinforcement of the NSD ability of the company under consideration. At greater amount of NSD ability an entrepreneurial culture can take preferable favourable position of this capacity over a learning society. Be that as it may, in time, a culture equipped towards looking for change and novelty will breakdown the convenience of existing information (Carlile and Rebentisch, 2003).One general pattern of progression in the automotive industry could be understood in the form of products progressively an empowering an agent for building up associations with clients and these do not prove to be the fundamental aspects of any developmental procedure of any organisational offer any longer. Further, organizations begin offering more products and other autonomous services so as to guarantee additional profit margin gain while undertaking the exploitation of the internal economies-of-scale. Models of such service administrations are to be identified as managing an account benefit as well as banking services which could be accessible for clients who could be not interested in product procurement and for clients who may not drive an automobile of a similar brand. The plan itself has high significance to the automobile industry. The plan of Blumberg (1991), characterizing services administrations to before-sales and after-sales can be exceptionally connected understandinghow much service administrations are offered to client before they really buy an automobile. This can demonstrate benefit introduction of an organization and specifically to what degree items assume a focal significance in in the offer of the organisation. Fascinating for outlining the service provisioning in the automobile industry is a plan proposed by Sawhney et al. (2004).This could assist in featuring what number and type of vehicle independent services organizations have, where street based mobility is taken as an essential client activity and movement indicative element. This plan can be utilised to perceive how expansive service based prospects related to those of the automotive manufacturers could be.
5. Conclusion
The comprehension of services administration has beenexperiencing a fundamental transformation, from characterisation of administrations as a specific category of market contributions with value additionprocess integrative of the NSD, to evaluation of the benefits as assets in value formation process for the customers. Clients survey the value estimation of new services based on an incentive in their own particular perspectives, which primarily could influence the process of NSD process execution. Regardless of whether another or new product or service administration is fruitful needs to do with the degree to which value of such services could be perceived by the customers and consumers. The context of perception on part of the customers and the consumers could be comprehended as an effective framework of systematic services which consecutively incorporates individuals with learning, abilities, innovation and different assets (Edvardsson et al., 2013).As service administrations are dependent upon the exercises of activities and communicative interactions, some of which are completed by the suppliers and the much of the rest by the client and perhaps some by other marketing network based personnel, the service improvement procedure and the exercises in the NSD procedures need to consider these variables, including the mappings (standards,norms, rules and tenets) which influence the operational factors regarding the formulation of values of products and services (Edvardsson et al., 2012). Along these lines, the responsibility of the development of the service strategy ought to be to create and adjust the incentive based value that the supplier guarantees to the client. The utilisation of the service administration framework (here, incorporated improvement groups assume a key job) to empower and secure the guaranteed positive perceptions of the client. In this way, service advancement methodology needs to do with the arrangement of assets, capacities and authoritative units, incorporating deriving values in anservice administration framework that empowers and encourages clients in their particular preferential setting of operations, value formulation circumstances and endeavours.Without the assistance derived from internal capabilities, administrative structures and effective organisational support culture, accomplishment in NSD can hardly be expected and market based sales operational success achievementcan never be accomplished (Menor and Roth, 2008). Vital key conditions should be ensured and also the understanding that the result of a NSD procedure is the essential for the administration has to be consistently developed and instated (Edvardsson et al., 2013). A potential boundary to enhancing NSD performance matrix can emerge from a misperception of the real multifaceted nature of NSD and that service operational improvement technique is the missing connection. The low level of effort investment in NSD signals could outline the insignificance of NSD for certain business organisations. Directors regularly trust that they have NSD processes which could be effectively utilised, that they are now effectively overseeing NSD and that they know how to accumulate and utilize client information.Various imperative administrative ramifications could be encountered when convictionsof the administrators are contrasted with those of the consequences of the corresponding research study. The most critical issue is that directors think little of the job of having a NSD system and adjusting NSD projects with internal resourcesand assets and abilities, while in the meantime, they concentrate on the formulation of the value with the new services. Having a technique for NSD ought to clearly enhance NSD performance standard, however that its impact ought to be more grounded than the other key variables was less anticipated. Rather than regarding NSD as something that simply occurs, supervisors must not just accentuate a NSD procedure that emphasises on the offer and the technique of the company, however should consider the point of origin of the NSD application to better perform value creation for customers.By offsetting this with the internal abilities and resourcesof the service administration framework, service sector based organizations ought to have the capacity to diminish the quantity of new yet incapable and less valuable services and products when these could be presented at the market scenarios. In spite of the fact that this research analysis has its benefits, it likewise has a few shortcomings as well. One such shortcoming of this examination is the utilization of emotional proportions of NSD execution. This investigation expands on existing sizes of NSD execution that were approved in past research. Future research examinations could incorporate target proportions of NSD performances and in a perfect world, track them over a more extended period. Since organizations put constrained assets in NSD and these are spread over an extensive range of operational regions in service based organisations, such a methodology is never to be utilised bereft of any trouble.The consequential outcomes of this study and research examination depend on a study based on a pilot contextual analysis at a considerable smaller size of selected samples of NSD in BMW. The corresponding stage is to incorporate business organizations in different nations in Europe and in addition in Asia. Additionally, repeating and broadening this research examination by exploring a different arrangement of services administrations through the customisation and institutionalization, cutting edge through ultra-sophistication of product specifics and service continuity through proper and versatile manufacturing inside a similar report can possibly make a huge commitment to the comprehension of the key factors in NSD. An extra constraint is the strategic operationalization of services administration development methodology. More research is expected to assess the best possible manner which the benefit organizations could set their administration improvement methodology in motion.
References
Johne, A. and C. Storey. 1998. New service development: a review of the literature
Zeithaml, V., A. Parasuraman, and L. Berry. 1985. Problems and strategies in service
Tatikonda, M. V. and V. A. Zeithaml. 2002. Managing the New Service Development
Papastathopoulou, P. and E.J.Hultink. 2012. New service development: An analysis of
Lovelock, C. and J. Wirtz. 2011. Services marketing: people, technology, strategy. London: Pearson.
Gadrey, J., F. Gallouj and O. Weinstein. 1995. New modes of innovation: How services benefit industry. International Journal of Service Industry Management. 6(3), pp. 4–16.
Cooper, R.G. and U.D. Brentani. 1991. New Industrial Financial Services: What Distinguishes the Winners.Journal of Product Innovation Management. 8 (1), pp. 75-90.
De Brentani, U. 1991. Success Factors in Developing New Business Services. European Journal of Marketing. 25(2), pp.33-59.
Easingwood, C.J. 1986. New Product Development For Service Companies. Journal of Product Innovation Management. 4, pp. 264-275
Menor, L.J. and A.V. Roth. 2008. New Service Development Competence and Performance: An Empirical Investigation in Retail Banking. Production andOperations Management.17 (3), pp. 267–284.
implementation, export marketing capabilities, and export venture performance”, Journal
Vorhies, D.W., Orr, L. and Bush, V. (2011), “Improving customer-focused marketing capabilities
Barney, J.B., (1991). Firm resources and sustained competitive Advantage, Journal of Management, 17:99–120
Teece, D.J., (2009). Dynamic Capabilities and Strategic Management: Organizing for Innovation and Growth. Oxford: University Press
- 24/7 Customer Support
- 100% Customer Satisfaction
- No Privacy Violation
- Quick Services
- Subject Experts



